折腾笔记[25]-使用VGGT进行基于图像的室内建图
摘要
使用VGGT进行基于单目图像(无imu)的室内建图, 但是图片不能重复, 无回环检测.使用docker容器一键启动, 可用gradio API进行函数式调用.
关键词
VGGT;Visual Geometry;3D reconstruction;docker;
原理简介
基于图像的三维空间/场景重建综述
[https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=image-to-3d]
[https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-fast-3d]
[https://huggingface.co/JeffreyXiang/TRELLIS-image-large]
[https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-fast-3d]
[https://huggingface.co/facebook/VGGT-1B]
[https://fast3r-3d.github.io/]
[https://huggingface.co/cyun9286/Align3R_DepthPro_ViTLarge_BaseDecoder_512_dpt]
[https://huggingface.co/spaces/cyun9286/Align3R]
[https://igl-hkust.github.io/Align3R.github.io/]
[https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.08376]
[https://huggingface.co/siyan824/reloc3r-224]
- Fast3R: Towards 3D Reconstruction of 1000+ Images in One Forward Pass
- [CVPR 2025] Align3R: Aligned Monocular Depth Estimation for Dynamic Videos
- [CVPR 2025] Reloc3r: Large-Scale Training of Relative Camera Pose Regression for Generalizable, Fast, and Accurate Visual Localization
- [CVPR 2025(Oral)] VGGT: Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer
1. 概述
基于图像的三维空间/场景重建是指从二维图像中恢复出三维场景的几何结构和外观信息。这一领域在计算机视觉、图形学和机器人学中具有重要意义,广泛应用于虚拟现实、增强现实、自动驾驶、文物保护等领域。近年来,随着深度学习技术的发展,基于图像的三维重建方法取得了显著进展,涌现出许多高效、准确的模型和算法。
2. 主要方法与模型
2.1 单视图重建
单视图重建是指从单张图像生成三维模型。这类方法通常依赖于深度学习模型,通过学习图像与三维几何之间的映射关系来生成三维模型。
-
TRELLIS-image-large
- 简介:TRELLIS 是一种基于结构化三维潜在空间的大规模三维生成模型。该模型通过条件图像生成三维模型,能够生成高质量的三维对象。
- 特点:模型基于 Transformer 架构,能够处理复杂的三维几何结构。其训练数据包括大量三维模型和对应的二维图像,通过端到端的训练方式,能够生成具有高分辨率和细节的三维模型。
- 应用:适用于艺术创作、设计和游戏开发等场景,能够快速生成高质量的三维模型。
- 资源:
- 项目页面:TRELLIS 项目页面
- 代码:TRELLIS 代码
-
Stable Fast 3D (SF3D)
2.2 多视图重建
多视图重建是指从多张图像中重建三维场景。这类方法通常利用多张图像之间的几何关系,通过特征匹配和优化算法来恢复三维结构。
-
Fast3R
- 简介:Fast3R 是一种高效的多视图三维重建方法,能够在单次前向传播中处理多达 1500 张图像,显著提高了重建速度。
- 特点:Fast3R 基于 Transformer 架构,通过并行处理多张图像,避免了传统方法中成对处理图像的高计算成本。它还利用了多种大规模训练技术,如 FlashAttention 2.0 和 DeepSpeed ZeRO-2,进一步提高了训练效率。
- 应用:适用于需要处理大规模图像数据的场景,如三维重建、虚拟现实和增强现实。
- 资源:
- 项目页面:Fast3R 项目页面
-
Align3R
- 简介:Align3R 是一种从单目视频中估计动态场景深度和相机姿态的方法。它能够生成时间一致的深度图、动态点云和相机姿态。
- 特点:Align3R 基于 DUSt3R 模型,通过优化和全局对齐技术,确保不同帧之间的深度图和相机姿态的一致性。该方法在处理动态场景时表现出色,能够处理复杂的运动和光照变化。
- 应用:适用于视频处理、增强现实和机器人导航等场景,能够实时生成高质量的深度图和相机姿态。
- 资源:
- 项目页面:Align3R 项目页面
- 代码:Align3R 代码
-
Reloc3r
- 简介:Reloc3r 是一种用于视觉定位的相对相机姿态回归框架。它通过大规模训练,能够快速、准确地估计查询图像相对于数据库图像的相机姿态。
- 特点:Reloc3r 采用对称的网络架构,通过相对姿态回归和运动平均模块,实现了高效的姿态估计。该方法在多个公共数据集上表现出色,具有良好的泛化能力和实时性。
- 应用:适用于增强现实、机器人导航和自动驾驶等场景,能够快速、准确地定位相机位置。
- 资源:
- 技术报告:Reloc3r 技术报告
2.3 大规模重建
大规模重建是指从大规模图像数据中重建三维场景。这类方法通常需要处理大量的图像数据,并利用高效的算法和模型来提高重建效率。
- VGGT
- 简介:VGGT 是一种基于视觉几何的 Transformer 模型,能够在大规模图像数据中进行高效的三维重建。
- 特点:VGGT 结合了视觉几何和 Transformer 架构,能够处理复杂的三维场景和大规模图像数据。该方法在 CVPR 2025 上获得了口头报告,展示了其在大规模重建任务中的优越性能。
- 应用:适用于大规模三维重建任务,如城市建模和文化遗产保护。
- 资源:
- 项目页面:VGGT 项目页面
3. 总结与展望
基于图像的三维重建领域近年来取得了显著进展,各种高效、准确的模型和算法不断涌现。未来,随着深度学习技术的进一步发展,基于图像的三维重建方法将在以下几个方面取得突破:
- 更高的重建效率:通过优化算法和硬件加速,进一步提高重建速度,实现实时重建。
- 更好的泛化能力:通过大规模数据训练和模型优化,提高模型在不同场景和数据集上的泛化能力。
- 更高质量的重建结果:通过改进模型架构和训练方法,生成更高质量的三维模型,包括更精细的几何细节和更逼真的纹理。
- 多模态融合:结合图像、点云、视频等多种数据模态,进一步提升三维重建的准确性和鲁棒性。
最近的相关研究包括:
- "MVSNet: Depth Inference for Multi-View Stereo by Training CNNs" - 提出了一种基于CNN的多视角立体深度推断方法。
- "ColMap: General Framework for Monocular and Multi-view 3D Reconstruction" - 提供了一个通用的单目和多视角3D重建框架。
- "NeRF: Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis" - 使用神经辐射场实现高质量的新视角合成。
- "DeepV2D: Video to Depth with Differentiable Projective Rendering" - 结合视频输入生成深度图。
这些方法大多关注特定任务,而VGGT则尝试以统一的方式解决多个任务。
VGGT简介
[https://github.com/facebookresearch/vggt]
[https://huggingface.co/spaces/facebook/vggt]
[https://huggingface.co/facebook/VGGT-1B]
[https://hub.baai.ac.cn/paper/18013881-674d-4928-96ab-99f256ac2885]
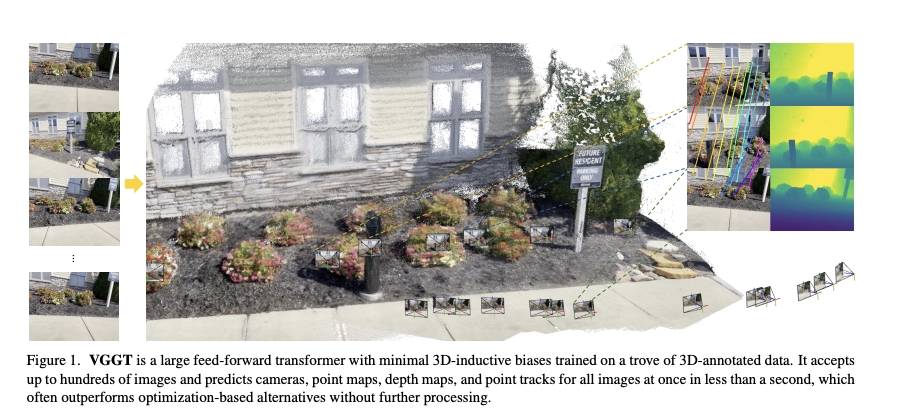
论文提出了 VGGT,这是一种前馈神经网络,能够直接从一个、几个或数百个视图中推断出场景的所有关键 3D 属性,包括相机参数、点地图、深度地图和 3D 点轨迹。这种方法在 3D 计算机视觉领域迈出了重要的一步,以往的模型通常受限于单一任务并专门针对这些任务设计。VGGT 方法还具有简单高效的特点,能够在不到一秒的时间内重建图像,并且其效果仍然优于需要通过视觉几何优化技术进行后处理的替代方法。该网络在多个 3D 任务中取得了最先进的结果,包括相机参数估计、多视角深度估计、稠密点云重建和 3D 点跟踪。论文还展示了使用预训练的 VGGT 作为特征提取骨干可以显著提升下游任务的效果,例如非刚性点跟踪和前馈式新视角合成。代码和模型已在 https://github.com/facebookresearch/vggt 公开提供。
该论文试图解决从单张或多张图像中同时推断场景的所有关键3D属性的问题,包括相机参数、深度图、点云和3D点轨迹。这是一个具有挑战性的问题,因为传统方法通常专注于单一任务,并依赖复杂的后处理步骤。
VGGT 是一种前馈神经网络,能够直接从一张或多张图像中推断出完整的3D场景信息。相比现有方法,它通过端到端的方式统一处理多个3D任务,而不需要额外的几何优化步骤。这种方法不仅简化了流程,还显著提高了效率和性能。
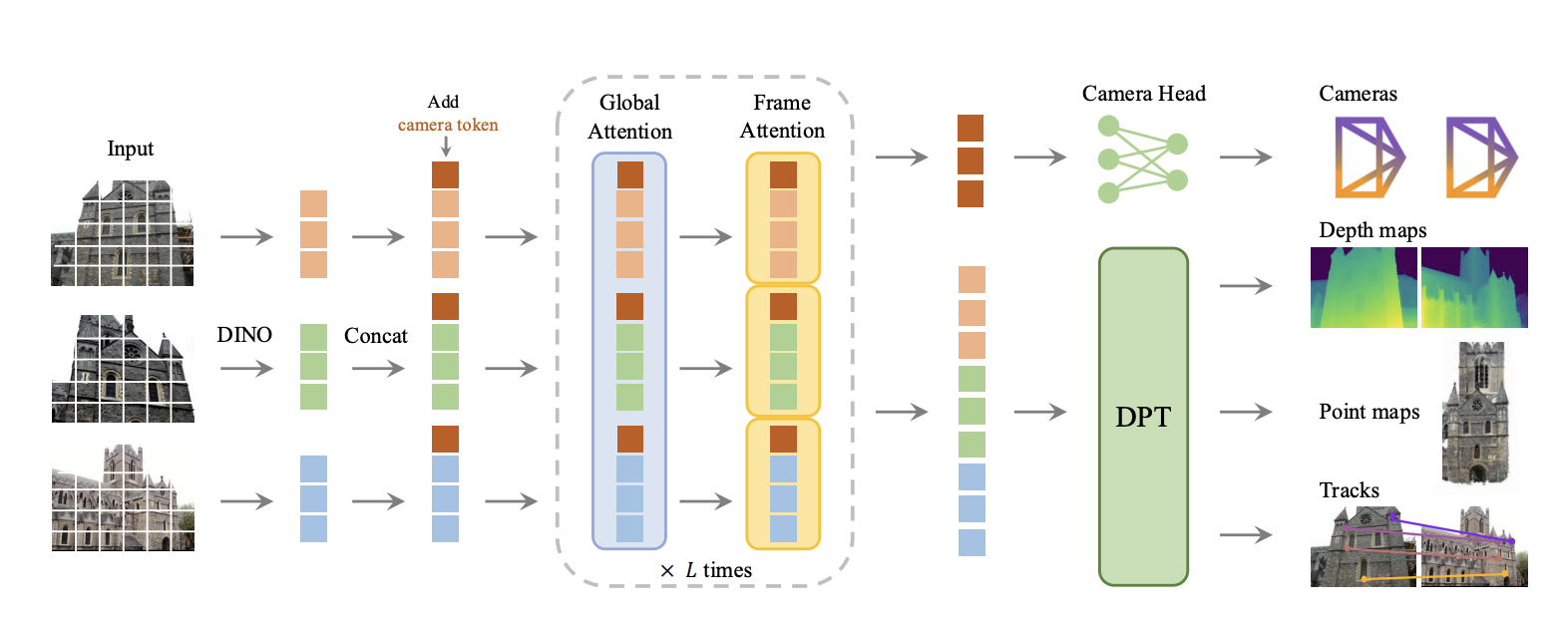
VGGT 首先使用 DINO 将输入图像分割成 tokens,并附加相机 tokens 用于相机预测。然后,它在帧内自注意力层和全局自注意力层之间交替。一个相机头部用于最终预测相机的外参和内参,而一个 DPT 头部则用于任何密集输出,例如深度图、点图或用于跟踪的特征图。
VGGT 在各种任务中均显著优于其他所有方法。请参阅论文以获取定量结果。在这里,我们还提供了与 DUSt3R 以及其他同期工作(例如 Fast3R 和 FLARE)的定性比较。
We present VGGT, a feed-forward neural network that directly infers all key 3D attributes of a scene, including camera parameters, point maps, depth maps, and 3D point tracks, from one, a few, or hundreds of its views. This approach is a step forward in 3D computer vision, where models have typically been constrained to and specialized for single tasks. It is also simple and efficient, reconstructing images in under one second, and still outperforming alternatives without their post-processing utilizing visual geometry optimization techniques. The network achieves state-of-the-art results in multiple 3D tasks, including camera parameter estimation, multi-view depth estimation, dense point cloud reconstruction, and point tracking. We also show that using pretrained VGGT as a feature backbone significantly enhances downstream tasks, such as non-rigid point tracking and feed-forward novel view synthesis.
VGGT first patchifies the input images into tokens by DINO, and appends camera tokens for camera prediction. It then alternates between frame-wise and global self attention layers. A camera head makes the final prediction for camera extrinsics and intrinsics, while a DPT head for any dense output, such as depth maps, point maps, or feature maps for tracking.
VGGT significantly outperforms all other methods across various tasks. Please refer to our paper for quantitative results. Here we also provide a qualitative comparison with DUSt3R and other concurrent works such as Fast3R and FLARE.
| 示意图 | 架构图 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
1. 问题定义与符号表示
VGGT的输入是一个图像序列 \((I_i)_{i=1}^N\),其中每个图像 \(I_i \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times H \times W}\) 观测同一3D场景。模型的目标是预测以下3D属性:
其中:
- \(g_i \in \mathbb{R}^9\) 表示相机参数(内参和外参)
- \(D_i \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W}\) 是深度图
- \(P_i \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times H \times W}\) 是点云图(在第一个相机的坐标系下)
- \(T_i \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times H \times W}\) 是用于点跟踪的特征图
2. 相机参数表示
相机参数 \(g_i\) 由以下部分组成:
其中:
- \(q_i \in \mathbb{R}^4\) 是旋转四元数
- \(t_i \in \mathbb{R}^3\) 是平移向量
- \(f_i \in \mathbb{R}^2\) 是视场角(FOV)
3. 3D几何关系
定义两个关键函数:
- 刚体变换函数:
将世界坐标系中的点 \(p\) 转换到相机坐标系 \(p'\)
- 投影函数:
将3D点 \(p\) 投影到2D图像坐标 \(y\)
深度值定义为:
其中 \(S_i \subset \mathbb{R}^3\) 表示场景表面
4. 网络架构
4.1 交替注意力机制
VGGT采用交替的自注意力机制:
- 帧内注意力(Frame-wise Self-Attention):
在单帧内计算
- 全局注意力(Global Self-Attention):
跨所有帧计算,公式同上但作用范围不同
4.2 损失函数
总损失函数为多任务损失:
各项损失具体形式:
- 相机损失(Huber损失):
- 深度损失(含不确定性):
- 点云图损失:
- 跟踪损失:
5. 坐标归一化
为避免尺度模糊性,对训练数据进行归一化:
- 将所有量转换到第一相机的坐标系
- 计算所有3D点到原点的平均欧氏距离 \(s\)
- 用 \(s\) 归一化相机平移 \(t\)、点云图 \(P\) 和深度图 \(D\)
6. 数学关系
各预测量之间存在数学关联:
- 从点云图和相机参数可推导深度:
- 从深度图和相机参数可重建点云:
- 从点云图可通过PnP算法估计相机参数
这种过完备的表示虽然存在冗余,但实验表明联合学习能提高性能。
使用huggingface Space的docker镜像
[https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/spaces-run-with-docker]
[https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/spaces-sdks-docker]
你可以使用 Docker 在本地运行大多数 Spaces。要查看下载和运行 Spaces 的 Docker 镜像的说明,请点击你的 Space 页面右上角的“使用 Docker 运行”按钮。
Spaces 支持自定义 Docker 容器,适用于超出 Streamlit 和 Gradio 范围的应用。Docker Spaces 让用户能够突破以往标准 SDK 的限制。无论是 FastAPI 和 Go 端点,还是 Phoenix 应用和 ML Ops 工具,Docker Spaces 都可以在许多不同的设置中提供帮助。
You can use Docker to run most Spaces locally. To view instructions to download and run Spaces’ Docker images, click on the “Run with Docker” button on the top-right corner of your Space page.
Spaces accommodate custom Docker containers for apps outside the scope of Streamlit and Gradio. Docker Spaces allow users to go beyond the limits of what was previously possible with the standard SDKs. From FastAPI and Go endpoints to Phoenix apps and ML Ops tools, Docker Spaces can help in many different setups.
使用gradio API提供函数式接口
[https://www.gradio.app/guides/getting-started-with-the-python-client]
Gradio Python 客户端使得使用任何 Gradio 应用作为 API 变得非常容易。例如,考虑这个 Hugging Face Space,它可以转录从麦克风录制的音频文件。使用 gradio_client 库,我们可以轻松地将 Gradio 用作 API,以编程方式转录音频文件。
The Gradio Python client makes it very easy to use any Gradio app as an API. As an example, consider this Hugging Face Space that transcribes audio files that are recorded from the microphone.
Using the gradio_client library, we can easily use the Gradio as an API to transcribe audio files programmatically.
pip install gradio_client
npm i -D @gradio/client
curl --version
curl -X POST https://facebook-vggt.hf.space/gradio_api/call/clear_fields -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"data": [
]}' \
| awk -F'"' '{ print $4}' \
| read EVENT_ID; curl -N https://facebook-vggt.hf.space/gradio_api/call/clear_fields/$EVENT_ID
示例:
from gradio_client import Client
client = Client("facebook/vggt")
result = client.predict(
api_name="/clear_fields"
)
print(result)
glb点云格式简介
[https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/11281679136]
GLB(GLTF Binary)和GLTF(GL Transmission Format)是一种用于在3D场景中存储和传输3D模型的文件格式。
glb 是一种用于存储三维场景和模型的高效二进制文件格式,glb是glTF 的二进制版本,由Khronos Group定义,该组织也负责OpenGL和WebGL等图形技术标准。
使用vscode预览glb点云
[https://github.com/google/model-viewer]
[https://github.com/cloudedcat/vscode-model-viewer.git]
VS code extension for viewing glTF models
- Install extension
- Open glb file in editor
- Press Ctrl + Shift + P
- Pick View: Reopen Editor With...
- Configure default editor for *.glb
- glFT
体验&本地部署
-
下载及导入镜像
- 百度云盘镜像(已包含模型权重
/home/user/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/model.pt, 已修改为可使用cpu或cuda推理):
通过网盘分享的文件:VGGT 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IH3qWMQMdMHpNZuTC9aHIA?pwd=zdfr 提取码: zdfr导入:
docker load -i biu_facebook_vggt-v2-amd64.tar # cpu版本 docker run -p 7863:7860 -d biu_face_vggt:v2-amd64 python app_cpu.py # cuda版本 docker run -p 7863:7860 -d biu_face_vggt:v2-amd64 python app.py- huggingface镜像(仅可cuda, 模型权重运行时才下载):
docker run -it -p 7863:7860 --platform=linux/amd64 --gpus all \ registry.hf.space/facebook-vggt:latest python app.py - 百度云盘镜像(已包含模型权重
-
提示✨: 默认工作目录为
/home/user/app
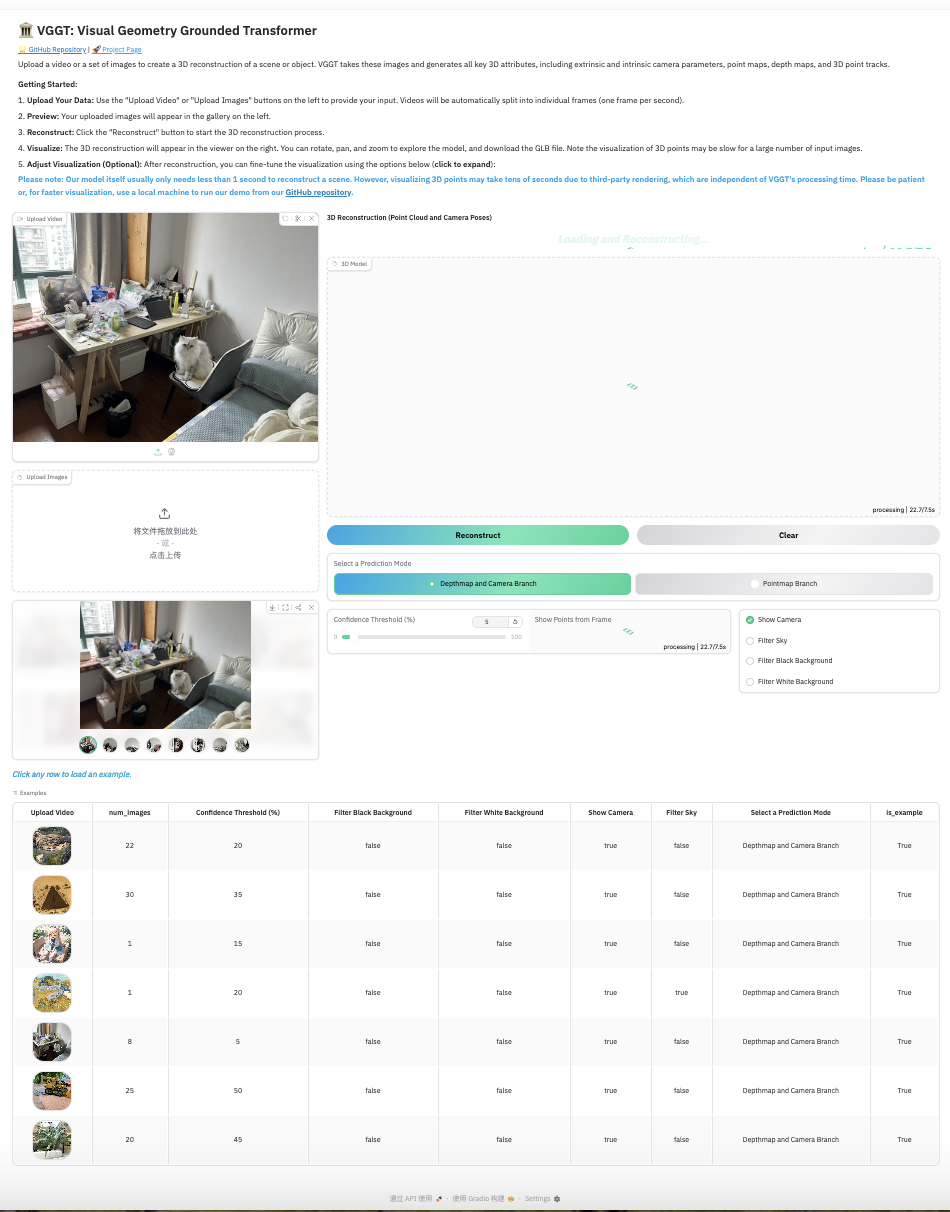
- 测试
- 方式1: 上传视频
- 方式2: 上传一张或多张图片
效果
| 运行界面 |
|---|
 |
| 室内图1 | 室内图2 | 室内图3 | 室内图4 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 室内图5 | 室内图6 | 室内图7 | 室内图8 |
|---|---|---|---|
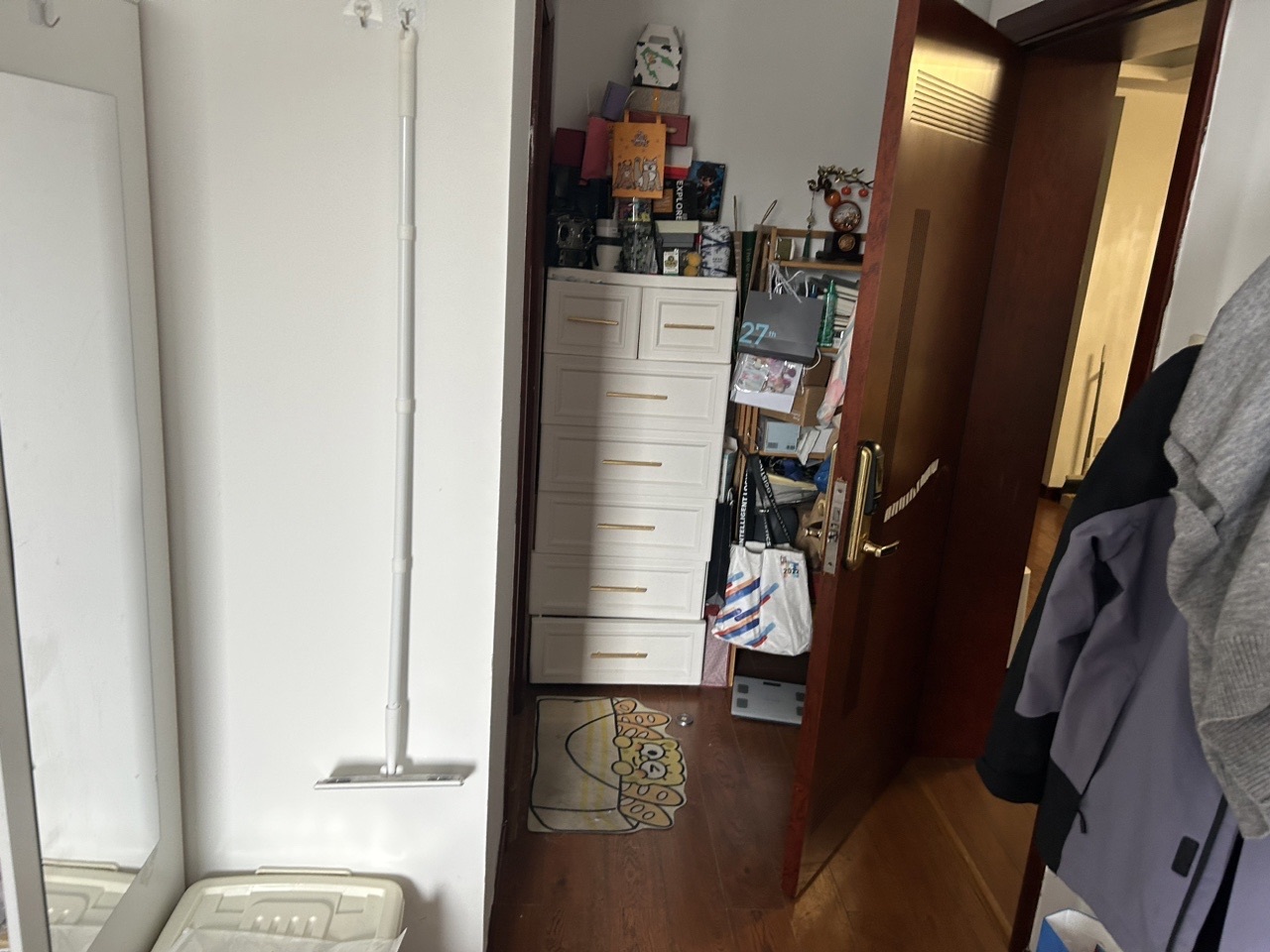 |
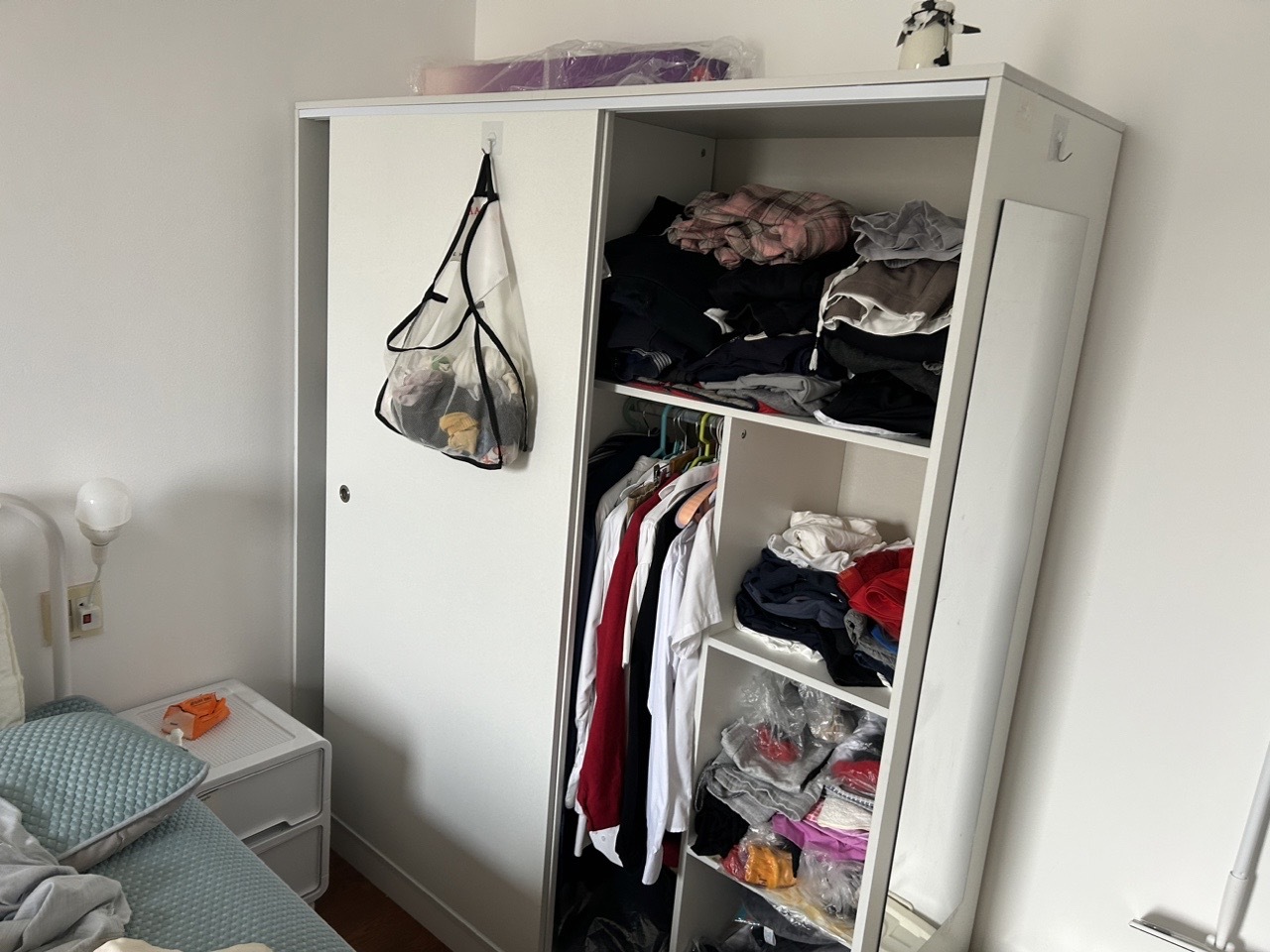 |
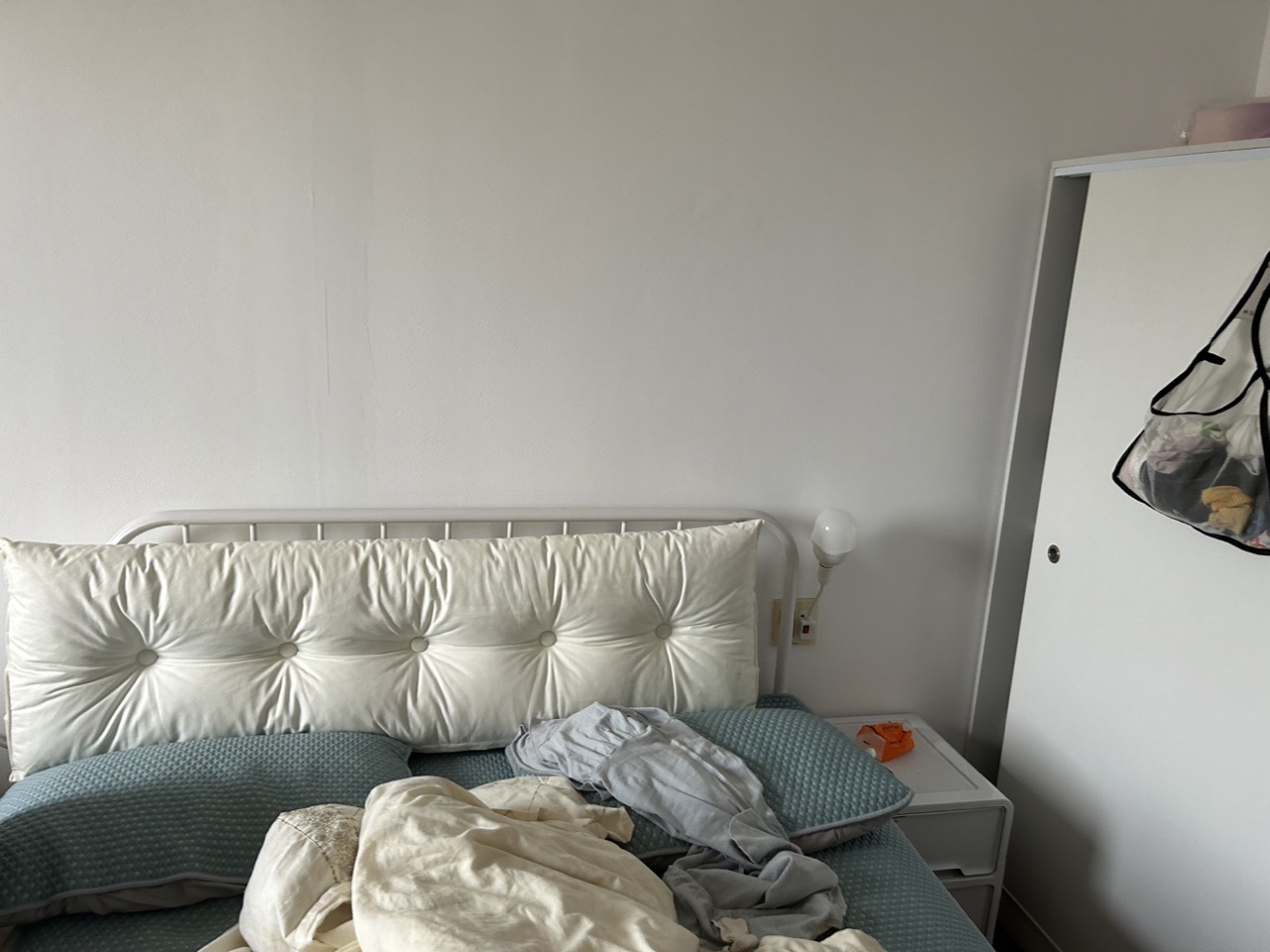 |
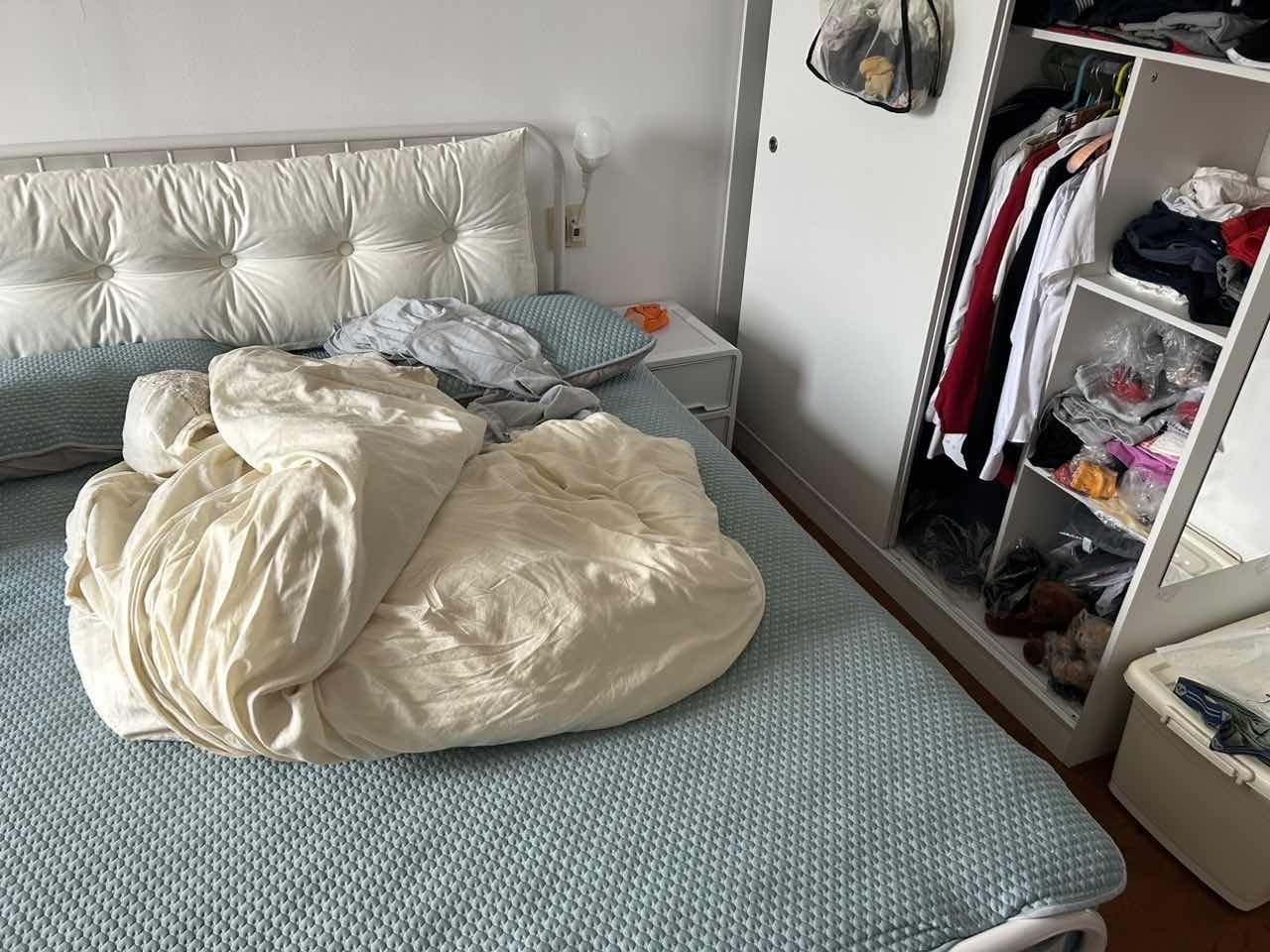 |
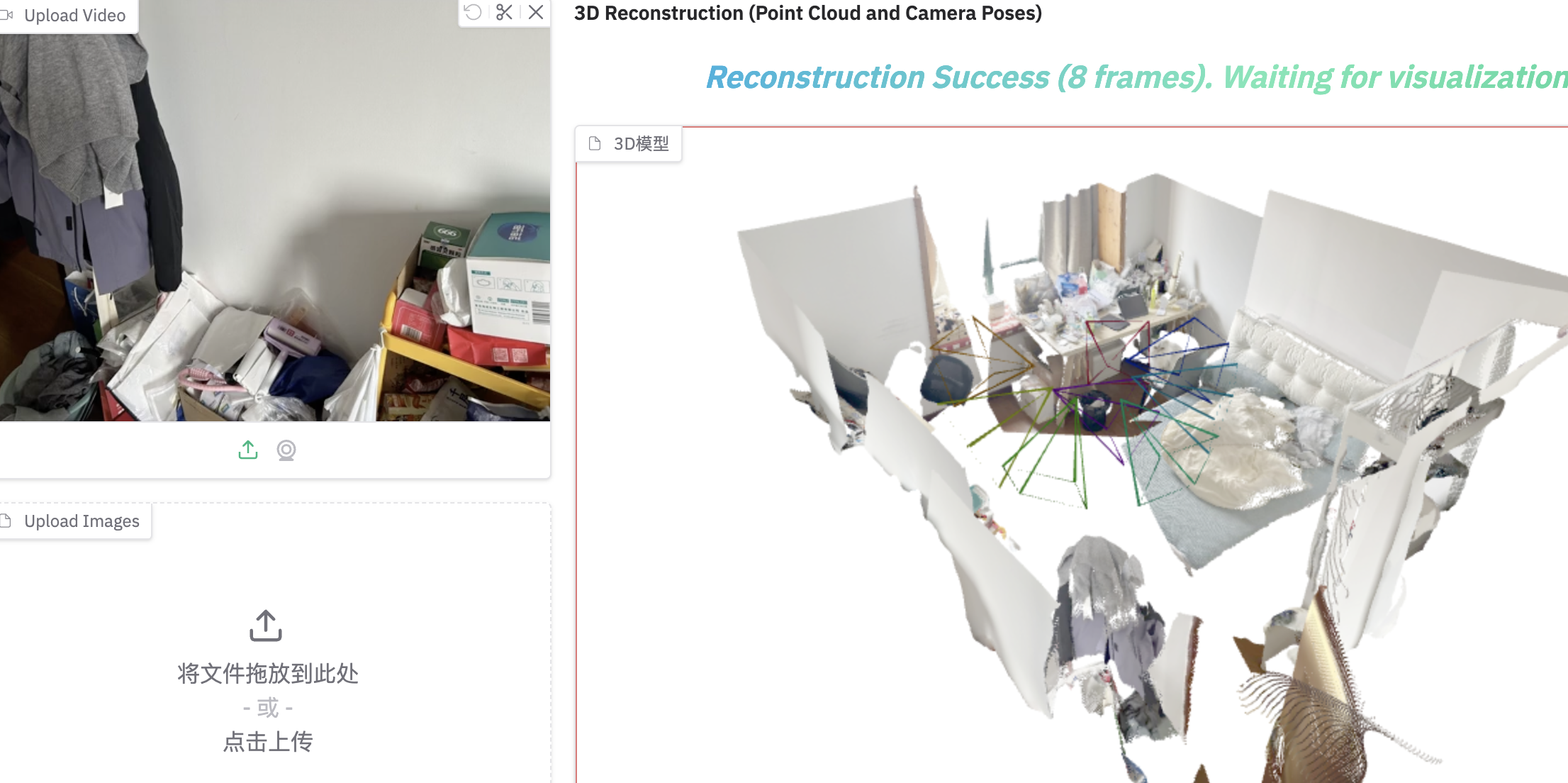
| 室内重建效果 |
|---|
 |
更新:
使用gradio_client的API方式调用:
[project]
name = "seekslam-examples"
version = "0.1.0"
description = "Add your description here"
readme = "README.md"
requires-python = ">=3.12"
dependencies = [
"dronekit>=2.9.2",
"gradio-client>=1.8.0",
"numpy>=2.1.3",
"ollama>=0.4.8",
"pillow>=11.2.1",
"pymavlink>=2.4.43",
"selenium>=4.31.0",
"tensorflow>=2.19.0",
"typing-extensions>=4.13.2",
]
[tool.uv.workspace]
members = []
代码:
# 使用gradio的API上传图片或视频进行建图并获取建图结果glb文件
# 原始图片
IMG_PATH = ["../assets/scene1.png"]
# 结果保存
RESULT_PATH = "../result"
# 文件名称(glb模型)
RESULT_NAME = "gradio_api_mapping.glb"
# 建图网页
WEB_URL = "http://192.168.31.20:7862"
##############################
# 内置库
import shutil
import os
import time
# gradio客户端
from gradio_client import file
import gradio_client as gr
##############################
def upload_files(client, input_images=None, input_video=None):
"""上传文件到Gradio应用并返回目标目录"""
try:
# 清除现有输入
client.predict(api_name="/clear_fields")
# 上传图片
if input_images:
print("正在上传图片...")
gradio_files = [file(img_path) for img_path in input_images]
# 上传文件并获取返回的实际目录路径
_, target_dir, _, _ = client.predict(
input_video=None,
input_images=gradio_files,
api_name="/update_gallery_on_upload_1"
)
print(f"图片上传完成,服务器返回的目标目录: {target_dir}")
# 从完整路径中提取目录名
if target_dir.startswith('/private'):
# 处理MacOS临时路径
dir_name = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(target_dir))
else:
dir_name = os.path.basename(target_dir)
print(f"使用的目标目录名: {dir_name}")
return dir_name
except Exception as e:
print(f"上传文件时出错: {str(e)}")
return None
def process_mapping(client, target_dir):
"""处理建图并获取GLB结果"""
try:
print(f"开始处理建图,使用目标目录: {target_dir}")
# 调用建图API
result = client.predict(
target_dir=target_dir,
conf_thres=50,
frame_filter="All",
mask_black_bg=False,
mask_white_bg=False,
show_cam=True,
mask_sky=False,
prediction_mode="Depthmap and Camera Branch",
api_name="/gradio_demo"
)
# 处理返回值
if isinstance(result, (list, tuple)):
model3d = result[0] # 第一个返回值应该是GLB文件路径
status_msg = result[1] if len(result) > 1 else ""
print("建图状态:", status_msg)
print("model3d", model3d)
return model3d
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理建图时出错: {str(e)}")
return None
def save_glb_file(glb_path, save_path, filename):
"""复制GLB文件到目标目录"""
try:
if not os.path.exists(save_path):
os.makedirs(save_path)
full_path = os.path.join(save_path, filename)
# 检查源文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(glb_path):
print(f"错误: 源文件 {glb_path} 不存在")
return None
print(f"正在复制GLB文件从 {glb_path} 到 {full_path}")
shutil.copy2(glb_path, full_path)
print(f"GLB文件已保存到: {full_path}")
return full_path
except Exception as e:
print(f"复制GLB文件时出错: {str(e)}")
return None
def main():
try:
# 创建客户端连接
print("正在连接Gradio服务器...")
client = gr.Client(WEB_URL)
print("连接服务器成功")
# 1. 上传文件并获取服务器返回的实际目录
target_dir = upload_files(client, input_images=IMG_PATH)
if not target_dir:
print("无法获取有效的目标目录")
return
# 2. 处理建图
glb_result = process_mapping(client, target_dir)
if not glb_result:
print("建图处理失败")
return
# 3. 保存结果
saved_path = save_glb_file(glb_result, RESULT_PATH, RESULT_NAME)
if saved_path:
print("处理完成,结果已保存")
else:
print("处理完成,但保存结果失败")
except Exception as e:
print(f"主程序出错: {str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
提示:
gradio_client下载文件:
[https://github.com/gradio-app/gradio/issues/4474]
**文件就在客户机**
I have similar problem. Trying to use gradle_client with bark, but I don't know how to download the output .wav file
I saw a file /tmp/26da2053892cd0648ba8b012705b9b6ccbcffa55/tmpqor5psui.wav created on my system but it just had Internal Server Error content
Hi @robinhad ! The output file is in your machine, not the remote machine running the space.
thanks @freddyaboulton! I got confused by those tmp files 😅
for unfamiliar user like me it would be great to have this in the docs, that's a place I have searched at first
Same here - getting local file path when using the gr.File output


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号