[CG learning] shading
== Diffuse Shading ==
🔥 对表面颜色的控制
🌲 diffuse reflection,漫反射
-
Lambertian Shading Model
现实中大多数物件表面都是非光滑的("matte")
![]()
lambertian surface 👉 朗伯表面就是理想情况的漫反射表面,不考虑观察角度的影响
A Lambertian surface for reflection is a surface that appears uniformly bright from all directions of view and reflects the entire incident light. Lambertian reflectance is the property exhibited by an ideal matte or diffusely reflecting surface.
-
Lambert's cosine law
基本定义:物体表面某点的颜色正比于其法向量与光照向量形成角度\(\theta\)的余弦值\(cos\theta\) 👇
\(c \propto |cos\theta|\) 用向量形式可以表达为 👉 \(1. \space c \propto max(0, \vec n·\vec l) \\ 2. \space c \propto |\vec n·\vec l|\)
-
影响因素
- diffuse reflectance \(c_r\) ⚠️ 根据颜色不同反射率也不同
- light intensity \(c_l\) 光照强度引起的颜色值变化,规范化到range[0,1]
-
基本形式 \(1. \space c \propto c_rc_lmax(0, \vec n·\vec l) \\ 2. \space c \propto c_rc_l|\vec n·\vec l|\)
- \(cos_\theta\) 小于0时理论上应该没有颜色,但是代入等式\((2)\)得到存在颜色,因此\((2)\)描述的是一个两侧对称光照的情况
-
-
Ambient Shading
\(c \propto max(0,\vec n·\vec l)\) 中存在一个明显的问题,背光处均为黑色,但在实际中光到处反射,使得背光处不可能为完全的黑色。
因此等式中还需要加入环境光\(c_a\) 👉 \(c\propto c_r(c_a+c_lmax(0, \vec n·\vec l))\)
🌲 由于RGB range \([0,1]^3\) ,可能需要进行clamp处理
-
Vertex-Based Diffuse Shading
-
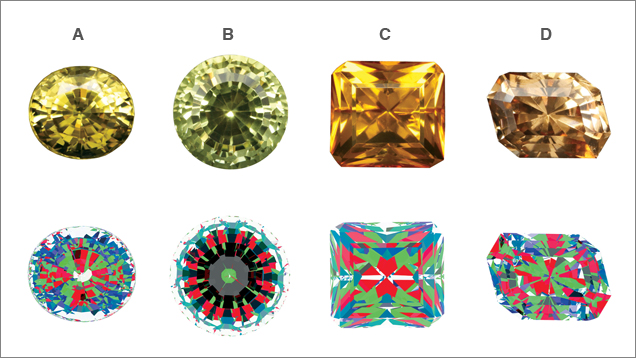
avoid faceted appearance
![image]()
https://www.gia.edu/gems-gemology/optimizing-face-up-appearance-in-colored-gemstone-faceting
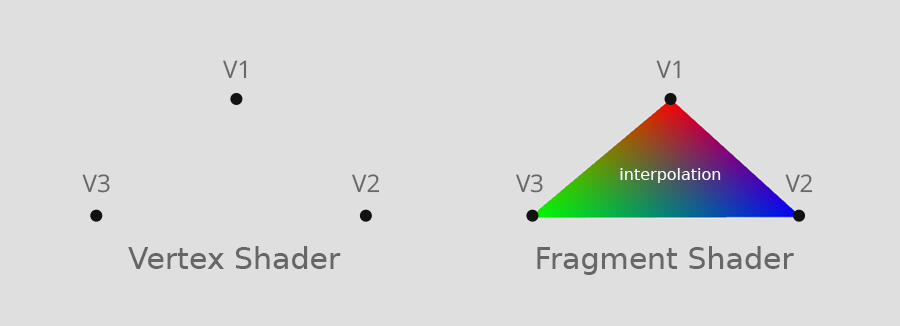
以triangle表面的法线向量(normal vector)来计算颜色值时,得到的颜色值会用于填充整个三角形面的每一个像素点,相邻两个三角形面如果颜色差异明显,会出现faceted appearence的问题。
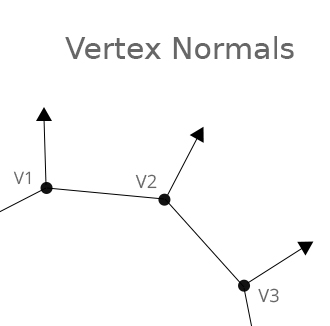
因此考虑将法线向量放到三角形的顶点上,计算出三角形各顶点的颜色值,再通过插值法得到整个三角形各像素点的颜色 👉 simpest way: just average the normals of triangles which shared that vertice.
![image]()
![image]()
http://benchung.com/basic-glsl-displacement-shader-three-js/
-
Surface Normal Vector Interpolation
interpolate vertex color and normal using barycentric coordinates\[\alpha = \frac{S_{cap}}{S_{abc}}\\ \beta = \frac{S_{abp}}{S_{abc}} \\ \theta = \frac{S_{bcp}}{S_{abc}} \]- vertex color 👉 \(c = \alpha c_0 + \beta c_1 + \gamma c_2\)
- vertex normal 👉 \(c = \alpha \vec c_0 + \beta \vec n_1 + \gamma \vec c_2\)
-
== Phong Shading ==
🔥 对高光颜色的控制
matte surface也会有highlights存在,且高光并非是以表面材料的颜色为主,从材料表面反射的散射光对整体颜色影响不大
-
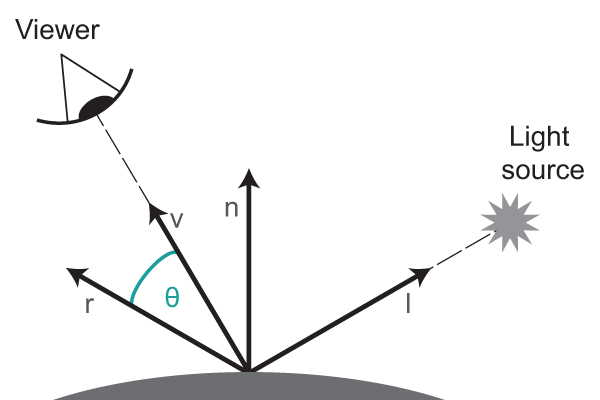
Phong Lighting Model
![image]()
https://www.geertarien.com/blog/2017/08/30/blinn-phong-shading-using-webgl/
当视线与反射光的夹角\(\theta\) 小于一定值时,我们就会看到高光
可以得到等式 \(c = c_l(\vec v·\vec r)\)
🌲v stands for view;当\(v = r\)时,反射光与视线重合,\(\vec v·\vec r = 1\) 👉 \(c = c_l\)
-
\(s\) Phong exponent
\(c = c_l(max(0,\vec v·\vec r))^s\)
🌲 s stands for specular,鉴于\(\vec v·\vec r\)得到的\(cos\theta\)值range[0,1],更大的Phong指数,会使得高光越小
The
sterm in the equation represents the roughness of the surface. A smooth surface, which should have a smaller highlight, has a larges. Since the cosine of the angle is a number on [0, 1], taking it to a power greater than 1.0 will make the number smaller. Therefore, a largesexponent will make for a small highlight.https://paroj.github.io/gltut/Illumination/Tut11 Phong Model.html
-
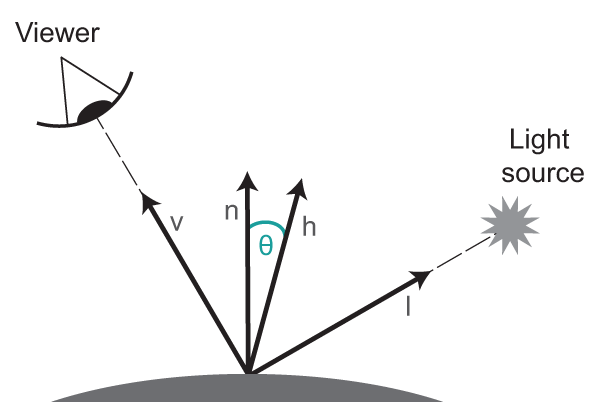
halfway vector 表达的等式
\(c = c_l(\vec h·\vec n)^s\)
-
\(\vec h = \frac{\vec v + \vec l}{||\vec v + \vec l||}\)
🌲 highlights appear when \(\vec h\) is near \(\vec n\)
![image]()
https://www.geertarien.com/blog/2017/08/30/blinn-phong-shading-using-webgl/
🌲 \(\theta_{new} = \frac{\theta_{old}}{2}\),因此此处的\(s\) 也能和\(c = c_l(max(0,\vec v·\vec r))^s\)的\(s\)有相同的控制效果
-
-
实际使用中通常将Lambertian shading model和Phong Lighting Model中的两个等式结合在一起
\[c = c_r(c_a + c_l max(0, \vec n · \vec l)) + c_l(\vec h · \vec n)^p \] -
再加入新的控制变量\(c_p\)用于控制高光的颜色
\[c = c_r(c_a + c_l max(0, \vec n · \vec l)) + c_lc_p(\vec h · \vec n)^p \]
-
== ☕️ ==
-
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition - Marschner Steve, Shirely Peter
-
https://paroj.github.io/gltut/Illumination/Tut11 Phong Model.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号