《重构-改善既有代码的设计》- 重新组织函数
所谓的重构就是在不改变代码外部行为(功能)的情况下对代码进行内部修改以实现代码可读性、可维护性、可复用性以及可扩展性的大幅度增加,便于后续进行扩展和维护(直观提高代码可读性,利于定位Bug并加以修复)。
避免出现 “too-long" 方法,要求方法表现的逻辑简洁明了(concise and easy to understand)。
🍎【Extract Method】- 提炼方法
将代码放入一个独立方法中,并让方法的名称具有自我描述性
特点:
- 功能模块化
- 模块集成化
- 局部变量局部化
- 初始变量分离化
处理对象:
- 过长方法
- 方法包含的代码逻辑复杂混乱,直观性差。
实现目标:
降低方法粒度,提高方法复用性,让高层函数读起来像是(just like)读注释一样。
方法粒度小便于后续的复写、复用和扩展
class Order {
private double price;
public Order(double price){
this.price = price;
}
double getAmount(){
return this.price;
}
}
public class Sample01 {
private Vector<Order> _orders;
private String _name;
public Sample01(String name){
this._name = name;
}
//【高层函数】遵守"单一指责型"这个原则,实现模块(方法)功能独立
void printOwing(){
printBanner(); // print banner
double outstanding = getOutstanding(); // calculate outstanding
printDetails(_name,outstanding); // print details
}
// calculate outstanding 【局部变量局部化】
private double getOutstanding() {
Enumeration e = _orders.elements();
double result = 0.0;
while(e.hasMoreElements()){
Order order = (Order)e.nextElement();
result += order.getAmount();
}
return result;
}
// print details
private void printDetails(String username, Double outstanding) {
System.out.println("username: " + username);
System.out.println("amount: " + outstanding);
}
// print banner
private void printBanner() {
System.out.println("*************************");
System.out.println("***** Customer Owes *****");
System.out.println("*************************");
}
}
/**
* the characteristic of Extract Method
* 1. 局部变量局部化
* 2. 初始变量分离化
* 3. 功能模块化
* 4. 模块集成化
* */
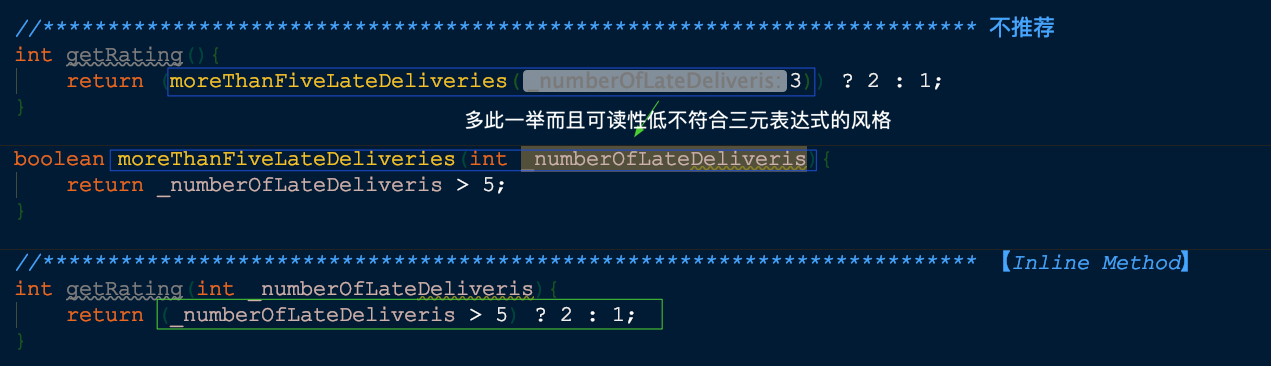
🍎【Inline Method】- 内联方法
在函数调用点插入函数本体,然后移除函数
处理对象: 代码之间太多的间接层(间接层有价值但不是所有的间接层都有价值)
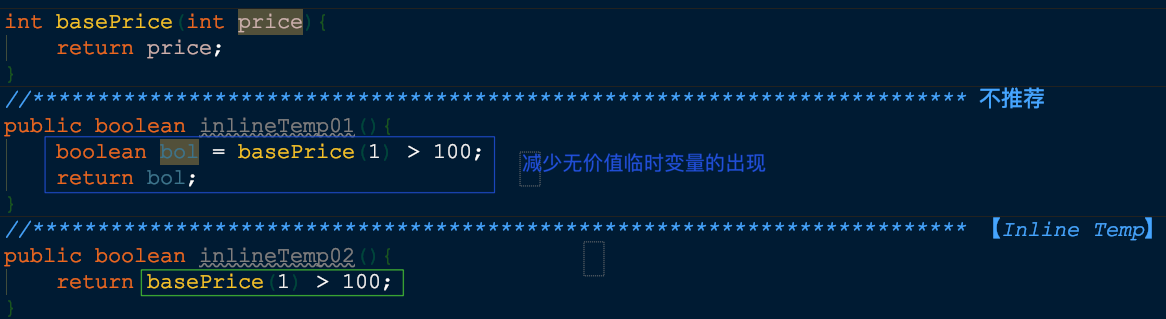
🍎【Inline Temp】- 内联临时变量
将所有对该变量的引用动作,替换为对它赋值的表达式本身
处理对象:减少临时变量的出现,只用通过内联表达式来达到临时变量的作用(内联临时变量要用于所替代临时变量只会被使用一次的情况下)
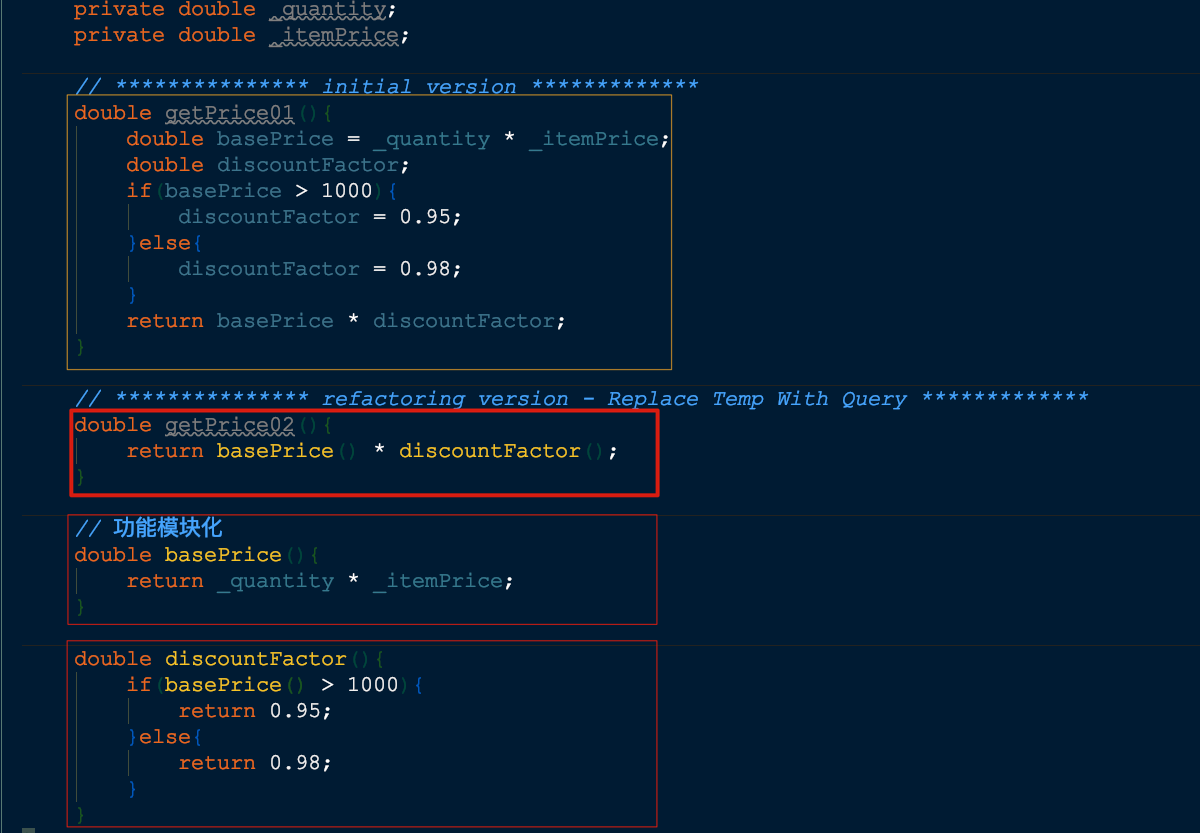
🍎【Replace Temp With Query】- 以查询取代临时变量
将这个表达式提炼到一个独立函数中。将这个临时变量的所有引用点替换为对新函数调用。
特点:
- 模块功能化
- 功能集成化
处理对象: 减少长函数的出现
确保提炼出来的函数无任何副作用,该函数并不修改任何对象内容。
运用此方法可能会存在性能方面的考虑,但如果性能真的出现问题可以在优化阶段解决。代码组织良好更有助于发现有效的优化方案
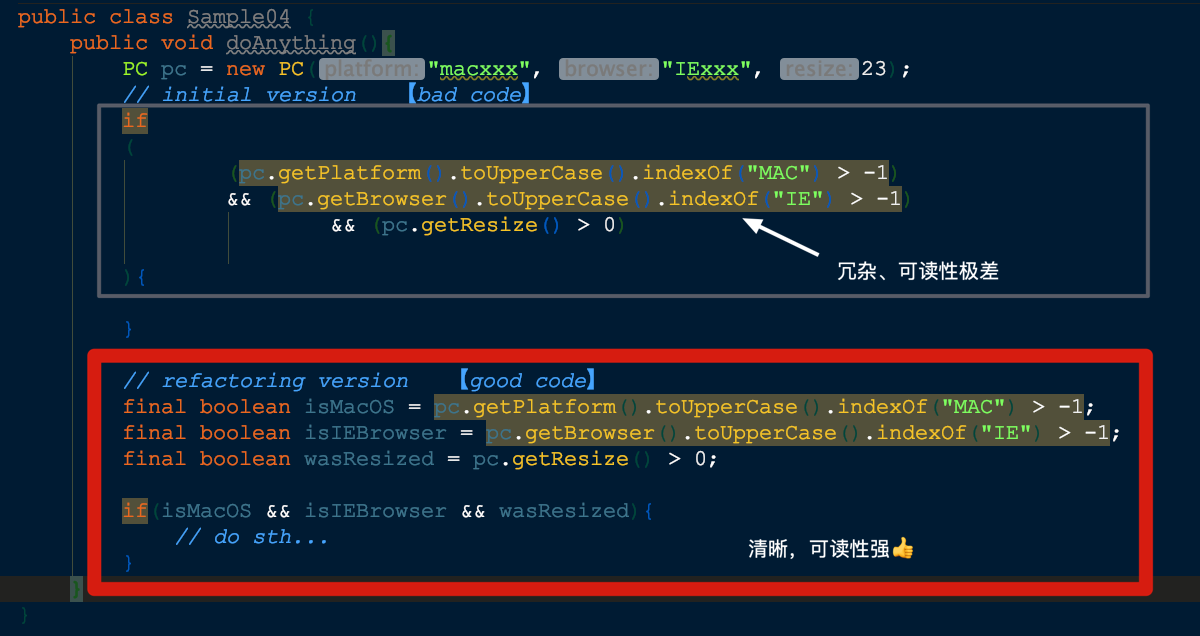
🍎【Introduce Explaining Variable】- 引入解释型变量
将该复杂表达式(或其中一部分)的结果放进一个临时比那辆,以此变量名称来解释表达式用途
处理好处: 通过自我描述性的变量代替冗杂、逻辑不清的表达式以提高代码可读性(concise and easy to understand)
public class Sample05 {
private double _quantity;
private double _itemPrice;
// *************** initial version 1.0.0 ***************
double calculatePrice01(){
// price is base_price - quantity_discount + shipping
return _quantity * _itemPrice -
Math.max(0, _quantity - 500) * _itemPrice * 0.05 +
Math.min(_quantity * _itemPrice * 0.1, 100.0);
}
// *************** 【Introduce Explaining Variables】initial version 1.0.1 ***************
double calculatePrice02(){
// price is base_price - quantity_discount + shipping
final double basePrice = _quantity * _itemPrice;
return basePrice -
Math.max(0, _quantity - 500) * _itemPrice * 0.05 +
Math.min(basePrice * 0.1, 100.0);
}
// *************** 【Introduce Explaining Variables】initial version 1.0.2 ***************
double calculatePrice03(){
// price is base price - quantity discount + shipping
final double basePrice = _quantity * _itemPrice;
final double quantityDiscount = Math.max(0, _quantity - 500) * _itemPrice * 0.05;
final double shipping = Math.min(basePrice * 0.1, 100.0);
return basePrice - quantityDiscount + shipping;
}
// *************** 【Extract Method】initial version 1.0.3 ***************
double calculatePrice04(){
return basePrice() - quantityDiscount() + shipping();
}
private double basePrice(){
return _quantity * _itemPrice;
}
private double quantityDiscount(){
return Math.max(0, _quantity - 500) * _itemPrice * 0.05;
}
private double shipping(){
return Math.min(basePrice() * 0.1, 100.0);
}
// Concise and easy to understand
}
🍎【Remove Assignments to Parameters】- 移除对参数的赋值
以一个临时变量取代该参数的位置
public class Sample07 {
// ****************【Remove Assignments To Parameters】version 1.0.0 ****************
int discount01(int inputVal, int quantity, int yearToDate){
if(inputVal > 50){
inputVal -= 2;
}
if(quantity > 100){
inputVal -= 1;
}
if(yearToDate > 10000){
inputVal -= 4;
}
return inputVal;
}
// ****************【Remove Assignments To Parameters】version 1.0.1 ****************
int discount02(int inputVal, int quantity, int yearToDate){
int result = inputVal;
if(inputVal > 50){
result -= 2;
}
if(quantity > 100){
result -= 1;
}
if(yearToDate > 10000){
result -= 4;
}
return result;
}
// ****************【Remove Assignments To Parameters】version 1.0.2 ****************
int discount03(final int inputVal, final int quantity, final int yearToDate){ // final: 1. 保证变量一致性 2. 防止出现参数再次赋值
int result = inputVal;
if(inputVal > 50){
result -= 2;
}
if(quantity > 100){
result -= 1;
}
if(yearToDate > 10000){
result -= 4;
}
return result;
}
// To implement compulsory no-assignment to parameter with the "final" keyword.(the "final" better use in too long method)
}
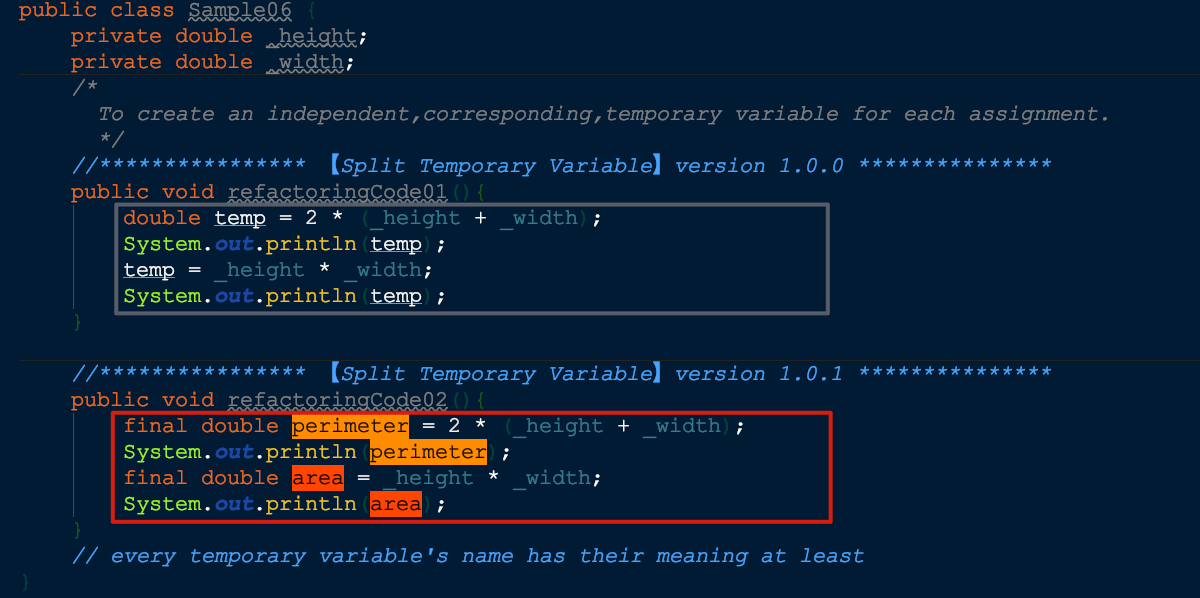
🍎【Split Temporary Variable】- 分解临时变量
针对每次赋值,创建一个独立、对应的临时变量(临时变量的唯一化和遵守单一职责的原则)
🍎【Replace Method With Method Object】- 以函数对象取代函数
将这个方法放进一个单独对象中,如此一来局部变量就成了对象内的字段。然后可以在同一个对象中将这个大型方法分解为多个小型方法。
处理对象: 无法拆解的方法
处理好处:将相对独立的代码从大型函数中提炼处理啊,就可以大大提高代码的可读性。
class Account{
private int inputVal;
private int quantity;
private int yearToDate;
// traditional Method
int gamma01(int inputVal, int quantity, int yearToDate){
int importantValue1 = (inputVal * quantity) + delta();
int importantValue2 = (inputVal * yearToDate) + 100;
if((yearToDate - importantValue1) > 100){
importantValue2 -= 20;
}
int importantValue3 = importantValue2 * 7;
// and so on
return importantValue3 - 2 * importantValue1;
}
int gamma02(int inputVal, int quantity, int yearToDate){ 【⭐️Nice Shot】
return new Gamma(this,inputVal,quantity,yearToDate).compute();
}
int delta(){
return 1;
}
}
// Method Object
class Gamma{
private final Account _account; // The _account field must be used anywhere in a function that calls the Account class
private int inputVal;
private int quantity;
private int yearToDate;
// 【extract method】
// private int importantValue1;
// private int importantValue2;
// private int importantValue3;
Gamma(Account source, int inputValArg, int quantityArg, int yearToDateArg){
this._account = source;
this.inputVal = inputValArg;
this.quantity = quantityArg;
this.yearToDate = yearToDateArg;
}
// refactoring method
int compute(){
if((yearToDate - importantValue1()) > 100){
return getImportantValue3(importantValue2() - 20) - 2 * importantValue1();
}
return getImportantValue3(importantValue2()) - 2 * importantValue1();
}
int importantValue1(){
return (inputVal * quantity) + _account.delta();
}
int importantValue2(){
return (inputVal * yearToDate) + 100;
}
int getImportantValue3(int val){
return val * 7;
}
}
🍎【Substitute Algorithm】- 替换算法
把某个算法替换为另一个更清晰的算法
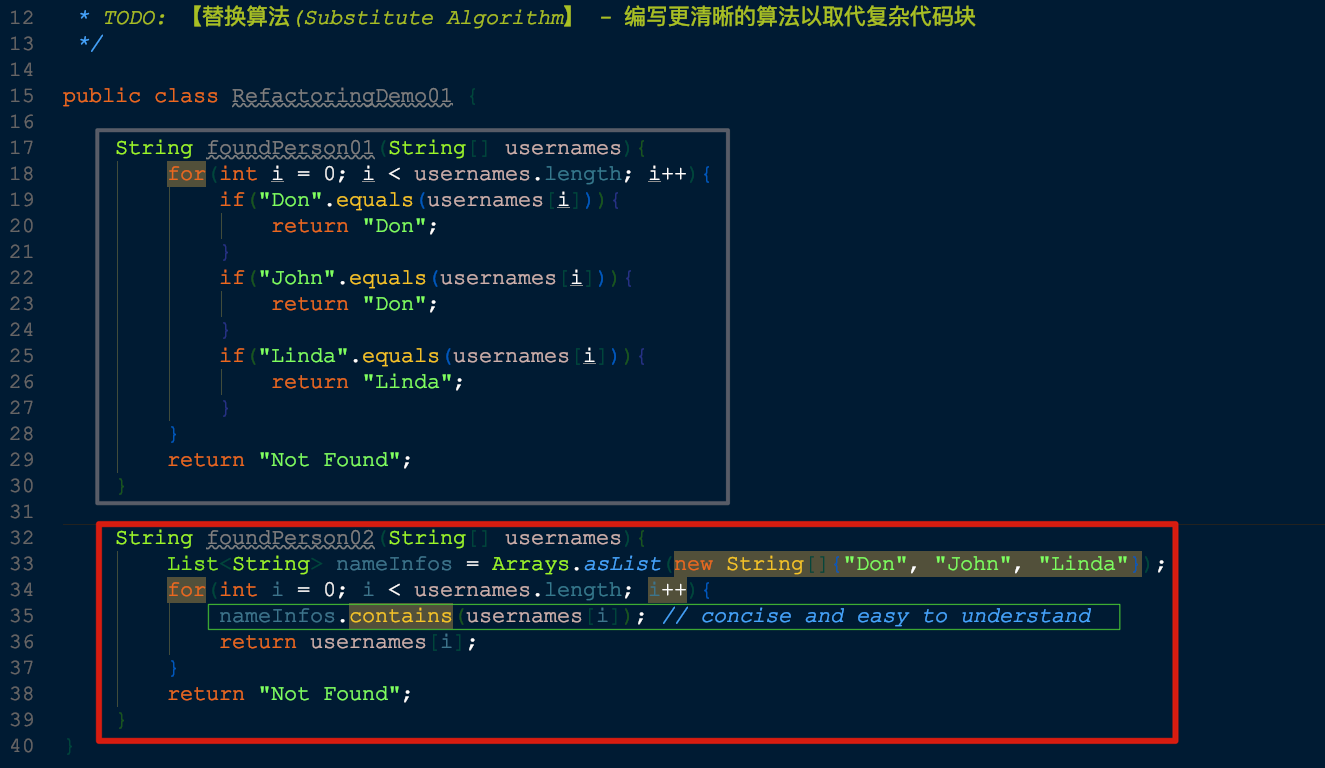
"重构"充分发挥
Divide and Conquer的思想,将复杂的东西分解为小块。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号