数学函数、字符和字符串
常用的数学函数
Math类中方法分为三类: 三角函数方法、指数函数方法和服务方法。
double型常量: Math.PI(π) 和 Math.E(自然对数的底)
三角函数方法:
| Method | DESC |
|---|---|
sin(radians) |
【正弦函数值】 |
cos(radians) |
【余弦函数值】 |
tan(radians) |
【正切函数值】 |
toRadians(degree) |
将度转换为弧度 |
toDegreee(radians) |
将弧度转换为度 |
asin(a) |
反三角正弦函数值 |
acos(a) |
反三角余弦函数值 |
atan(a) |
反三角正切函数值 |
sin、cos & tan 的参数都是以【弧度】
1° = π / 180
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(60))); // 0.5000000000000001
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.PI / 3)); // 0.5000000000000001
指数函数方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
exp(x) |
返回e的x次方 |
| log(x) | 返回x的自然底数 |
| log10(x) | 返回x的以10为低的对数 |
| pow(a, b) | 返回a的b次方 |
| sqrt(x) | 对于 x >= 0 的数字,返回x的平方 |
public class SampleDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.exp(1)); // 2.718281828459045
System.out.println(Math.log(Math.E)); // 1.0
System.out.println(Math.log10(10)); // 1.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3)); // 8.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(3, 2)); // 9.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(4.5, 2.5)); // 42.95673695708276
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(4)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(4, 0.5)); // 2.0
}
}
🌈
Math.sqrt(num)is equal toMath.pow(num, 0.5), 它们都是用来求平方根的。
取整方法
Math类之中包含5个取整方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ceil(x) |
x向上取整为最接近它的整数 |
floor(x) |
x向下取整为最接近它的整数 |
rint(x) |
x取整为它最接近的整数以中间值为基准,在偶数条件下且上下距离相等返回偶数 |
round(x) |
如果x是单精度数,返回(int)Math.floor(x + 0.5),如果x是双精度数,返回(long)Math.floor(x+0.5) |
System.out.println(Math.ceil(2.1)); // 3.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-2.1)); // -2.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(2.1)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(-2.1)); // -3.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(2.1)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(2.4)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(2.6)); // 3.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(2.9)); // 3.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(2.5)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.rint(-2.5)); // -2.0
/*
* Math.round(x) [Warning]
* ⭐️ x 是单精度 则返回的是 (int)Math.floor(x+0.5)
* ⭐️ x 是双精度 则返回的是 (float)Math.floor(x+0.5)
* */
System.out.println(Math.round(3.5)); // 4(long)
System.out.println(Math.round(3)); // 3(int)
System.out.println(Math.round(-0.9)); // (long)-Math.floor(0.9 + 0.5) = -1(long)
System.out.println(Math.round(-1)); // (int)-Math.floor(1 + 0.5) = -1(int)
注意
Math.rint(num) 和Math.round(num)的用法
Math.rint(num)中num是靠近最近的整数
Math.round(num) = Math.floor(num + 0.5)对于单精度结果为int类型 对于双精度结果为long类型
min、max和abs方法
System.out.println(Math.min(123, 321)); // 123
System.out.println(Math.max(123, 321)); // 321
System.out.println(Math.abs(-123)); // 123
要警惕💊就是对于只要比较的数据中有浮点数据那么返回的内容就是浮点内容
System.out.println(Math.max(2.5, 3)); // 3.0
System.out.println(Math.min(2.5, 2)); // 2.0
System.out.println(Math.max(3, 2.5)); // 3.0
System.out.println(Math.min(2, 2.5)); // 2.0
random()方法
Math.random() => [0.0,1.0)
(0.0 <= Math.random() < 1.0) 返回 double数据类型
System.out.println(Math.random()); // [0.0 ~ 1.0) eg: 0.10659138555127168
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 10)); // 1 - 9 eg: 2
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 50)); // 5 - 45 eg: 13
// 如果想要获取 a ~ (a+b) 之间的一个随机整数,不包括 (a+b) ===> (int)(a + Math.random() * b)
// eg: [321 ~ 589)之间的随机整数 321 + Math.random() * 268
System.out.println((int)(321 + Math.random() * 268)); // eg: 507
实例:返回[5.5 ~ 55.5]的一个随机数
public class SampleDemo01 {
public static final double FIVE_COEFFICIENT = 5.0;
public static final double FIFTY_FIVE_COEFFICIENT = 55.0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
System.out.println(getDigitalNum());
}
}
/**
* [5.5, 55.5]之间的整数
* */
public static double getDigitalNum(){
double temp = getDigitalNum00();
if(temp == FIVE_COEFFICIENT){
return getDigitalNumP01();
}
if(temp == FIFTY_FIVE_COEFFICIENT){
return getDigitalNumP02();
}
return temp + getDigitalNum03();
}
/**
* [5.5,5.9]
* */
private static double getDigitalNumP01(){
return FIVE_COEFFICIENT + getDigitalNum02();
}
/**
* [55.1,55.5]
* */
private static double getDigitalNumP02(){
return FIFTY_FIVE_COEFFICIENT + getDigitalNum01();
}
/**
* [5,55]之间的整数
* */
private static double getDigitalNum00(){
return (int)(5 + Math.random() * 51);
}
/**
* [0.0,0.5]之间的小数
* */
private static double getDigitalNum01(){
return (int)(0 + Math.random() * 6) / 10.0;
}
/**
* [0.5,0.9]之间的小数
* */
private static double getDigitalNum02(){
return (int)(5 + Math.random() * 5) / 10.0;
}
/**
* [0.0, 0.9]之间的小数
* */
private static double getDigitalNum03(){
return (int)(0 + Math.random() * 9) / 10.0;
}
}
字符数据类型和操作
字符数据类型表示单个字符即用
``来表示单个字符。字符型直接量用单引号括好
char letter = 'A';
char numChar = '5';
字符串变量必须在双引号中 eg:
"A"
字符变量必须在单引号中 eg:'A'
Unicode和ASCII码
一个字符是由0和1构成的字符序列的形式进行存储的
编码表(encoding scheme)定义该如何编码每个字符
一个16bit的Unicode码占2Byte,以\u开头的4位十六进制表示。范围: '\u0000' - '\uFFFF'.
ASCII码表
'0'~'9' -> 48 ~ 57 -> \u0030 ~ \u0039
'A'~'Z' -> 65 ~ 90 -> \u0041 ~ \u005A
'a'~'z' -> 97 ~ 122 -> \u0061 ~ \u007A
char char01 = 'A';
char char02 = '\u0041';
System.out.println(char01 == char02); // true
System.out.println(char01); // A
System.out.println(char02); // A
特殊字符的转义序列
Java中定义一种特殊的标记来表示特殊字符,这种标记称之为转义序列,转义序列是由反斜杠()后面加上一个字符或一些数字位组成。
转义序列
| 转义序列 | 名称 |
| ---- | ---- |
|\b| 退格键 |
|\t| Tab键 |
|\n| 换行符 |
|\f| 换页符 |
|\r| 回车符 |
|\\| 反斜杠 |
|\"| 双引号 |
反斜杠
</code>称之为转义字符。作为特殊字符 要显示这个字符就需要使用转移序列</code>
System.out.println("\\t is a tab character");
终端打印: \t is a tab character
字符型数据与数值型数据之间的转换
char型数据可以转换成任意一种数值类型。
将一个浮点值转换成char类型时,需要将浮点值转换成int型数据,然后将这个整型值转换成char型数据。
char ch = (char)65.25; // Decimal 65 is assigned to ch
System.out.println(ch); // A
将一个'char'类型数据转换成数值型数据,这个字符的Unicode码就会被转换成某个特定的数值类型。
int i = (int)'A'; // The Unicode of character A is assigned to i
System.out.println(i); // i is 65
int numA = 2 + 'a'; // numA is 99
方法
描述
isDigit(ch) 是字符,返回true
isLetter(ch)是字母,返回true
isLetterOrDigit(ch)是字符或字母其一,返回true
isLowerCase(ch)小写字母,返回true
isUpperCase(ch)大写字母,返回false
toLowerCase(ch)字符的小写形式
toUpperCase(ch)字符的大写形式
char c01 = 'A';
char c02 = 'a';
System.out.println("c02 with uppercase style: " + Character.toUpperCase(c02)); // c02 with uppercase style: A
System.out.println("c01 with lowercase style: " + Character.toLowerCase(c01)); // c01 with lowercase style: a
char x = 'a';
char y = 'c';
System.out.println(++x); // b
System.out.println(y++); // c
System.out.println(x - y); // -2
编写代码,产生随机的小写字母
String类型
字符串是一个字符序列 => String(reference type)。任何Java类都可以将变量表示为引用类型。
String是由final修饰的不可以改变的数据类型
方法
描述
length()获取字符串中字符的个数
charAt(index)根据索引位置获取字符串中指定字符
toUpperCase()转换成大写
toLowerCase()转换成小写
trim删除字符串的前后空白
concat连接两个字符串
String s01 = "hello";
String s02 = "world";
System.out.println(s01.concat(s02)); // helloworld
System.out.println(s01); // hello
在字符串中进行越界访问即msg.charAt(msg.length())会产生的异常是 StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.【StringIndexOutOfBoundsException】: String index out of range: 10
at java.base/java.lang.StringLatin1.charAt(StringLatin1.java:47)
at java.base/java.lang.String.charAt(String.java:693)
at ink.baselearn.unit02.SampleDemo03.main(SampleDemo03.java:14)
String msg01 = "Hi" + 12 / 5;
String msg02 = "Hi" + 12 + 5;
System.out.println("msg01: " + msg01);// msg01: Hi2
System.out.println("msg02: " + msg02);// msg02: Hi125
对于字符串的操作要知道所有的产生新的字符串都是新的,意思是String是final修饰的一旦定义就不可以改变。
trim() 用于删除字符串的前后空白 ===》 产生新的字符串。
从控制台读取字符串
-
next() 是读取以空白字符结束的字符串(即 ''、'\t'、'\f'、‘\r’或'\n')
-
nextLine()是读取一整行文本通过按下回车键为结束标志的字符串
字符串比较
| 方法 | 描述 |
| s1.equals(s2)| 比较s1和s2两个字符串的值是否相等,区分大小写 |
| s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)| 比较s1和s2两个字符串,不区分大小写 |
| s1.compareTo(s2) | 进行字符串比较, >0、=0、<0的整数,表明s1是大于、等于、小于s2 |
| s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)| 进行字符串的比较,不区分大小写|
| startsWith(prefix) | 以...为前缀|
| endsWith(suffix) | 以...为后缀|
| s1.contains(s2) | s1是否包含s2字符串|
String s01 = "Hi";
String s02 = "Hi";
String s03 = s01;
System.out.println(s01 == s02); // false ❌ true ✅ s02和s01都是在常量池中的内容
System.out.println(s01 == s03); // true
System.out.println(s01.equals(s02)); // true
// 牵扯到申请堆内存空间
// "==" 对引用类型比较的是栈指针(引用变量在栈内存中存储的引用)是否相同
String s001 = new String("Hi");
String s002 = new String("Hi");
String s003 = s001;
System.out.println(s001 == s002); // false 涉及到栈内存的比较
System.out.println(s01.equals(s002)); // true
System.out.println(s001 == s003); // true
如果使用 >、>=、< 或 <= 这样的比较操作符来比较两个字符串,就会出现语法错误,要使用compareTo()进行比较(按字典顺序Unicode码)
实例: 实现字符串的按照字母进行排序
public class SampleDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] cityNameArr = new String[5];
System.out.println("Enter 5 cities' name: ");
cityNameArr[0] = input.next();
cityNameArr[1] = input.next();
cityNameArr[2] = input.next();
cityNameArr[3] = input.next();
cityNameArr[4] = input.next();
System.out.println("the original order of arr: " + Arrays.toString(cityNameArr));
System.out.println("==========================Alphabetical Order==========================");
System.out.println("the alphabetical order of arr: " + Arrays.toString(orderByAlphabeticalOrder(cityNameArr)));
}
private static String[] orderByAlphabeticalOrder(String[] cityNameArr) {
for (int i = 0; i < cityNameArr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < cityNameArr.length; j++) {
if (cityNameArr[i].compareTo(cityNameArr[j]) > 0) {
String temp = cityNameArr[i];
cityNameArr[i] = cityNameArr[j];
cityNameArr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return cityNameArr;
}
}
// Enter 5 cities' name:
// Beijing Shanghai Xuzhou Nanjing Suzhou
// the original order of arr: [Beijing, Shanghai, Xuzhou, Nanjing, Suzhou]
// ==========================Alphabetical Order==========================
// the alphabetical order of arr: [Beijing, Nanjing, Shanghai, Suzhou, Xuzhou]
获得子字符串
s.charAt(index)用于提取字符串s中的某个特定的字符。也可以使用String类中的substring方法从字符串中提取子字符串。
String类中包含的获取子字符串的方法:
方法
描述
substring(beginIndex)从特定位置beginIndex开始到字符串的结尾
substring(beginIndex, endIndex)从特定位置beginIndex开始到字符串的endIndex,但不包括endIndex索引上面的字符
String msg = "HelloWorld";
System.out.println(msg.substring(5)); // World
System.out.println(msg.substring(0,5)); // Hello
获取字符串中的字符或子字符串
方法
描述
indexOf(ch)
返回字符串中出现的第一个ch的下标。如果没有匹配的,返回-1
indexOf(ch, fromIndex)
返回字符串中fromIndex之后出现的第一个ch的下标。如果没有匹配的,返回-1
indexOf(s)
返回字符串中出现的第一个字符串s的下标。如果没有匹配的,返回-1
indexOf(s, fromIndex)
返回字符串中fromIndex之后出现的第一个字符串s的下标,如果没有返回-1
lastIndexOf(ch)
返回字符串中最后出现ch的下标。如果没有匹配的,返回-1
lastIndexOf(ch, fromIndex)
返回字符串中fromIndex之前出现的第一个字符串s的下标。如果没有匹配
lastIndexOf(s)
返回字符串中最后出现的字符串s的下标,如果没有匹配的,返回-1
lastIndexOf(s, fromIndex)
返回字符串中fromIndex之前出现的第一个字符串
String msg = "HelloWorld";
System.out.println(msg.indexOf('o')); // 4
System.out.println(msg.lastIndexOf('o')); // 6
System.out.println(msg.lastIndexOf('o', 8)); // 6
System.out.println(msg.lastIndexOf('o', 5)); // 4
lastIndexOf(x, fromIndex) 是指在fromIndex之前出现的第一个
indexOf(x, fromIndex) 是指在fromIndex之后出现的第一个
String username = "Wang zhuang";
int k = username.indexOf(" ");
System.out.println("last name: " + username.substring(0, k)); // last name: Wang
System.out.println("first name: " + username.substring(k + 1)); // first name: zhuang
字符串和数字之间的转换:
-> 将字符串转换成int类型 : Integer.parseInt(msg)
-> 将字符串转换成double类型: Double.parseDouble(msg)
-> 其他类型转换成String类型:
int num = 520;
String numStr01 = num + ""; // 第一种方法
String numStr02 = String.valueOf(num); // 第二种方法
课后习题
String s1 = "Welcome to Java";
String s2 = "Programming is fun";
s1.indexOf('j'); // -1 因为s1中没有j
s1.startsWith("Wel"); // true
s1.endsWith("Java"); // true
System.out.println("Welcome" + 'a' + 1); // Welcomea1
System.out.println('a' + 1 + "Welcome"); // 98Welcome
字符串在编程中是非常基础的内容。使用字符串进行编程的能力对于❄️学习Java编程非常关键。
class Lottery {
private int firstNum;
private int secondNum;
public Lottery() {
}
public Lottery(int firstNum, int secondNum) {
this.firstNum = firstNum;
this.secondNum = secondNum;
}
public int getFirstNum() {
return firstNum;
}
public int getSecondNum() {
return secondNum;
}
public String toString() {
return "【firstNum: " + getFirstNum() + " , secondNum: " + getSecondNum() + "】";
}
}
public class LotteryMatchSystem {
// 【Refactoring Code】 - Introduce Explaining Variables
private static final int RANDOM_FACTOR = 10;
// the privatization of constructor method that represents all of methods in the class should be prefixed with "public static"
private LotteryMatchSystem() {
}
/**
* creates one number[0,9] randomly
*
* @return the number between 0 and 9
*/
private static int generateNumber() {
return (int) (Math.random() * RANDOM_FACTOR);
}
/**
* generates a lottery object with two attributes
*
* @return the lottery
*/
private static Lottery createLottery() {
return new Lottery(generateNumber(), generateNumber());
}
/*
rules:
compare full num and order -> 10000
compare full num and no order-> 3000
compare one num-> 1000
compare no full num and no order -> No Match
*/
/**
* matches the two lottery object's value between <code>realLottery</code> and <code>guessLottery</code>
*
* @param realLottery the lottery object that creates automatically
* @param guessLottery the lottery object that creates manually
* @return the comparative result of the two lottery objects
*/
private static String compareResultOfLottery(Lottery realLottery, Lottery guessLottery) {
if (compareNumberValue(realLottery.getFirstNum(), guessLottery.getFirstNum())
&& compareNumberValue(realLottery.getSecondNum(), guessLottery.getSecondNum())) {
return "10000$";
}
if (compareNumberValue(realLottery.getFirstNum(), guessLottery.getSecondNum())
&& compareNumberValue(realLottery.getSecondNum(), guessLottery.getFirstNum())) {
return "3000$";
}
if (compareNumberValue(realLottery.getFirstNum(), guessLottery.getFirstNum())
|| compareNumberValue(realLottery.getSecondNum(), guessLottery.getSecondNum())
|| compareNumberValue(realLottery.getFirstNum(), guessLottery.getSecondNum())
|| compareNumberValue(realLottery.getSecondNum(), guessLottery.getFirstNum())) {
return "1000$";
}
return "NO MATCH!!!";
}
private static boolean compareNumberValue(int realNum, int guessNum) {
return realNum == guessNum;
}
/**
* the client of LotteryMatchSystem
*/
public static void lotteryMatchSystemClient() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the first number: ");
int firstGuessNum = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the second number: ");
int secondGuessNum = scanner.nextInt();
Lottery guessLottery = new Lottery(firstGuessNum, secondGuessNum);
Lottery realLottery = createLottery();
String result = compareResultOfLottery(realLottery, guessLottery);
System.out.println("==============MATCH RESULT=============");
System.out.println("result: " + result);
System.out.println(guessLottery.toString());
System.out.println(realLottery.toString());
}
}
// Enter the first number:
// 3
// Enter the second number:
// 4
// ==============MATCH RESULT=============
// result: NO MATCH!!!
// 【firstNum: 3 , secondNum: 4】
// 【firstNum: 6 , secondNum: 7】
// Enter the first number:
// 1
// Enter the second number:
// 1
// ==============MATCH RESULT=============
// result: 1000$
// 【firstNum: 1 , secondNum: 1】
// 【firstNum: 1 , secondNum: 9】
格式化控制台输出 - system.out.printf(format, item1, item2 ... itemk)
double amount = 12618.98;
double interestRate = 0.0013;
double interest = amount * interestRate;
System.out.println("Interest is $" + interest); // Interest is $16.404674
System.out.println("Interest is $" + MathUtil.formatNumberWithSpecifiedScale(interest, 2)); // Interest is $16.4
System.out.printf("Interest is $%.2f \n" , MathUtil.formatNumberWithSpecifiedScale(interest, 2)); // Interest is $16.40
System.out.printf("Interest is $%4.2f", interest); // Interest is $16.40
-
格式控制符组成
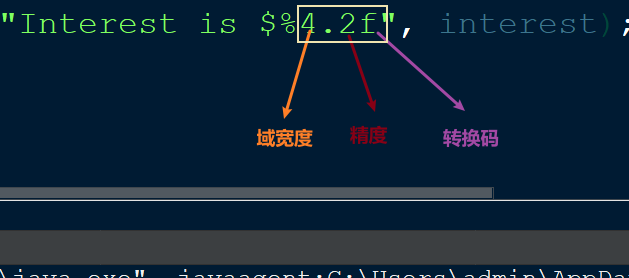
-
常用的格式标识符
标识符
输出
%b布尔值
%c字符
%s字符串
%f浮点值
%d十进制整数
%e科学计数法表示
- 宽度和精度的使用
举例
说明
%5c
输出字符并在这个字符的基础上加上4个空格
%6b
输出的布尔值要把true和false考虑在内如果使true前面再加上2个空格,如果使false前面再加上1个空格
%5d
输出的整数条目,至少为5,如果不超过5用空格补足,如果超过5自动增宽
%10.2f
10这个域宽度要把小数点和保留2为小数位考虑在内,这样前面分配至少7位数字
%12s
12作为字符串的域宽度,保证小于12用空格补足12位,超过12自动增加宽度
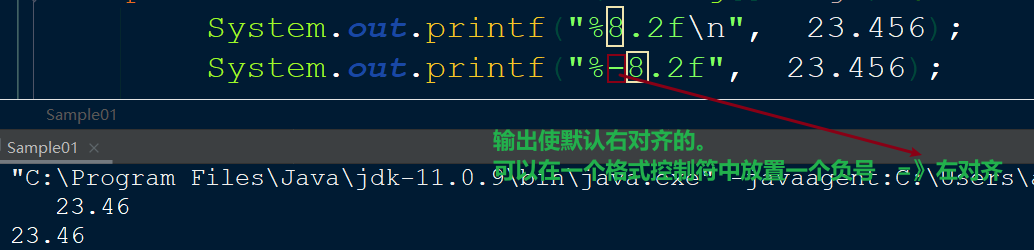
如果要让输出的数据格式中带有百分号——【%】 则需要在格式控制符中使用——【%%】
System.out.printf("%8.2f%% \n", 23.456); // 23.46%
科学计数法基本规则: eg: 32.32表示成科学计数法: 3.232000e+01
Key Items
char type(char类型) instance method(实例方法) encoding(编码) static method(静态方法)
escape character(转义字符) escape sequence(转义序列) supplementary Unicode(补足Unicode码)
format specifier(格式标识符)whitespace character(空白字符)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号