1. 本周学习总结
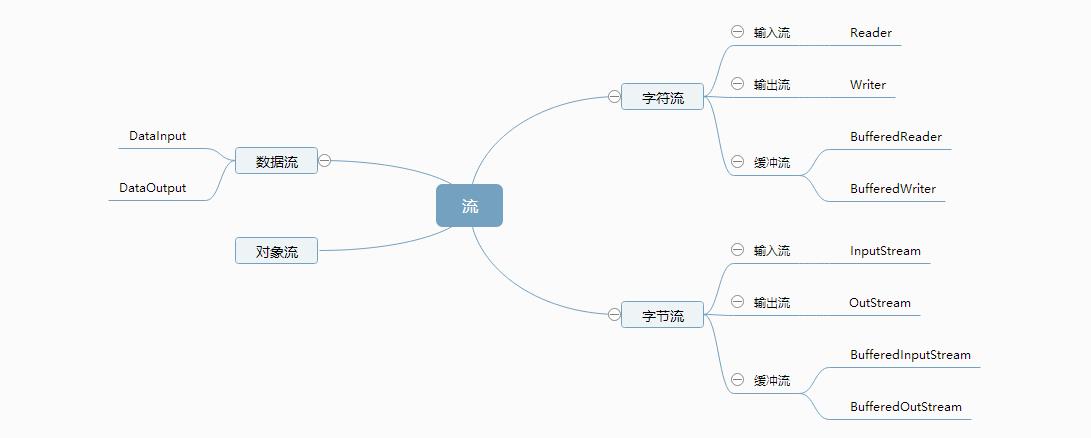
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多流与文件相关内容。
2. 书面作业
将Student对象(属性:int id, String name,int age,double grade)写入文件student.data、从文件读出显示。
1. 字符流与文本文件:使用 PrintWriter(写),BufferedReader(读)
1.1 生成的三个学生对象,使用PrintWriter的println方法写入student.txt,每行一个学生,学生的每个属性之间用|作为分隔。使用Scanner或者BufferedReader将student.txt的数据读出。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123104
public class TextFileTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = new Student(1,"yang", 12, 1);
students[1] = new Student(2,"zhang", 10, 1);
students[2] = new Student(3,"wu", 10, 1);
try
{
// save all employee records to the file employee.dat
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("student.txt");
writeData(student, out);
out.close();
// retrieve all records into a new array
Scanner in = new Scanner(new FileReader("student.txt"));
Student[] newStudent = readData(in);
in.close();
// print the newly read employee records
for (Student e : newStudent)
System.out.println(e);
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
1.2 生成文件大小多少?分析该文件大小
文件大小51字节
1.3 如果调用PrintWriter的println方法,但在后面不close。文件大小是多少?为什么?
0字节 因为并没有数据被实际写入文件,数据在程序终止的时候丢失在缓冲区了;
使用flush方法之后恢复正常.
2. 缓冲流
2.1 使用PrintWriter往文件里写入1千万行(随便什么内容都行),然后对比使用BufferedReader与使用Scanner从该文件中读取数据的速度(只读取,不输出),使用哪种方法快?请详细分析原因?
使用BufferedReader更快,因为BufferedReader是将数据先写到缓冲区,再写到硬盘,使用缓冲方式可以减少真正的底层I/O操作,效率就比Scanner更高。
2.2 将PrintWriter换成BufferedWriter,观察写入文件的速度是否有提升。
有提升,因为BufferedWriter也同样是使用了缓冲方式,减少对底层的I/O操作,提高了效率。
3. 字符编码
3.1 现有EncodeTest.txt 文件,该文件使用UTF-8编码。使用FileReader与BufferedReader将EncodeTest.txt的文本读入并输出。是否有乱码?为什么会有乱码?如何解决?(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123104
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("EncodeTest.txt");
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is,"utf-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr);

3.2 编写一个方法convertGBK2UTF8(String src, String dst),可以将以GBK编码的源文件src转换成以UTF8编码的目的文件dst。
//201521123104
public void convertGBK2UTF8(String src, String dst)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(src);
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(dst);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(os);
String gbk=bf.readLine();
while(gbk!=null)
{
String utf=new String(gbk,"UTF-8");
pw.println(utf);
}
bf.close();
pw.close();
os.close();
}
4. 字节流、二进制文件:DataInputStream, DataOutputStream、ObjectInputStream
4.1 参考DataStream目录相关代码,尝试将三个学生对象的数据写入文件,然后从文件读出并显示。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123104
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.txt");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream (fos);
try
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
dos.writeInt(students[i].getId());
dos.writeInt(students[i].getAge());
dos.writeDouble(students[i].getGrade());
dos.writeUTF(students[i].getName());
}
}
finally
{
dos.close();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("student.txt");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
try
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println(dis.readInt()+"|"+dis.readInt()+"|"+dis.readDouble()+"|"+dis.readUTF());
}
}
finally
{
dis.close();
}
4.2 生成的文件有多大?分析该文件大小?将该文件大小和题目1生成的文件对比是大了还是小了,为什么?
生成文件大小66字节
4.3 使用wxMEdit的16进制模式(或者其他文本编辑器的16进制模式)打开student.data,分析数据在文件中是如何存储的。
5. Scanner基本概念组装对象
编写public static List
7. 文件操作,编写一个程序,可以根据指定目录和文件名,搜索该目录及子目录下的所有文件,如果没有找到指定文件名,则显示无匹配,否则将所有找到的文件名与文件夹名显示出来。
7.1 编写public static void findFile(String path,String filename)函数,以path指定的路径为根目录,在其目录与子目录下查找所有和filename相同的文件名,一旦找到就马上输出到控制台。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
8. 正则表达式
8.1 如何判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式?尝试编程进行验证。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
3. 码云及PTA
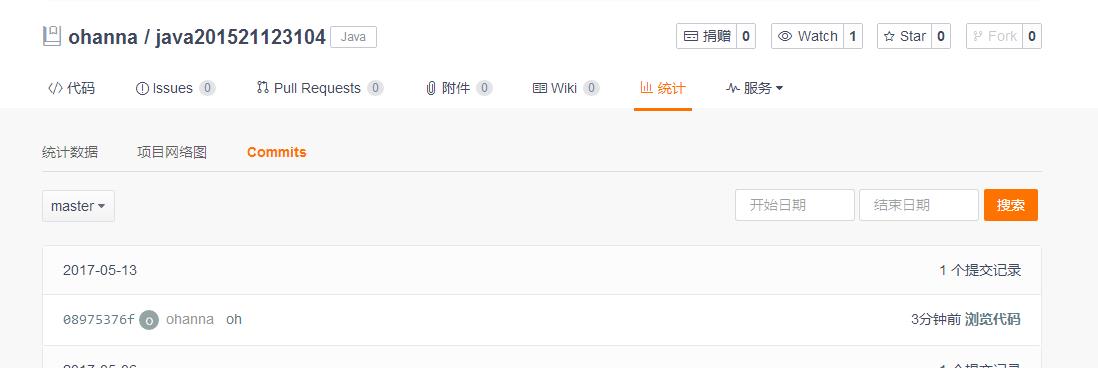
3.1. 码云代码提交记录,在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号