C#多线程编程04-异步编程await和async
using System.Text.Json; using var client = new HttpClient(); var taskGetList = client.GetStringAsync("https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/"); //var response = taskGetList.Result;//该属性将阻塞主线程 var response = await taskGetList; //await后面的代码被视为主线程,看起来像同步运行所有内容 var doc = JsonDocument.Parse(response); JsonElement root = doc.RootElement; JsonElement result = root.GetProperty("results"); JsonElement first = result[0]; Console.WriteLine(first.GetProperty("name")); Console.WriteLine(first.GetProperty("url")); Console.WriteLine("This is the end of the program."); Console.ReadLine();
1、将所有内容放入一个方法中并且它是async方法,那么它实际上是异步运行而不是同步运行。
使用await方法
using System.Text.Json; //主线程 OutputFirstPokemonAsync(); Console.WriteLine("This is the end of the program."); Console.ReadLine(); async void OutputFirstPokemonAsync() { //主线程 using var client = new HttpClient(); //第一个任务 var taskGetList = client.GetStringAsync("https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/"); //await 可以返回值 var response = await taskGetList;//遇到await关键字,主线程被释放,主线程可以处理其它事情 //后续方法均被视为GetStringAsync任务的延续,该延续将在另外一个新的任务中执行 var doc = JsonDocument.Parse(response); JsonElement root = doc.RootElement; JsonElement result = root.GetProperty("results"); JsonElement first = result[0]; Console.WriteLine(first.GetProperty("name")); Console.WriteLine(first.GetProperty("url"));
2、await的特点
await关键字之后的所有内容都被视为延续,当程序运行到await关键字时,调用线程立即被释放,以便它可以自由地做任何其他事情。
await可以返回值
使用await关键字时,它会抛出聚合异常集合中的第一个异常
当使用async和await关键字时,系统会帮助管理同步上下文(invoke方法)
3、await语法
通常当你使用async和await关键字时,是在方法或函数内部使用的。
async Task methodName(...) { ... await SomeTask; //任务的延续 }
若async的方法不返回任何类型时,此方法的类型是Task类型
internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Starting to do work "); WorkAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Press enter to exit"); Console.ReadLine(); } //void返回类型仅在事件处理程序使用 async static Task WorkAsync() { await Task.Delay(2000); //awai后面的代码均为Task的延续 Console.WriteLine("Work is done."); } }
存在返回值的函数
class Program { //Main方法返回类型必须是Task或Task<int>,异步方法返回void时,无法等待其完成 async static Task Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Starting to do work "); var data = await FetchDataAsync(); Console.WriteLine($"data is fetched:{data}"); Console.WriteLine("Press enter to exit"); Console.ReadLine(); } static async Task<string> FetchDataAsync() { await Task.Delay(2000); Console.WriteLine("FetchDataAsync is done"); return "Complex data"; } //void返回类型仅在事件处理程序使用 async static Task WorkAsync() { await Task.Delay(2000); //awai后面的代码均为Task的延续 Console.WriteLine("Work is done."); } }
4、await使用的线程
class Program { //Main方法返回类型必须是Task或Task<int>,异步方法返回void时,无法等待其完成 async static Task Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine($"1、 Main Thread id: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); // Console.WriteLine("Starting to do work "); var data = await FetchDataAsync(); Console.WriteLine($"Data is fetched:{data}"); Console.WriteLine($"2、 Thread id: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); //Console.WriteLine("Press enter to exit"); Console.ReadLine(); } static async Task<string> FetchDataAsync() { Console.WriteLine($"3、 await Before Thread id: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); await Task.Delay(2000); Console.WriteLine($"4、 await After Thread id: {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); Console.WriteLine("FetchDataAsync is done"); return "Complex data"; } }
执行结构
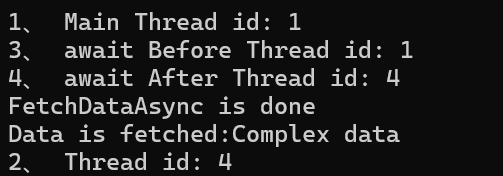
1、 Main Thread id: 1 # 主线程开始
3、 await Before Thread id: 1 # 同步部分仍在主线程
4、 await After Thread id: 4 # 异步完成后可能切换到线程池线程
FetchDataAsync is done
Data is fetched:Complex data
2、 Thread id: 4 # Main方法中await之后,继续在线程池线程执行
5、返回值的延续操作
一:await在任务完成后返回结果,以便你可以在之后的的延续中使用它。
二、await关键字之后的所有内容都被视为一个延续。
using System.Text.Json; using var client = new HttpClient(); var ListJson = await client.GetStringAsync("https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/"); //获取第一个宝可梦的URL var doc = JsonDocument.Parse(ListJson); JsonElement root = doc.RootElement; JsonElement result = root.GetProperty("results"); JsonElement first = result[0]; var url = first.GetProperty("url").ToString(); //获取第一个宝可梦的详细消息 var FristGetDetailJson = await client.GetStringAsync(url); //获取高度和名字 doc = JsonDocument.Parse(FristGetDetailJson); root = doc.RootElement; Console.WriteLine($"name: {root.GetProperty("name")}"); Console.WriteLine($"height: {root.GetProperty("height")}"); Console.WriteLine("This is the end of the program."); Console.ReadLine();
6、使用await处理异常
var tasks = new[] { Task.Run(()=>throw new InvalidOperationException("InvalidOperationException")), Task.Run(() => throw new ArgumentException("ArgumentException")), Task.Run(() => throw new Exception("Exception")) }; await Task.WhenAll(tasks); //抛出第一个异常 Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit");
7、await与同步上下文
await关键字之后的所有内容都被视为任务的延续,
在UI线程中,同步上下文的作用是确保异步操作完成后的回调(即await之后的代码)在UI线程上执行,从而允许安全地更新UI控件
await关键字会捕获当前的同步上下文(如果存在的话)。在UI线程中,这个同步上下文就是UI线程的上下文。
当异步操作完成时,await会尝试在捕获的同步上下文中执行其后续代码。这意味着,即使异步操作是在后台线程上完成的,await之后的代码也会被封送(marshal)回UI线程执行


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号