【d2l】3.2.线性回归从零实现
【d2l】3.2.线性回归从零实现
生成数据集
本次使用\(\text w [2, -3.4]^\top\)、\(b = 4.2\)和噪声\(\epsilon\)生成数据集和标签
代码中为了简化问题,将标准差设置为0.01
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples):
"""生成 y = Xw + b + 噪声"""
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w)))
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
其中features每一行都包含一个二维样本,labels每一行都包含一个标签值(标量)
print(f'features: {features[0]}\nlabel: {labels[0]}')
features: tensor([ 2.1537, -2.2505])
label: tensor([16.1533])
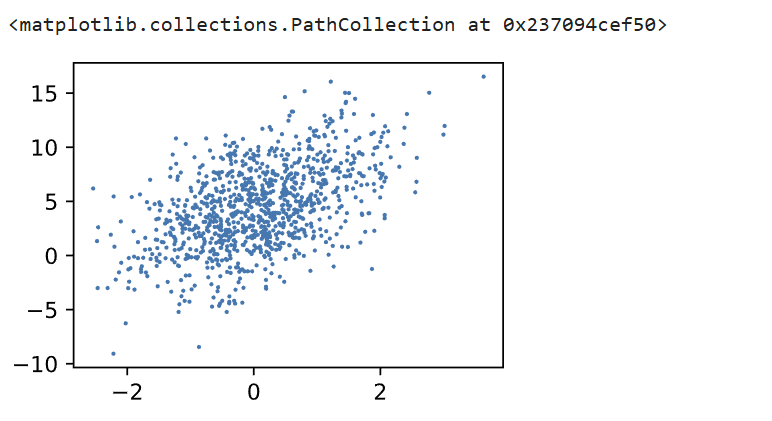
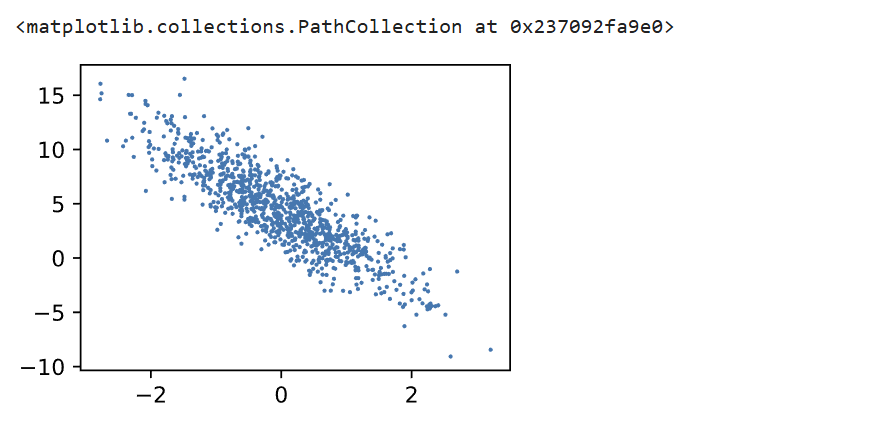
通过生成某一维features和labels的散点图可以直观看出线性关系
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, (0)].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, (1)].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
读取数据集
由于需要抽取小批量样本来对于模型进行更新,因此有必要定义一个函数来抽取样本
定义一个data_iter函数,该函数接受批量大小、特征矩阵和标签向量作为输入,生成大小为batch_size的小批量。每个小批量包含一组特征和标签
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i : min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
以下是一个小型的测试:
batch_size = 10
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print(X, '\n', y)
break
tensor([[ 0.8772, -1.2216],
[-1.1384, -0.4372],
[ 1.3860, -1.8847],
[ 2.3808, -0.8306],
[-0.8442, -0.5185],
[-1.9760, 0.1422],
[ 2.1241, -0.8893],
[-1.1176, -0.1472],
[ 0.8191, 1.1800],
[-0.6468, 0.6817]])
tensor([[10.1006],
[ 3.4129],
[13.3894],
[11.8007],
[ 4.2835],
[-0.2343],
[11.4744],
[ 2.4490],
[ 1.8172],
[ 0.5862]])
初始化模型参数
在训练之前需要先初始化模型参数
本次实验中从均值为0,标准差为0.01的正态分布中抽取随机数初始化权重,并将偏置初始化为0
并且为了使用自动微分,要设置requires_grad = True
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size = (2, 1), requires_grad = True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad = True)
定义必要组件
首先是定义模型,对于线性回归模型来说就是矩阵-向量乘法后加上偏置
def linreg(X, w, b):
"""线性回归模型"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
接着是定义损失函数,利用的是均方损失
def squared_loss(y_hat, y):
"""均方损失"""
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2 / 2
最后定义优化算法,像前文说的是sgd
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size):
"""小批量随机梯度下降"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
torch.no_grad()指的是在参数更新过程中并不会建立计算图,因为param本身requires_grad = True,如果没有关掉的话会使得乘上lr的行为被记录,这是我们不需要的
然后就是如同之前说的更新方式,注意/batch_size,因为loss本身是在求和后自动微分,因此要消除批量大小对于结果的影响
最后需要梯度清零,因为梯度默认累加,如果不清零会造成事实性错误
训练
训练流程的迭代过程如下:
- 计算梯度
- 更新参数
函数就很好写了
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = d2l.linreg
loss = d2l.squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y)
l.sum().backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()) : f}')
结果如下
epoch 1, loss 0.059939
epoch 2, loss 0.000297
epoch 3, loss 0.000055
再观察相对误差
print(f'w的估计误差:{true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差:{true_b - b}')
w的估计误差:tensor([ 0.0013, -0.0007], grad_fn=<SubBackward0>)
b的估计误差:tensor([0.0009], grad_fn=<RsubBackward1>)
简洁实现
事实上一些常用的损失函数、优化算法等都在torch有实现,因此在实际训练过程中调包就行了
(此处为3.3的内容,因此3.3不再单开专题)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号