Ray Tracing in One Weekend Part2
#include <iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include "v3d.h"
#include "ray.h"
#include "color.h"
using namespace std;
// Type aliases for vec3
using point3 = vec3; // 3D point
using color = vec3; // RGB color
inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const vec3& v) {
return out << v.e[0] << ' ' << v.e[1] << ' ' << v.e[2];
}
inline vec3 operator+(const vec3& u, const vec3& v) {
return vec3(u.e[0] + v.e[0], u.e[1] + v.e[1], u.e[2] + v.e[2]);
}
inline vec3 operator-(const vec3& u, const vec3& v) {
return vec3(u.e[0] - v.e[0], u.e[1] - v.e[1], u.e[2] - v.e[2]);
}
inline vec3 operator*(const vec3& u, const vec3& v) {
return vec3(u.e[0] * v.e[0], u.e[1] * v.e[1], u.e[2] * v.e[2]);
}
inline vec3 operator*(double t, const vec3& v) {
return vec3(t * v.e[0], t * v.e[1], t * v.e[2]);
}
inline vec3 operator*(const vec3& v, double t) {
return vec3(t * v.e[0], t * v.e[1], t * v.e[2]);
}
inline vec3 operator/(vec3 v, double t) {
return vec3((1 / t) * v.e[0], (1 / t) * v.e[1], (1 / t) * v.e[2]);
//(1 / t) * v;
}
inline double dot(const vec3& u, const vec3& v) {
return u.e[0] * v.e[0]
+ u.e[1] * v.e[1]
+ u.e[2] * v.e[2];
}
inline vec3 cross(const vec3& u, const vec3& v) {
return vec3(u.e[1] * v.e[2] - u.e[2] * v.e[1],
u.e[2] * v.e[0] - u.e[0] * v.e[2],
u.e[0] * v.e[1] - u.e[1] * v.e[0]);
}
inline vec3 unit_vector(vec3 v) {
return vec3(v.e[0] / v.length(), v.e[1] / v.length(), v.e[2] / v.length());
}
bool hit_sphere(const point3& center, double radius, const ray& r) {
vec3 oc = r.origin() - center;
auto a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction());//t2b⋅b+2tb⋅(A−C)+(A−C)⋅(A−C)−r2=0 函数关于t, P(t)=A+tb
auto b = 2.0 * dot(oc, r.direction());
auto c = dot(oc, oc) - radius * radius;
auto discriminant = b * b - 4 * a * c;
return (discriminant > 0);
}
color ray_color(const ray& r) {
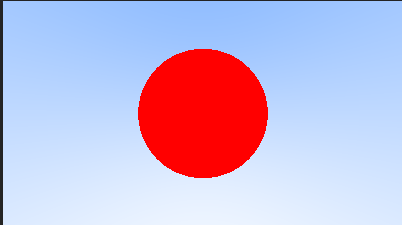
if (hit_sphere(point3(0, 0, -1), 0.5, r))//如果打中了球,在球的范围内,就变成红色
return color(1, 0, 0);
vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());
//显示蓝色背景
auto t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
return (1.0 - t) * color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t * color(0.5, 0.7, 1.0);
}
int main()
{
// Image
const auto aspect_ratio = 16.0 / 9.0;
const int image_width = 400;
const int image_height = static_cast<int>(image_width / aspect_ratio);
// Camera
auto viewport_height = 2.0;
auto viewport_width = aspect_ratio * viewport_height;
auto focal_length = 1.0;
auto origin = point3(0, 0, 0);
auto horizontal = vec3(viewport_width, 0, 0);
auto vertical = vec3(0, viewport_height, 0);
auto lower_left_corner = origin - horizontal / 2 - vertical / 2 - vec3(0, 0, focal_length);
// Render
ofstream file("graph1-1.ppm");
file << "P3\n" << image_width << ' ' << image_height << "\n255\n";
for (int j = image_height - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
std::cerr << "\rScanlines remaining: " << j << ' ' << std::flush;
for (int i = 0; i < image_width; ++i) {
auto u = double(i) / (image_width - 1);
auto v = double(j) / (image_height - 1);
auto add = lower_left_corner + u * horizontal + v * vertical - origin;
ray r(origin, add);
color pixel_color = ray_color(r);
write_color(file, pixel_color);
}
}
std::cerr << "\nDone.\n";
}
更新:问题已解决,没有理解endif的意思,在endif后面的内容都会不进行编译
出现了一点小问题,inline函数需要放到主程序而不是头文件才能正常调用,否则会出现双重定义的bug,暂时还没有解决
inline 函数:
关键字inline 必须与函数定义体放在一起才能使函数成为内联,即不能先定义后写具体内容
最好把inline函数的定义放到头文件中,在每个调用该inline函数的文件中包含该头文件。这种方法保证对每个inline函数只有一个定义,否则可能会报错多次定义



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号