针对燃油运输类车辆调度问题设计的蚁群算法模型
一、问题建模
1. 问题特征
- 多车辆协同:N辆油罐车从集货中心出发
- 多客户配送:M个客户点(加油站/储油库)
- 双目标优化: 最小化总运输成本(燃油消耗+车辆折旧) 最大化客户满意度(准时送达率)
- 核心约束: 车辆载重限制(≤20吨) 硬时间窗(客户要求送达时间) 油耗非线性模型(与载重、坡度相关)
2. 数学模型
目标函数:
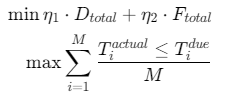
约束条件:

二、蚁群算法设计
1. 信息素结构
% 三维信息素矩阵:[路径][车辆][时间窗]
pheromone = rand(N_path, N_vehicle, T_max) * 0.1;
2. 启发式信息设计
多维度启发因子:
% 距离启发因子(距离倒数)
eta_distance = 1 ./ distance_matrix;
% 油耗启发因子(非线性模型)
eta_fuel = 1 ./ (a*distance + b*load + c*grade);
% 时间窗启发因子(剩余时间权重)
eta_time = 1 ./ (due_time - current_time);
3. 状态转移规则
概率计算:
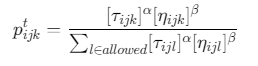
动态参数调整:
alpha = 1.2; % 信息素重要度
beta = 3.5; % 启发式重要度
rho = 0.15; % 信息素挥发系数
4. 多目标协同机制
帕累托前沿更新:
% 非支配排序
[fronts, ~] = non_dominated_sort(costs, satisfactions);
% 拥挤度计算
crowding_distance = calculate_crowding(fronts);
% 外部档案更新
archive = update_archive(fronts, crowding_distance);
三、算法实现流程
1. 初始化阶段
% 参数设置
num_ants = 30; % 蚂蚁数量
max_iter = 200; % 最大迭代次数
Q = 100; % 信息素增量常数
% 数据预处理
[distance_matrix, time_matrix, fuel_matrix] = preprocess_data();
% 初始信息素
pheromone = ones(N_path, N_vehicle);
2. 蚂蚁路径构建
for ant = 1:num_ants
current_node = depot;
unvisited = 1:M;
path = [];
while ~isempty(unvisited)
% 计算转移概率
probabilities = calculate_probabilities(current_node, unvisited);
% 轮盘赌选择
next_node = roulette_wheel_selection(probabilities);
% 更新路径
path = [path, next_node];
unvisited(unvisited == next_node) = [];
current_node = next_node;
end
% 返回仓库
path = [path, depot];
% 计算目标函数值
[cost, satisfaction] = evaluate_solution(path);
% 更新外部档案
update_archive(path, cost, satisfaction);
end
3. 信息素更新
% 信息素挥发
pheromone = (1 - rho) * pheromone;
% 信息素增强
for i = 1:num_ants
path = ants(i).path;
delta_pheromone = Q / calculate_total_cost(path);
for j = 1:length(path)-1
pheromone(path(j), path(j+1)) = ...
pheromone(path(j), path(j+1)) + delta_pheromone;
end
end
四、MATLAB实现示例
1. 主程序框架
%% 参数设置
num_customers = 50;
num_vehicles = 8;
depot = [0,0];
%% 数据生成
[customers, demands, time_windows] = generate_data(num_customers);
%% 算法运行
aco = AntColonyOptimizer(num_ants, max_iter);
[best_path, costs, satisfactions] = aco.optimize(customers, demands, time_windows);
%% 结果可视化
plot_solution(best_path, depot);
2. 核心类定义
classdef AntColonyOptimizer
properties
num_ants
max_iter
alpha
beta
rho
Q
end
methods
function obj = AntColonyOptimizer(num_ants, max_iter)
obj.num_ants = num_ants;
obj.max_iter = max_iter;
obj.alpha = 1.2;
obj.beta = 3.5;
obj.rho = 0.15;
obj.Q = 100;
end
function [best_path, costs, satisfactions] = optimize(obj, customers, demands, time_windows)
% 初始化信息素
pheromone = ones(size(customers,1)+1);
best_cost = inf;
best_satisfaction = 0;
for iter = 1:obj.max_iter
% 蚂蚁路径构建
paths = cell(obj.num_ants,1);
costs = zeros(obj.num_ants,1);
satisfactions = zeros(obj.num_ants,1);
for ant = 1:obj.num_ants
path = construct_path(pheromone, customers, demands, time_windows);
[cost, satisfaction] = evaluate_solution(path);
if cost < best_cost
best_cost = cost;
best_path = path;
end
paths{ant} = path;
costs(ant) = cost;
satisfactions(ant) = satisfaction;
end
% 信息素更新
pheromone = update_pheromone(pheromone, paths, costs);
end
end
end
end
参考代码 根据蚁群算法,建立蚁群算法模型,适合燃油运输类,车辆调度类问题 www.youwenfan.com/contentcnk/78758.html
五、应用场景
- 多能源车辆调度: 支持柴油/电动/混动车辆混合调度 考虑充电桩位置与充电时间
- 危险品运输优化: 增加安全距离约束 事故风险路段规避
- 动态需求响应: 处理客户临时增减货需求 基于强化学习的动态重调度


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号