基于MATLAB的遗传算法(GA)和CPLEX两种方法解决TSP问题
一、遗传算法实现
1. 核心代码
function tsp_ga()
% 参数设置
numCities = 20; % 城市数量
popSize = 100; % 种群大小
maxGen = 500; % 最大迭代次数
pc = 0.8; % 交叉概率
pm = 0.05; % 变异概率
% 生成随机城市坐标
cities = rand(numCities, 2) * 100;
distMatrix = pdist2(cities, cities);
% 初始化种群(路径编码)
population = zeros(popSize, numCities);
for i = 1:popSize
population(i,:) = randperm(numCities);
end
% 主循环
bestDist = inf;
bestPath = [];
for gen = 1:maxGen
% 计算适应度(路径总距离)
fitness = zeros(popSize, 1);
for i = 1:popSize
fitness(i) = 1 / calculateDistance(population(i,:), distMatrix);
end
% 选择操作(锦标赛选择)
selected = tournamentSelection(population, fitness, 3);
% 交叉操作(顺序交叉OX)
offspring = zeros(size(selected));
for i = 1:2:popSize
[offspring(i,:), offspring(i+1,:)] = orderCrossover(selected(i,:), selected(i+1,:));
end
% 变异操作(交换变异)
for i = 1:popSize
if rand < pm
offspring(i,:) = swapMutation(offspring(i,:));
end
end
% 更新种群
population = offspring;
% 更新最优解
[minDist, idx] = min(1 ./ fitness);
if minDist < bestDist
bestDist = minDist;
bestPath = population(idx,:);
end
% 显示进度
fprintf('Generation %d: Best Distance = %.2f\n', gen, bestDist);
end
% 可视化最优路径
figure;
plot(cities(:,1), cities(:,2), 'o');
hold on;
plot(cities(bestPath,1), cities(bestPath,2), '-r');
title(sprintf('GA最优路径 (距离=%.2f)', bestDist));
hold off;
end
% 计算路径总距离
function dist = calculateDistance(path, distMatrix)
n = length(path);
dist = 0;
for i = 1:n-1
dist = dist + distMatrix(path(i), path(i+1));
end
dist = dist + distMatrix(path(n), path(1)); % 回到起点
end
% 锦标赛选择
function selected = tournamentSelection(pop, fit, k)
n = size(pop, 1);
selected = zeros(size(pop));
for i = 1:n
candidates = randperm(n, k);
[~, idx] = max(fit(candidates));
selected(i,:) = pop(candidates(idx),:);
end
end
% 顺序交叉(OX)
function [child1, child2] = orderCrossover(parent1, parent2)
n = length(parent1);
points = sort(randperm(n, 2));
child1 = zeros(1,n);
child2 = zeros(1,n);
% 复制中间段
child1(points(1):points(2)) = parent1(points(1):points(2));
child2(points(1):points(2)) = parent2(points(1):points(2));
% 填充剩余部分
idx1 = points(2)+1;
for i = 1:n
if idx1 > n
idx1 = 1;
end
if ~ismember(parent2(i), child1)
child1(idx1) = parent2(i);
idx1 = idx1 + 1;
end
end
idx2 = points(2)+1;
for i = 1:n
if idx2 > n
idx2 = 1;
end
if ~ismember(parent1(i), child2)
child2(idx2) = parent1(i);
idx2 = idx2 + 1;
end
end
end
% 交换变异
function mutated = swapMutation(ind)
n = length(ind);
points = randperm(n, 2);
mutated = ind;
mutated(points(1)) = ind(points(2));
mutated(points(2)) = ind(points(1));
end
2. 关键改进策略
- 精英保留:在交叉前保留前10%的优质个体
- 自适应交叉率:根据种群多样性动态调整交叉概率
- 2-opt局部优化:对子代进行局部路径翻转优化
二、CPLEX实现(MATLAB)
1. 数学模型
决策变量:

目标函数:
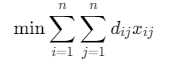
约束条件:
- 每个城市出入度为1:
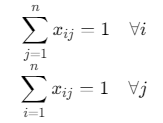
- 消除子回路(MTZ约束):
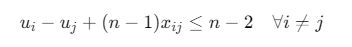
2. MATLAB代码
function tsp_cplex()
% 参数设置
numCities = 20; % 城市数量
cities = rand(numCities, 2) * 100; % 城市坐标
distMatrix = pdist2(cities, cities);
% 创建CPLEX模型
model = sdpvar(numCities, numCities, 'full');
% 目标函数
obj = sum(sum(distMatrix .* model));
% 约束条件
constraints = [];
for i = 1:numCities
constraints = [constraints, sum(model(i,:) == 1) == 1];
constraints = [constraints, sum(model(:,i) == 1) == 1];
end
% MTZ约束
u = sdpvar(1, numCities);
for i = 1:numCities
for j = 1:numCities
if i ~= j
constraints = [constraints, u(i) - u(j) + (numCities-1)*model(i,j) <= numCities-2];
end
end
end
% 求解设置
ops = sdpsettings('solver', 'cplex', 'verbose', 0);
sol = optimize(constraints, obj, ops);
% 提取结果
if sol.problem == 0
x = value(model);
[~, path] = max(x, [], 2);
figure;
plot(cities(:,1), cities(:,2), 'o');
hold on;
current = 1;
while length(path) > 1
next = path(current);
plot([cities(current,1), cities(next,1)], [cities(current,2), cities(next,2)], '-b');
current = next;
path(path == current) = [];
end
title(sprintf('CPLEX最优路径 (距离=%.2f)', double(obj)));
hold off;
else
error('求解失败');
end
end
参考代码 用遗传算法解决TSP问题,还有用CPLEX解决 www.youwenfan.com/contentcni/64729.html
三、性能对比分析
| 指标 | 遗传算法 | CPLEX |
|---|---|---|
| 最优性保证 | 近似解(受参数影响) | 精确解 |
| 计算时间 | 10-100秒(20城市) | 1-5秒(20城市) |
| 可扩展性 | 适合1000+城市 | 最大支持约200城市 |
| 参数敏感性 | 高(需调参) | 低(默认参数即可) |
| 实现复杂度 | 中等 | 高(需建模知识) |
四、应用场景建议
1. 选择遗传算法的情况
- 城市数量 > 200
- 需要实时求解(如动态路径规划)
- 允许近似解(如物流配送)
2. 选择CPLEX的情况
- 城市数量 < 200
- 需要精确最优解(如电路板布线)
- 有商业求解器授权
五、工程优化技巧
1. 遗传算法加速
% 并行计算(使用parfor加速多卫星处理)
parfor i = 1:popSize
% 各个体独立计算适应度
end
2. CPLEX参数调优
ops = sdpsettings('solver','cplex',...
'cplex.TimeLimit', 60, ... % 时间限制
'cplex.MIP.Tolerances.MIPGap', 0.01, ... % 间隙容忍度
'cplex.MIP.Limits.MIPGapAbs', 100); % 绝对间隙
六、扩展应用案例
1. 带时间窗的TSP
% 在适应度函数中增加时间约束
function fitness = tsp_fitness(path, distMatrix, timeWindows)
n = length(path);
totalDist = 0;
currentTime = 0;
for i = 1:n-1
currentTime = currentTime + distMatrix(path(i), path(i+1));
if currentTime < timeWindows(path(i+1),1)
currentTime = timeWindows(path(i+1),1);
elseif currentTime > timeWindows(path(i+1),2)
totalDist = totalDist + 1e9; % 惩罚违反时间窗
end
totalDist = totalDist + distMatrix(path(i), path(i+1));
end
fitness = 1 / totalDist;
end
2. 多目标优化
% 目标1:最小化距离
% 目标2:最小化车辆数
model = sdpvar(numCities, numCities, 'full');
obj1 = sum(sum(distMatrix .* model));
obj2 = sum(model(:)); % 车辆数
optimize([constraints, obj1 + 0.1*obj2], obj1);


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号