Linux 中 xargs 选项中-I将左侧变量传入{}
001、
a、总变量传入
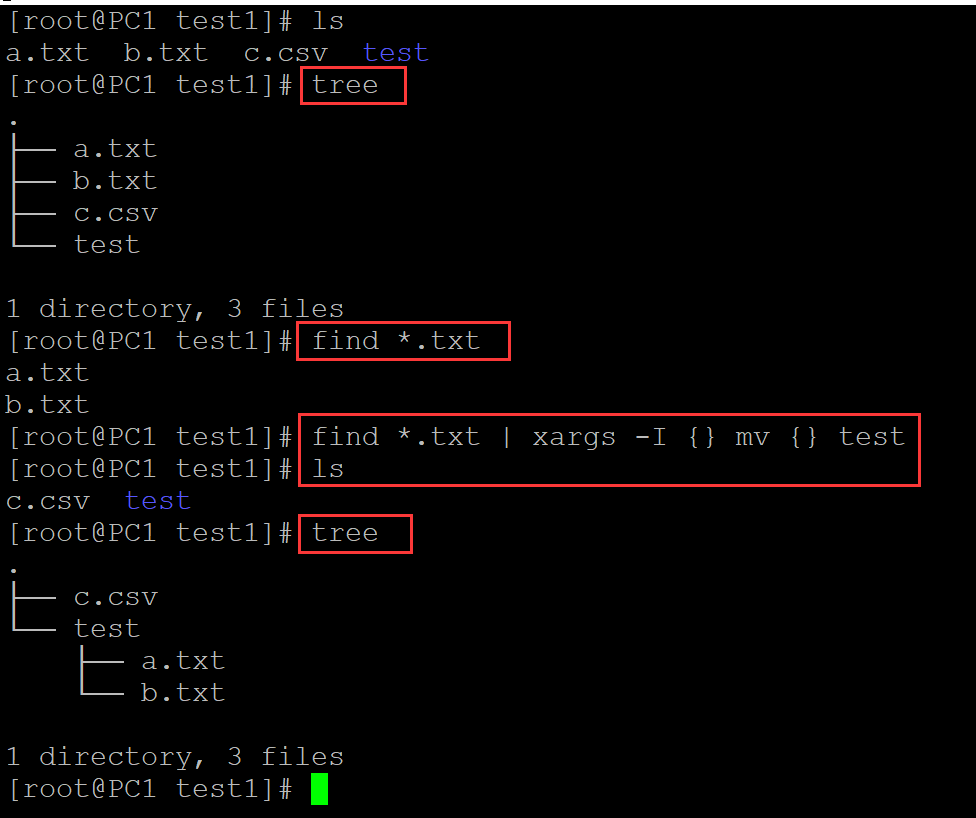
[root@PC1 test1]# ls ## 测试文件及目录 a.txt b.txt c.csv test [root@PC1 test1]# tree ## 查看目录结构 . ├── a.txt ├── b.txt ├── c.csv └── test 1 directory, 3 files [root@PC1 test1]# find *.txt a.txt b.txt [root@PC1 test1]# find *.txt | xargs -I {} mv {} test ## xargs 中 -I选项实现将左侧变量传入 {}; 然后结合mv移动至test目录 [root@PC1 test1]# ls c.csv test [root@PC1 test1]# tree . ├── c.csv └── test ├── a.txt └── b.txt 1 directory, 3 files
b、单个变量传入
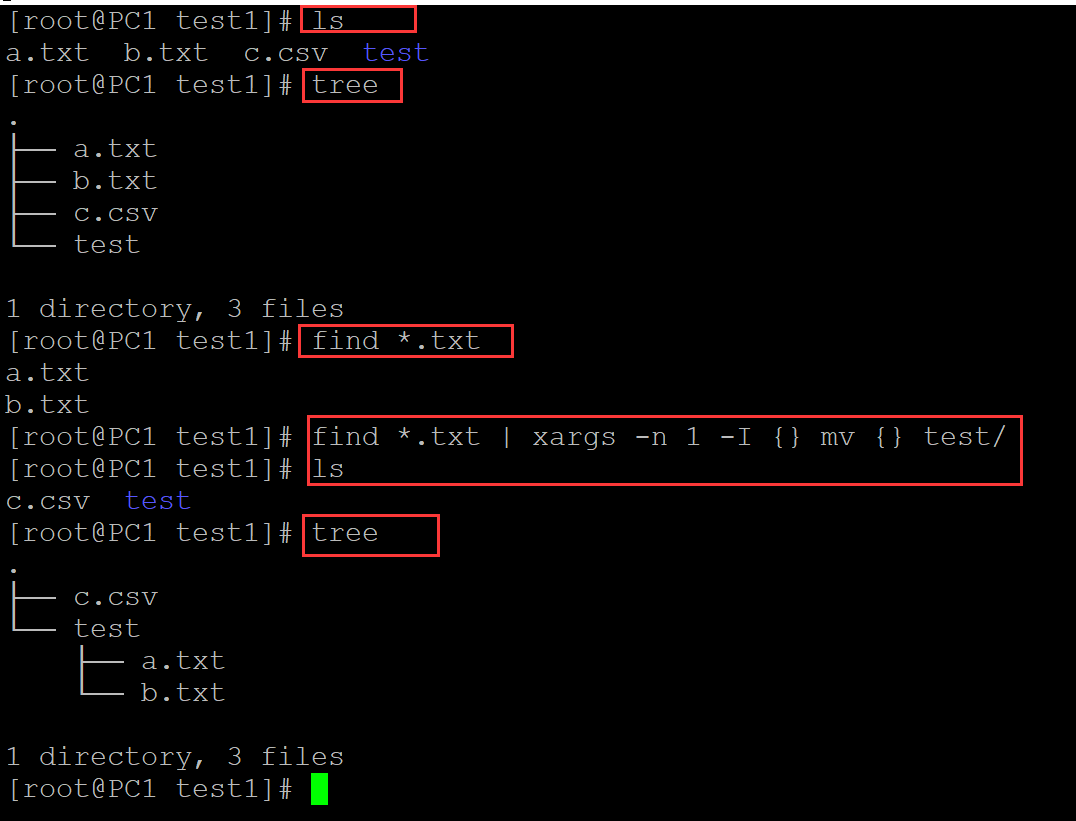
[root@PC1 test1]# ls ## 测试文件及目录 a.txt b.txt c.csv test [root@PC1 test1]# tree . ├── a.txt ├── b.txt ├── c.csv └── test 1 directory, 3 files [root@PC1 test1]# find *.txt a.txt b.txt [root@PC1 test1]# find *.txt | xargs -n 1 -I {} mv {} test/ ## -I选项将单个变量传入{} [root@PC1 test1]# ls c.csv test [root@PC1 test1]# tree . ├── c.csv └── test ├── a.txt └── b.txt 1 directory, 3 files
。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号