linux中实现将宽列数据按照指定列数堆叠输出
001、方法1, cut + 循环
[root@pc1 test01]# ls a.txt [root@pc1 test01]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050 [root@pc1 test01]# for i in $(seq 1 2 $(head -n 1 a.txt | awk '{print NF}')); do let j=$i+1; cut -d " " -f $i-$j a.txt >> result.txt; done [root@pc1 test01]# ls a.txt result.txt [root@pc1 test01]# cat result.txt 001 002 011 012 021 022 031 032 041 042 003 004 013 014 023 024 033 034 043 044 005 006 015 016 025 026 035 036 045 046 007 008 017 018 027 028 037 038 047 048 009 010 019 020 029 030 039 040 049 050
002、 xargs 实现
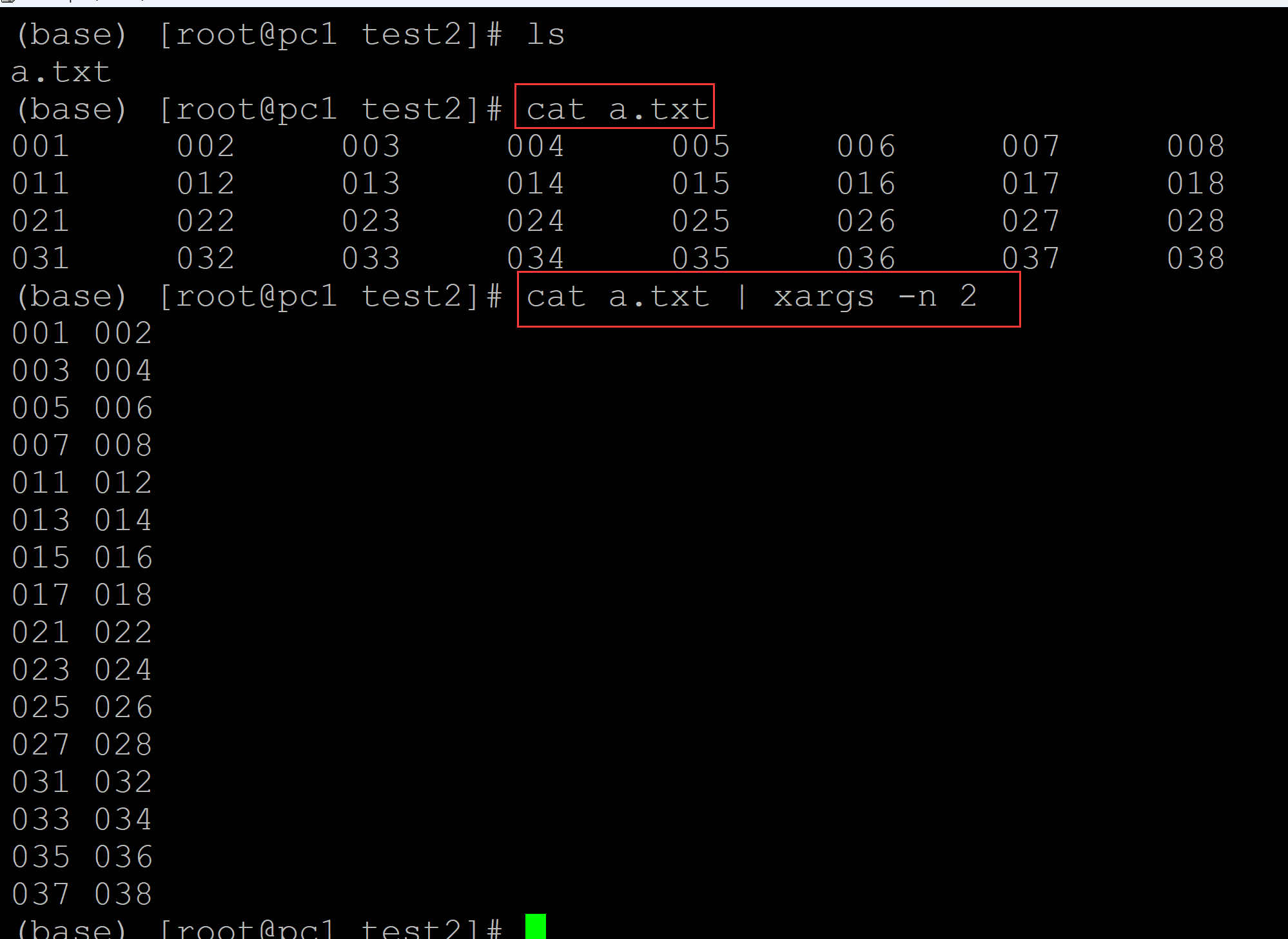
(base) [root@pc1 test2]# ls a.txt (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt | xargs -n 2 ## 每两行转换为一列 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038
003、 sed + awk实现
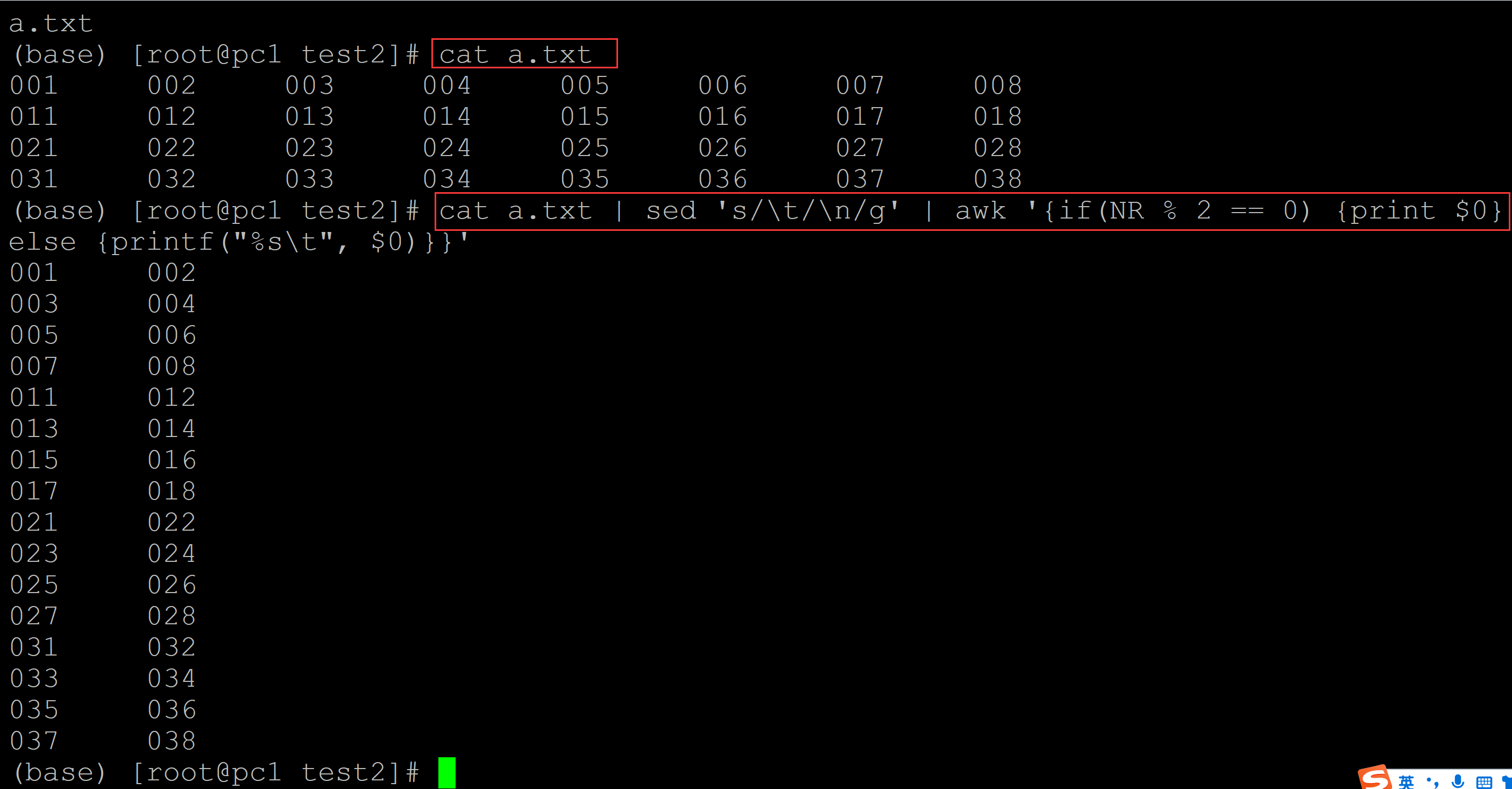
(base) [root@pc1 test2]# ls a.txt (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt | sed 's/\t/\n/g' | awk '{if(NR % 2 == 0) {print $0} else {printf("%s\t", $0)}}' 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038
004、awk
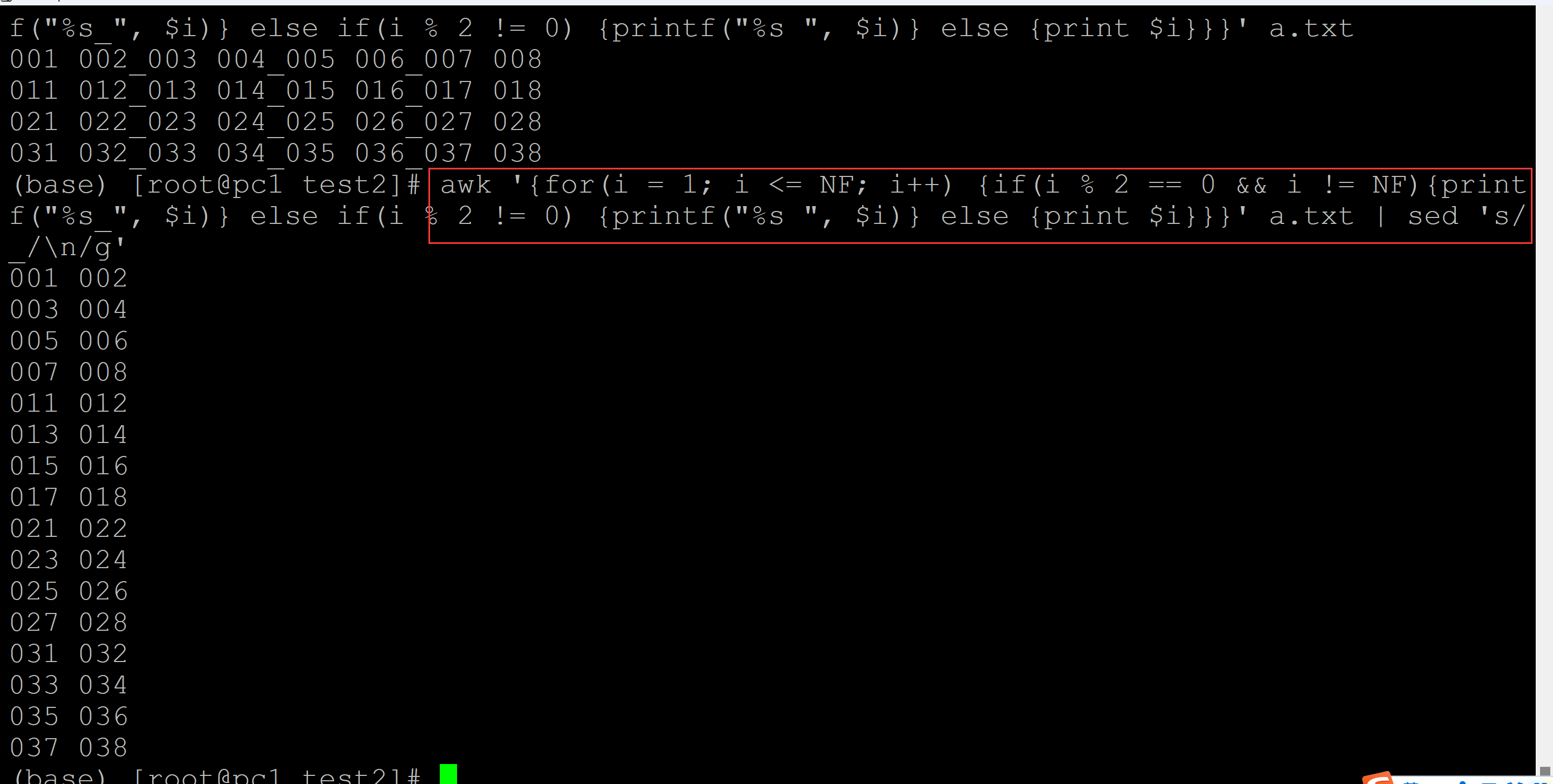
(base) [root@pc1 test2]# ls a.txt (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# awk '{for(i = 1; i <= NF; i++) {if(i % 2 == 0 && i != NF){printf("%s_", $i)} else if(i % 2 != 0) {printf("%s ", $i)} else {print $i}}}' a.txt 001 002_003 004_005 006_007 008 011 012_013 014_015 016_017 018 021 022_023 024_025 026_027 028 031 032_033 034_035 036_037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# awk '{for(i = 1; i <= NF; i++) {if(i % 2 == 0 && i != NF){printf("%s_", $i)} else if(i % 2 != 0) {printf("%s ", $i)} else {print $i}}}' a.txt | sed 's/_/\n/g' 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038
005、 python实现
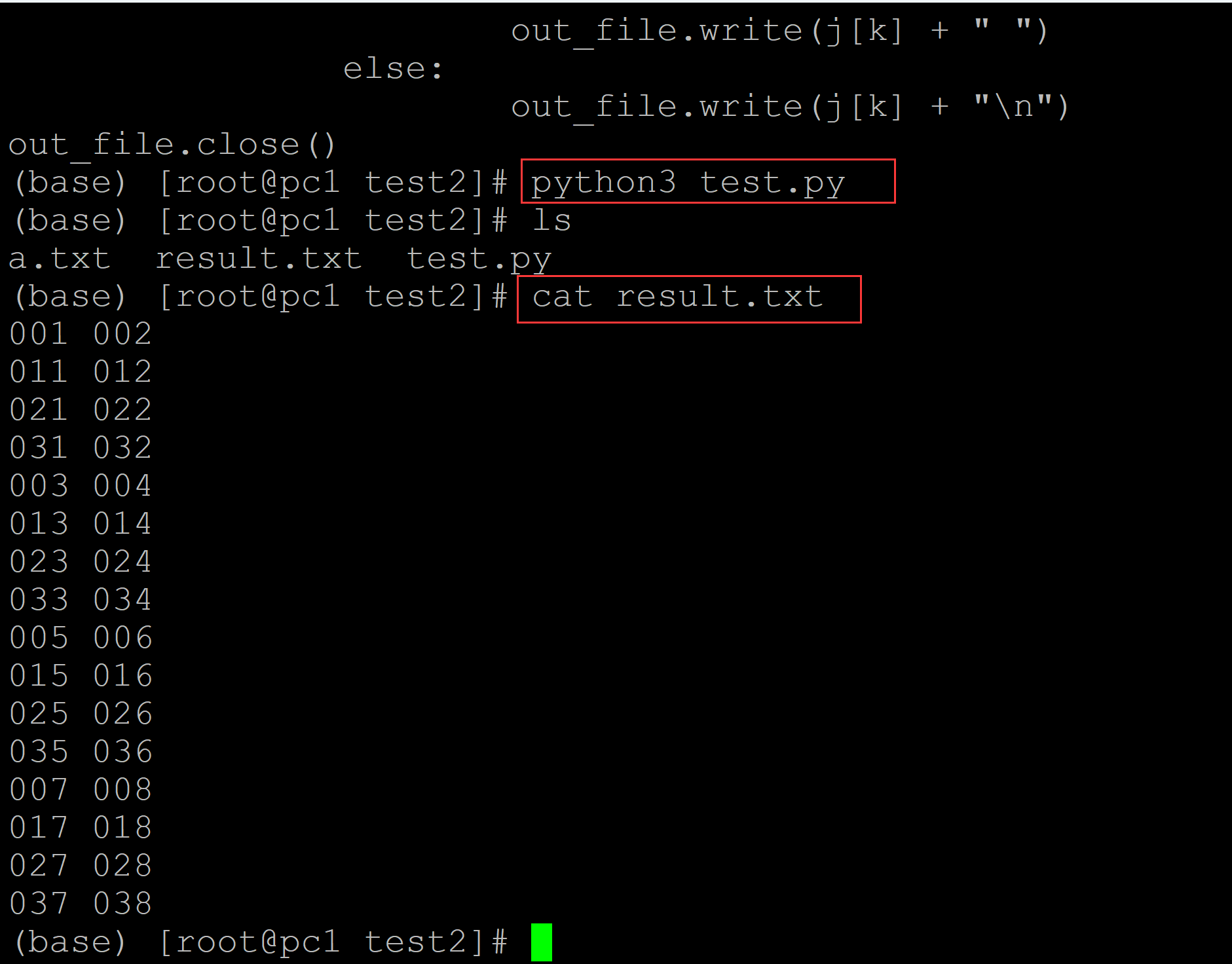
(base) [root@pc1 test2]# ls a.txt test.py (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat a.txt ## 测试数据 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat test.py ## 转换程序 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- in_file = open("a.txt", "r") out_file = open("result.txt", "w") length = len(in_file.readlines()[0].strip().split("\t")) in_file.close() in_file = open("a.txt", "r") dict1 = dict() for i in range(0,length,2): dict1[i] = [] for i in in_file: i = i.strip().split("\t") for j in range(len(i)): for k in dict1: if k == j or k + 1 == j: dict1[k].append(i[j]) in_file.close() for i,j in dict1.items(): for k in range(len(j)): if k % 2 == 0: out_file.write(j[k] + " ") else: out_file.write(j[k] + "\n") out_file.close() (base) [root@pc1 test2]# python3 test.py ## 执行程序 (base) [root@pc1 test2]# ls a.txt result.txt test.py (base) [root@pc1 test2]# cat result.txt ## 运行结果 001 002 011 012 021 022 031 032 003 004 013 014 023 024 033 034 005 006 015 016 025 026 035 036 007 008 017 018 027 028 037 038 (base) [root@pc1 test2]#
。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号