WashU Epigenome Browser | ChIP-seq | DNase-Seq | ATAC-seq | 表观
补充:
ATAC-seq并没有比DNase-seq的peak质量好,只是起始量要求低,所以可以拓展到scATAC-seq。
DHS的peak和H3K27ac的比较相似,都是开放的,可以转录的区域。
epigenetic mark主要有四种:
- chromatin accessibility
- nucleosome positioning - 这个是单独的一类,不熟,但是要有意识
- histone tail modifications
- enhancer–promoter interactions
track可视化神器:
- WashU Epigenome Browser (老版)
- WashU Epigenome Browser (新版,loading有点卡)
顺便搞清楚ChIP-seq的各种marker
- H3K4me1 - major enhancer, also contain promoter (don't know active state)
- H3K4me3 - active promoter
- H3K27ac - transcripted/active
- H3K27me3 - repressed promoter
常见的组合:
H3K4me1 + H3K27ac = active enhancer (次要的active promoter,但不准)
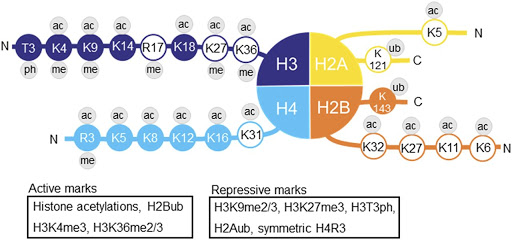
名字的含义:【H3是指第三个histone,K4是指histone tail的位置,me3是指甲基化的个数】
H3K4me3 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H3. It is a mark that indicates the tri-methylation at the 4th lysine residue of the histone H3 protein and often involved in the regulation of gene expression.
open chromatin
- DNase-Seq - DHSs site
- ATAC-seq - 新技术,但也不是全能
In genetics, DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) are regions of chromatin that are sensitive to cleavage by the DNase I enzyme. In these specific regions of the genome, chromatin has lost its condensed structure, exposing the DNA and making it accessible.
These regions have been shown to map many types of cis-regulatory elements including promoters, enhancers, insulators, silencers and locus control regions. A high-throughput measure of these regions is available through DNase-Seq.
DNase-seq and ATAC-seq are based on the use of cleavage enzymes (DNase-I and Tn5, respectively), which recognize and cleave DNA in open chromatin regions. Sequencing and the alignment of reads from these fragments allows the detection of open chromatin by identifying genomic intervals with many reads [1, 2]. However, the presence of transcription factors (TFs) bound to the DNA prevents the enzyme from cleavage in an otherwise nucleosome-free region. This leaves small regions, referred to as footprints, where read coverage suddenly drops within peak regions of high coverage.
进入实操,打开表观基因组浏览器
点击tracks,找到Roadmap Epigenomics Integrative Analysis Hub,选择Observed DNase and ChIP-seq Pvalue and Normalized RPKM RNAseq signal tracks【P-value格式的tracks】
选择一个熟悉的cell line:GM12878,全选track,最后留下:
- H3K4me1, 标记了大部分的enhancer,部分promoter,不分活性
- H3K27ac, 标记了大部分的enhancer,部分promoter,活化的
- H3K4me3, 标记了活化的promoter
- DNase, 开放DNA区域,功能区域的汇总,不包括coding的
- RNAseq Pos, 比对到正链的RNAseq
- RNAseq Neg, 比对到负链的RNAseq
选择一个熟悉的gene:BCL11A
左右拖动查看多个基因,是否与注释的功能对上了。

特别注意:
- 区别peak和signal,ChIP-seq是需要control的,control和抗体抓的都是有peak的,但是signal就是对比后的结果【roadmap里面的pvalue和foldchange的track】
- 检查你的ChIP-seq的signal是不是太多了,如果任意区域都有信号的话,那你load的肯定是peak,没有对control做校正,需要算pvalue和foldchange
- refseq的注释太少了,所以很多peak或signal都看不出来是什么,一般都要用gencode
参考:
Identification of transcription factor binding sites using ATAC-seq
From reads to insight: a hitchhiker’s guide to ATAC-seq data analysis

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号