[Java] 深入理解 : Spring PropertySource
1 概述:Spring PropertySource/配置属性源
- 在Spring中,PropertySource 通常用来加载外部配置文件中的属性,比如
application.properties或者其他自定义的属性文件。
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource(注解,spring-context 模块)org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource(抽象类,spring-core模块:依赖 context 模块)
-
PropertySource可以被 Environment 对象加载,并通过Environment来获取属性值。 -
Spring提供了多种实现
PropertySource抽象类的方式,包括:
- ResourcePropertySource:从资源文件中加载属性。
- MapPropertySource:基于Map的属性源。
- SystemEnvironmentPropertySource:从系统环境变量中加载属性。
- SystemPropertiesPropertySource:从系统属性中加载属性。
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource (注解)
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(PropertySources.class)
public @interface PropertySource {
String name() default "";
String[] value();
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound() default false;
// A specific character encoding for the given resources, e.g. "UTF-8".
String encoding() default "";
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factory() default PropertySourceFactory.class;
}
org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource (抽象类)
package org.springframework.core.env;
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
protected final String name;
protected final T source;
public PropertySource(String name, T source) {
Assert.hasText(name, "Property source name must contain at least one character");
Assert.notNull(source, "Property source must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.source = source;
}
public PropertySource(String name) {
this(name, (T) new Object());
}
/**
* Return the name of this {@code PropertySource}.
*/
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
/**
* Return the underlying source object for this {@code PropertySource}.
*/
public T getSource() {
return this.source;
}
public boolean containsProperty(String name) {
return (getProperty(name) != null);
}
@Nullable
public abstract Object getProperty(String name);
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(getName());
}
public static PropertySource<?> named(String name) {
return new ComparisonPropertySource(name);
}
public static class StubPropertySource extends PropertySource<Object> {
public StubPropertySource(String name) {
super(name, new Object());
}
/**
* Always returns {@code null}.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String name) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* A {@code PropertySource} implementation intended for collection comparison
* purposes.
*
* @see PropertySource#named(String)
*/
static class ComparisonPropertySource extends StubPropertySource {
private static final String USAGE_ERROR =
"ComparisonPropertySource instances are for use with collection comparison only";
public ComparisonPropertySource(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public Object getSource() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
}
2 基本应用
案例1 : 基于 内含 PropertySource(s) 的 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer除了 继承并实现org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderSupport类的本地属性源加载功能 ; 还是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的核心实现类,实现了其 Spring Bean 生命周期的重要接口postProcessBeanFactory
详情参见: [Java/Spring] 深入理解 : Spring BeanFactory - 博客园/千千寰宇 ,搜索 "PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer"
首先,在 application.properties 配置文件中定义一些属性:
app.name=MyApp
app.version=1.0
然后,在Spring配置类中加载PropertySource:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
// PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer : 内置3大关键属性 : MutablePropertySources propertySources 【关键】 、 PropertySources appliedPropertySources、 Environment environment;
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
configurer.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("application.properties"));
return configurer;
}
}
- [class]
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PlaceholderConfigurerSupport extends PropertyResourceConfigurer(关键) implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware- [abstract class]
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyResourceConfigurer extends PropertiesLoaderSupport(关键) implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered- [abstract class]
org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderSupport(关键)
PropertiesLoaderSupport含关键方法 :public void setLocations(Resource... locations)
- 接下来,在应用程序中使用
@Value注解来注入属性值:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Value("${app.name}")
private String appName;
@Value("${app.version}")
private String appVersion;
public void displayProperties() {
System.out.println("App Name: " + appName);
System.out.println("App Version: " + appVersion);
}
}
- 通过
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer类加载了application.properties文件作为PropertySource,然后通过@Value注解将属性值注入到MyBean类中。
补充:1个实际应用的同类型案例
import cn.xxxx.bdp.diagnosticbox.env.enums.EnvironmentTypeEnum;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml;
import java.util.Properties;
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class DatasourceConfiguration {
// PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer : 内置3大关键属性 : MutablePropertySources propertySources 【关键】 、 PropertySources appliedPropertySources、 Environment environment;
private final static String ENV_CODE_PARAM = "env.code";
/**
* 读取指定外部配置文件中的属性值
* @return
*/
@SneakyThrows
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "datasourcePropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer") // 当目标 bean 不存在时,创建下面描述的 bean
public PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer datasourcePropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
/**
* PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
* 1 作为一个 BeanFactoryPostProcessor , 用于解析spring环境中的属性占位符,并从指定的属性源中替换占位符的值。
* 2 可借此读取指定外部配置文件中的属性值
* 3 不设置要读取的资源时默认读 application.* 配置文件
*/
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
String environmentCode = System.getProperty( ENV_CODE_PARAM );//eg : JVM Option Arguments : "-Denv.code=tvop-hw-cn-dev"
properties.setProperty( ENV_CODE_PARAM , environmentCode);
String datasourceResourceConfigFile = String.format( "application-ds-%s.yml" , environmentCode ); //eg: "application-ds-tvop-hw-cn-dev.yml"
Resource datasourceResources = new ClassPathResource(datasourceResourceConfigFile);
log.info("datasourceResources.exists : {}, environmentCode: {}", datasourceResources.exists() , environmentCode );// properties.get("env.code")
if(datasourceResources.exists()){
//configurer.setLocation( datasourceResources ); //方式1
//方式2-1 (YAML 配置被打平为 KV对)
//YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yaml = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
//yaml.setResources( datasourceResources );
//yaml.getObject() : 解析结果(DEMO) : { "app.datasources.enable": true, "app.datasources.list[0].name": "xxx-hw-cn-dev-mysql-bigdata", "app.datasources.list[0].url": "mysql://{{host}}:{{port}}", "app.datasources.list[0].password": "123456", "app.datasources.list[0].extensionProperties[0].value": "value1", "app.datasources.list[0].extensionProperties[0].key": "key1", "app.datasources.list[0].username": "rwuser", }
//properties.putAll( yaml.getObject() );
//configurer.setProperties( properties );
//方式2-2 (YAML 配置逐层解析,)
Yaml yaml = new Yaml();
Map<String, Object> yamlConfigs = yaml.load( datasourceResources.getInputStream() );
//解析结果(DEMO) : { "app.datasources": { "enable": true, "list": [ { "name": "xxx-hw-cn-dev-mysql-bigdata", "url": "mysql://{{host}}:{{port}}", "username": "rwuser", "password": "123456", "extensionProperties": [ { "key": "key1", "value": "value1" } ] } ] } }
Map<String, Object> appDatasourcesConfig = (Map<String, Object>) yamlConfigs.get("app.datasources");
List<Map<String, Object>> datasourceListConfig = (List<Map<String, Object>>) appDatasourcesConfig.get("list");
log.info("datasourceListConfig:{}", JSON.toJSONString(datasourceListConfig));
datasourceListConfig.stream().forEach( datasourceConfig -> {
DataSource dataSource = parseToDataSource( datasourceConfig );
log.info("dataSource:{}", JSON.toJSONString(dataSource));
properties.put( dataSource.getDatasourceName() , dataSource );
} );
//configurer.setProperties( properties );
}
configurer.setProperties( properties ); //方式3
//configurer.setPlaceholderPrefix("#{");
//configurer.setPlaceholderSuffix("}");
return configurer;
}
}
案例2 : 基于 @PropertySource 注解
@PropertySource注解的主要作用:
将外部化配置解析成
key-value键值对"存入"Spring容器的Environment环境中,以便在Spring应用中可以通过@Value、或者占位符${key}的形式来使用这些配置。
- my.properties和my2.properties的具体内容:
# my.properties
key1=自由之路
# my2.properties
key1=程序员
key2=自由之路
- PropertyConfig、App
// @PropertySource需要和@Configuration配个使用
// @PropertySource加载的配置文件时需要注意加载的顺序,后面加载的配置会覆盖前面加载的配置
// @PropertySource支持重复注解
// value值不仅支持classpath表达式,还支持任意合法的URI表达式
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/my.properties",encoding = "UTF8")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/my2.properties",encoding = "UTF8", ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
public static class PropertyConfig {
}
@Component
public class App {
@Value("${key1:default-val}")
private String value;
@Value("${key2:default-val2}")
private String value2;
}
Spring容器启动时,会将my.properties和my2.properties的内容加载到
Environment中,并在App类的依赖注入环节,将key1和key2的值注入到对应的属性。
3 PropertySourceFactory : 自定义 PropertySource 的工厂
PropertySource 注解 的 factory 属性
- 阅读
@PropertySource的源代码,我们发现还有一个factory属性。从这个属性的字面意思看,我们不难猜测出这个属性设置的是用于产生PropertySource的工厂。
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(PropertySources.class)
public @interface PropertySource {
String name() default "";
String[] value();
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound() default false;
String encoding() default "";
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factory() default PropertySourceFactory.class;
}
PropertySource (配置属性源) 的常用实现类、及 PropertySourceFactory 的默认实现
-
要深入理解 PropertySourceFactory,我们先要知道以下的背景知识。
-
在Spring中,配置的来源有很多。Spring 将配置来源统一抽象成 PropertySource 这个抽象类,Spring中内建的常用的 PropertySource 有以下这些
- EnumerablePropertySource (抽象类)
- [abstract class]
org.springframework.core.env.EnumerablePropertySource<T> extends PropertySource<T>
- MapPropertySource
- [class]
org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource extends EnumerablePropertySource<Map<String, Object>>
- CommandLinePropertySource
- PropertiesPropertySource
- [class]
org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource extends MapPropertySource
- SystemEnvironmentPropertySource
- ResourcePropertySource
- [class]
org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePropertySource extends PropertiesPropertySource
-
ResourcePropertySource这个类将一系列配置来源统一成ResourcePropertySource,可以说是对 PropertySource 的进一步封装。 -
PropertySourceFactory接口,用于产生 PropertySource。
Spring中,
PropertySourceFactory默认的实现是DefaultPropertySourceFactory,用于生产ResourcePropertySource。
案例3 : 基于自定义 PropertySourceFactory————YamlMapSourceFactory
- 经过上面的介绍,我们知道如果没有配置
@PropertySource的factory属性的话,默认的PropertySourceFactory使用的就是DefaultPropertySourceFactory。 - 当然,我们也可以自定义 PropertySourceFactory,用于“生产”我们自定义的
PropertySource。
下面就演示一个将
yaml配置文件 解析成MapPropertySource的使用案列:
- YamlMapSourceFactory
/**
* Spring中内置的解析yaml的处理器
* YamlProcessor
* - YamlMapFactoryBean --> 解析成 Map
* - YamlPropertiesFactoryBean --> 解析成 Properties
*/
public class YamlMapSourceFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
YamlMapFactoryBean yamlMapFactoryBean = new YamlMapFactoryBean();
yamlMapFactoryBean.setResources(resource.getResource());
Map<String, Object> map = yamlMapFactoryBean.getObject();
return new MapPropertySource(name, map);
}
}
// 加了 factory 属性,必须加 name 属性
// 有了 factory 机制,我们可以做很多自定义的扩展,比如配置可以从远程来
@PropertySource(name = "my.yaml",value = "classpath:/my.yaml",encoding = "UTF8", factory = YamlMapSourceFactory.class)
public static class PropertyConfig {
...
}
原理简析与小结
到这边我们对 @PropertySource 已经有了一个感性的认识,知道了其主要作用是将各种类型的外部配置文件以key-value的形式加载到 Spring 的 Environment 中。
这个部分我们从源码的角度来分析下 Spring 是怎么处理 @PropertySource 这个注解的。
分析源码可以加深我们对 @PropertySource 的认识(看源码不是目的,是为了加深理解,学习Spring的设计思想)。
@PropertySource 注解的处理是在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 中进行触发的。最终会调用到
ConfigurationClassParser的processPropertySource方法。
ConfigurationClassParser#processPropertySource
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware- SpringBoot 应用启动过程中,通过后置处理器去触发 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。 然后再调用 ConfigurationClassParser类解析
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
...
processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
...
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser( //初始化解析器
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
parser.parse(candidates); //解析
parser.validate();//验证
...
...
}
}

org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser
ConfigurationClassParser 它是解密 configuration 的关键,其主要用于解析带有
@Configuration注解的类
@Configuration注解表明该类用作配置类,其中可以定义bean和Spring容器应如何初始化和管理这些bean。

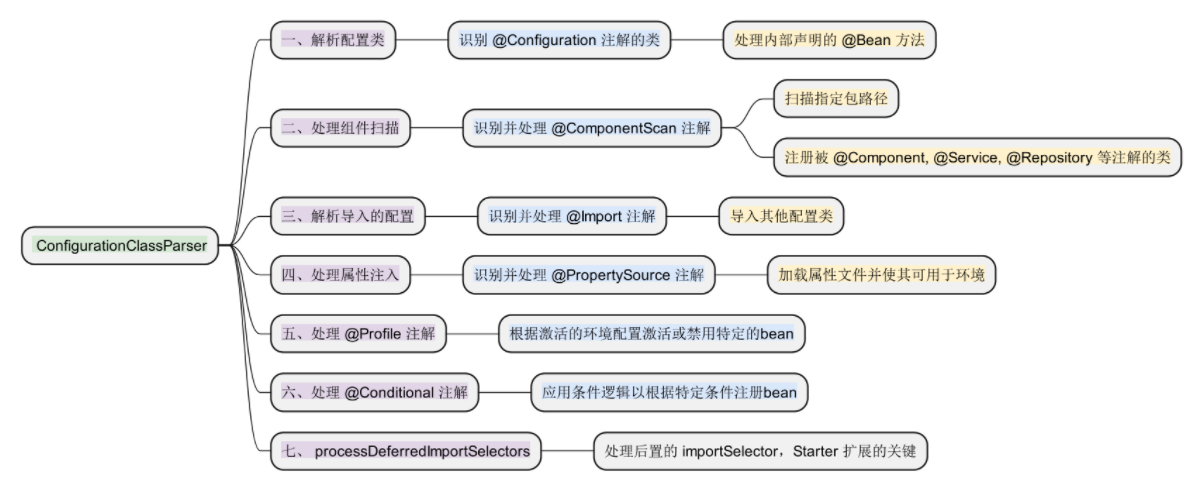
主要作用:
- 解析导入的配置:@Import 注解允许一个配置类导入另一个配置类。ConfigurationClassParser解析这些@Import注解,确保所有导入的配置也被处理和应用。
- 处理属性注入:通过@PropertySource注解,可以指定一些属性文件,这些属性文件中的属性可以被注入到Spring管理的bean中。ConfigurationClassParser负责解析这些注解,并确保属性文件被加载且其值可用于注入。
- 处理@Conditional注解: Spring框架 允许在bean 的注册过程中使用条件逻辑, @Conditional 注解及其派生注解(例如 @ConditionalOnClass , @ConditionalOnProperty 等)使得只有在满足特定条件时,才会进行 bean 的注册。 ConfigurationClassParser 负责解析这些条件注解并应用其逻辑。
- processDeferredImportSelectors#processImports 处理扩展配置( Starter 能够被处理的核心分支)
// ConfigurationClassParser#processPropertySource
private void processPropertySource(AnnotationAttributes propertySource) throws IOException {
String name = propertySource.getString("name");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
name = null;
}
String encoding = propertySource.getString("encoding");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(encoding)) {
encoding = null;
}
String[] locations = propertySource.getStringArray("value");
Assert.isTrue(locations.length > 0, "At least one @PropertySource(value) location is required");
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = propertySource.getBoolean("ignoreResourceNotFound");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClass = propertySource.getClass("factory");
// 如果有自定义工厂就使用自定义工厂,没有自定义工厂就使用DefaultPropertySourceFactory
PropertySourceFactory factory = (factoryClass == PropertySourceFactory.class ?
DEFAULT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_FACTORY : BeanUtils.instantiateClass(factoryClass));
// 遍历各个location地址
for (String location : locations) {
try {
// location地址支持占位符的形式
String resolvedLocation = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
// 获取Resource
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(resolvedLocation);
addPropertySource(factory.createPropertySource(name, new EncodedResource(resource, encoding)));
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException | FileNotFoundException | UnknownHostException | SocketException ex) {
// Placeholders not resolvable or resource not found when trying to open it
if (ignoreResourceNotFound) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Properties location [" + location + "] not resolvable: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
总的来说,Spring处理 @PropertySource 的源代码非常简单,这边就不再过多赘述了。
X 参考文献
- Spring——PropertySource 详解 - CSDN
- Spring注解系列——@PropertySource - 博客园
- 第七节 ConfigurationClassParser 源码分析 - CSDN 【推荐】
- Spring Boot 加载配置文件 - CSDN 【推荐】
- 方式1:@Value 读取
- 方式2:@ConfigurationProperties
- 方式3:@PropertySource 读取指定名称文件
- 方式4:Environment 读取

本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen
关于博文:评论和私信会在第一时间回复,或直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
日常交流:大数据与软件开发-QQ交流群: 774386015 【入群二维码】参见左下角。您的支持、鼓励是博主技术写作的重要动力!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号