[Java] 深入理解 : Spring BeanFactory
1 概述:Spring BeanFactory
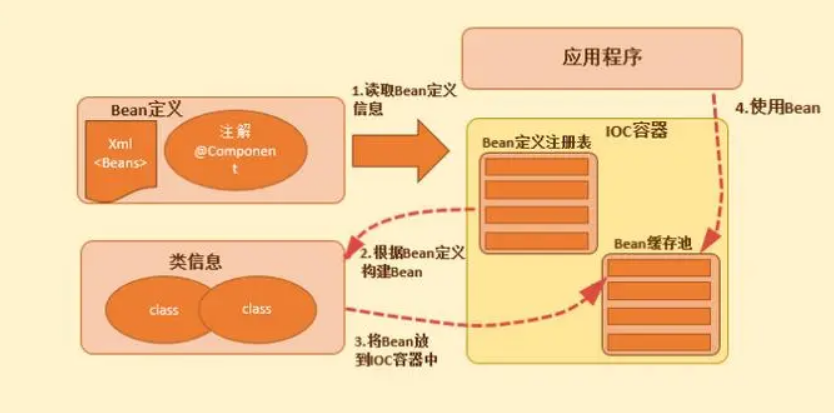
1.1 什么是 BeanFactory : Spring Bean 容器的抽象接口
- BeanFactory 是Spring框架(
spring-beans模块)中的一个接口,它是一个工厂类,用来创建和管理Spring中的Bean对象。 - BeanFactory接口定义了Spring容器的基本规范和行为,它提供了一种机制来将配置文件中定义的Bean实例化、配置和管理起来。
1.2 BeanFactory 所属模块: Spring Context
1.3 BeanFactory 的作用
- BeanFactory的主要作用是提供Bean的创建、配置、初始化和销毁等基本操作。
- 它可以根据配置文件或注解来创建并管理Bean实例,并提供了各种方法来获取和操作Bean实例。
1.4 BeanFactory 的接口定义
org.springframework.beans.factory源码的文档描述
这是访问Spring bean容器的根接口。
这是bean容器的基本客户端视图;
其他接口如ListableBeanFactory和org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory可用于特定目的。
这个接口是由包含许多bean定义的对象实现的,每个bean定义由一个String名称唯一标识。根据bean定义,工厂将返回所包含对象的独立实例(Prototype设计模式)或单个共享实例(Singleton设计模式的高级替代方案,其中实例是工厂范围内的单例)。返回哪种类型的实例取决于bean工厂配置:API是相同的。从Spring 2.0开始,根据具体的应用程序上下文(例如:web环境中的“请求”和“会话”作用域)。
这种方式的关键在于 BeanFactory 是应用程序组件的注册中心,并集中化应用程序组件的配置(例如,单个对象不再需要读取属性文件)。详情请参阅“专家一对一J2EE设计与开发”的第4章和第11章,了解这种方法的好处。
请注意,通常最好依赖依赖注入(“推送”配置)通过 setter 或 构造函数 来配置应用程序对象,而不是使用任何形式的“拉”配置,如BeanFactory查找。
Spring的依赖注入功能,是使用这个BeanFactory接口及其子接口实现的。
通常, BeanFactory 将加载存储在配置源(如XML文档)中的bean定义,并使用
org.springframework.beans包来配置bean。
但是,实现可以根据需要直接在Java代码中返回它创建的Java对象。对于如何存储定义没有任何限制:LDAP、RDBMS、XML、属性文件等。鼓励实现支持bean之间的引用(依赖注入)。
与ListableBeanFactory中的方法相反,如果这是一个HierarchicalBeanFactory,则该接口中的所有操作也将检查父工厂。如果在这个工厂实例中没有找到bean,将询问直接的父工厂。这个工厂实例中的bean应该覆盖任何父工厂中同名的bean。
BeanFactory 实现应该尽可能地支持标准的Bean生命周期接口。初始化方法的完整集合及其标准顺序为:
- BeanNameAware's setBeanName
- BeanClassLoaderAware's setBeanClassLoader
- BeanFactoryAware's setBeanFactory
- EnvironmentAware's setEnvironment
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware's setEmbeddedValueResolver
- ResourceLoaderAware's setResourceLoader (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware's setApplicationEventPublisher (only applicable when running in an application context)
- MessageSourceAware's setMessageSource (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ApplicationContextAware's setApplicationContext (only applicable when running in an application context)
- ServletContextAware's setServletContext (only applicable when running in a web application context)
- postProcessBeforeInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
- InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
- a custom init-method definition
- postProcessAfterInitialization methods of BeanPostProcessors
- On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:
- postProcessBeforeDestruction methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
- DisposableBean's destroy
- a custom destroy-method definition
- BeanFactory 的接口定义
所属模块:
spring-beans
SPRING 版本 : 5.2.15.RELEASE
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType);
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(ResolvableType requiredType);
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Class<?> getType(String name, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
String[] getAliases(String name);
)
1.5 BeanFactory 中 Bean 的生命周期
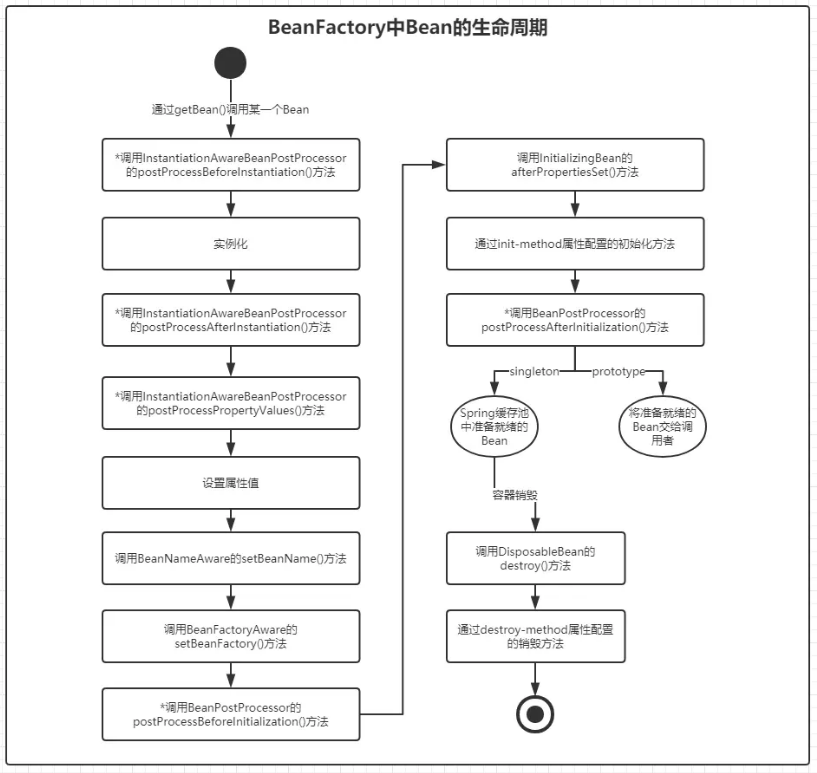
Bean 生命周期
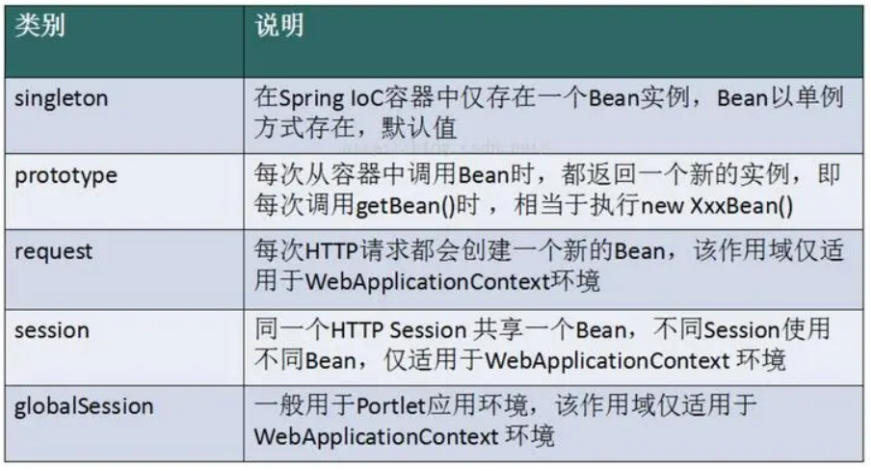
Bean 的作用域
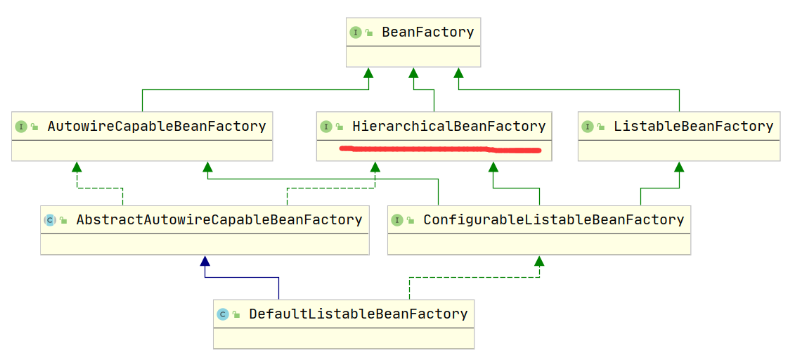
1.6 BeanFactory 的实现类
-
BeanFactory 接口有多个实现类,其中最常用的是
XmlBeanFactory和DefaultListableBeanFactory。 -
XmlBeanFactory是通过
XML文件来配置Bean的实例化、配置和管理的,而 DefaultListableBeanFactory 则是通过Java代码 来配置Bean的实例化、配置和管理的。

节选
-
spring-beans 模块
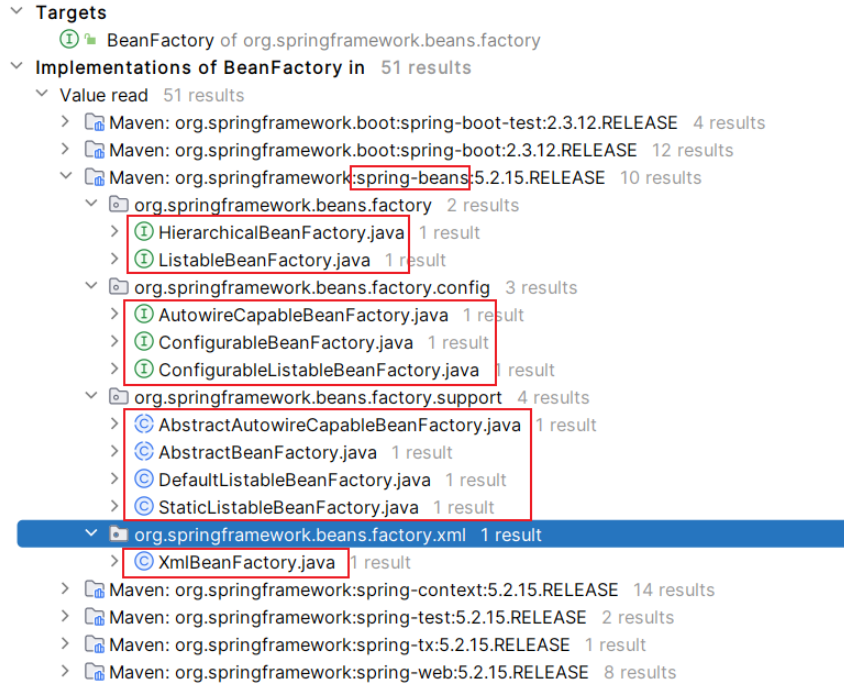
-
spring-context 模块
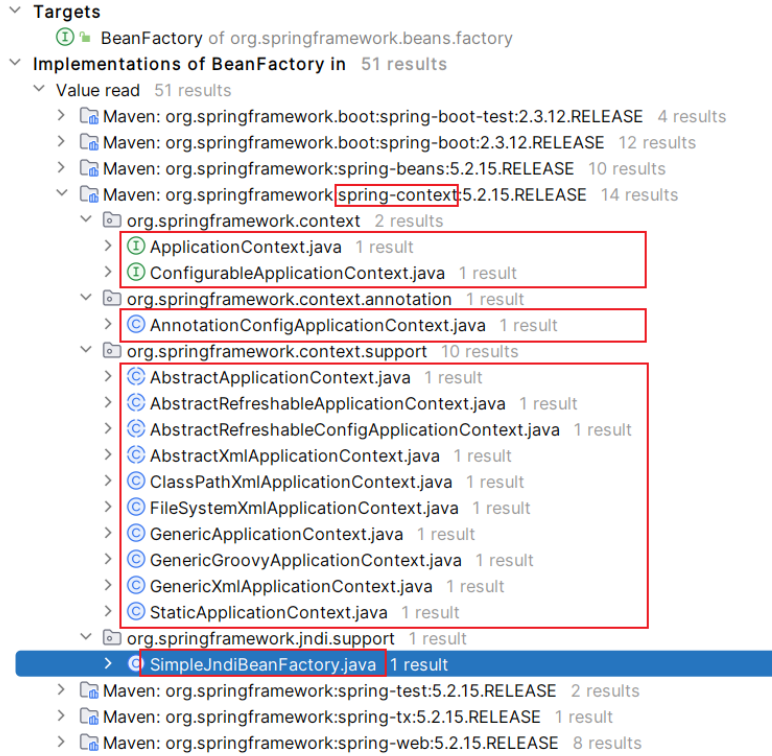
-
spring-tx 模块

-
spring-web 模块
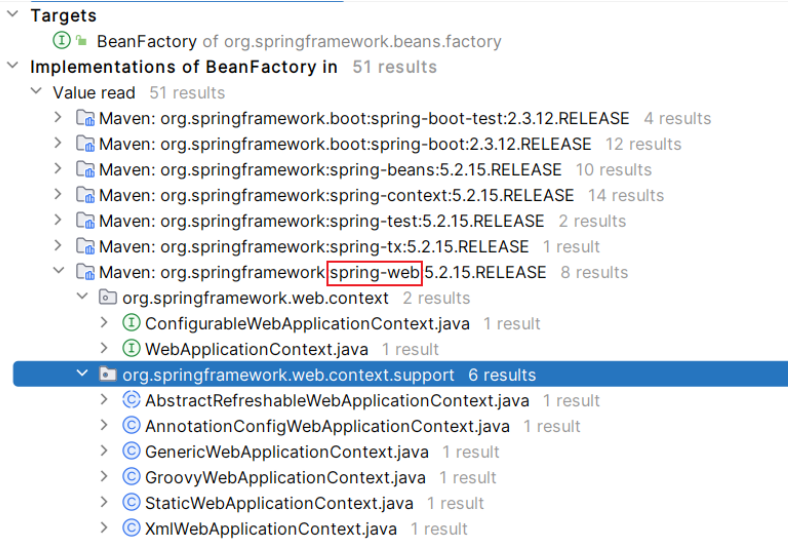
-
spring-boot 模块
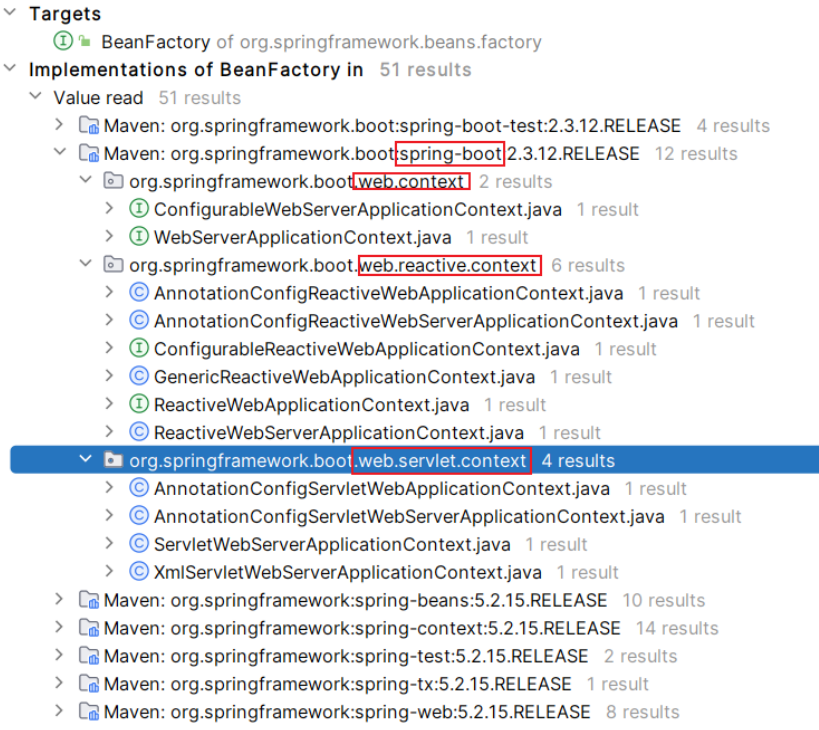
-
spring-boot-test 模块
2 BeanFactory的使用
BeanFactory的创建
- BeanFactory的创建有三种方式:XML配置方式、Java配置方式和注解配置方式。
1)XML配置方式
在使用XML配置方式时,需要在配置文件中定义Bean的实例化、配置和管理信息。
下面是一个简单的XML配置文件示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.example.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
</beans>
在上面的示例中,定义了3个Bean:userService、userDao和dataSource。其中,userService和userDao之间存在依赖关系,userService依赖于userDao,而userDao又依赖于dataSource。
2)Java配置方式
在使用Java配置方式时,需要编写Java代码来定义Bean的实例化、配置和管理信息。
下面是一个简单的Java配置类示例:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public UserService userService() {
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.setUserDao(userDao());
return userService;
}
@Bean
public UserDao userDao() {
UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
userDao.setDataSource(dataSource());
return userDao;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
return dataSource;
}
}
在上面的示例中,使用了@Configuration注解来标识该类是一个配置类,并使用@Bean注解来定义Bean的实例化、配置和管理信息。
在AppConfig类中,定义了3个Bean:userService、userDao和dataSource。其中,userService和userDao之间存在依赖关系,userService依赖于userDao,而userDao又依赖于dataSource。
3)注解配置方式
在使用注解配置方式时,需要在Bean类上添加相应的注解来标识该类是一个Bean,并进行相应的配置信息。
下面是一个简单的注解配置类示例:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
return dataSource;
}
}
BeanFactory的配置
在BeanFactory的配置中,主要包括Bean的定义、依赖和属性等方面。
1)Bean的定义
在Bean的定义中,主要包括Bean的类型、ID和作用域等方面。
下面是一个简单的Bean定义示例:
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserService" scope="singleton"/>
在上面的示例中,定义了一个ID为userService,类型为com.example.UserService,作用域为singleton的Bean。
2)Bean的依赖
在Bean的依赖中,主要包括Bean之间的依赖关系和依赖注入方式等方面。
下面是一个简单的Bean依赖示例:
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.example.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
在上面的示例中,userService依赖于userDao,而userDao又依赖于dataSource。在userService中,使用了标签来注入userDao的实例,而在userDao中,同样使用了标签来注入dataSource的实例。
3)Bean的属性
在Bean的属性中,主要包括Bean的各种属性信息,如普通属性、集合属性和引用属性等。
下面是一个简单的Bean属性示例:
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserService">
<property name="name" value="John"/>
<property name="age" value="30"/>
<property name="hobbies">
<list>
<value>reading</value>
<value>writing</value>
<value>traveling</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
在上面的示例中,定义了一个userService的Bean,并设置了name、age、hobbies和userDao等属性。其中,name和age是普通属性,而hobbies是集合属性,它包含了三个值:reading、writing和traveling。userDao是引用属性,它依赖于另一个Bean实例。
3 BeanFactory的初始化
在BeanFactory的初始化中,主要包括BeanFactoryAware接口、InitializingBean接口和init-method属性等方面。
1)BeanFactoryAware接口
如果一个Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,那么它将能够获取到当前Bean所在的BeanFactory实例。
下面是一个简单的BeanFactoryAware接口示例:
public class MyBean implements BeanFactoryAware {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
在上面的示例中,MyBean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,并重写了setBeanFactory()方法。该方法将传入的BeanFactory实例保存到了类成员变量beanFactory中。
2)InitializingBean接口
如果一个Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,那么它将能够在Bean实例化后、依赖注入后、属性设置后进行一些初始化操作。下面是一个简单的InitializingBean接口示例:
4 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口重要实现类: PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
背景:读取配置文件配置项,并赋给 Java Bean
有的时候,我们需要读取配置文件中的属性,将其作为成员变量赋给对应的Bean。
方式1: beans xml 配置文件
一种方式是,如下通过xml配置:
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
方式2:@Value
又或者,使用 @Value 注解,通过Java代码配置:
public class JdbcBean {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.user}")
private String user;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
}
那么这个是如何实现的呢?
原来,Spring提供了一种配置解析的功能,在Spring3.1版本之前是通过 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 实现的。
而3.1之后则是通过 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 实现的。
Spring已经发展到5.x了,所以今天我们主要来解析一下 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 。
自定义一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
我们可以在代码中,创建一个 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,并指定它解析的配置文件地址,如下:
@Bean
public PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(){
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySources = null;
try{
propertySources = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("application.properties");
propertySources.setLocation(classPathResource);
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return propertySources;
}
使用注解方式
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class JdbcBean {
...
}
源码分析 : BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口实现类: PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
关系分析
org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
public class PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer extends PlaceholderConfigurerSupport implements EnvironmentAware {
//全部属性字段
public static final String LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "localProperties";
/**
* {@value} is the name given to the {@link PropertySource} that wraps the
* {@linkplain #setEnvironment environment} supplied to this configurer.
*/
public static final String ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "environmentProperties";//加载 系统属性、bootstrap.* 、配置的 profile 的 application.* 、远程配置中心(nacos)等 spring 正统配置文件的配置
@Nullable
private MutablePropertySources propertySources;
@Nullable
private PropertySources appliedPropertySources;
@Nullable
private Environment environment;
//构造器及方法: ... 略
...
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PlaceholderConfigurerSupport
public abstract class PlaceholderConfigurerSupport
extends PropertyResourceConfigurer // PropertyResourceConfigurer 实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口
implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware {
...
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyResourceConfigurer
public abstract class PropertyResourceConfigurer
extends PropertiesLoaderSupport // org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderSupport : 用于加载 localProperties
implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered { // PropertyResourceConfigurer 实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口
...
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor【重要】
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; //关键接口
}
- 补充:
org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderSupport
public abstract class PropertiesLoaderSupport {
// 所有属性:
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Nullable
protected Properties[] localProperties; // 关键属性: 加载本地配置
protected boolean localOverride = false;
@Nullable
private Resource[] locations;
private boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = false;
@Nullable
private String fileEncoding;
private PropertiesPersister propertiesPersister = new DefaultPropertiesPersister();
...
}
Spring Bean的创建过程
首先,我们来看一下Bean的创建过程(AbstractApplicationContext的refresh过程中的一些调用),由于这个过程在这里不是我们主要要讲解的。
所以,大略体会一下,并且记住其中有一个叫
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的,后面我们还会提到它,Spring Bean 创建过程如下:
- 实例化 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现类
- 调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory
- 实例化 BeanPostProcessor 实现类
- 调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor/#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
- 实例化 Bean
- 调用InstantiationAwareBeanProcessor/#postProcessAfterInstantiation
- 调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor/#postProcessPropertyValues
- 为Bean注入属性
- 调用BeanNameAware/#setBeanName
- 调用BeanClassLoaderAware/#setBeanClassLoader
- 调用BeanFactoryAware/#setBeanFactory
- 调用BeanPostProcessor/#postProcessBeforeInitialization
- 调用 InitializingBean/#afterPropertiesSet
- 调用Bean的init-method
- 调用BeanPostProcessor/#postProcessAfterInitialization
配置属性源加载:postProcessBeanFactory => environmentProperties / localProperties

在Spring3.1之后,建议使用 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 来取代 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer。
可以发现,其实 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的一个子类,所以在Bean的创建过程中可以得知,在执行过程中会调用 postProcessBeanFactory,所以我们查找下对应的方法,定义如下:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (this.propertySources == null) {
this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
if (this.environment != null) {
this.propertySources.addLast(
new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {//environmentProperties PropertySource
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.source.getProperty(key);
}
}
);
}
try {
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) {
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else {
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
//处理属性
processProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources));
this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources;
}
我们其实不难发现,属性来源分为两种:
-
以 Environment 为属性源的 environmentProperties
-
通过 loadProperties(Properties props) 加载本地资源文件作为属性源的 localProperties。
属性源加载完毕后,将占位符替换为属性源中的属性。
占位符解析 :processProperties、doProcessProperties
属性源都加载完毕,接下来就是占位符的填充,源码如下:
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {
//this.placeholderPrefix为 ${
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);
//this.placeholderSuffix为 }
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);
//this.valueSeparator为 :
propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);
// 使用lambda表达式创建一个StringValueResolver
StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {
// 解析占位符,此处只能解析占位符
String resolved = (ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?
propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :
propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));
if (trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
return (resolved.equals(nullValue) ? null : resolved);
};
// 调用父类的 doProcessProperties 把属性扫描到 Bean 的身上去
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
//排除自身&&必须是同一个beanFactory
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
// 解析别名目标名称和别名中的占位符
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
//在嵌入值(例如注释属性)中解析占位符
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}
小结:PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer工作原理
上面就是对 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 工作原理的源码解析,概括来说分为两步:
-
属性源装配
- environmentProperties
- localProperties
-
占位符解析
- 解析占位符中的key
- 将key替换成对应的属性值
获取 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer Bean
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 因为汇聚了Environment、多个PropertySource;所以它能够控制取值优先级、顺序,并且还提供了访问的方法,后期再想获取也不成问题。
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
// 通过它,可以把生效的配置都拿到
@Autowired
private PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer;
public void getData() {
Environment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
PropertySources appliedPropertySources = configurer.getAppliedPropertySources();
System.out.println(environment.containsProperty("bean.scope")); //false 注意环境里是没有这个key的
System.out.println(appliedPropertySources);
// 获取环境的和我们自己导入的
PropertySource<?> envProperties = appliedPropertySources.get(PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
PropertySource<?> localProperties = appliedPropertySources.get(PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
System.out.println(envProperties.getSource() == environment); //true 可以看到这个envProperties的source和环境里的是同一个
System.out.println(localProperties.containsProperty("bean.scope"));//true 本地配置里是包含这个属性的
}
其他:PropertyOverrideConfigurer、PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer、...
还有另外一个类PropertyOverrideConfigurer,PropertyOverrideConfigurer类似于PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
与 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 不同的是:PropertyOverrideConfigurer 利用属性文件的相关信息,覆盖XML 配置文件中定义。
即PropertyOverrideConfigurer允许XML 配置文件中有默认的配置信息。
需要注意的是Properties属性文件:
beanName.property=value //第一个.前面一定是beanName
请保证这个beanName一定存在。
它会根据beanName找到这个bean,然后override这个bean的相关属性值的。
因为这个类使用得相对较少,但使用步骤基本同上,因此此处就不再叙述了。
X 参考文献
X 参考文献
- 【Spring】BeanFactoryPostProcessor与BeanPostProcessor - CSDN //TODO
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor - CSDN //TODO
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的典型应用
- springbean生命周期通俗一点_spring为啥是单例模式 - 腾讯云//TODO
- Spring核心模块
- BeanFactory、ApplicationContext和FactoryBean的区别
- BeanFactory:BeanFactory 是 IoC 容器的顶级接口,是IoC容器的最基础实现,也是访问Spring容器的根接口,负责对bean的创建,访问等工作。实现类功能比较单一,BeanFactory接口实现的容器,特点是在每次获取对象时才会创建对象。
- ApplicationContext:继承了BeanFactory接口,拥有BeanFactory的全部功能,并且扩展了很多高级特性,每次容器启动时就会创建所有的对象。Spring 框架 的 默认 IOC 容器。
- Spring IOC容器启动加载流程
- Bean 的生命周期

本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen
关于博文:评论和私信会在第一时间回复,或直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
日常交流:大数据与软件开发-QQ交流群: 774386015 【入群二维码】参见左下角。您的支持、鼓励是博主技术写作的重要动力!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号