ROS中Service编程实现
简介
实现一个代码,创建一个服务,控制小海龟的运动
C++
1.代码
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h>
#include <std_srvs/Trigger.h> //服务数据类型是std_srvs/Trigger
ros::Publisher turtle_vel_pub;
bool pubCommand = false;
bool commandCallback(std_srvs::Trigger::Request &req, std_srvs::Trigger::Response &res)
{
pubCommand = !pubCommand;
//显示请求数据
ROS_INFO("Publish turtle velocity command [%s]",pubCommand == true ? "Yes" : "No");
//设置反馈数据
res.success = true;
res.message = "Change turtle command state";
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//初始化节点
ros::init(argc, argv, "turtle_command_server");
//创建节点句柄
ros::NodeHandle n;
//创建一个名为/turtle_command的server,注册回调函数commandCallback
ros::ServiceServer command_service = n.advertiseService("/turtle_command", commandCallback);
//创建一个Publisher, 发布名为/turtle/cmd_vel的topic,消息类型为geometry_msgs::Twsit,队列长度为10
turtle_vel_pub = n.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("/turtle1/cmd_vel", 10);
//循环等待回调函数
ROS_INFO("Ready to receive turtle command");
//设置循环频率
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
while(ros::ok())
{
//查看一次回调函数列表
ros::spinOnce();
//如果标志为true,则发布速度质量
if(pubCommand)
{
geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;
vel_msg.linear.x = 2.0;
vel_msg.angular.z = 2.0;
turtle_vel_pub.publish(vel_msg);
}
//按照循环频率延时
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
注意
回调函数会传入两个参数一个是request,一个是responce
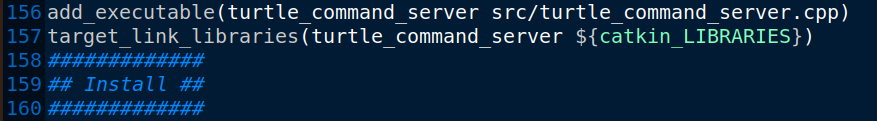
2.在CMakeLists中添加编译依赖
add_executable(turtle_command_server src/turtle_command_server.cpp)
target_link_libraries(turtle_command_server ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
注意
catkin_LIBRARIES是前小写后大写
3.编译
回到工作目录
catkin_make
4.修改环境变量
source src/setup.bash
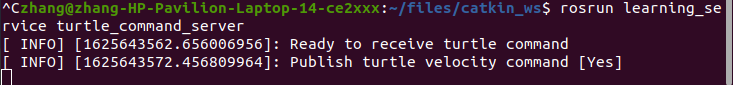
5.执行
rosrun learning_service turtle_command_server
执行后就会产生一个turtle_command的服务
6.调用服务
rosservice call /turtle_command "{}"
7.结果
- 调用服务

- 执行服务操作后产生反馈
- 结果小海龟画圆

python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#该程序将执行/turtle_command服务,服务数据类型std_srvs/Trigger
import rospy
import _thread, time
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from std_srvs.srv import Trigger, TriggerResponse
pubCommand = False
turtle_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size = 10)
def command_thread():
while True:
if pubCommand:
vel_msg = Twist()
vel_msg.linear.x = 0.5
vel_msg.angular.z = 0.2
turtle_vel_pub.publish(vel_msg)
time.sleep(0.1)
def commandCallback(req):
global pubCommand
pubCommand = bool(1 - pubCommand)
#显示请求数据
rospy.loginfo("Publish turtle velocity command![%d]",pubCommand)
#反馈数据
return TriggerResponse(1, "Change turtle command state!")
def turtle_command_server():
#初始化节点
rospy.init_node('turtle_command_server')
#创建一个名为/turtle_command的server, 注册回调函数commandCallback
s = rospy.Service('/turtle_command', Trigger, commandCallback)
#循环等待回调函数
print("Ready to receive turtlre command")
_thread.start_new_thread(command_thread, ())
rospy.spin()
if __name__ == '__main__':
turtle_command_server()
运行的步骤和前几篇文章是一样的。
运行代码后会出现名为turtle_command的service。这是自己定义的
总结
实现服务器的步骤大概是
- 初始化节点
- 创建Server实例
- 循环等待服务请求,进入回调函数
- 在回调函数中完成服务功能的处理,并反馈应答数据
本文来自博客园,作者:墨镜一戴谁也不爱,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hnuzmh/p/16196552.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号