P5540 [BalkanOI2011] timeismoney | 最小乘积生成树
不妨将 和 分别作为 放入平面直角坐标系,题目要求即求一个 最小的点对 。
不难发现 可能最小值所在的点一定为一个左下凸壳。
虽然生成树的个数极多,但是期望的在左下凸壳的点较少,找到这些最小值点即可。
接下来考虑如何求:
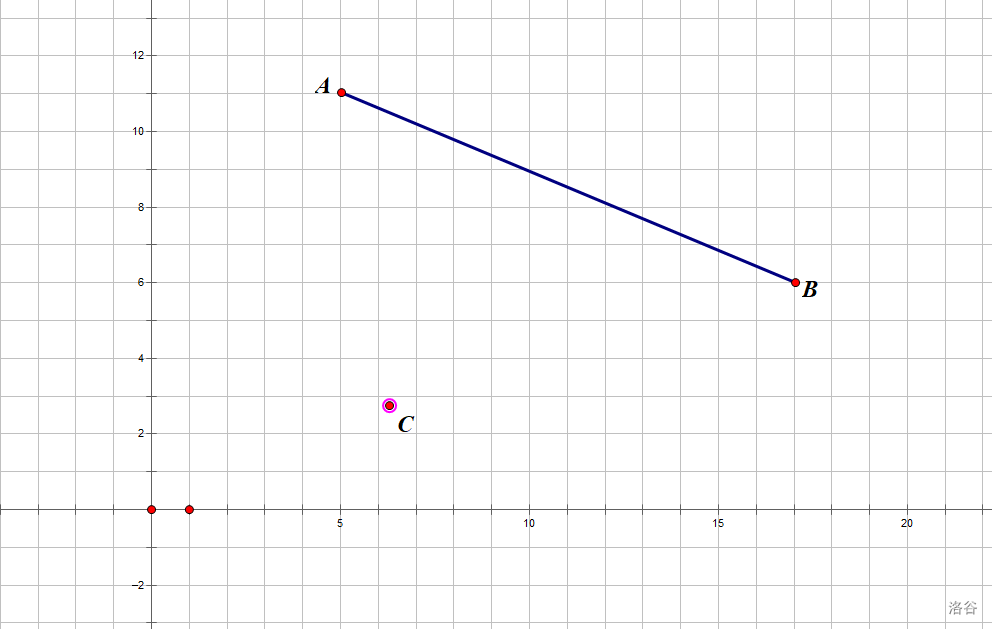
考虑三个点 。其中 点未知, 已知。
我们可以考虑求出离 最远的在其左下的点 ,然后分治求 和 的答案。
即最大化 。
。
需最大化 ,即考虑最小化 。
。
显然只有 和 为变量, 均为定值。
所以将 作为权值求最小生成树即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
class CG
{
public:
struct Point
{
int x, y;
Point(int _x, int _y): x(_x), y(_y){}
Point()
{
x = y = 0;
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
friend Vector operator-(const Vector a, const Vector b)
{
return Vector(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
};
int cj(CG::Vector a, CG::Vector b)
{
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
CG::Point ans = CG::Point(1e9, 1e9);
int n, m;
int u[N], v[N], a[N], b[N];
class Union_Find
{
public:
int fa[N];
void Init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;
}
int find(int u)
{
return fa[u] == u ? u : fa[u] = find(fa[u]);
}
void merge(int u, int v)
{
fa[find(u)] = find(v);
}
};
struct Edge
{
int u, v, w, aaa, bbb;
bool operator<(const Edge& x) const
{
return w < x.w;
}
}c[N];
Union_Find uf;
class Kruskal
{
public:
CG::Point kruskal()
{
CG::Point res = CG::Point(0, 0);
sort(c + 1, c + m + 1);
uf.Init();
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m && cnt < n - 1; i++)
{
int u = c[i].u, v = c[i].v;
if (uf.find(u) != uf.find(v))
{
cnt++;
uf.merge(u, v);
res.x += c[i].aaa;
res.y += c[i].bbb;
}
}
if (res.x * res.y < ans.x * ans.y || (res.x * res.y == ans.x * ans.y && res.x < ans.x))
{
ans = res;
}
return res;
}
}k;
void solve(CG::Point x, CG::Point y)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
c[i].w = (y.x - x.x) * c[i].bbb + (x.y - y.y) * c[i].aaa;
}
CG::Point C = k.kruskal();
if (cj(y - x, C - x) >= 0) return;
solve(x, C);
solve(C, y);
}
signed main()
{
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld", &u[i], &v[i], &a[i], &b[i]);
u[i]++;
v[i]++;
c[i].aaa = a[i];
c[i].bbb = b[i];
c[i].u = u[i], c[i].v = v[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
c[i].w = c[i].aaa;
}
CG::Point A = k.kruskal();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
c[i].w = c[i].bbb;
}
CG::Point B = k.kruskal();
solve(A, B);
printf("%lld %lld\n", ans.x, ans.y);
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号