SE3转换关系
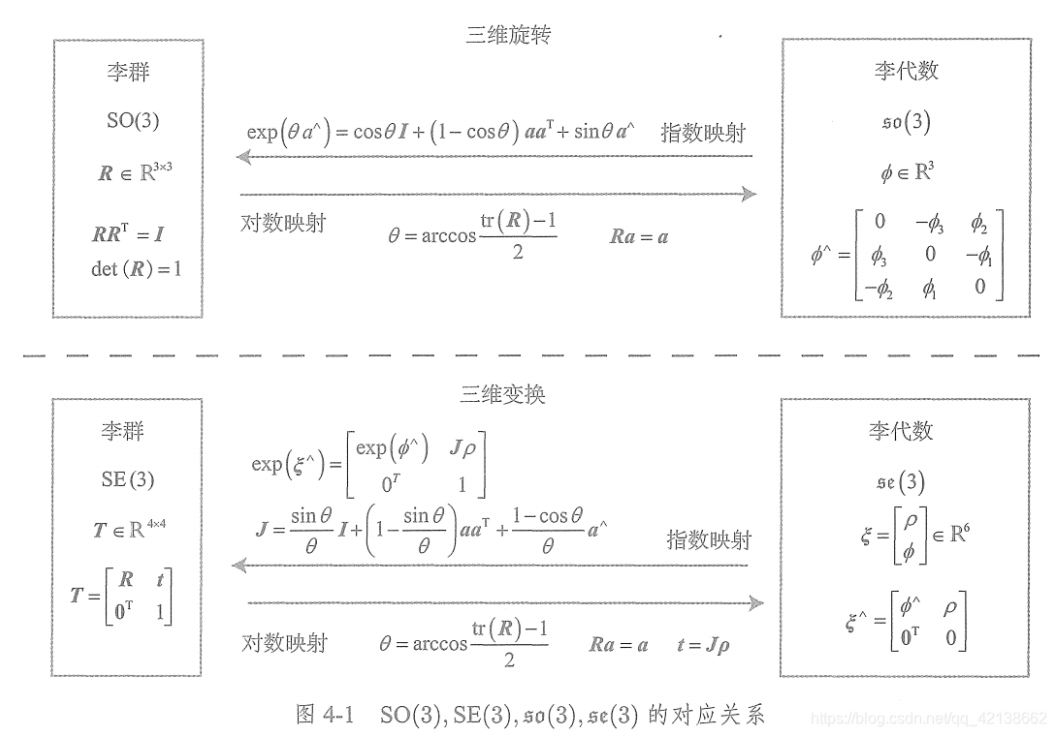

https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/47766990
==============
更新量转化
Eigen::Map<const Vector6> update(update_);
更新参数
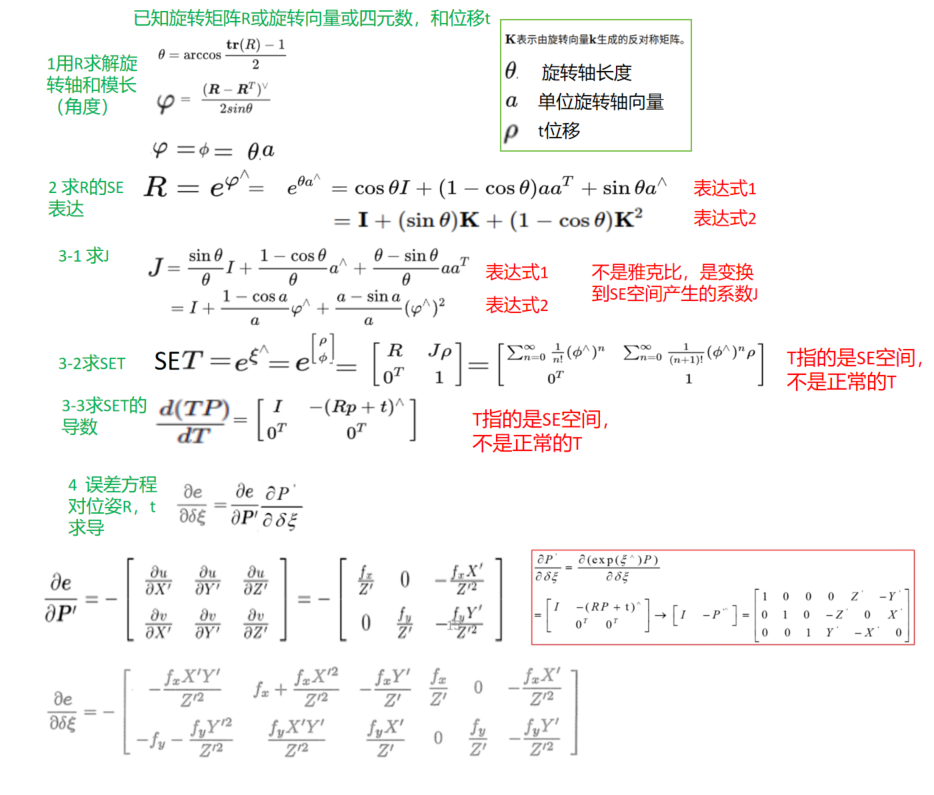

1旋转向量
(旋转)
一个向量,绕旋转轴n,转动的角度Θ 得到新的向量位置

2旋转矩阵(旋转)
角度 R 3*3

3-1旋转矩阵==>旋转向量
3-1-1先求出角度
两边的迹(矩阵对角线元素的和)
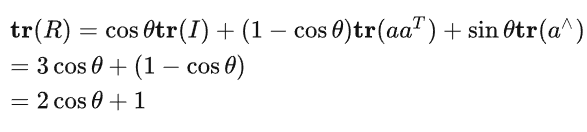
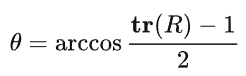
3-1-2然后再求出旋转轴n=[ux,uy,uz]


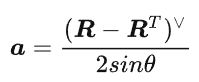
3-2 旋转向量==>旋转矩阵
https://www.cnblogs.com/gooutlook/p/16356118.html
叉乘表示法
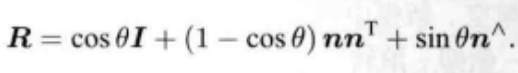
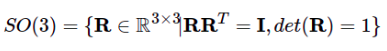
另一种表达式 矩阵形式 代码实现
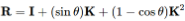

3-3 旋转矩阵转化李代数
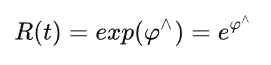
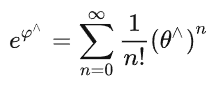
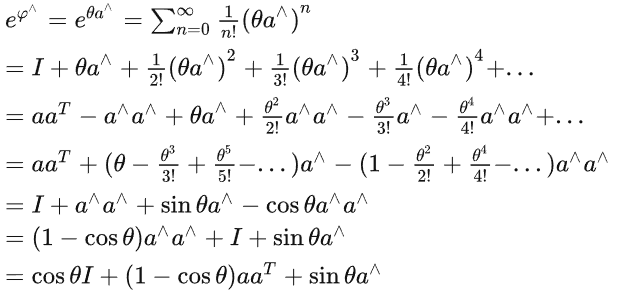
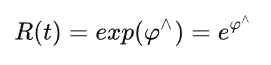

给定一个R,可以转换成一个反对称矩阵,进一步转化成 旋转向量,进一步拆解为 单位旋转轴和轴长度
求解j角度
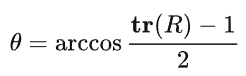
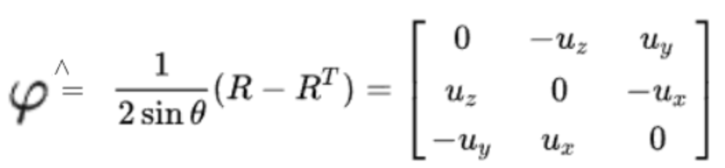
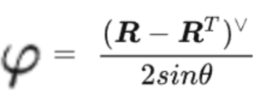
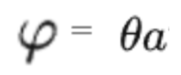
反对称矩阵等于一个 旋转向量,进一步等于 单位旋转轴*旋转轴长度
3-4 R 转换求导结果
给定一个R,可以写成指数形式
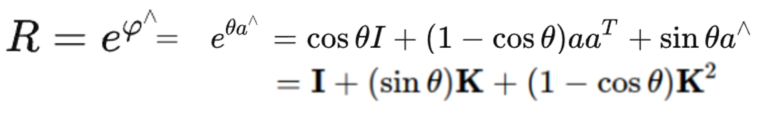
其中
![]() 向量模长
向量模长
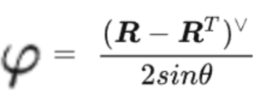 1*3的旋转向量 也表示为k
1*3的旋转向量 也表示为k
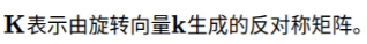
1对R求导,可以转变为对![]() ,
,![]() 求导,a是连续的可加。
求导,a是连续的可加。
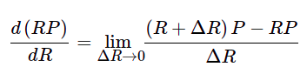 不成立的
不成立的
2对E(A)求导,需要 计算E(A+dA)
第二行使用了左乘BCH近似,如果使用右乘BCH近似,可以得到相反的形式。
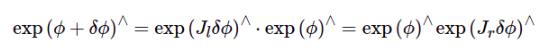
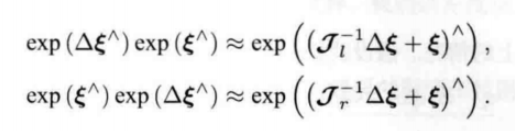
3-4-1 对时间求导
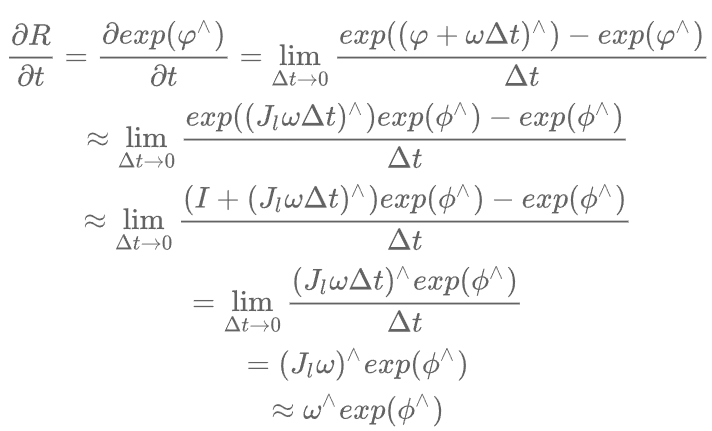
3-4-2-1 定义在李代数上的增量
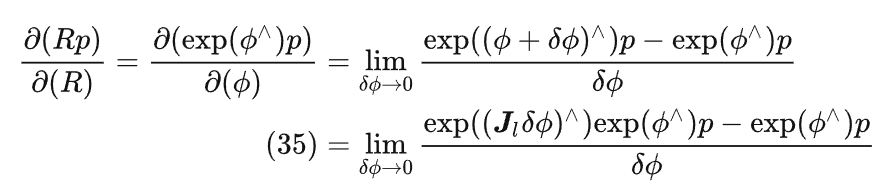
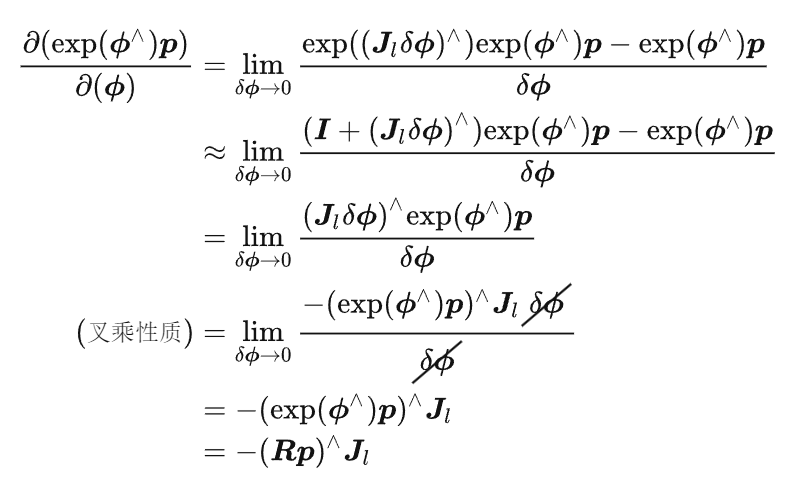
结果中存在一个左雅各比矩阵 J ,计算该矩阵比较麻烦,于是需要介绍扰动模型来给出更简单的李代数求导的计算方法。
3-4-2-2 定义在李代数上的增量
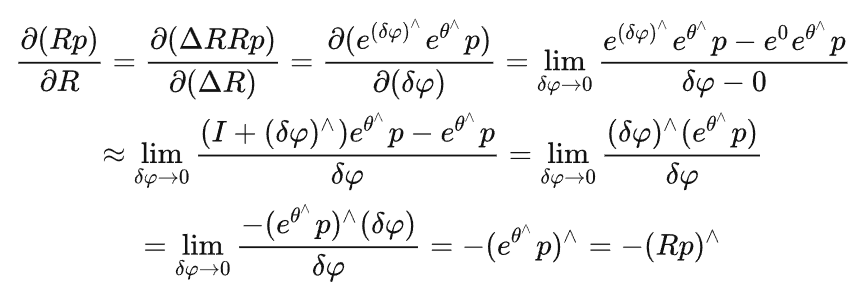
另一种李代数的求导方式是对旋转矩阵进行一次扰动 ΔR ,然后看结果中相对于该扰动的变化率。这个扰动可以乘在左边或者右边,结果有些许差异,十四讲中以左扰动为例进行演示:
4 T 变换矩阵 (旋转+位移)
4-0 目标求解
T导数 (T+dT-T)/dt
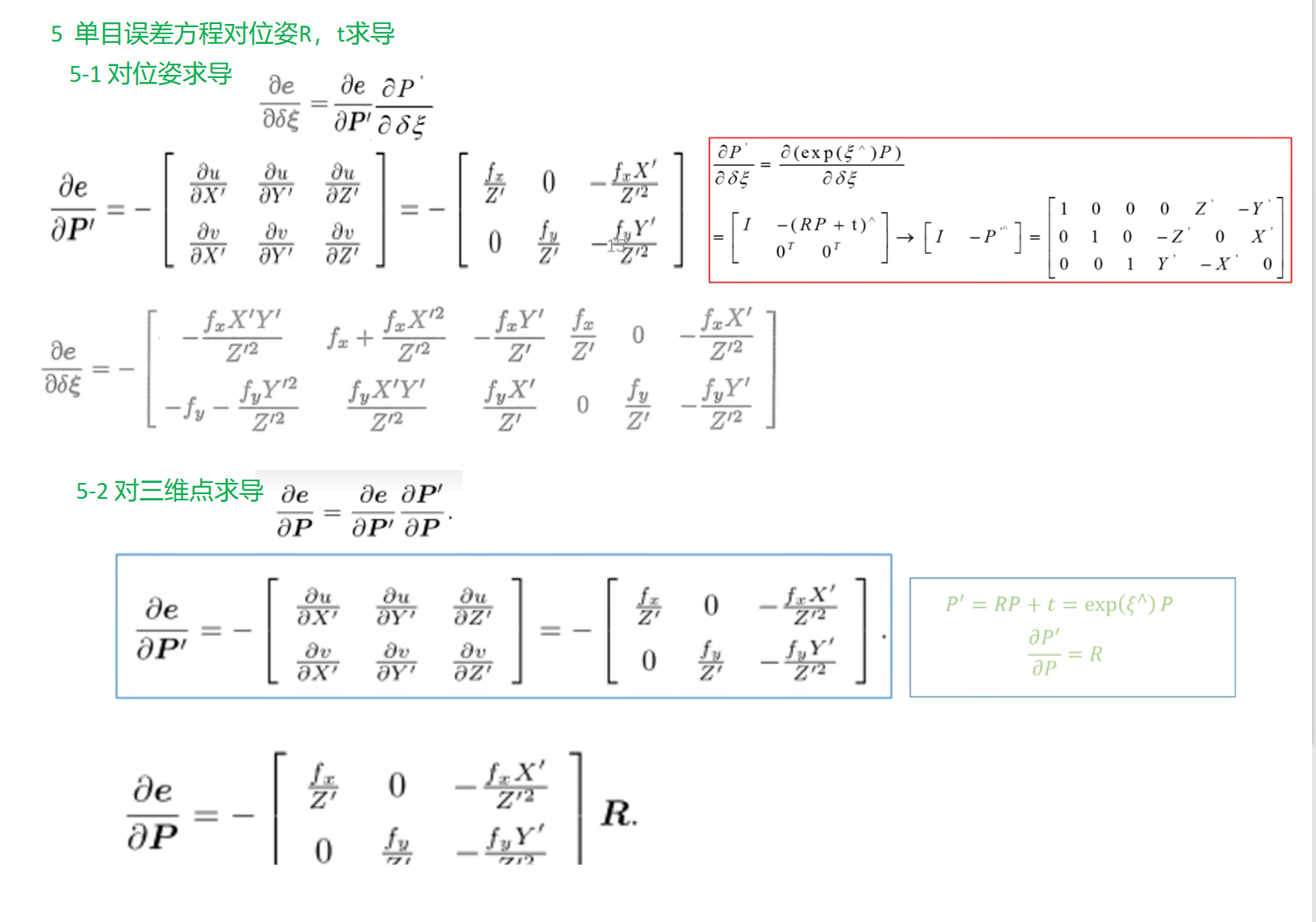
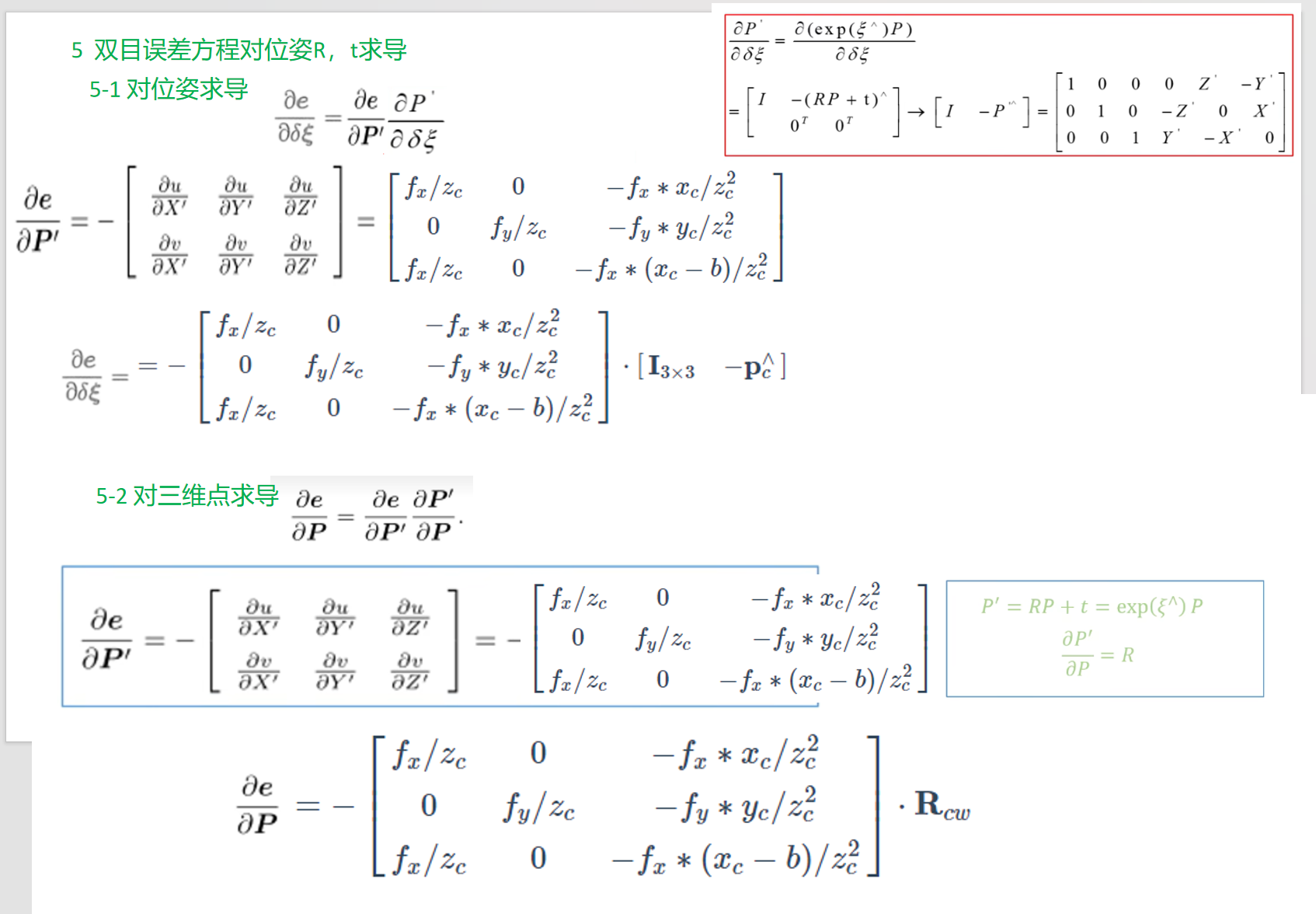
为了位姿优化,需要T对R,t两部分求导。
但是T不能直接对R求导,求导需要加上微小量,t是相加性质, 但是R不是相加性质,且R具有正交约束限制,因此需要转换T。
4-1 定义
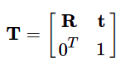
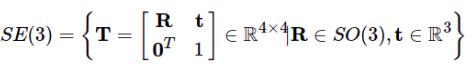
4-2 T映射到E空间
借助于R对应一个三维旋转向量,转化到E空间
定义T对应一个[三维平移,三维旋转向量]的6维向量,转化到E空间

其中
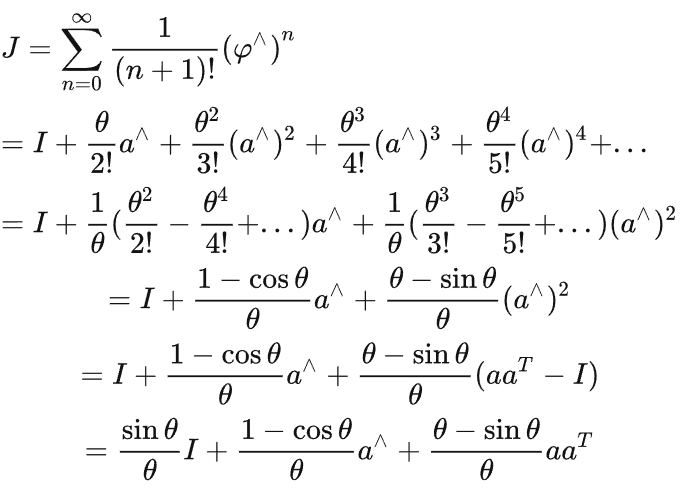
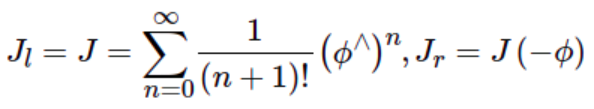

另一种表达式
https://ethaneade.com/lie.pdf
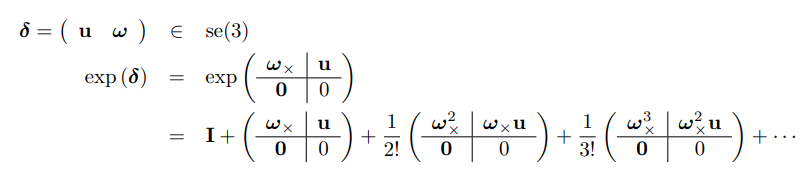

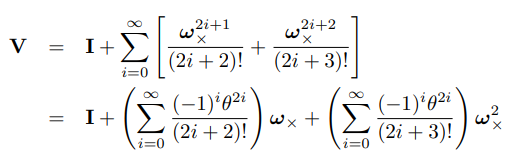
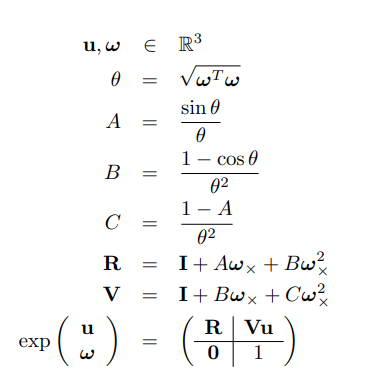
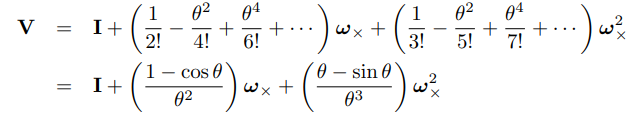
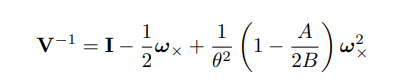

结果
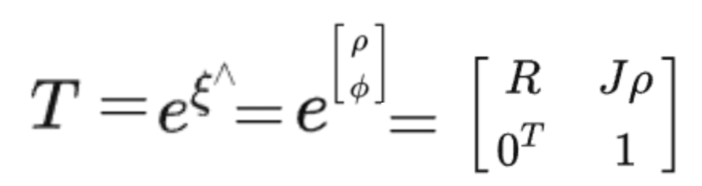
其中

首先用R求出旋转轴长度和单位选转向量
![]() 向量模长
向量模长
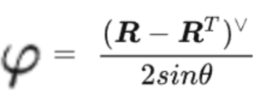 1*3的旋转向量
1*3的旋转向量
然后求出R的具体表达式
![]()
接着构造J
![]()
左乘形式的Jl
![]()
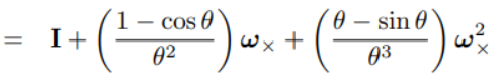
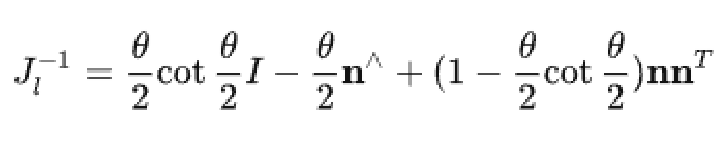
然后计算p
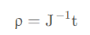
最后得到T
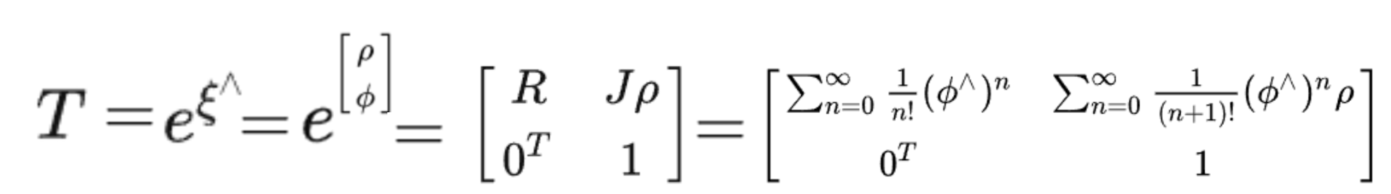
4-2 T目标求导
转化T到E指数上,就可以利用伴随性质求导
对E(T)求导,需要 计算E(T+dT)
第二行使用了左乘BCH近似,如果使用右乘BCH近似,可以得到相反的形式。
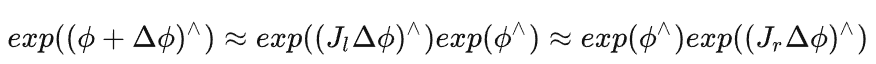
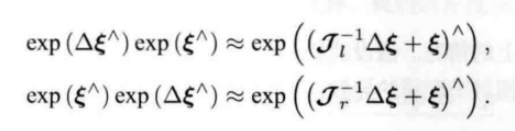
如同R T使用定义在李代数上的增量更加方便
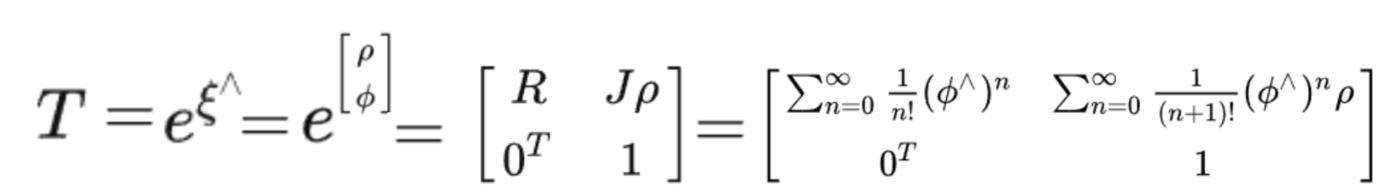

3-4-2-1 定义在李代数上的增量(不用)
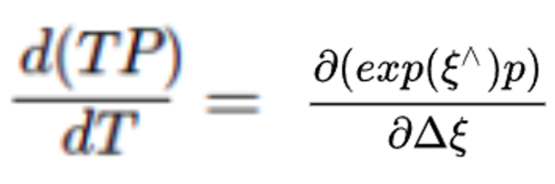
下面把R替换成T一样使用,但是不用,因为每次算左右扰动J
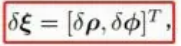
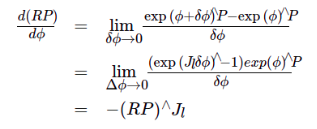
3-4-2-2 定义在李代数上的增量
左扰动



右扰动

Sophus上的简单使用
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#include <Eigen/Core>//导入eigen库的核心组件
#include <Eigen/Geometry>//导入eigen库的几何组件
#include "sophus/se3.h"
#include "sophus/so3.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// 沿Z轴转90度的旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(M_PI / 2, Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 1)).toRotationMatrix();
Sophus::SO3 SO3_R(R); // Sophus::SO(3)可以直接从旋转矩阵构造
Sophus::SO3 SO3_v(0, 0, M_PI / 2); // 亦可从旋转向量构造
Eigen::Quaterniond q(R); // 或者四元数
Sophus::SO3 SO3_q(q);
// 上述表达方式都是等价的
// 输出SO(3)时,以so(3)形式输出
cout << "SO(3) from matrix: " << SO3_R << endl;
cout << "SO(3) from vector: " << SO3_v << endl;
cout << "SO(3) from quaternion :" << SO3_q << endl;
// 使用对数映射获得它的李代数
Eigen::Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();
cout << "so3 = " << so3.transpose() << endl;
// hat 为向量到反对称矩阵
cout << "so3 hat=\n" << Sophus::SO3::hat(so3) << endl;
// 相对的,vee为反对称到向量
cout << "so3 hat vee= " << Sophus::SO3::vee(Sophus::SO3::hat(so3)).transpose() << endl; // transpose纯粹是为了输出美观一些
// 增量扰动模型的更新
Eigen::Vector3d update_so3(1e-4, 0, 0); //假设更新量为这么多
Sophus::SO3 SO3_updated = Sophus::SO3::exp(update_so3) * SO3_R;
cout << "SO3 updated = " << SO3_updated << endl;
/********************萌萌的分割线*****************************/
cout << "************我是分割线*************" << endl;
// 对SE(3)操作大同小异
Eigen::Vector3d t(1, 0, 0); // 沿X轴平移1
Sophus::SE3 SE3_Rt(R, t); // 从R,t构造SE(3)
Sophus::SE3 SE3_qt(q, t); // 从q,t构造SE(3)
cout << "SE3 from R,t= " << endl << SE3_Rt << endl;
cout << "SE3 from q,t= " << endl << SE3_qt << endl;
// 李代数se(3) 是一个六维向量,方便起见先typedef一下
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log();
cout << "se3 = " << se3.transpose() << endl;
// 观察输出,会发现在Sophus中,se(3)的平移在前,旋转在后.
// 同样的,有hat和vee两个算符
cout << "se3 hat = " << endl << Sophus::SE3::hat(se3) << endl;
cout << "se3 hat vee = " << Sophus::SE3::vee(Sophus::SE3::hat(se3)).transpose() << endl;
// 最后,演示一下更新
Vector6d update_se3; //更新量
update_se3.setZero();
update_se3(0, 0) = 1e-4d;
Sophus::SE3 SE3_updated = Sophus::SE3::exp(update_se3) * SE3_Rt;
cout << "SE3 updated = " << endl << SE3_updated.matrix() << endl;
return 0;
}
G2O上的SE3Quat使用
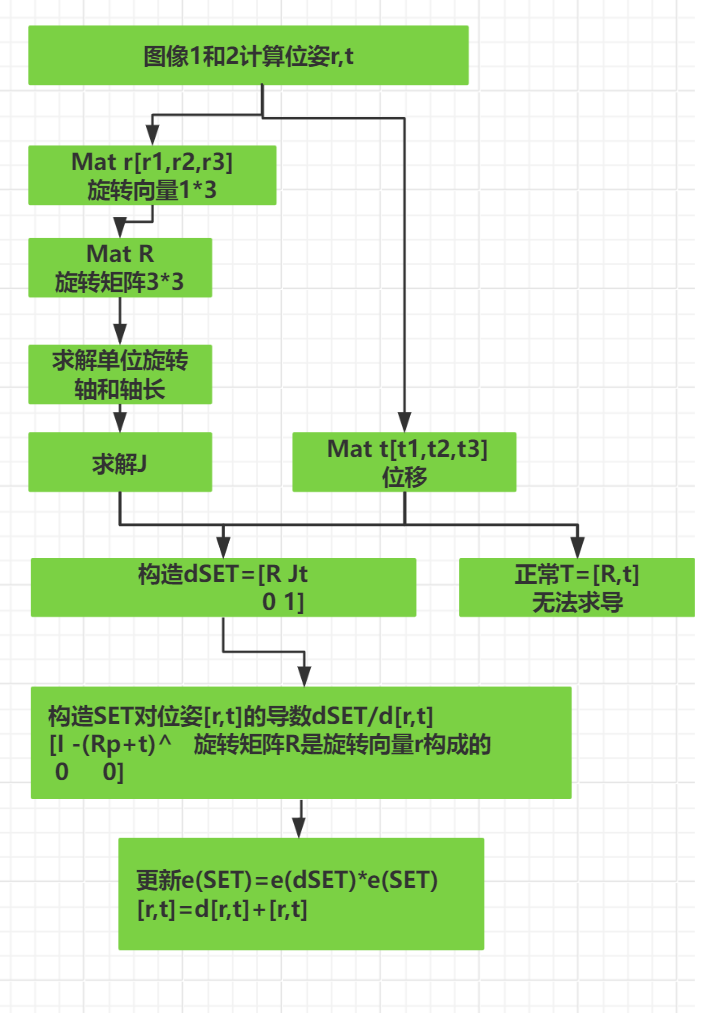
最后代码
T=[R t]=[r1,r2,r3,t1,t2,t3] 转换到SET e(T)
static SE3Quat exp(const Vector6& update) {
Vector3 omega;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) omega[i] = update[i];
Vector3 upsilon;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) upsilon[i] = update[i + 3];
double theta = omega.norm();
Matrix3 Omega = skew(omega);
Matrix3 R;
Matrix3 V;
if (theta < cst(0.00001)) {
Matrix3 Omega2 = Omega * Omega;
R = (Matrix3::Identity() + Omega + cst(0.5) * Omega2);
V = (Matrix3::Identity() + cst(0.5) * Omega + cst(1.) / cst(6.) * Omega2);
} else {
Matrix3 Omega2 = Omega * Omega;
R = (Matrix3::Identity() + std::sin(theta) / theta * Omega +
(1 - std::cos(theta)) / (theta * theta) * Omega2);
V = (Matrix3::Identity() +
(1 - std::cos(theta)) / (theta * theta) * Omega +
(theta - std::sin(theta)) / (std::pow(theta, 3)) * Omega2);
}
return SE3Quat(Quaternion(R), V * upsilon);
}
转换回来
Vector6 log() const {
Vector6 res;
Matrix3 _R = _r.toRotationMatrix();
double d = cst(0.5) * (_R(0, 0) + _R(1, 1) + _R(2, 2) - 1);
Vector3 omega;
Vector3 upsilon;
Vector3 dR = deltaR(_R);
Matrix3 V_inv;
if (std::abs(d) > cst(0.99999)) {
omega = 0.5 * dR;
Matrix3 Omega = skew(omega);
V_inv = Matrix3::Identity() - cst(0.5) * Omega +
(cst(1.) / cst(12.)) * (Omega * Omega);
} else {
double theta = std::acos(d);
omega = theta / (2 * std::sqrt(1 - d * d)) * dR;
Matrix3 Omega = skew(omega);
V_inv = (Matrix3::Identity() - cst(0.5) * Omega +
(1 - theta / (2 * std::tan(theta / 2))) / (theta * theta) *
(Omega * Omega));
}
upsilon = V_inv * _t;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
res[i] = omega[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
res[i + 3] = upsilon[i];
}
return res;
}
python 版本代码
import numpy as np
from scipy.linalg import expm,logm
from numpy import pi,sin,cos,tan,arccos,matmul
from numpy.linalg import norm
# from robotools import Euler_Rodrigues,SE3tose3
np.set_printoptions(precision=3,suppress=True)
deg = pi/180
def vec2sM(vec):
return np.array([
[0,-vec[2],vec[1]],
[vec[2],0,-vec[0]],
[-vec[1],vec[0],0]
])
def sM2vec(sM):
return np.array([sM[2][1],sM[0][2],sM[1][0]])
def upgradeStoE(Screw):
'''
规定:Screw=(S,S0),单位旋量screw=(s,s0),Screw=theta*screw
规定:omg为三维的单位向量,OMG = theta*omg,
把运动旋量Screw∈se(3),转换(升维)成T的矩阵对数E矩阵
#E=Eu*theta,其中theta为转角,Eu为单位螺旋对应的矩阵对数
'''
theta = norm(Screw[:3])
if abs(theta)<1e-5:
theta = norm(Screw[-3:])
screw = Screw.reshape((6,1))/theta
omg,vel = screw[:3],screw[-3:]
sMomg = vec2sM(omg)
bottom = np.array([[0,0,0,0]])
Eu = np.r_[np.c_[sMomg,vel],bottom]
E = Eu.astype(float)*theta
return E
def degradeEtoS(Ematrix):
'''
输入:李代数的4×4标准表示E矩阵
输出:对应的李代数向量形式Screw
'''
OMG,VEL = sM2vec(Ematrix[:3,:3]).reshape(3,1),Ematrix[:3,3].reshape(3,1)
theta = np.linalg.norm(OMG)
if abs(theta)<1e-5:
theta = norm(VEL)
omg,vel = OMG/theta,VEL/theta
screw = np.vstack((omg,vel))
Screw = (screw*theta).reshape(1,6)
return Screw
def expEtoT(E):
'''输入:李代数的4×4标准表示矩阵E
Step1:通过反对称矩阵sMOMG提取出theta
Step2:通过theta获得单位标准表示矩阵Eu
Step3:使用Euler_Rodrigues公式计算Trans矩阵
'''
sMOMG = sM2vec(E[:3,:3]) #OMG改为sMOMG
V = E[:3,3]
theta = norm(sMOMG)
if abs(theta)<=1e-5:
theta = norm(V)
I = np.eye(3)
bottom = np.array([[0,0,0,1]]).reshape((1,4))
T = np.vstack((np.hstack((I,V.reshape(3,1))),bottom))
return T
Eu = E/theta
I = np.eye(4)
T = I + sin(theta)*Eu + (1-cos(theta))*matmul(Eu,Eu)
return T
def logTtoE(T):
'''输入齐次转移矩阵T,得到对应李代数se(3)的4×4标准表示矩阵E
思路:
Step1:提取旋转矩阵R和位置坐标向量p
Step2:通过旋转矩阵的迹计算转角theta和反对称矩阵:此处要注意theta=0时的特殊情况
Step3:通过sM2vec函数求omg向量
Step4:通过Ginv函数和theta与p计算v
Step5:拼接矩阵(sMomg,v)*theta和(0,0,0,1)为E矩阵
'''
I = np.eye(3)
R,p = T[:3,:3],T[:3,3]
theta = arccos((np.trace(R)-1)/2)
if abs(theta) < 1e-5:
omg = np.array([0,0,0]) #这句感觉可以不写
theta = norm(p)
E = np.vstack((np.hstack((I,p/theta)),np.array([0,0,0,1])))
return E
omg = sM2vec((R-R.transpose())/(2*sin(theta)))
sMomg = vec2sM(omg)
Ginv = 1/theta*I-1/2*sMomg+(1/theta-0.5/tan(theta/2))*np.matmul(sMomg,sMomg)
v = matmul(Ginv,p.reshape((3,1)))
E = np.vstack((np.hstack((sMomg,v))*theta,np.array([[0,0,0,0]])))
return E
s = np.array([0,0,0,3.37,-3.37,0])
theta = pi/6
Twist = s*theta
E = upgradeStoE(Twist)
T = expEtoT(E)
# T = expm(E)
# EM= logTtoE(T)
EM = logm(T)
Screw = degradeEtoS(EM)
print(f"Twist={Twist}")
print(f"E={E}")
print(f"T={T}")
print(f"EM ={EM}")
print(f"Screw={Screw}")


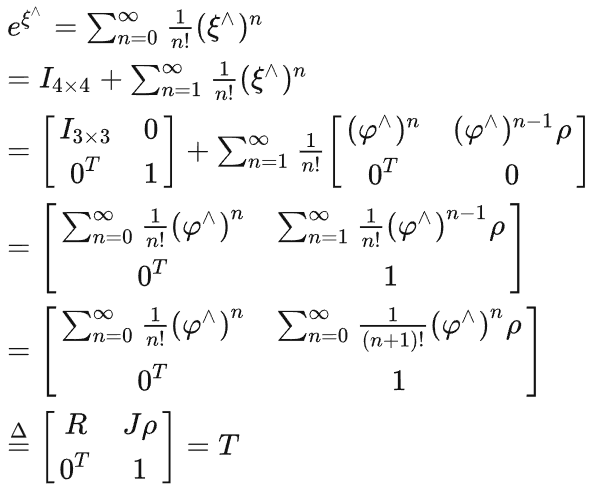

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号