一维PN结的数值模拟
问题描述
(可参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/ghzhan/articles/17031958.html)
考虑一个经典的PN结模型,掺杂浓度为 \(N_a=N_d=10^{16} cm^{-3}\), 求解其电势分布.
经典近似
一维泊松方程为:
PN 结两端电势为
内建电场为:
根据耗尽层近似, 假设耗尽层宽度为 \(W\), 靠近 P 型的宽度为 \(w_p\), 靠近 N 型的宽度为 \(w_n\). 其一维泊松方程可写为:
根据边界条件 \(E(-w_p) = E(w_n) = 0, V(-w_p) = V_p, V(w_n) = V_n\), 可求得耗尽层宽度为:
迭代方法
事实上,耗尽层近似方法并不是一个很准确的方法。通常需要对泊松方程迭代求解来得到稳定的电势分布。下面介绍几种相关的迭代方法。
常规迭代
一维泊松方程为:
其中,
因此可得到:
通过有限差分, 可将 \(\frac{d^2V}{dx^2}\) 变换成矩阵形式 \(DV/a^2\), 其中 \(a\) 是差分网格密度, \(D\) 是三对角矩阵
把泊松方程写成矩阵形式:
\(V_0\) 是与边界条件有关的常数项,这里为 \(V_0 = [V_p,0,...,0,V_n]\), 因此迭代方程为:
这里的 0.01 可视情况设置。
结果如下:
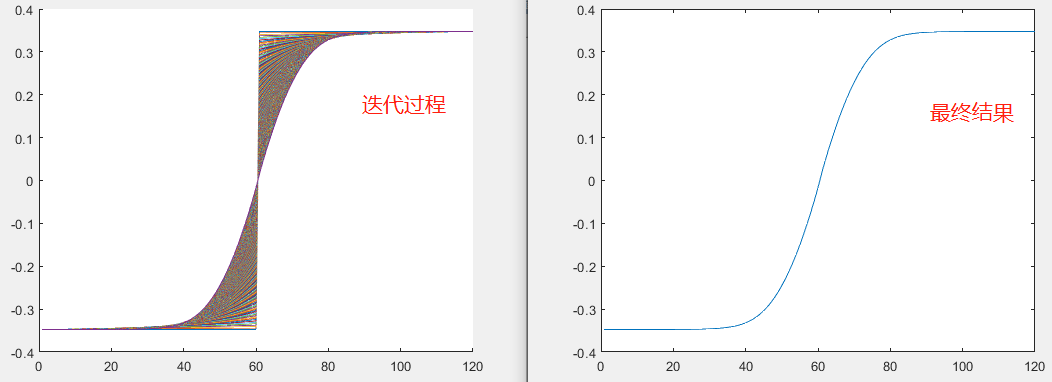
Newton-Raphson
New-Raphson 方法是常用来求解非线性方程的根的方法.
因此,对于一系列的方程
对于 泊松方程为
\(\Delta V^l\) 为
上式重新写为:
其中:
对于本题中的PN结,
因此,根据 M 和 R 矩阵便可得到 \(\Delta V\), 再进行相应的迭代.
结果如下:
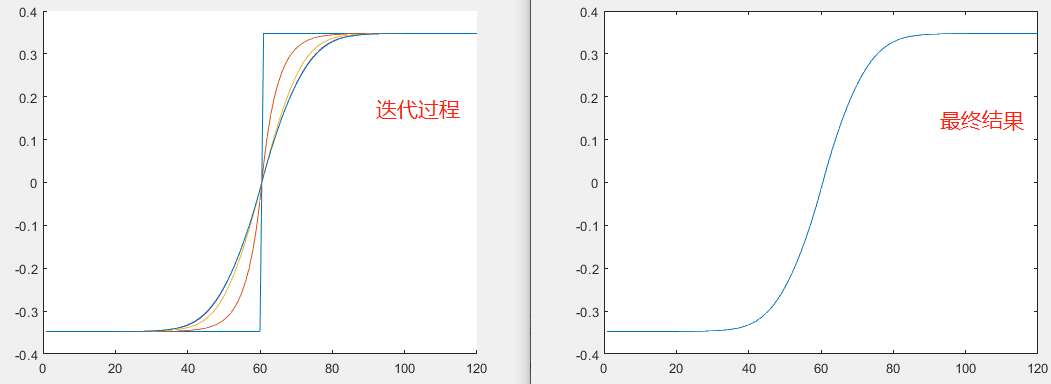
不难发现,这种迭代方法收敛很快.
Gummel 方法
"Implicit numerical schemes have to be used to solve the highly non-linear coupled Schro¨dinger–Poisson
system. Moreover, the Newton–Raphson method is not appropriate since the density does not depend
locally on the potential. Therefore, for a given potential Vn at the step n, we propose to implicit the
scheme as follows"
暂时码住. 参考文献 3.
参考文献
[1] Sunhee Lee PhD thesis. Purdue University. Appedix B. https://engineering.purdue.edu/gekcogrp/publications/theses/PhD_11_2011_Sunhee_Lee_PhD_Thesis_main.pdf
[2] R. A. Jabr, et al., Newton-Raphson solution of Poisson's equation in a pn diode. International Jounral of Electrical Engineering Eduction 44, 2007.
[3] Finley R. Shapiro, The Numerical solution of Poisson's equation in a pn Diode using a spreadsheet. IEEE TED 38, 4, 1995.
[4] E. Polizzi, N. Ben Abdallah. Subband decomposition approach for the simulation of quantum electron transport in nanostructures. Journal of Computational Physics 202, 150-180 2005.
[5] i-H. Tan, G. L. Snider, L. D. Chang, and E. L. Hu. A self‐consistent solution of Schrödinger–Poisson equations using a nonuniform mesh. Journal of Applied Physics 68, 4071–4076 (1990).
[6] https://github.com/PanosGnk/diode_model/blob/master/src/diode.m
[7] https://github.com/LaurentNevou
[8] https://github.com/SungHyunCha/NEGF_DGMOS
[9] https://github.com/giovannipizzi/SchrPoisson-2DMaterials
[10] https://ww2.mathworks.cn/matlabcentral/answers/270196-i-am-currently-writing-a-code-to-solve-poisson-equation-in-1d-for-a-pn-diode-by-iterative-newton-rap?s_tid=prof_contriblnk
[11] Arnout Beckers. Robust Simulation of Poisson’s Equation in a P-N Diode Down to 1 µK. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.02836v1.pdf
[12] https://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/L6/poisson/pn_poisson_calc_live.html
附件
点击查看代码
clear all;
epsilon = 1.05*1e-12; %F/cm
q = 1.6*1e-19;% C
kT = 0.02585;% eV
n0 = 1.45*1e10; %cm^-3
theta = 1e-6;
m = 120;
Na = 1e16;
Nd = 1e16;
VP = -kT*log(Na/n0);
VN = kT*log(Nd/n0);
Na = [Na*ones(m/2,1);0*ones(m/2,1)];
Nd = [0*ones(m/2,1);Nd*ones(m/2,1)];
V=zeros(m,1);
V(1:m/2,1)=VP; %VP has to be predefined as in (7)
V(m/2+1:m,1)=VN; %VN has to be predefined as in (8)
D2=(2*diag(ones(1,m)))-(diag(ones(1,m-1),1))-(diag(ones(1,m-1),-1));
V0 = [VP;zeros(m-2,1);VN];
beta = q*theta*theta/epsilon;
figure;
Error = 10;
while Error > 1e-3
hold on;
plot(V)
rho = Nd - Na - 2*n0*sinh(V/kT);
V_new = inv(D2)*V0 + inv(D2)*beta*(rho);
dv = V_new - V;
%Error = norm(dv,2)/sqrt(m)
Error = max(max(abs(dv)))
V = V + 0.1*dv;
end
figure;
plot(V)
V=zeros(m,1);
V(1:m/2,1)=VP; %VP has to be predefined as in (7)
V(m/2+1:m,1)=VN; %VN has to be predefined as in (8)
D2=-(2*diag(ones(1,m)))+(diag(ones(1,m-1),1))+(diag(ones(1,m-1),-1));
V0 = [VP;zeros(m-2,1);VN];
beta = q*theta*theta/epsilon;
figure;
Error = 10;
while Error > 1e-16
hold on;
plot(V)
drho_dv = -2*n0/kT*cosh(V/kT);
rho = Nd - Na - 2*n0*sinh(V/kT);
M = -D2 - diag(beta*drho_dv);
R = D2*V + V0 + beta*rho;
dv = inv(M)*R;
V = V + dv;
Error = norm(dv,2)/sqrt(m);
end
figure;
plot(V)
点击查看代码
clear all;
% temperature
% (temperature-dependent band-gap and intrinsic carrier concentration is not implemented)
T = 300; % in degree K
% permittivity of vacuum
eps_0 = 8.854187813e-12; % in As/Vm
% relative permittivity
eps_r = 12;
% absolute permittivity
epsilon = eps_0 * eps_r; % in As/Vm
% Boltzmann constant
kB = 1.380658e-23; % in J/K
% elementary charge
q = 1.60217733e-19; % in As
% intrinsic carrier concentration of SI
ni = 1.45e16; % in 1/m^3
% band gap energy of SI
Eg = 1.12; % in eV
% lower grid bound
xmin = str2double("-4e-6"); % in m
% upper grid bound
xmax = str2double("4e-6"); % in m
% number of grid points
N = round(str2double("1000"));
doping_profile = "abrupt_pnp";
maxIter = round(str2double("1000"));
alpha = 1e-6;
% grid points (sampling)
x = linspace(xmin,xmax,N).';
% step-size
dx = x(2)-x(1);
% grid extension (needed for central differences)
xg = [ min(x)-dx;x;max(x)+dx ];
% load doping profile
[NA,ND] = doping_profiles(doping_profile,x);
% initializing electron concentration
n = ND;
% initializing hole concentration
p = NA;
% initializing electric potential
V = zeros(size(xg));
Vinit = band_initialization(NA,ND,ni,q,kB,T);
V(2:N+1) = Vinit;
V(1) = V(2); % boundary
V(end) = V(end-1); % boundary
V_old = V;
% figure;
% plot(x,V(2:N+1))
% loop for Newton-Raphson Iterations
for k=1:maxIter
% updating charge carrier concentrations
n = ni*exp(q*V(2:N+1)/(kB*T));
p = ni*exp(-q*V(2:N+1)/(kB*T));
% charge density
% (assuming that the dopants are totally ionized)
rho = q*(p - n + ND - NA);
% charge density change due to the internal potential
drho_dV = -2*q^2*ni/(kB*T) * cosh(q*V(2:N+1)/(kB*T));
% finite difference formulation for the potential
d2V_dx2 = ( V(1:N,1) - 2*V(2:N+1,1) + V(3:N+2,1) )/(dx^2);
% non-linear equation system
Mjj_k = 2/(dx^2) - 1/epsilon*drho_dV;
M_off = 1/(dx^2)*ones(N,1);
M_k = spdiags([-M_off Mjj_k -M_off],-1:1,N,N);
R_k = 1/epsilon*rho + d2V_dx2;
% solving for potential changes
delta_V = M_k\R_k;
% Newton-Raphson Step (updating the potential)
%V(2:N+1) = V(2:N+1)+(0.98^k)*delta_V;
V(2:N+1) = V(2:N+1)+delta_V;
% stopping criteria
if( norm( (V - V_old), "inf" ) < alpha )
break;
end
V_old = V;
end
% calculating the electric field
E = -diff(V(1:N+1))/dx;
% build in voltage
Vbi = abs(V(end)-V(1));
disp(['Number of Newton-Raphson Iterations: ',num2str(k)])
disp(['build in voltage: Vbi = ',num2str(Vbi),'V'])
set(groot, ...
'DefaultTextInterpreter', 'LaTeX',...
'DefaultAxesTickLabelInterpreter', 'LaTeX',...
'DefaultLegendInterpreter', 'LaTeX',...
'DefaultAxesFontName', 'LaTeX',...
'DefaultFigureColor', 'w', ...
'DefaultAxesLineWidth', 0.5, ...
'DefaultAxesXColor', 'k', ...
'DefaultAxesYColor', 'k', ...
'DefaultAxesFontUnits', 'points', ...
'DefaultAxesFontSize', 15, ...
'DefaultAxesFontName', 'Helvetica', ...
'DefaultLineLineWidth', 1.5, ...
'DefaultTextFontUnits', 'Points', ...
'DefaultTextFontSize', 20, ...
'DefaultTextFontName', 'Helvetica', ...
'DefaultAxesBox', 'on', ...
'DefaultAxesTickLength', [0.01 0.01],...
'defaultAxesXGrid','on',...
'defaultAxesYGrid','on',...
'defaultfigureposition',[50 50 1080 400],...
'defaultAxesTitleFontSize',1.3);
% plot chosen doping profile
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,NA,'b','DisplayName','$N_A$','LineWidth',1.5)
plot(x,ND,'r','DisplayName','$N_D$','LineWidth',1.5)
plot(x,(ND-NA),'g--','DisplayName','$N_D - N_A$','LineWidth',1.5)
title('doping concentrations')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('$N(x)$ in $1$/$m^3$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,p,'b','DisplayName','$p$','LineWidth',1.5)
plot(x,n,'r','DisplayName','$n$','LineWidth',1.5)
title('carrier concentrations')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('$n(x),p(x)$ in $1$/$m^3$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,rho,'b','DisplayName','$\rho$','LineWidth',1.5)
title('charge density')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('$\rho(x)$ in $As$/$m^3$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,E,'b','DisplayName','$E$','LineWidth',1.5)
title('electric field')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('$E(x)$ in $V$/$m$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,V(2:N+1),'b','DisplayName','$V$','LineWidth',1.5)
title('potential')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('$V(x)$ in $V$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
figure, hold on, grid minor;
plot(x,-V(2:N+1)+Eg/2,'r','DisplayName','conduction band','LineWidth',1.5)
plot(x,-V(2:N+1)-Eg/2,'b','DisplayName','valence band','LineWidth',1.5)
title('band diagram')
xlabel('$x$ in $m$')
ylabel('energy in $eV$')
legend_obj = legend();
legend_obj.Location = 'northeastoutside';
hold off;
function V = band_initialization(NA,ND,ni,q,kB,T)
% if needed, add bias voltage to this function
dN = ND - NA;
V = zeros(size(dN));
for i=1:length(V)
if( abs(dN) >= ni )
V(i) = sign(dN(i))*kB*T/q*log(abs(dN(i))/ni);
end
end
end
function [NA,ND] = doping_profiles(str,x)
switch str
case 'abrupt'
NA = 1E14*ones(size(x)); % 1/cm^3
NA = NA*1e6; % 1/m^3
ND = [ zeros(size(x(x<0))); ones(size(x(x>=0))) ] * 2E14; % 1/cm^3
ND = ND*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'linear'
alpha = 1e19*100e6; % 1/m^4
NA = zeros(size(x));
ND = zeros(size(x));
for i=1:length(x)
if( x(i) <= 0 )
NA(i) = -alpha*x(i);
elseif( x(i) > 0 )
ND(i) = alpha*x(i);
end
end
case 'hyper_abrupt'
NA=1E15*exp(0.5*(x/1e-6)).*heaviside(-x); % 1/cm^3
NA = NA*1e6; % 1/m^3
ND=1E15*exp(0.5*(-x/1e-6)).*heaviside(x); % 1/cm^3
ND = ND*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'abrupt_pnp'
NA = ( heaviside(-x-1e-6)*5E15 + heaviside(x+1e-6)*1E15 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
ND = ( heaviside(x+1e-6)*3E15 - heaviside(x-1e-6)*3E15 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'abrupt_npn'
ND = ( heaviside(-x-1e-6)*5E15 + heaviside(x+1e-6)*1E15 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
NA = ( heaviside(x+1e-6)*3E15 - heaviside(x-1e-6)*3E15 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'abrupt_pnpn'
NA = ( heaviside(-x-2e-6)*1E18 + ( heaviside(x-2e-6) - heaviside(x-3e-6) )*0.8E18 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
ND = ( ( heaviside(x+2e-6) - heaviside(x-2e-6) )*5E17 + heaviside(x-3e-6)*1.2E18 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'abrupt_npnp'
ND = ( heaviside(-x-2e-6)*1E18 + ( heaviside(x-2e-6) - heaviside(x-3e-6) )*0.8E18 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
NA = ( ( heaviside(x+2e-6) - heaviside(x-2e-6) )*5E17 + heaviside(x-3e-6)*1.2E18 )*1e6; % 1/m^3
case 'arbitrary'
[NA,ND] = myProfile(x);
otherwise
error(['[ERROR]: ',str,' is not a valid doping profile!'])
end
end
function [NA,ND] = myProfile(x)
NA = 1E14*ones(size(x)); % 1/cm^3
NA = NA*1e6; % 1/m^3
ND = exp( -(x/1e-6).^2 )*1e15; % 1/cm^3
ND = ND*1e6; % 1/m^3
end



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号