参考
Cocos Creator 性能优化:DrawCall(全面!) - Creator 2.x - Cocos中文社区
【乐府】突破动态合图-你真的把动态合图用对了吗? - Creator 2.x - Cocos中文社区
3.8.2动态合图问题 - Creator 3.x - Cocos中文社区
一 什么是动态合图
动态合图是cocos提供的功能,在项目运行时动态将贴图合并到一张大图,以此减少drawcall。
动态合图条件
合图条件在源码atlas-manager.ts中,条件是 开启动态合图 + 图集未满 + 图片未参与动态合图 + 图片勾选packable + 采样符合条件,符合这些条件即可参与动态合图。
atlas-manager.ts:
if (!this._enabled || this._atlasIndex >= this._maxAtlasCount
|| !spriteFrame || spriteFrame.original) return null;
if (!spriteFrame.packable) return null;
// hack for pixel game,should pack to different sampler atlas
const sampler = spriteFrame.texture.getSamplerInfo();
if (sampler.minFilter !== Filter.LINEAR || sampler.magFilter !== Filter.LINEAR || sampler.mipFilter !== Filter.NONE) {
return null;
}
开启动态合图
将动态合图设置代码加入项目脚本最外层,不要写在onLoad/start函数中,确保项目加载过程中即使生效。
const { ccclass, property, menu } = _decorator;
//是否在将贴图上传至 GPU 之后删除原始图片缓存,删除之后图片将无法进行 动态合图。
//web平台不需要开启,因为web平台Image占用内存小。
//小游戏平台默认开启,避免内存占用过高。
macro.CLEANUP_IMAGE_CACHE = false;
//动态合图开关
DynamicAtlasManager.instance.enabled = true;
export default class Main {
}
图片需要勾选Packable选项
该选项默认勾选,所以无需自己去逐个设置
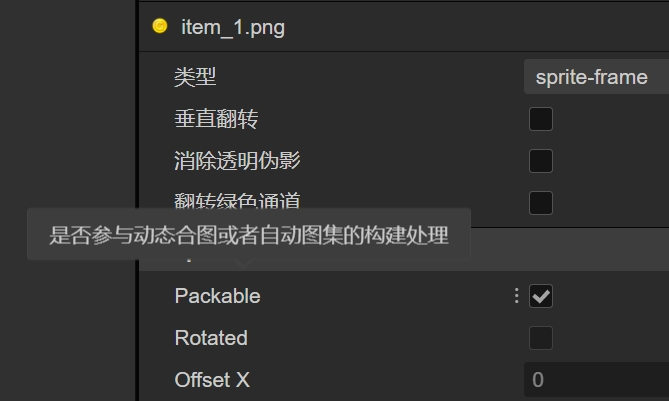
动态合图类的设置
maxFrameSize:可以添加进图集的最大尺寸,如果图片高或宽大于512,那么就无法进行动态合图。默认512。
maxAtlasCount:可以创建的图集最大数量,一张图集满了以后,会创建一张新的进行合图,最大支持5张。默认5。
textureSize:创建图集的宽高,默认是2048x2048。
DynamicAtlasManager.instance.maxFrameSize = 512; //可以添加进图集的图片的最大尺寸
DynamicAtlasManager.instance.maxAtlasCount = 5; //可以创建的最大图集数量
DynamicAtlasManager.instance.textureSize = 2048; //创建的图集的宽高
1 源码位置
Creator\3.8.2\resources\resources\3d\engine\cocos\2d\utils\dynamic-atlas\atlas-manager.ts
2 动态合图调用流程
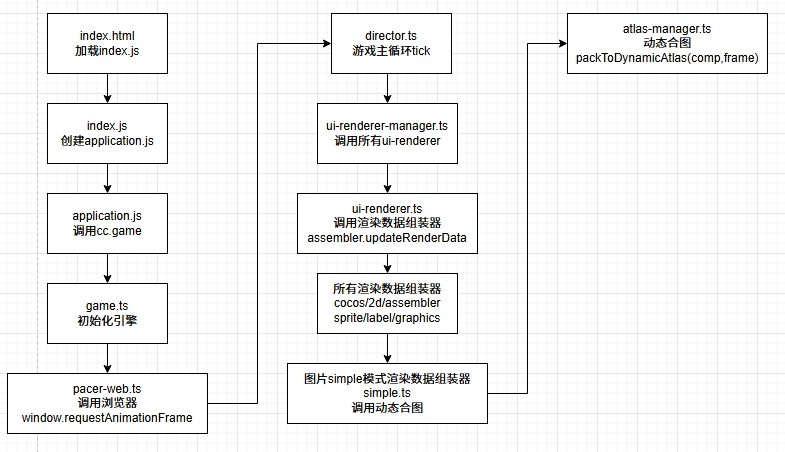
3 源代码
public packToDynamicAtlas (comp, frame): void {
if (EDITOR_NOT_IN_PREVIEW || !this._enabled) return;
//图片未合图过_original=null,勾选了可合并packagble=true,高宽>0,则进行合图。
//_original={_texture, _x, _y} 保存着原纹理。
if (frame && !frame._original && frame.packable && frame.texture && frame.texture.width > 0 && frame.texture.height > 0) {
const packedFrame = this.insertSpriteFrame(frame);
if (packedFrame) {
frame._setDynamicAtlasFrame(packedFrame);
}
}
}
public insertSpriteFrame (spriteFrame): {
x: number;
y: number;
texture: DynamicAtlasTexture;
} | null {
if (EDITOR_NOT_IN_PREVIEW) return null;
//已合图过_original!=null,图集达最大值_maxAtlasCount=5不可合图
if (!this._enabled || this._atlasIndex === this._maxAtlasCount
|| !spriteFrame || spriteFrame._original) return null;
//图片可合并packable=false,不可合图
if (!spriteFrame.packable) return null;
// hack for pixel game,should pack to different sampler atlas
const sampler = spriteFrame.texture.getSamplerInfo();
//采样器sampler为线性LINEAR时不可合图
if (sampler.minFilter !== Filter.LINEAR || sampler.magFilter !== Filter.LINEAR || sampler.mipFilter !== Filter.NONE) {
return null;
}
//图集不存在,则创建一张
let atlas = this._atlases[this._atlasIndex];
if (!atlas) {
atlas = this.newAtlas();
}
//图集无空白位置可合并图片,则创建一张新的图集合并
const frame = atlas.insertSpriteFrame(spriteFrame);
if (!frame && this._atlasIndex !== this._maxAtlasCount) {
atlas = this.newAtlas();
return atlas.insertSpriteFrame(spriteFrame);
}
return frame;
}
public insertSpriteFrame (spriteFrame: SpriteFrame): {
x: number;
y: number;
texture: DynamicAtlasTexture;
} | null {
const rect = spriteFrame.rect;
// Todo:No renderTexture
const texture = spriteFrame.texture as Texture2D;
//根据小图纹理id保存纹理,info[texture.getId()] = {texture,x,y},根据x,y、texture.width、texture.height可从大图上获取小图
const info = this._innerTextureInfos[texture.getId()];
//小图起始位置
let sx = rect.x;
let sy = rect.y;
if (info) {
sx += info.x;
sy += info.y;
} else {
const width = texture.width;
const height = texture.height;
//小图在大图上排列方式从左到右,从上到下,第2张图在第1张图右边2像素
//当第1行排满了,从第2行开始排,第2行起始位置x=2,y=第1行最高的图往下
if ((this._x + width + space) > this._width) {
this._x = space;
this._y = this._nexty;
}
//获取当前行height最高的图,当作下一行y起始位置。例如第1行排列有3张图,height分别是100,200,150,则以200为下一行起始y位置。
if ((this._y + height + space) > this._nexty) {
this._nexty = this._y + height + space;
}
//y轴排列不下,则返回null,表示大图没有位置合并小图了
if (this._nexty > this._height) {
return null;
}
//textureBleeding默认true,较小的帧更有可能受到线性滤波器的影响,这里可能是处理线性滤波器造成的影响
if (cclegacy.internal.dynamicAtlasManager.textureBleeding) {
// Smaller frame is more likely to be affected by linear filter
if (width <= 8 || height <= 8) {
//texture.image! 中的 ! 是一个 非空断言操作符(Non-null Assertion Operator),它告诉编译器:
//"我确定 texture.image 不是 null 或 undefined,请直接使用它,不要报错。"
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y + 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y + 1);
}
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x, this._y + 1);
}
//把小图绘制到大图上
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x, this._y);
//缓存小图,以便下次复用
this._innerTextureInfos[texture.getId()] = {
x: this._x,
y: this._y,
texture,
};
this._count++;
//保存当前小图在大图上起始位置
sx += this._x;
sy += this._y;
//更新下一次合图时的起始位置
this._x += width + space;
}
//返回小图所在的大图以及大图上的起始位置,通过以下数据可以从大图上找到小图
const frame = {
x: sx,
y: sy,
texture: this._texture,
};
//保存小图,用于销毁图集时删除小图上的合图相关数据
this._innerSpriteFrames.push(spriteFrame);
return frame;
}
public _setDynamicAtlasFrame (frame): void {
if (!frame) return;
this._original = {
_texture: this._texture,
_x: this._rect.x,
_y: this._rect.y,
};
this._texture = frame.texture;
this._rect.x = frame.x;
this._rect.y = frame.y;
this._calculateUV();
}
合图排列源码在atlas.ts中,排列规则是从左到右,从上到下。
第一行排满了,就从第二行开始排,第二行y起点以第一行最高的图height为起点。
atlas.ts:
const width = texture.width;
const height = texture.height;
//小图在大图上排列方式从左到右,从上到下,第2张图在第1张图右边2像素
//当第1行排满了,从第2行开始排,第2行起始位置x=2,y=第1行最高的图往下
if ((this._x + width + space) > this._width) {
this._x = space;
this._y = this._nexty;
}
//获取当前行height最高的图,当作下一行y起始位置。例如第1行排列有3张图,height分别是100,200,150,则以200为下一行起始y位置。
if ((this._y + height + space) > this._nexty) {
this._nexty = this._y + height + space;
}
//y轴排列不下,则返回null,表示大图没有位置合并小图了
if (this._nexty > this._height) {
return null;
}
如下打印的动态合图,第二行有一个非常高的方块图,那么第三行会以这个高的方块height为y轴起点,导致第二行有大量空白的地方。
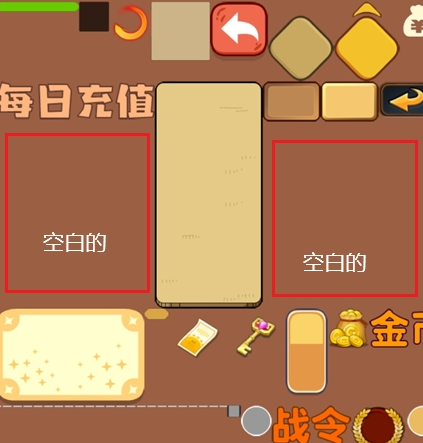
项目运行后,3.x版本没有提供显示动态图集到场景的接口,需要效仿2.x的cc.dynamicAtlasManager.showDebug(true) 接口写一个。
1 自动图集的图片可以参与动态合图吗?
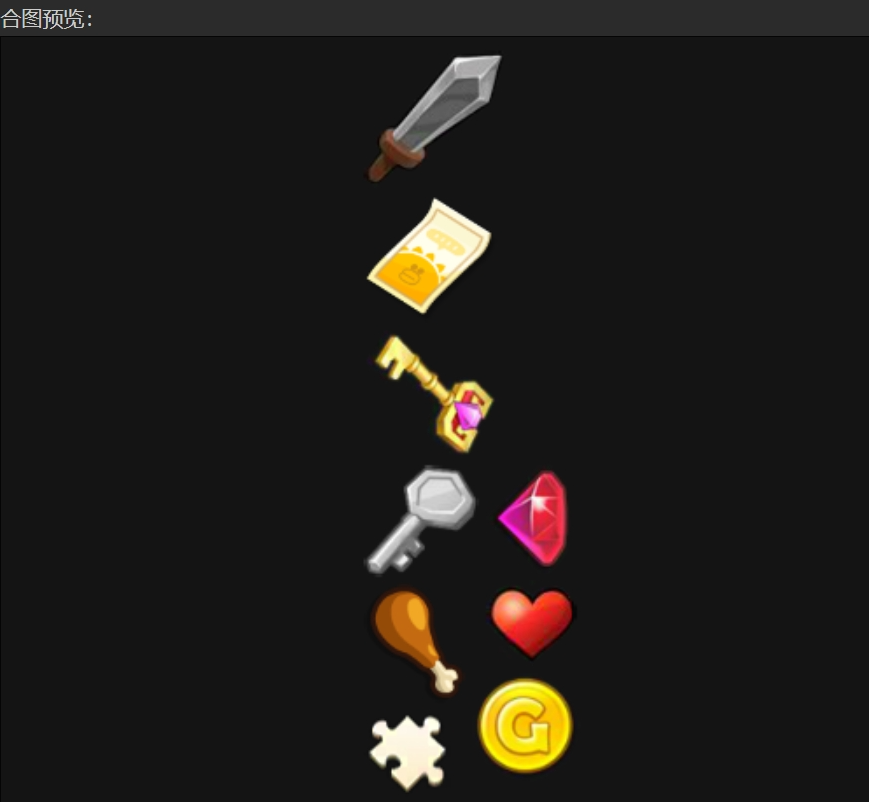
可以。但是动态合图是将整个自动图集合并,而不是单个图片。
例如下图,是物品的自动图集,即使场景中只使用了金币,但是自动合图会将整个图集合并,包括武器、钥匙都会合并到自动合图中,而不是只合并金币。
还有就是通常项目会把通用按钮、图标等合成一张大图,这个大图基本明显都会超过1024x1024,所以无法进行动态合图。
2 Label的Bitmap和Char模式可以动态合图吗?
Char模式不能。
Bitmap模式可以。
Char模式是将文字合并到char自己的1024x1024(2.4.x版本是2048x2048)图集上,这个图集尺寸已经超出了自动合图条件,所以不能。
Bitmap模式可以,使用描边、阴影、加粗后都能合图。但是会重复合图,不能复用。
例如下图,一个弹窗中有一个Bitmap模式的Label,内容是“Bitmap文本”,当不停的打开和关闭这个弹窗时,文本内容会重复的进行动态合图。
因为动态合图缓存图片时是用texture.id来识别的,缓存[texture.id] = 图片,文本每次的texture.id不一样,所以无法复用。
若要复用,必须修改源码,效仿char模式,char模式能复用是因为使用文字的颜色、尺寸、字体等属性hashCode后作为识别缓存的key值,缓存[code] = 图片,每次hashCode值一致,所以能复用。
3 BMFont可以动态合图吗?
可以。
4 骨骼动画可以动态合图吗?
不能。
5 资源release后会重复动态合图
资源release释放后,再次加载,会重复进行动态合图。
6 怎么重建图集?
主动调用reset会重建图集
DynamicAtlasManager.instance.reset();
切换场景时,引擎会自动重建图集
director.loadScene或runScene
atlas-manager.ts:
/**
* @en
* Reset all dynamic atlases, and all existing ones will be destroyed.
*
* @zh
* 重置所有动态图集,已有的动态图集会被销毁。
*
* @method reset
*/
public reset (): void {
for (let i = 0, l = this._atlases.length; i < l; i++) {
this._atlases[i].destroy();
}
this._atlases.length = 0;
this._atlasIndex = -1;
}
7 textureBleeding是什么?
atlas.ts中有一段代码,涉及到一个属性textureBleeding。
atlas.ts:
if (cclegacy.internal.dynamicAtlasManager.textureBleeding) {
// Smaller frame is more likely to be affected by linear filter
if (width <= 8 || height <= 8) {
//texture.image! 中的 ! 是一个 非空断言操作符(Non-null Assertion Operator),它告诉编译器:
//"我确定 texture.image 不是 null 或 undefined,请直接使用它,不要报错。"
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y + 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y + 1);
}
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x - 1, this._y);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x + 1, this._y);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x, this._y - 1);
this._texture.drawTextureAt(texture.image!, this._x, this._y + 1);
}
TextureBleeding是纹理渗色。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号