华容道 BFS DFS C++ Python 短程序
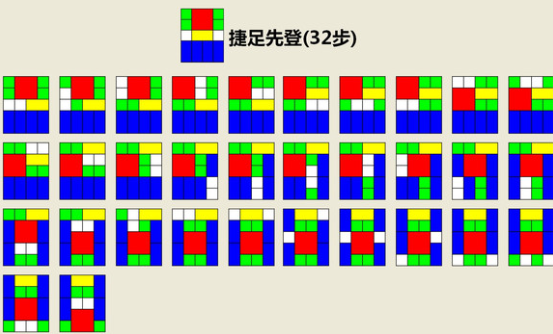
图片来自百度华容道吧。第二/三步卒子像军棋的工兵在铁道上跑——32步比我们的局面变化数少。
注释掉if (a[0][1] == 3) { print_path(); break; } // 判断找到解
则:queue_tail = 14,950,080:从此局面出发有这么多,和这个不矛盾。程序没崩当然令人欣喜,不过该数还不到1500万。“诗云”版华容道?
在Intel N100上,C++版处理上述局面耗时0.017s, queue_tail=10,440.
〔究极优化版 〕
- 10个x放在xs里,10个y放在ys里,xs和ys可同时计算 (多发射、乱序执行)
- 增加b[5][4], 不用popcnt了。1表示空,0表示占用,can_move时少些!
- 曹操能向右移动的条件是新位置的上下两格都是空,能向下移动的条件是新位置的左右两格都是空
- 能向左上移动时,大家都不用考虑W和H
- 卒特殊处理。i >= 6判断是否是卒。横竖条个数不定,卒总是4个
- 循环展开,用宏代替inline不了的函数(所有)
- 简化和减少Hash,误判些局面走弯路,换来速度的提升(此图的连通性很强)
- std::set底层是树,unordered_set底层是Hash表?Hash表用自己的。(未做)
- unordered_set::reserve(500万)效果很好,多一条语句的事
- Profile-Guided Optimization (PGO)没效果
Python程序blks没有做成函数的局部变量或参数的原因,我忘了。import了deepcopy但没有(再)用。应该不是负优化,比如100层,每层都只动了第一个块。
E = ' ' # 全角空格 class Brd: def __str__(m): return '\n'.join([''.join(r) for r in m.b]) def totuple(m): return tuple(tuple(r) for r in m.b) def put(m, blks): m.b = [[E] * 4 for _ in range(5)] for b in blks: if b.x < 0 or b.x + b.w > 4 or b.y < 0 or b.y + b.h > 5: return False for y in range(b.y, b.y + b.h): for x in range(b.x, b.x + b.w): if m.b[y][x] != E: return False m.b[y][x] = b.name return True class Blk: def __init__(m, name, x, y, w = 1, h = 1): m.name = name; m.x = x; m.y = y; m.w = w; m.h = h; m.old = [] def step(m, dx, dy): m.old.append((m.x, m.y)); m.x += dx; m.y += dy def back(m): (m.x, m.y) = m.old.pop() brd = Brd() # 全局临时brd. # 每个blk有自己的old[],等于我们自己管理一些堆栈。 blks = [ Blk('曹', 1, 0, 2, 2), Blk('关', 1, 2, 2, 1), Blk('张', 0, 3, 1, 2), Blk('黄', 1, 3, 1, 2), Blk('赵', 2, 3, 1, 2), Blk('马', 3, 3, 1, 2), Blk('甲', 0, 0), Blk('乙', 0, 1), Blk('丙', 3, 0), Blk('丁', 3, 1) ] cc = blks[0] brd.put(blks); seen = set(); path = [] def search (n): if cc.y == 3: return True s = str(brd) # 都可以,速度本例看不出差别 # s = brd.totuple() if s in seen: return False seen.add(s) for b in blks: for (dx, dy) in ((-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)): b.step(dx, dy) if brd.put(blks): path.append(str(brd)) if search(n + 1): return True path.pop() b.back() return False import sys sys.setrecursionlimit(10000) if search(0): print(len(path), path[-1], path[0], sep='\n\n')
// alias gcc='g++ -msse4.2'
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <nmmintrin.h> #include <set> using namespace std; const char* NM[] = { "曹", "关", "张", "黄", "赵", "马", "丁", "丙", "乙", "甲" }; const int W[] = { 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 }; const int H[] = { 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 }; const int D[4][2] = { 0, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, 0 }; struct State { uint64_t xys; // xy坐标们 int p; // 局面路径的previous // int next; // Hash表里的next bool operator< (const State& that) const { return xys < that.xys; } State& operator= (int a[10][2]); void toary(int a[10][2]); void operator= (const char* s); void print(); }; State& State::operator= (int a[10][2]) { xys = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { uint64_t x = a[i][0], y = a[i][1]; xys |= ((x << 3) | y) << (i * 5); } return *this; } void State::toary (int a[10][2]) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { uint xy = xys >> (i * 5); a[i][0] = (xy >> 3) & 3; // x a[i][1] = xy & 7; // y } } void State::operator= (const char* s) { int a[10][2] = {}, p = 6; for (int x = 3; x >= 0; x--) for (int y = 4; y >= 0; y--) { #define CASE(c, i) case c: a[i][0] = x; a[i][1] = y; break; switch (s[x * 5 + y]) { CASE('c', 0) CASE('g', 1) // 曹关 CASE('z', 2) CASE('h', 3) // 张黄 CASE('l', 4) CASE('m', 5) // 子龙(l) 马 case 'p': a[p][0] = x; a[p++][1] = y; // pawn } } *this = a; } void State::print () { const char* b[5][4] = {}; int a[10][2]; toary(a); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { int x = a[i][0], y = a[i][1]; for (int yy = y; yy < y + H[i]; yy++) for (int xx = x; xx < x + W[i]; xx++) b[yy][xx] = NM[i]; } for (int y = 0; y < 5; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < 4; x++) printf("%s", b[y][x] ? : " "); puts(""); } puts(""); } enum { QMAX = 100 * 1000 * 1000 }; State states[QMAX + 40]; int qh, qt = 1; // queue head, tail set<State> seen; // 改Hash表,和states二合一
// unordered_set<uint64_t>, states[i].xys
bool can_move (int a[10][2], int i, int j) { // 无论成功失败, a[i]都被修改,需要被恢复 // 别优化,a[i][0]和a[i][1]要一起改 const int x = (a[i][0] += D[j][0]); const int y = (a[i][1] += D[j][1]); if (x < 0 || x + W[i] > 4) return false; if (y < 0 || y + H[i] > 5) return false; uint32_t bits = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { const int x = a[i][0], y = a[i][1]; for (int yy = y; yy < y + H[i]; yy++) for (int xx = x; xx < x + W[i]; xx++) bits |= 1 << (yy * 4 + xx); } return _mm_popcnt_u32(bits) == 18; } // 逆序输出。图片里的一步可能等于我们的多步。 void print_path () { int p = qh; while (p != -1) { states[p].print(); p = states[p].p; } } int main () { states[0] = "pp zz""ccghh""ccgll""pp mm"; states[0].p = -1; seen.insert(states[0]); for (; (qt < QMAX) && (qh < qt); qh++) { int a[10][2]; states[qh].toary(a); if (a[0][1] == 3) { print_path(); break; } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { if (can_move(a, i, j)) { states[qt] = a; if (seen.find(states[qt]) == seen.end()) { seen.insert(states[qt]); states[qt++].p = qh; } // a[0][1]和(xys & 7)都是曹操的y坐标,按它排序? } a[i][0] -= D[j][0]; a[i][1] -= D[j][1]; } } return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号