SoftGLRender源码:Buffer系列类
简介
SoftGLRender针对图像存储,设计了一系列图像缓冲区(Buffer)模板类,以支持不同的内存布局(线性、分块、Morton曲线),主要用于图形渲染或图像处理中高效存储和访问像素数据.
使用模板类,能支持任意像素类型T(如uint8_t,float,自定义结构).
三种内存布局:
-
线性布局(Layout_Linear):像素按行优先连续存储(data[x + y * width])。
-
分块布局(Layout_Tiled):将图像划分为 4x4 的小块,提升局部性(适合 GPU 纹理缓存)。
-
Morton布局(Layout_Morton):使用 Z 阶曲线(Morton Code)存储,优化空间局部性(减少缓存失效)。
对应下面3个枚举值:
enum BufferLayout {
Layout_Linear,
Layout_Tiled,
Layout_Morton,
};
类图关系
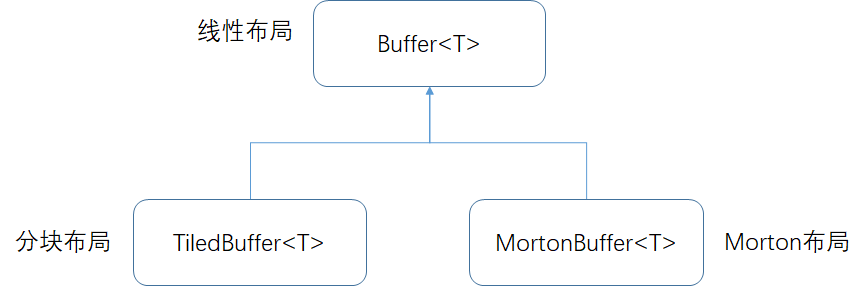
基类Buffer<T>
线性布局的Buffer,适用于绝大多数需要存储图像的情况.
数据成员:
-
width_,height_:图像逻辑尺寸 -
innerWidth_,innerHeight_:实际存储尺寸(可能因对齐或分块大于逻辑尺寸) -
data_:像素数据(通过std::shared_ptr管理内存)
// linear layout buffer
template<typename T>
class Buffer {
...
protected:
size_t width_ = 0; // 逻辑宽度
size_t height_ = 0; // 逻辑高度
size_t innerWidth_ = 0; // 实际宽度
size_t innerHeight_ = 0; // 实际高度
std::shared_ptr<T> data_ = nullptr; // 像素数据
size_t dataSize_ = 0; // 实际占用bytes, 值为innerWidth_ * innerHeight_;
}
核心方法:
-
create():分配内存并初始化布局 -
convertIndex():将(x,y)坐标转换为内存索引(虚函数,子类可重写) -
get()/set():安全访问像素 -
copyRawDataTo():复制数据到外部缓冲区(可选垂直翻转)
分配内存
create()分配内存并初始化布局. 用户需要提供图像宽度、高度,存放像素数据的线性数组(可选).
默认的布局,不需要padding,即图像的实际尺寸 = 逻辑尺寸.
public:
virtual void initLayout() {
innerWidth_ = width_;
innerHeight_ = height_;
}
void create(size_t w, size_t h, const uint8_t* data = nullptr) {
if (w > 0 && h > 0) { // check input
if (width_ == w && height_ == h) { // same size
return;
}
width_ = w;
height_ = h;
initLayout();
dataSize_ = innerWidth_ * innerHeight_;
// 申请像素存储空间
data_ = MemoryUtils::makeBuffer<T>(dataSize_, data);
}
}
销毁内存
销毁由create申请的资源,需要:
- 清空数据成员;
- 设置像素数据指针
data_为nullptr,会自动释放内存.
public:
virtual void destroy() {
width_ = 0;
height_ = 0;
innerWidth_ = 0;
innerHeight_ = 0;
dataSize_ = 0;
data_ = nullptr;
}
坐标转换
实际存储像素数据(data_[]),是一块一维线性空间,而图像是原点在左上角的二维空间. 访问图像使用的是(x,y)坐标,如何转换为一维线性空间的索引呢?
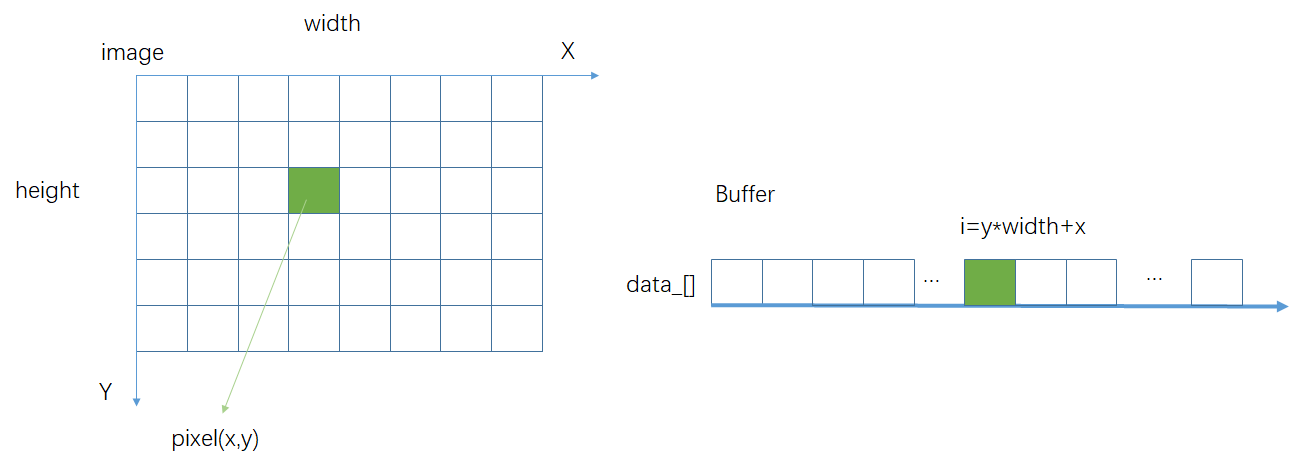
图像在线性空间中,是逐行存储的. 于是,索引对应关系:
image index(x,y) <=> array index [i]
// convert image index (x, y) to vector index [i]
virtual inline size_t convertIndex(size_t x, size_t y) const {
return x + y * innerWidth_;
}
访问指定位置像素
通过convertIndex实现快捷、方便、安全的访问指定位置的图像像素数据.
inline T* get(size_t x, size_t y) {
T* ptr = data_.get();
if (ptr != nullptr && x < width_ && y < height_) {
return &ptr[convertIndex(x, y)];
}
return nullptr;
}
inline void set(size_t x, size_t y, const T& pixel) {
T* ptr = data_.get();
if (ptr != nullptr && x < width_ && y < height_) {
ptr[convertIndex(x, y)] = pixel;
}
}
getter/setter
这部分很简单,不细述.
思考:为什么只能读data_、width_、height_这些数据,而不能写?
答:因为图像的尺寸涉及底层像素数据的存储,不能随意更改位置、大小,各项属性必须匹配;否则,可能造成异常问题.
public:
inline T* getRawDataPtr() const {
return data_.get();
}
inline size_t getRawDataSize() const {
return dataSize_;
}
inline size_t getRawDataBytesSize() const {
return dataSize_ * sizeof(T);
}
inline size_t getWidth() const {
return width_;
}
inline size_t getHeight() const {
return height_;
}
emtpy()判空
empty()判断图像是否为空.
思考:为什么用data_==nullptr判断图像是否为空,而不是width_=height_=0?
答:理论上,是一样的. 因为只有构造图像尺寸(宽、高>0)才会分配data_对应的缓存空间.
public:
inline bool empty() const {
return data_ == nullptr;
}
拷贝出像素数据
copyRawDataTo将data_[]存放的所有像素数据拷贝到用户指定的out缓存. 垂直翻转flip_y可选.
public:
void copyRawDataTo(T* out, bool flip_y = false) const {
T* ptr = data_.get();
if (ptr != nullptr) {
if (!flip_y) {
memcpy(out, ptr, dataSize_ * sizeof(T));
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < innerHeight_; i++) {
memcpy(out + innerWidth_ * i, ptr + innerWidth_ * (innerHeight_ - 1 - i),
innerWidth_ * sizeof(T));
}
}
}
}
清除像素数据
clear()清除data_[]存放的所有像素数据,但不释放存储空间.
inline void clear() const {
T* ptr = data_.get();
if (ptr != nullptr) {
memset(ptr, 0, dataSize_ * sizeof(T));
}
}
设置像素数据
setAll(val)设置data_[]中所有像素为指定值.
inline void setAll(T val) const {
T* ptr = data_.get();
if (ptr != nullptr) {
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize_; i++) {
ptr[i] = val;
}
}
}
工厂方法
Buffer<T>提供了2个static 工厂方法,用于创建std::shared_ptr包裹的Buffer<T>或派生类对象:
makeDefault():根据宏(SOFTGL_TEXTURE_TILED/MORTON)选择布局,默认布局为Layout_Linear.makeLayout():由用户传入参数,动态指定布局
// 工厂方法
// 根据宏静态选择创建不同布局的Buffer
template<typename T>
inline std::shared_ptr<Buffer<T>> Buffer<T>::makeDefault(size_t w, size_t h) {
std::shared_ptr<Buffer<T>> ret = nullptr;
#if SOFTGL_TEXTURE_TILED
ret = std::make_shared<TiledBuffer<T>>();
#elif SOFTGL_TEXTURE_MORTON
ret = std::make_shared<MortonBuffer<T>>();
#else
ret = std::make_shared<Buffer<T>>();
#endif
ret->create(w, h);
return ret;
}
// 根据参数动态选择创建不同布局的Buffer
template<typename T>
inline std::shared_ptr<Buffer<T>> Buffer<T>::makeLayout(size_t w, size_t h, BufferLayout layout) {
std::shared_ptr<Buffer<T>> ret = nullptr;
switch (layout) {
case Layout_Tiled: {
ret = std::make_shared<TiledBuffer<T>>();
break;
}
case Layout_Morton: {
ret = std::make_shared<MortonBuffer<T>>();
break;
}
case Layout_Linear:
default: {
ret = std::make_shared<Buffer<T>>();
}
}
ret->create(w, h);
return ret;
}
e.g. 当我们想创建一个长宽为w, h的图像缓冲区时,可以直接这样创建std::shared_ptr<Buffer<RGBA>>:
auto buffer = Buffer<RGBA>::makeDefault(w, h);
派生类TiledBuffer<T>
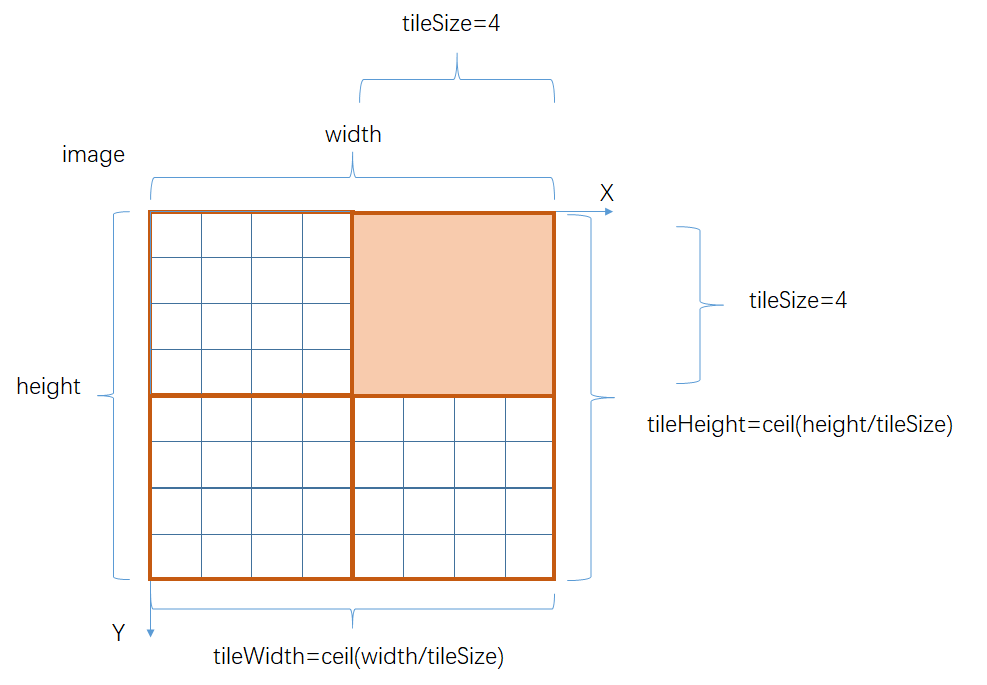
TiledBuffer<T> 是分块布局的Buffer.
特点:
- 将图像按 tileSize x tileSize(默认 4x4)划分成小块
- 每块 tile 连续存储,提高局部访问效率
- 用位运算加速
(x,y)到线性地址的映射
分块布局优势:适合GPU并行处理(特别是移动GPU),如纹理采样,从而提高渲染效率.
TiledBuffer<T>存放像素数据的底层结构,还是其基类Buffert<T>,不同的是TiledBuffer<T>按4x4大小对图像进行分块.
分块布局的逻辑布局
// tiled layout buffer
template<typename T>
class TiledBuffer : public Buffer<T> {
public:
void initLayout() override {
tileWidth_ = (this->width_ + tileSize_ - 1) / tileSize_;
tileHeight_ = (this->height_ + tileSize_ - 1) / tileSize_;
this->innerWidth_ = tileWidth_ * tileSize_;
this->innerHeight_ = tileHeight_ * tileSize_;
}
BufferLayout getLayout() const override {
return Layout_Tiled;
}
private:
const static int tileSize_ = 4; // 4 x 4
const static int bits_ = 2; // tileSize_ = 2^bits_
size_t tileWidth_ = 0; // 分块宽度, 即水平分块数
size_t tileHeight_ = 0; // 分块高度, 即垂直分块数
};
坐标变换
TiledBuffer<T>按tileSize_ x tileSize_大小对图像进行分块,因此,将图像像素(x,y)转换为线性坐标时,可以先考虑分块的坐标,然后再考虑分块内的坐标.
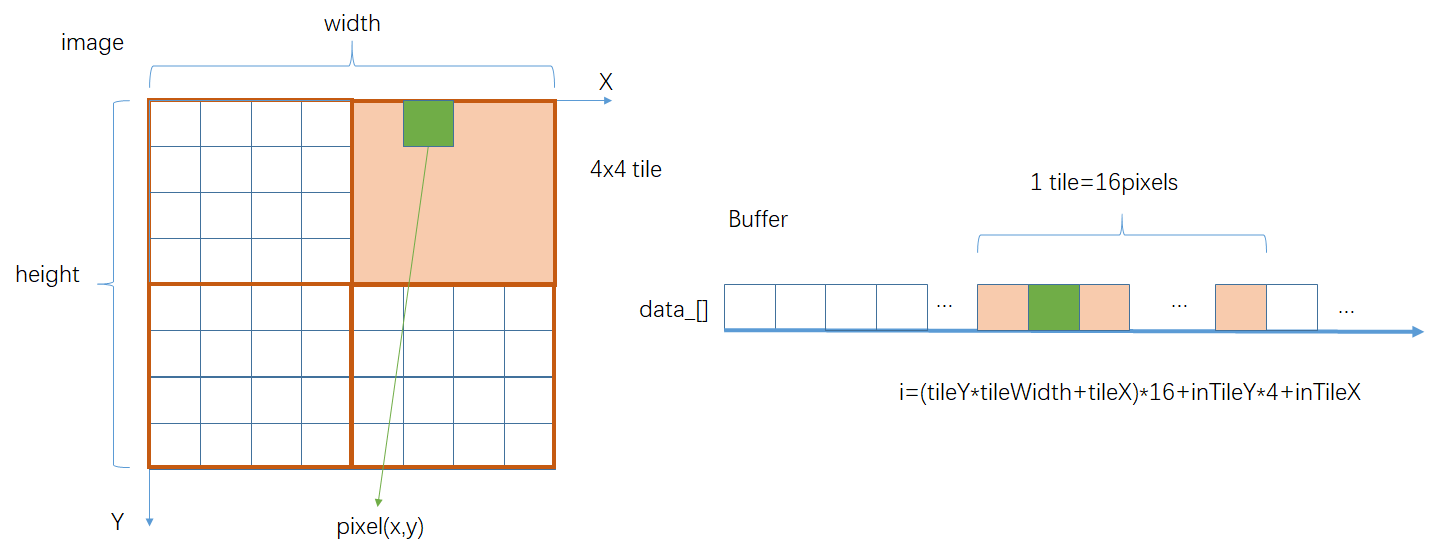
public:
inline size_t convertIndex(size_t x, size_t y) const override {
uint16_t tileX = x >> bits_; // 分块X编号, x / tileSize_
uint16_t tileY = y >> bits_; // 分块Y编号, y / tileSize_
uint16_t inTileX = x & (tileSize_ - 1); // 分块内x值, x % tileSize_
uint16_t inTileY = y & (tileSize_ - 1); // 分块内y值, y % tileSize_
return ((tileY * tileWidth_ + tileX) << bits_ << bits_) + (inTileY << bits_) + inTileX;
}
tips: 用位运算是为了加速运算.
派生类MortonBuffer<T>
由于项目未用到,暂时略.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号