Overview of Polymorphism -多态的分类
多态有类型系统衍生。
有限类型、无限类型、确定类型。
Classifications
Christopher Strachey (1967) introduced the concept of polymorphism informally into procedural programming languages by distinguishing functions
- that work differently on different argument types
- that work uniformly on a range of argument types
He defined the former as ad-hoc polymorphism and the latter as parametric polymorphism:
"Ad-Hoc polymorphism is obtained when a function works, or appears to work, on several different types (which may not exhibit a common structure) and may behave in unrelated ways for each type. Parametric polymorphism is obtained when a function works uniformly on a range of types; these types normally exhibit some common structure." (Strachey, 1967)
![]()
Cardelli and Wegner (1985) expanded Strachey's distinction to accommodate object-oriented languages. They distinguished functions
- that work on a finite set of different and potentially unrelated types
- coercion
- overloading
- that work on a potentially infinite number of types across some common structure
- inclusion
- parametric

Inclusion polymorphism is specific to object-oriented languages.
https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~oop244/pages/content/adhoc.html
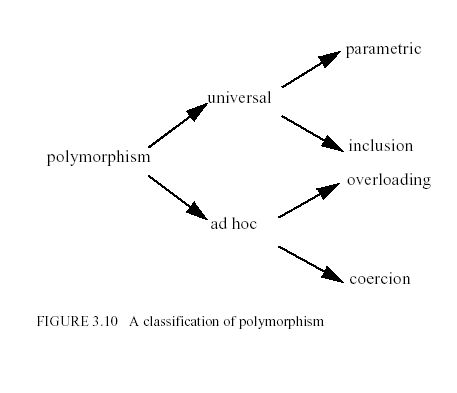
Level 1 - universal vs, ad hoc polymorphism
- functions that are universally polymorphic work uniformly for an infinite set of types
all of which have some common structure
- execute the same code for all admissible types
- execute the same code for all admissible types
- An ad hoc polymorphic function is just a syntactic abbreviation for small set of
different monomorphic functions.
http://www.cs.kent.edu/~durand/CS43101Fall2004/DT-TypeSystems.html





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号