一种在block design中,使用dma+fifo+触发模块的采集模式记录
这个方式其实比较麻烦,但是确实是可用的,简单来讲,就是用普通FIFO代替了stream fifo 来实现稳定,大容量的dma传输(代码在最后面),这边做下记录(实际最好还是用stream fifo),不过还是建议使用我另一篇随笔里的方法。https://www.cnblogs.com/daydaygood/p/18811676
Get_trigger_and_data模块是用来给fifo产生数据、写时钟和写使能,在fifo full信号满的时候停止写使能,在外部start_flag信号为高的时候开始写使能。
jesd_data_parse模块是自定义axi模块,用来给fifo产生读时钟和读使能,读时钟是固定的,读使能来自后级dma驱动的ready和jesd_daa_parse模块里vallid信号的耦合,这里其实做了一步数据位宽转换,64-32。

jesd_data_parse模块与后级的dma模块相连接。

所有关联的模块的复位信号来自于dma的复位信号输出。写时钟250MHz,数据64位宽,读时钟100MHz,数据32位宽。

下面是IP核具体设置,实际可根据经验和需求自行打磨。
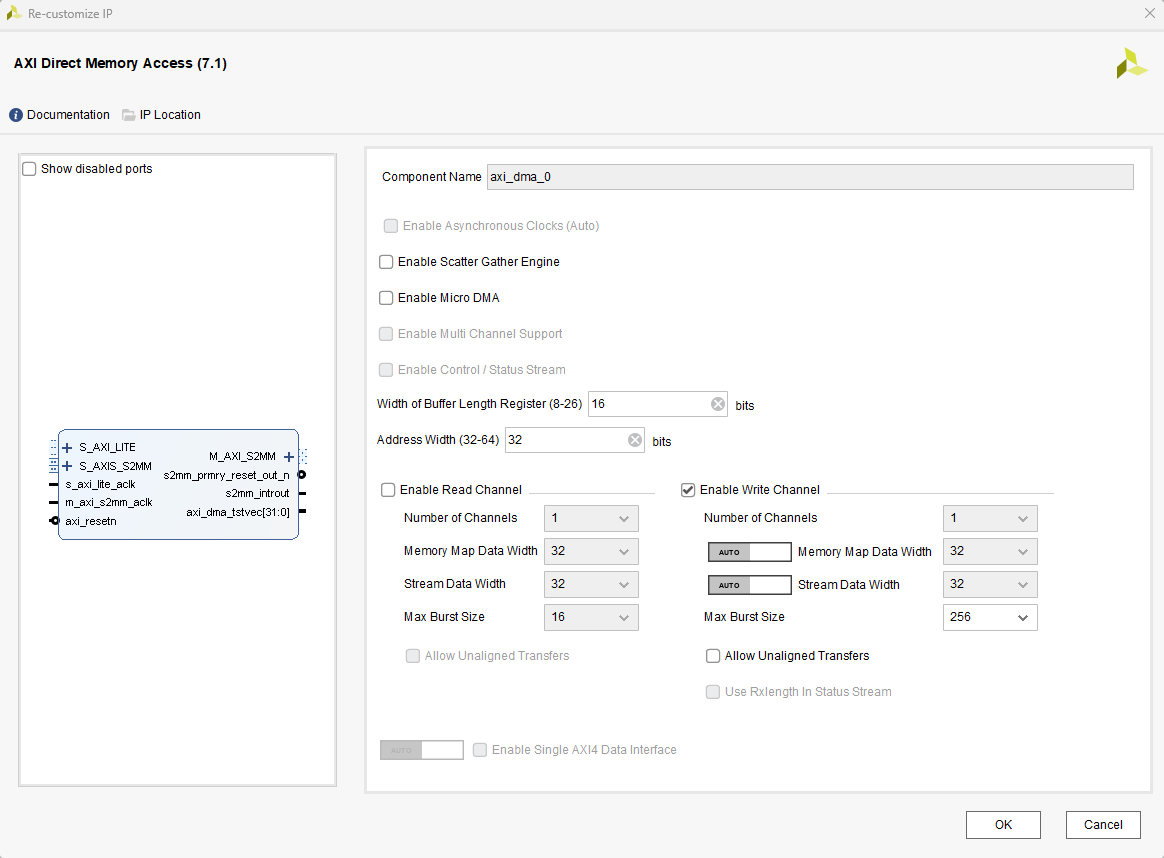

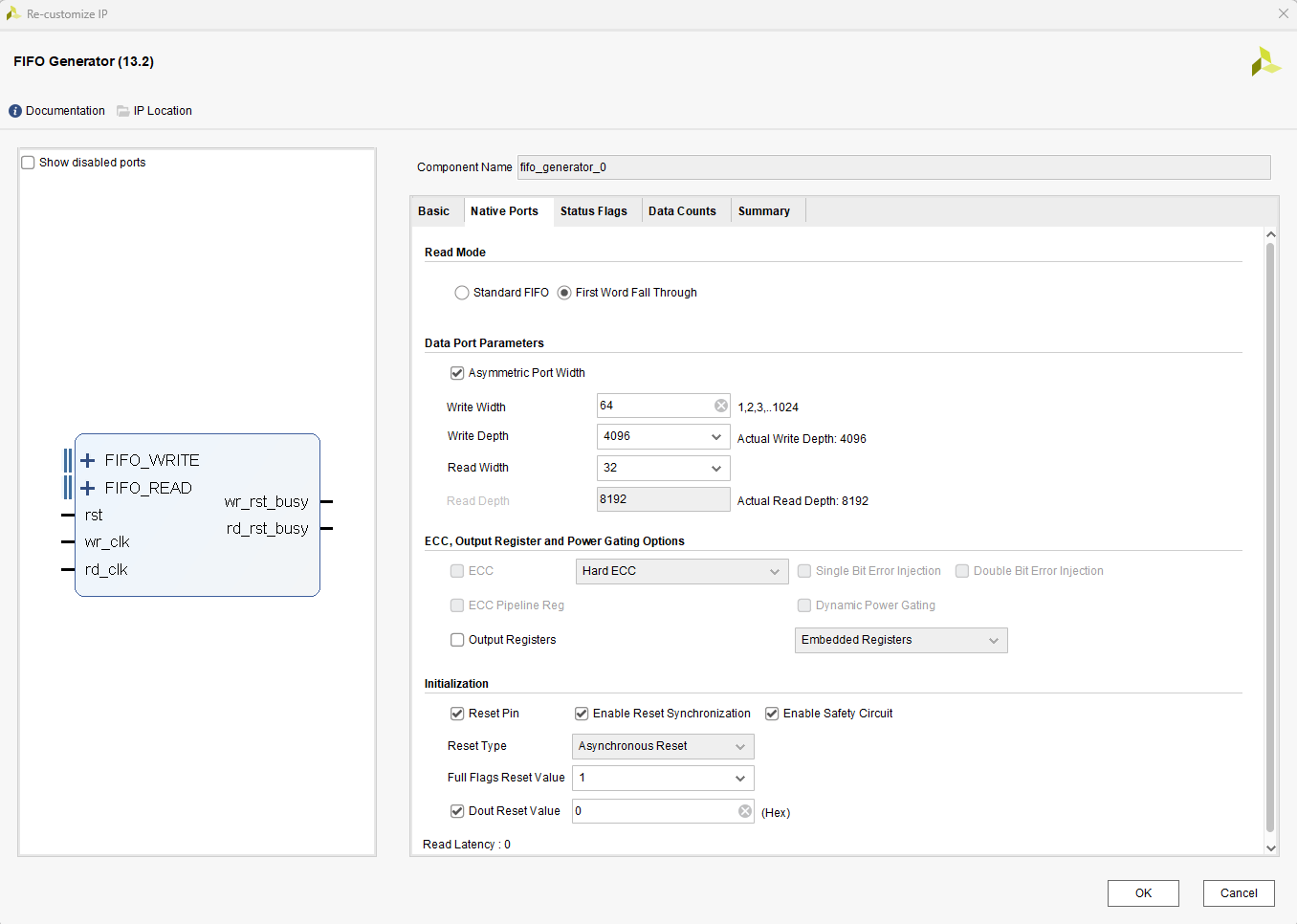

下面是rtl和自定义IP核代码,实际可根据经验和需求自行打磨。
点击查看代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module Get_trigger_and_data_generate(
input wire M_AXIS_ACLK,
input wire M_AXIS_ARESETN,
input wire glblclk,
input wire [63:0] rx_data,
input wire start_flag,
input wire full,
output wire [63:0] adc_data_64,
output reg wr_en,
output wire wr_clk
);
wire [15:0] adc_sample_1;
wire [15:0] adc_sample_2;
wire [15:0] adc_sample_3;
wire [15:0] adc_sample_4;
assign adc_sample_1 = {{2{rx_data[31]}}, rx_data[31:24], rx_data[63:58]};
assign adc_sample_2 = {{2{rx_data[23]}}, rx_data[23:16], rx_data[55:50]};
assign adc_sample_3 = {{2{rx_data[15]}}, rx_data[15: 8], rx_data[47:42]};
assign adc_sample_4 = {{2{rx_data[ 7]}}, rx_data[7 : 0], rx_data[39:34]};
assign adc_data_64 = {adc_sample_4,adc_sample_3,adc_sample_2,adc_sample_1};
// for fifo wr_en
always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin
if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin
wr_en <= 1'd0;
end else if (full) begin
wr_en <= 1'd0;
end else if (start_flag) begin
wr_en <= 1'd1;
end
end
assign wr_clk = glblclk;
endmodule
点击查看代码
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ps
module jesd_data_parse_v1_0_M00_AXIS #
(
// Users to add parameters here
// User parameters ends
// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line
// Width of S_AXIS address bus. The slave accepts the read and write addresses of width C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH.
parameter integer C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH = 32,
// Start count is the number of clock cycles the master will wait before initiating/issuing any transaction.
parameter integer C_M_START_COUNT = 32
)
(
// Users to add ports here
output wire rd_clk,
output wire rd_en,
input wire [31:0] data,
// User ports ends
// Do not modify the ports beyond this line
// Global ports
input wire M_AXIS_ACLK,
//
input wire M_AXIS_ARESETN,
// Master Stream Ports. TVALID indicates that the master is driving a valid transfer, A transfer takes place when both TVALID and TREADY are asserted.
output wire M_AXIS_TVALID,
// TDATA is the primary payload that is used to provide the data that is passing across the interface from the master.
output wire [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TDATA,
// TSTRB is the byte qualifier that indicates whether the content of the associated byte of TDATA is processed as a data byte or a position byte.
output wire [(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8)-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TSTRB,
// TLAST indicates the boundary of a packet.
output wire M_AXIS_TLAST,
// TREADY indicates that the slave can accept a transfer in the current cycle.
input wire M_AXIS_TREADY
);
// Total number of output data
localparam NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS = 8192;
// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the
// value of the ceiling of the log base 2.
function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth);
begin
for(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1)
bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1;
end
endfunction
// WAIT_COUNT_BITS is the width of the wait counter.
localparam integer WAIT_COUNT_BITS = clogb2(C_M_START_COUNT-1);
// bit_num gives the minimum number of bits needed to address 'depth' size of FIFO.
localparam bit_num = clogb2(NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS);
// Define the states of state machine
// The control state machine oversees the writing of input streaming data to the FIFO,
// and outputs the streaming data from the FIFO
localparam [1:0] IDLE = 2'b00, // This is the initial/idle state
INIT_COUNTER = 2'b01, // This state initializes the counter, once
// the counter reaches C_M_START_COUNT count,
// the state machine changes state to SEND_STREAM
SEND_STREAM = 2'b10; // In this state the
// stream data is output through M_AXIS_TDATA
// State variable
reg [1:0] mst_exec_state;
// Example design FIFO read pointer
reg [bit_num-1:0] read_pointer;
// AXI Stream internal signals
//wait counter. The master waits for the user defined number of clock cycles before initiating a transfer.
reg [WAIT_COUNT_BITS-1 : 0] count;
//streaming data valid
wire axis_tvalid;
//streaming data valid delayed by one clock cycle
reg axis_tvalid_delay;
//Last of the streaming data
wire axis_tlast;
//Last of the streaming data delayed by one clock cycle
reg axis_tlast_delay;
//FIFO implementation signals
wire [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] stream_data_out;
wire tx_en;
//The master has issued all the streaming data stored in FIFO
reg tx_done;
// I/O Connections assignments
assign M_AXIS_TVALID = axis_tvalid_delay;
assign M_AXIS_TDATA = stream_data_out;
assign M_AXIS_TLAST = axis_tlast_delay;
assign M_AXIS_TSTRB = {(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}};
// Control state machine implementation
always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK)
begin
if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN)
// Synchronous reset (active low)
begin
mst_exec_state <= IDLE;
count <= 0;
end
else
case (mst_exec_state)
IDLE:
// The slave starts accepting tdata when
// there tvalid is asserted to mark the
// presence of valid streaming data
//if ( count == 0 )
begin
mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER;
count <= 0;
end
//else
// begin
// mst_exec_state <= IDLE;
// end
INIT_COUNTER:
// The slave starts accepting tdata when
// there tvalid is asserted to mark the
// presence of valid streaming data
if ( count == C_M_START_COUNT - 1 )
begin
mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM;
end
else
begin
count <= count + 1;
mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER;
end
SEND_STREAM:
// The example design streaming master functionality starts
// when the master drives output tdata from the FIFO and the slave
// has finished storing the S_AXIS_TDATA
if (tx_done)
begin
mst_exec_state <= IDLE;
end
else
begin
mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM;
end
endcase
end
//tvalid generation
//axis_tvalid is asserted when the control state machine's state is SEND_STREAM and
//number of output streaming data is less than the NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS.
assign axis_tvalid = ((mst_exec_state == SEND_STREAM) && (read_pointer < NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS));
// AXI tlast generation
// axis_tlast is asserted number of output streaming data is NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1
// (0 to NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1)
assign axis_tlast = (read_pointer == NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1);
// Delay the axis_tvalid and axis_tlast signal by one clock cycle
// to match the latency of M_AXIS_TDATA
always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK)
begin
if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN)
begin
axis_tvalid_delay <= 1'b0;
axis_tlast_delay <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
axis_tvalid_delay <= axis_tvalid;
axis_tlast_delay <= axis_tlast;
end
end
//read_pointer pointer
always@(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin
if(!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin
read_pointer <= 0;
tx_done <= 1'b0;
end else case (mst_exec_state)
SEND_STREAM :begin
if (read_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1) begin
tx_done <= 1'b0;
if (tx_en)
// read pointer is incremented after every read from the FIFO
// when FIFO read signal is enabled.
begin
read_pointer <= read_pointer + 1;
end
end else begin
// tx_done is asserted when NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS numbers of streaming data
// has been out.
tx_done <= 1'b1;
end
end
default: begin
read_pointer <= 0;
tx_done <= 1'b0;
end
endcase
end
assign tx_en = M_AXIS_TREADY && axis_tvalid;
assign rd_clk = M_AXIS_ACLK;
assign rd_en = tx_en;
assign stream_data_out = data;
//FIFO read enable generation
// Add user logic here
endmodule




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号