foundationpose 自定义数据集制作以及成功运行demo
Foundationpose 数据集制作以及在WSL2上面成功运行自己的数据集
1. 环境准备
可以参考这一篇进行环境配置WSL2搭建foundationpose
如果是使用docker 可以查看这个github上的Run with WSL2
2. Foundationpose 数据集分析
具体的一些可以看这一篇Foundationpose数据集制作
这里做一些细节的补充。
分析官方的数据集文件,如下图:
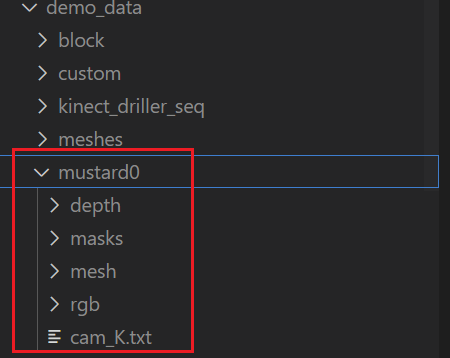
数据集主要分为5个部分:
-
depth: 深度图文件夹,用于保存相机采集到的深度图。(具体采集代码后面贴出)
-
masks: 彩色相机第一帧mask图片,后续的检测是根据这个文件的mask图片进行位姿估计。
注意:这个的文件名要与depth以及rgb的第一张图片文件名保持一致不然运行会报错
官方的如下:
![image]()
-
mesh: 这个是保存模型以及模型纹理的文件夹。
包括:
textured_simple.obj :物体的模型文件
textured_simple.obj.mtl :物体的模型文件与纹理文件之间的调用桥梁
texture_map.png :物体的纹理文件 保存了物体的皮肤特征
三个文件 -
rgb: 彩色图片文件夹,用于保存相机读取的彩色图片数据集
-
cam_K.txt: 保存了相机的内参矩阵(注意保存的是彩色视频流的相机内参)
3. 制作自己的数据集
3.1 采集rgb以及depth图片
这里使用的是Intel RealSense D435进行采集的,具体代码如下:
import pyrealsense2 as rs
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import json
from datetime import datetime
def setup_realsense():
"""配置并启动RealSense摄像头"""
print("RealSense")
# 创建管道
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
# 启用彩色和深度流
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)
# 启动管道
profile = pipeline.start(config)
# 获取深度传感器和深度比例
depth_sensor = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor()
depth_scale = depth_sensor.get_depth_scale()
print(f"深度比例系数: {depth_scale}")
# 创建对齐对象(深度对齐到彩色)
align_to = rs.stream.color
align = rs.align(align_to)
return pipeline, align, depth_scale
def capture_rgbd_data(output_dir, num_frames=1000, capture_interval=0.5):
"""
采集RGB-D数据
参数:
output_dir: 输出目录
num_frames: 要采集的帧数
capture_interval: 采集间隔(秒)
"""
# 创建输出目录
rgb_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "rgb")
depth_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "depth")
os.makedirs(rgb_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(depth_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 设置摄像头
pipeline, align, depth_scale = setup_realsense()
# 获取相机内参
frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames()
aligned_frames = align.process(frames)
color_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame()
intr = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics
camera_params = {
"width": intr.width,
"height": intr.height,
"fx": intr.fx,
"fy": intr.fy,
"ppx": intr.ppx,
"ppy": intr.ppy,
"depth_scale": depth_scale
}
# 保存相机参数
with open(os.path.join(output_dir, "camera_params.json"), "w") as f:
json.dump(camera_params, f, indent=4)
print(f"开始采集 {num_frames} 帧数据,间隔 {capture_interval}秒...")
try:
frame_count = 0
while frame_count < num_frames:
# 等待帧
frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames()
# 对齐深度帧到彩色帧
aligned_frames = align.process(frames)
# 获取对齐后的帧
depth_frame = aligned_frames.get_depth_frame()
color_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame()
if not depth_frame or not color_frame:
continue
# 转换为numpy数组
depth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())
color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())
# cv2.imwrite("test.png", depth_image)
# 生成时间戳
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S_%f")
# 保存图像
rgb_filename = os.path.join(rgb_dir, f"frame_{timestamp}.png")
depth_filename = os.path.join(depth_dir, f"frame_{timestamp}.png")
cv2.imwrite(rgb_filename, color_image)
cv2.imwrite(depth_filename, depth_image)
print(f"已采集帧 {frame_count + 1}/{num_frames}")
frame_count += 1
# 显示预览
depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(
cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
# 水平堆叠图像
images = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))
# 显示图像
cv2.namedWindow('RealSense Capture', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.imshow('RealSense Captrue', images)
# 等待间隔或按键
key = cv2.waitKey(int(capture_interval * 1000))
if key == ord('q'):
break
finally:
# 停止管道
pipeline.stop()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("采集完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 配置输出目录
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
output_directory = f"realsense_capture_{timestamp}"
# 开始采集
capture_rgbd_data(output_directory, num_frames=2000, capture_interval=0.001)
3.2 获取摄像头内参矩阵
前面的代码已经将摄像头内参保存好,采集完成后会自动保存为以下文件:

# 获取相机内参
frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames()
aligned_frames = align.process(frames)
color_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame()
intr = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics
camera_params = {
"width": intr.width,
"height": intr.height,
"fx": intr.fx,
"fy": intr.fy,
"ppx": intr.ppx,
"ppy": intr.ppy,
"depth_scale": depth_scale
}
接下来是将获取的内参矩阵进行转换为和官方文件要求的
import json
import sys
def main():
json_file = "camera_params.json"
try:
# 读取 JSON 文件
with open(json_file, 'r') as f:
camera_params = json.load(f)
# 提取内参
fx = camera_params["fx"]
fy = camera_params["fy"]
ppx = camera_params["ppx"]
ppy = camera_params["ppy"]
# 构造3x3内参矩阵
matrix = [
[fx, 0.0, ppx],
[0.0, fy, ppy],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
]
# 生成格式化的矩阵文本
matrix_text = ""
for row in matrix:
formatted_row = " ".join([f"{val:.18e}" for val in row])
matrix_text += formatted_row + "\n"
# 保存到 cam_K.txt 文件
with open("cam_K.txt", 'w') as f:
f.write(matrix_text)
print(f"内参矩阵已成功保存到 cam_K.txt 文件")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误: 文件 '{json_file}' 不存在")
sys.exit(1)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"错误: 文件 '{json_file}' 不是有效的 JSON 格式")
sys.exit(1)
except KeyError as e:
print(f"错误: JSON 文件中缺少必要的参数: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生未知错误: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.3 制作mask第一帧图片
这里我使用了Grounded-segment-anything进行了分割,具体配置看Grounded-segment-anything官方配置 以及CSDN Grounded-segment-anything配置
将Grounded-segment-anything环境搭建好后,先下载sam_hq_vit_b.pth (可能需要使用魔法)
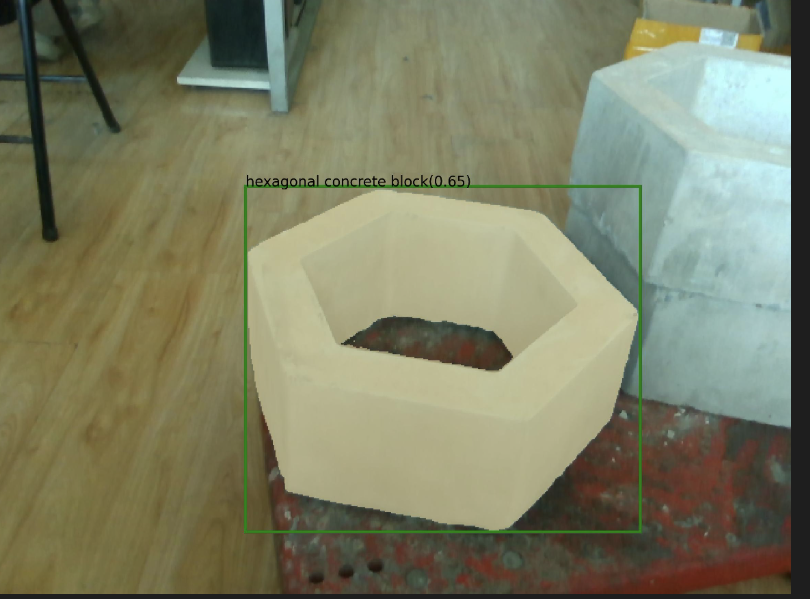
然后运行下面这个代码可以得到mask.jpg(text_prompt = "left hexagonal concrete block" # largest "left hexagonal concrete block"要修改成自己对应的目标即可)
我这里描述的是下面这张图

import argparse
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "GroundingDINO"))
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "segment_anything"))
# Grounding DINO
import GroundingDINO.groundingdino.datasets.transforms as T
from GroundingDINO.groundingdino.models import build_model
from GroundingDINO.groundingdino.util.slconfig import SLConfig
from GroundingDINO.groundingdino.util.utils import clean_state_dict, get_phrases_from_posmap
# segment anything
from segment_anything import (
sam_model_registry,
sam_hq_model_registry,
SamPredictor
)
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载图片
def load_image(image_path):
# load image
image_pil = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB") # load image
transform = T.Compose(
[
T.RandomResize([800], max_size=1333),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
]
)
image, _ = transform(image_pil, None) # 3, h, w
return image_pil, image
# 加载模型
def load_model(model_config_path, model_checkpoint_path, bert_base_uncased_path, device):
args = SLConfig.fromfile(model_config_path)
args.device = device
args.bert_base_uncased_path = bert_base_uncased_path
model = build_model(args)
checkpoint = torch.load(model_checkpoint_path, map_location="cpu")
load_res = model.load_state_dict(clean_state_dict(checkpoint["model"]), strict=False)
print(load_res)
_ = model.eval()
return model
# 得到Grounding_DINO模型的检测框输出
def get_grounding_output(model, image, caption, box_threshold, text_threshold, with_logits=True, device="cpu"):
caption = caption.lower()
caption = caption.strip()
if not caption.endswith("."):
caption = caption + "."
model = model.to(device)
image = image.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(image[None], captions=[caption])
logits = outputs["pred_logits"].cpu().sigmoid()[0] # (nq, 256)
boxes = outputs["pred_boxes"].cpu()[0] # (nq, 4)
logits.shape[0]
# filter output
logits_filt = logits.clone()
boxes_filt = boxes.clone()
filt_mask = logits_filt.max(dim=1)[0] > box_threshold
logits_filt = logits_filt[filt_mask] # num_filt, 256
boxes_filt = boxes_filt[filt_mask] # num_filt, 4
logits_filt.shape[0]
# get phrase
tokenlizer = model.tokenizer
tokenized = tokenlizer(caption)
# build pred
pred_phrases = []
for logit, box in zip(logits_filt, boxes_filt):
pred_phrase = get_phrases_from_posmap(logit > text_threshold, tokenized, tokenlizer)
if with_logits:
pred_phrases.append(pred_phrase + f"({str(logit.max().item())[:4]})")
else:
pred_phrases.append(pred_phrase)
return boxes_filt, pred_phrases
# 展示mask
def show_mask(mask, ax, random_color=False):
if random_color:
color = np.concatenate([np.random.random(3), np.array([0.6])], axis=0)
else:
color = np.array([30/255, 144/255, 255/255, 0.6])
h, w = mask.shape[-2:]
mask_image = mask.reshape(h, w, 1) * color.reshape(1, 1, -1)
ax.imshow(mask_image)
# 展示检索框
def show_box(box, ax, label):
x0, y0 = box[0], box[1]
w, h = box[2] - box[0], box[3] - box[1]
ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((x0, y0), w, h, edgecolor='green', facecolor=(0,0,0,0), lw=2))
ax.text(x0, y0, label)
# 保存mask数据
def save_mask_data(output_dir, mask_list, box_list, label_list):
value = 0 # 0 for background
mask_img = torch.zeros(mask_list.shape[-2:])
for idx, mask in enumerate(mask_list):
mask_img[mask.cpu().numpy()[0] == True] = value + idx + 1
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(mask_img.numpy())
plt.axis('off')
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output_dir, 'mask.jpg'), bbox_inches="tight", dpi=300, pad_inches=0.0)
json_data = [{
'value': value,
'label': 'background'
}]
for label, box in zip(label_list, box_list):
value += 1
name, logit = label.split('(')
logit = logit[:-1] # the last is ')'
json_data.append({
'value': value,
'label': name,
'logit': float(logit),
'box': box.numpy().tolist(),
})
with open(os.path.join(output_dir, 'mask.json'), 'w') as f:
json.dump(json_data, f)
def main():
# 直接初始化参数,不使用 argparse 解析命令行
config_file = "GroundingDINO/groundingdino/config/GroundingDINO_SwinT_OGC.py"
grounded_checkpoint = "groundingdino_swint_ogc.pth"
sam_version = "vit_b"
sam_checkpoint = None
sam_hq_checkpoint = "sam_hq_vit_b.pth" # 填入sam-hq相应路径
use_sam_hq = True # 是否使用 sam-hq
image_path = "test.png"
text_prompt = "left hexagonal concrete block" # largest "left hexagonal concrete block"
output_dir = "outputs"
box_threshold = 0.3
text_threshold = 0.25
device = "cuda"
bert_base_uncased_path = None # 如果有 BERT 相关路径,填入相应路径
# 创建输出目录
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 加载图像
image_pil, image = load_image(image_path)
image_pil.save(os.path.join(output_dir, "raw_image.jpg"))
# 加载 Grounding DINO 模型
model = load_model(config_file, grounded_checkpoint, bert_base_uncased_path, device=device)
# 运行 Grounding DINO 进行目标检测 先看能否运行到这步 如果不能再启用修改浮点数
# 可以考虑预先保存分割框的位置
image = image.half()
model = model.half()
boxes_filt, pred_phrases = get_grounding_output(model, image, text_prompt, box_threshold, text_threshold,
device=device)
# 初始化 SAM-HQ 预测器
print(f"Using SAM-HQ model: {sam_hq_checkpoint}")
predictor = SamPredictor(sam_hq_model_registry[sam_version](checkpoint=sam_hq_checkpoint).to(device))
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
predictor.set_image(image)
# 变换 box 坐标
size = image_pil.size
H, W = size[1], size[0]
for i in range(boxes_filt.size(0)):
boxes_filt[i] = boxes_filt[i] * torch.Tensor([W, H, W, H])
boxes_filt[i][:2] -= boxes_filt[i][2:] / 2
boxes_filt[i][2:] += boxes_filt[i][:2]
boxes_filt = boxes_filt.cpu()
transformed_boxes = predictor.transform.apply_boxes_torch(boxes_filt, image.shape[:2]).to(device)
# 进行分割
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict_torch(
point_coords=None,
point_labels=None,
boxes=transformed_boxes.to(device),
multimask_output=False,
)
# **调整 mask 大小**
target_size = (480, 640) # 目标 mask 分辨率
masks_resized = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(masks.float(), size=target_size, mode="nearest")
# 绘制分割结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image)
for mask in masks_resized:
show_mask(mask.cpu().numpy(), plt.gca(), random_color=True)
for box, label in zip(boxes_filt, pred_phrases):
show_box(box.numpy(), plt.gca(), label)
plt.axis('off')
plt.savefig(
os.path.join(output_dir, "grounded_sam_output_hexagona_brick.jpg"),
bbox_inches="tight", dpi=300, pad_inches=0.0
)
print("成功保存分割后的数据 Saved grounded sam output")
# 保存分割数据
save_mask_data(output_dir, masks_resized, boxes_filt, pred_phrases)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
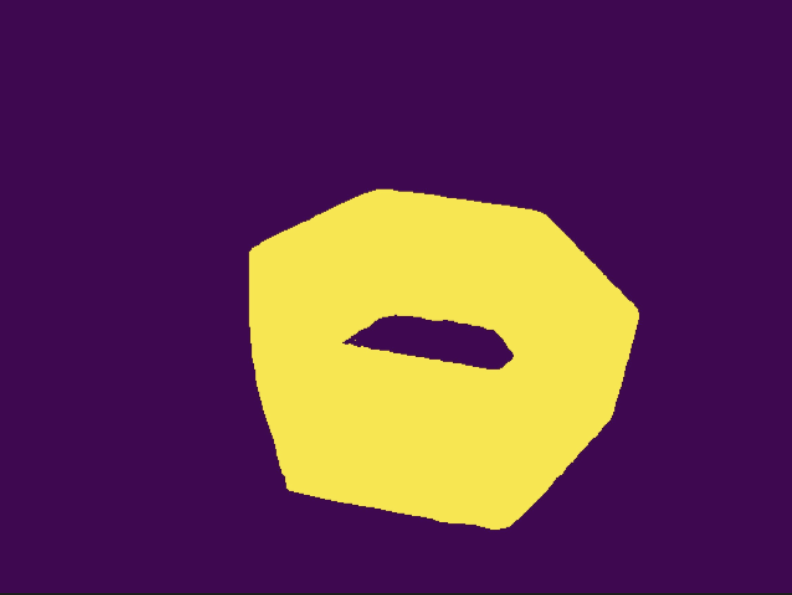
再运行一下下面的代码将得到的最后分割好的图片:
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def resize_and_convert_to_png(input_path, output_path, width=640, height=480):
# 读取图片
image = cv2.imread(input_path)
# 检查图片是否正确读取
if image is None:
print(f"Error: 无法读取图片 {input_path}")
return
# 调整大小
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (width, height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# 确保输出路径是 PNG 格式
output_path = os.path.splitext(output_path)[0] + ".png"
# 保存图片为 PNG 格式
cv2.imwrite(output_path, resized_image)
print(f"已保存调整后的 PNG 图片: {output_path}")
# 示例用法
input_image_path = "outputs/mask.jpg" # 输入图片路径
output_image_path = "outputs/mask_out.png" # 输出文件路径(会自动转换为 PNG)
resize_and_convert_to_png(input_image_path, output_image_path)
# 读取图片
image_path = "outputs/mask_out.png"
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 转换为HSV颜色空间,以便提取黄色区域
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# 定义黄色的HSV范围
lower_yellow = np.array([20, 100, 100])
upper_yellow = np.array([30, 255, 255])
# 创建掩码,提取黄色区域
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_yellow, upper_yellow)
# 创建黑白图像:黄色区域变白色,其余变黑色
result = np.zeros_like(image) # 先创建黑色背景
result[mask > 0] = [255, 255, 255] # 将黄色区域变为白色
# 转换为灰度图
result_gray = cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 保存处理后的图片
output_path = "outputs/1742097201894254684.png"
cv2.imwrite(output_path, result_gray)
# 显示处理后的图片
plt.imshow(result_gray, cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
得到mask的图片如下:
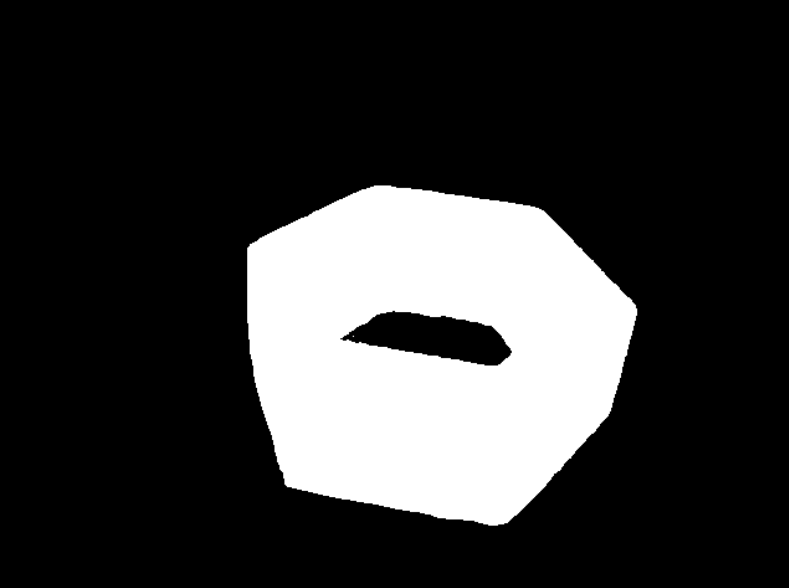
3.4 mesh文件的制作
- 通过官方的BundleSDF进行模型重建。
- 可以使用AR软件对物体进行模型重建,我使用的是Apple Store 里的AR Code进行的,不过这个需要注意这个只支持iPhone 12 以上并且需要是PRO版本的(有深度相机) 或者是iPad PRO M1以上的才行。
- 使用stable-fast-3d (需要魔法)
可以从下面的链接看相应的一些信息:
Stable Fast 3D(SF3D):单张图片快速生成高质量3D模型
模型重建完可以参照前面的Foundation_pose在自己的物体上复现指南 ,再把相应的文件放到mesh文件夹下即可
4. 运行
4.1 运行自己的demo
数据集制作完成后即可运行
代码如下:
# Copyright (c) 2023, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
#
# NVIDIA CORPORATION and its licensors retain all intellectual property
# and proprietary rights in and to this software, related documentation
# and any modifications thereto. Any use, reproduction, disclosure or
# distribution of this software and related documentation without an express
# license agreement from NVIDIA CORPORATION is strictly prohibited.
from estimater import *
from datareader import *
import argparse
if __name__=='__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
code_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
parser.add_argument('--mesh_file', type=str, default=f'{code_dir}/demo_data/realsense_capture_20250620_155827/mesh/hexagona_brick.obj')
parser.add_argument('--test_scene_dir', type=str, default=f'{code_dir}/demo_data/realsense_capture_20250620_155827')
parser.add_argument('--est_refine_iter', type=int, default=5)
parser.add_argument('--track_refine_iter', type=int, default=2)
parser.add_argument('--debug', type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument('--debug_dir', type=str, default=f'{code_dir}/debug')
args = parser.parse_args()
set_logging_format()
set_seed(0)
mesh = trimesh.load(args.mesh_file)
debug = args.debug
debug_dir = args.debug_dir
os.system(f'rm -rf {debug_dir}/* && mkdir -p {debug_dir}/track_vis {debug_dir}/ob_in_cam')
to_origin, extents = trimesh.bounds.oriented_bounds(mesh)
bbox = np.stack([-extents/2, extents/2], axis=0).reshape(2,3)
scorer = ScorePredictor()
refiner = PoseRefinePredictor()
glctx = dr.RasterizeCudaContext()
est = FoundationPose(model_pts=mesh.vertices, model_normals=mesh.vertex_normals, mesh=mesh, scorer=scorer, refiner=refiner, debug_dir=debug_dir, debug=debug, glctx=glctx)
logging.info("estimator initialization done")
reader = YcbineoatReader(video_dir=args.test_scene_dir, shorter_side=None, zfar=np.inf)
for i in range(len(reader.color_files)):
logging.info(f'i:{i}')
color = reader.get_color(i)
depth = reader.get_depth(i)
if i==0:
mask = reader.get_mask(0).astype(bool)
pose = est.register(K=reader.K, rgb=color, depth=depth, ob_mask=mask, iteration=args.est_refine_iter)
if debug>=3:
m = mesh.copy()
m.apply_transform(pose)
m.export(f'{debug_dir}/model_tf.obj')
xyz_map = depth2xyzmap(depth, reader.K)
valid = depth>=0.001
pcd = toOpen3dCloud(xyz_map[valid], color[valid])
o3d.io.write_point_cloud(f'{debug_dir}/scene_complete.ply', pcd)
else:
pose = est.track_one(rgb=color, depth=depth, K=reader.K, iteration=args.track_refine_iter)
os.makedirs(f'{debug_dir}/ob_in_cam', exist_ok=True)
np.savetxt(f'{debug_dir}/ob_in_cam/{reader.id_strs[i]}.txt', pose.reshape(4,4))
if debug>=1:
center_pose = pose@np.linalg.inv(to_origin)
vis = draw_posed_3d_box(reader.K, img=color, ob_in_cam=center_pose, bbox=bbox)
vis = draw_xyz_axis(color, ob_in_cam=center_pose, scale=0.1, K=reader.K, thickness=3, transparency=0, is_input_rgb=True)
cv2.imshow('1', vis[...,::-1])
cv2.waitKey(1)
if debug>=2:
os.makedirs(f'{debug_dir}/track_vis', exist_ok=True)
imageio.imwrite(f'{debug_dir}/track_vis/{reader.id_strs[i]}.png', vis)
输入以下命令
python run_my_demo.py --debug 2
4.2 运行结果
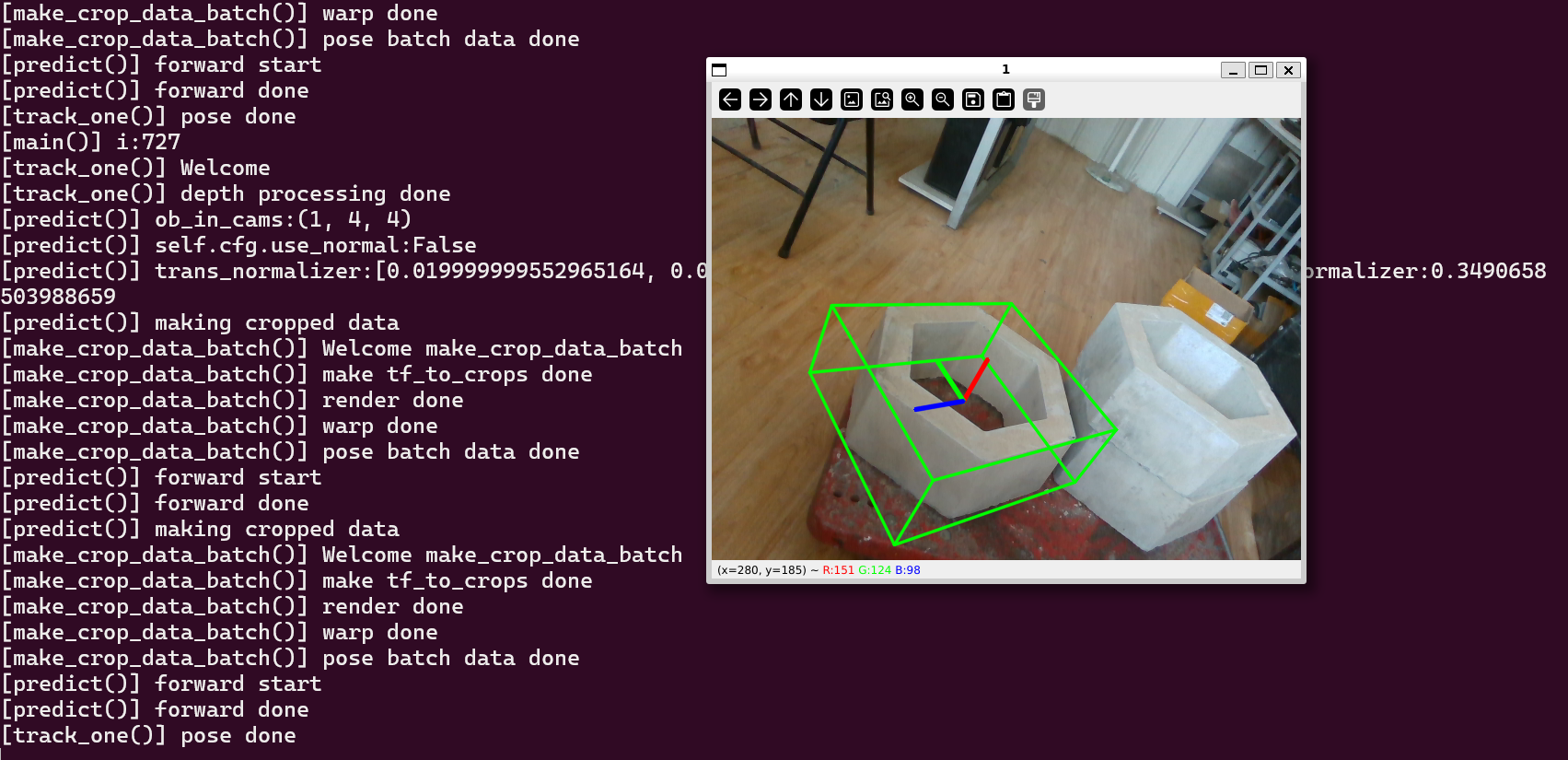
5. 下一步计划
制作LineMod训练集以及将该项目部署到jetson上面,控制然后进行目标抓取。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号