实验四
同名覆盖原则:由于基类和派生类的函数名一样,系统无法按原则(原则:先基类,然后对象,最后派生类)调用,就覆盖了。
二元作用域分辨符:可以通过派生类名和作用域分辨符来访问派生类中的同名成员。
类型兼容原则:类型兼容原则是指在需要基类对象的任何地方,都可以使用公有派生类的对象来替代。
通过公有继承,派生类得到了基类中除构造函数、析构函数之外的所有成员。这样,公有派生类实际具备了基类的所有功能,凡是基类能解决的问题,
公有派生类都可以解决。类型兼容原则中所指的替代包含以下情况。
(1)派生类的对象可以隐含转换为基类对象。
(2)派生类的对象可以初始化基类的对象。
(3)派生类的指针可以隐含转换为基类的指针。
在替代后,派生类对象就可以作为基类的对象使用,但只能使用从基类继承的成员。
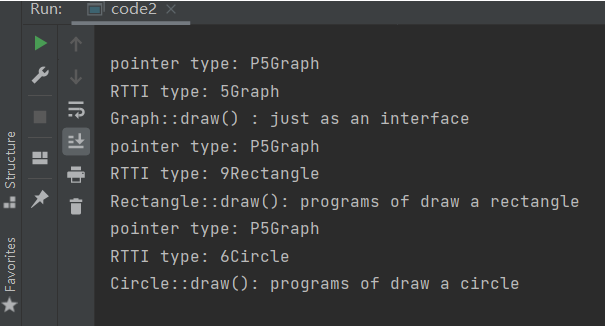
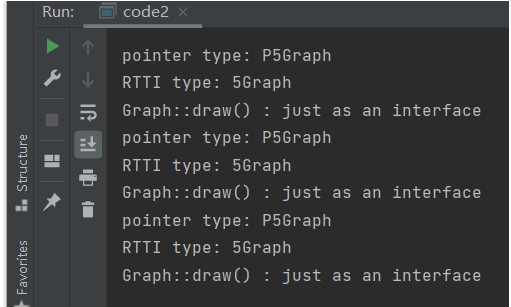
virtual:定义一个函数为虚函数,不代表函数为不被实现的函数。定义他为虚函数是为了允许用基类的指针来调用子类的这个函数。
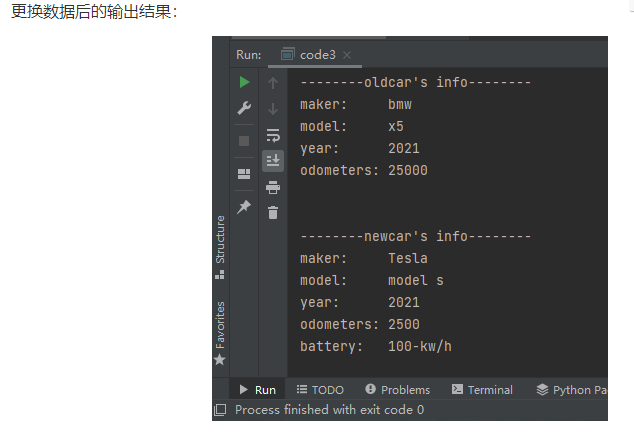
//Car.h #ifndef CODE2_CAR_H #define CODE2_CAR_H #include "string" #include "iostream" using namespace std; class Car { public: Car(string ma, string mo, int y) { maker = std::move(ma); model = std::move(mo); year = y; odometers = 0; } ~Car() = default; void update_odometers(double o) { odometers = o; } void info() { cout << "maker: " << maker << endl; cout << "model: " << model << endl; cout << "year: " << year << endl; cout << "odometers: " << odometers << endl; } string get_maker() { return maker; } string get_model() { return model; } int get_year() const { return year; } double get_odometers() const { return odometers; } private: string maker; string model; int year; double odometers; }; #endif //CODE2_CAR_H
//Battery.h #ifndef CODE2_BATTERY_H #define CODE2_BATTERY_H class Battery { public: Battery(int c = 70) { capacity = c; } ~Battery() = default; double get_capacity() { return capacity; } void change_capacity(double b) { capacity = b; } private: double capacity; }; #endif //CODE2_BATTERY_H
#ifndef CODE2_ELECTRICCAR_H #define CODE2_ELECTRICCAR_H #include "string" #include "iostream" #include "Car.h" #include "Battery.h" using namespace std; class ElectricCar : public Car { public: ElectricCar(string ma, string mo, int y, double b = 70) : Car(ma, mo, y) { battery.change_capacity(b); } ~ElectricCar() = default; void info() { cout << "maker: " << get_maker() << endl; cout << "model: " << get_model() << endl; cout << "year: " << get_year() << endl; cout << "odometers: " << get_odometers() << endl; cout << "battery: " << battery.get_capacity() << "-kw/h" << endl; } private: Battery battery; }; #endif //CODE2_ELECTRICCAR_H
//task3.cpp #include <iostream> #include "ElectricCar.h" int main() { using namespace std; // test class of Car Car oldcar("Audi", "a4", 2016); cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl; oldcar.update_odometers(25000); oldcar.info(); cout << endl; // test class of ElectricCar ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016); newcar.update_odometers(2500); cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n"; newcar.info(); }
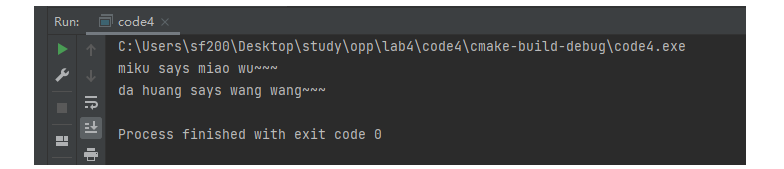
//pets.h #ifndef CODE4_PETS_H #define CODE4_PETS_H #include "iostream" #include "string" using namespace std; class MachinePets { private: string nickname; public: MachinePets(const string s) { nickname = s; } ~MachinePets() = default; string get_nickname() { return nickname; } virtual string talk() {} }; class PetCats : public MachinePets { public: PetCats(const string s) : MachinePets(s) {} string talk() { return "miao wu~~~"; } }; class PetDogs : public MachinePets { public: PetDogs(const string s) : MachinePets(s) {} string talk() { return "wang wang~~~"; } }; #endif //CODE4_PETS_H
//task4.cpp #include <iostream> #include "pets.h" void play(MachinePets *ptr) { std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << std::endl; } int main() { PetCats cat("miku"); PetDogs dog("da huang"); play(&cat); play(&dog); }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号