双指针算法
双指针算法
大致格式如下:
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
while(j < i && check(i, j)) j++;
//每道题目的具体逻辑
}
核心思想:
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
//O(n^2)的复杂度
}
}
将上述朴素算法优化到O(n);
例题(一):
输入一个字符串,把其中的每一个单词输出出来。
输入:abc def ghi
输出:
abc
def
ghi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char str[1000];
gets(str);
int len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int j = i;
while(j < len && str[j] != ' ') j++;
//这道题的具体逻辑
for(int k = i; k < j; k++){
cout << str[k];
}
cout << endl;
i = j;
}
return 0;
}
例题(二)
核心思路:*
- 遍历
数组a中的每一个元素a[i], 对于每一个i,找到j使得双指针[j, i]维护的是以a[i]结尾的最长连续不重复子序列,长度为i - j + 1, 将这一长度与ans的较大者更新给ans。 - 对于每一个i,如何确定j的位置:由于
[j, i - 1]是前一步得到的最长连续不重复子序列,所以如果[j, i]中有重复元素,一定是a[i],因此右移j直到a[i]不重复为止(由于[j, i - 1]已经是前一步的最优解,此时j只可能右移以剔除重复元素a[i],不可能左移增加元素,因此,j具有“单调性”、本题可用双指针降低复杂度)。 - 用
数组cnt[]记录子序列a[j ~ i]中各元素出现次数,遍历过程中对于每一个i有四步操作:cin元素a[i]->将a[i]出现次数cnt[a[i]]加1->若a[i]重复则右移j(cnt[a[j]]要减1)->确定j及更新当前长度i - j + 1给ans。
代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], cnt[N]; //cnt[]频率标记数组
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++){
cnt[a[i]] ++;
while(cnt[a[i]] > 1){ //只要a[i]的次数大于1
cnt[a[j]] --; //先减次数
j++; //再右移
}
ans = max(ans, i - j + 1 ); //更新答案
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
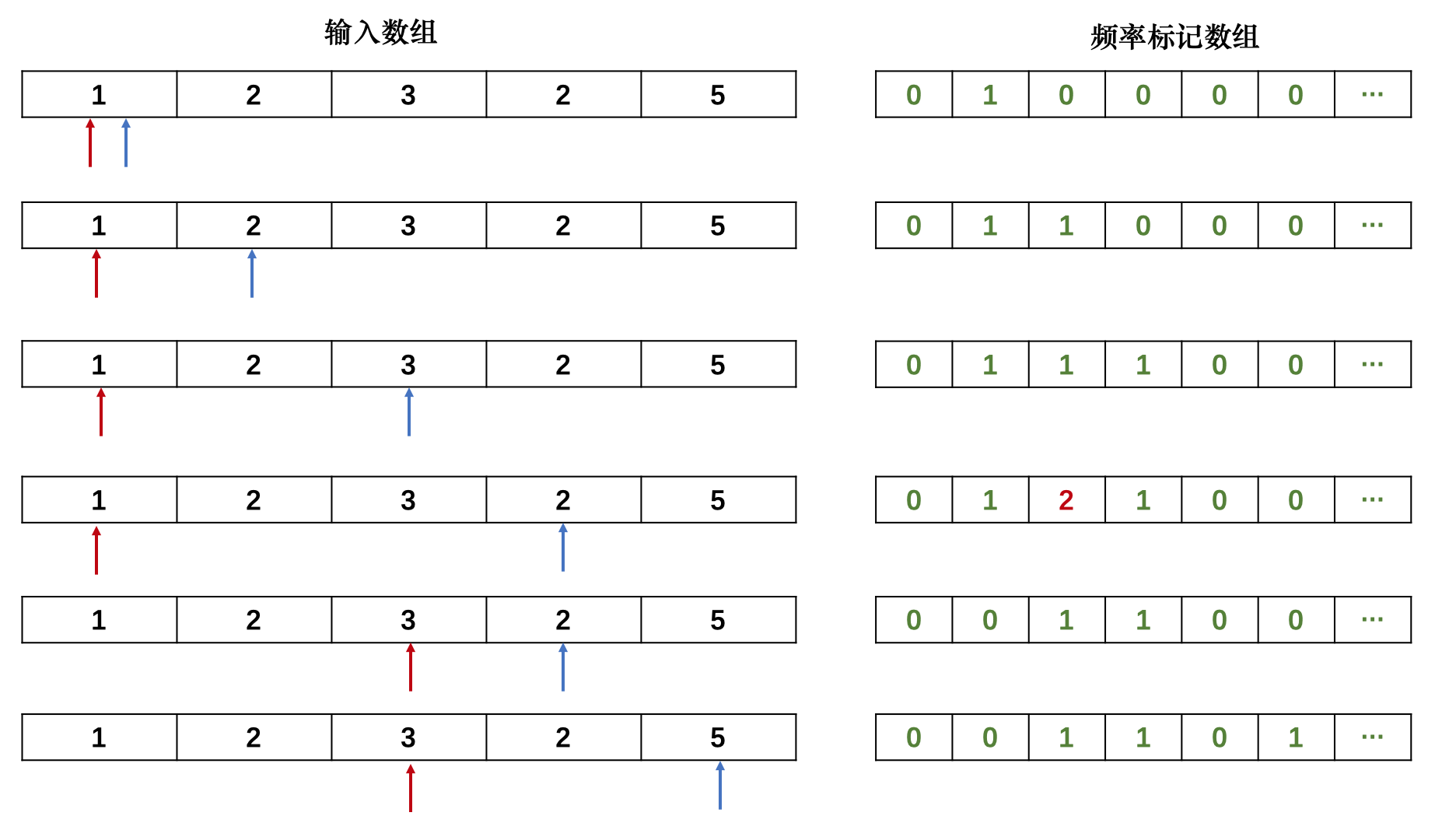
图解如下:
蓝指针为i,红指针为j;
例题(三)
数组元素的目标和
题目关键:
数组是按升序排列的
(双指针) O(n)
i从 0开始 从前往后遍历
j从 m - 1开始 从后向前遍历
和纯暴力的O(n^2) 算法的区别就在于:j指针不会回退
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
long long a[N], b[N];
int main(){
int n, m, x;
cin >> n >> m >> x;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 0, j = m - 1; i < n; i++){
while(j >= 0 && a[i] + b[j] > x) j--;
if(j >= 0 && a[i] + b[j] == x) cout << i << ' ' << j << endl;
}
return 0;
}
div.3 C. Traffic Light(双指针)
思路:
我们需要维护的序列是:每一个颜色\(c\)到离它最近的绿灯的距离。找到这类序列的最大距离。同时,注意红绿灯的状态是周期性的。
如何处理周期性?
我们要维护的序列一定可以在两个周期内找到\(ans\),所以可以把字符串复制一次,这样就很好地处理了红绿灯周期性的问题。
为了避免数组越界的问题,可以倒着找,从后往前找,找到绿灯就记录一下位置,如果遇到颜色\(c\),就更新答案\(ans=max(ans, last - i)\),\(last\)是绿灯出现在颜色\(c\)之前最近的一次,\(i\)是当前时间。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define bug(x) cout<<#x<<"=="<<x<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int inf = 0xc0c0c0c0;
void solve() {
int n;
char c;
cin >> n >> c;
string s;
cin >> s;
s = s + s;
int last = 0;
int ans = inf;
for (int i = s.size(); i >= 0; i--) {
if (s[i] == 'g') {
last = i;
}
if (s[i] == c) {
int len = last - i;
ans = max(ans, len);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
总结:
常见问题分类:
(1) 对于一个序列,用两个指针维护一段区间
(2) 对于两个序列,维护某种次序,比如归并排序中合并两个有序序列的操作



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号