ANNOVA test (one-way test and two-way test and bootstrapping)
对于ANNOVA的理解
什么情况下可以使用annova:
- More than 2 populations
对于多种不同药物对于某种疾病的效果的研究;比较不同国家指标的研究 - More than 1 predictive variable (factor)
锻炼和饮食对于健康的影响; effect of genetic background and drugs on stress levels - 如果是多way test
2-way test: 2 factors, 比如effect of age and sex on salary
One-way annova
Null hypothesis: means of different <> groups are the same (老师标准写法)
或者说
Null hypothesis: There is no effects of class attendance or previous grades on course performance
Alternative hypothesis: means of different <> groups are not the same
核心思想:组内差异对比组间差异,如果这两者差异大就说明组内之间确实有差异;否则可以认为没有什么组间差异
统计前假设条件:
- Independent random sampling
We believe that this is true given the description of the experiment itself - normality of residuals (distance from group mean)
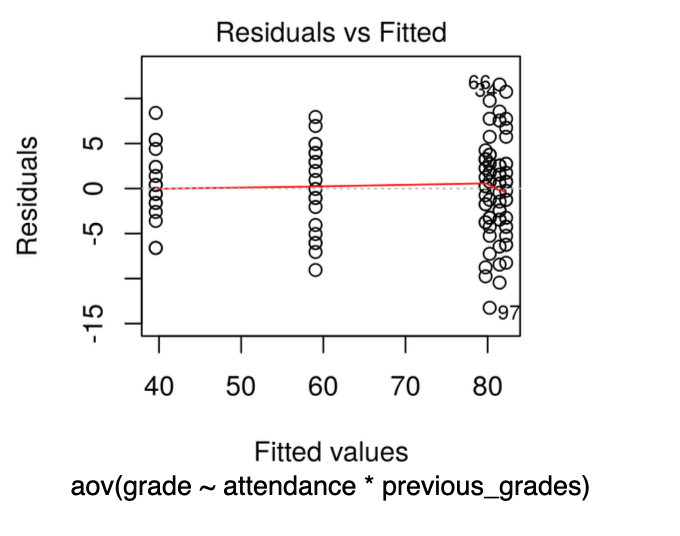
model <- aov(grade ~ attendance * previous_grades) # 这个地方,老师似乎认为没有理由能不使用interaction
hist((resid(model), main = "residuals")# 选一个,方法一
shapiro.test(resid(model)) #方法二
- Equality of variances
通过作图,“residuals vs fitted” plot进行查看
plot(model,1)
好的情况:
接下来查看统计量
summary(model)
实例结果:
Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
Treatment 2 4.46 2.228 1.064 0.353
Measurement 1 2.05 2.049 0.979 0.328
Residuals 47 98.39 2.093
进行完ANNOVA 测试后,如果还想要知道具体是哪一组不同于另外几组,可以采用post-hoc tests。比如Tukey's HSD test
TukeyHSD(model)
如果想要探索,也可以思考两个factor之间是否有interaction, hypotheses变化:
• H0: There is no interaction between class attendance and previous grades
• HA: There is an interaction between class attendance and previous grades




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号