Tensorflow2 高级操作
合并与分割
tf.concat([a,b],axis=)
a = tf.ones([3,5,5])
b = tf.ones([3,5,5])
c = tf.concat([a,b],axis=0)
print(c.shape)
(6, 5, 5)
不改变纬度 在某一维度上拼接 两张纸变成一张
tf.stack([a,b],axis=)
改变纬度 两张纸叠加在一起
d = tf.stack([a,b],axis=0)
print(d.shape)
(2, 3, 5, 5)
tf.unstack(a,axis=)
减少纬度 将两张纸拿开 stack的逆过程
a,b = tf.unstack(d,axis=0)
print(a.shape)
print(b.shape)
(3, 5, 5)
(3, 5, 5)
tf.split(d,axis=,num_or_size_splits=[])
切分,concat的逆过程
res = tf.split(d,axis=-1,num_or_size_splits=[2,2,1])
print(res[0].shape)
print(res[1].shape)
print(res[2].shape)
print(type(res))
(2, 3, 5, 2)
(2, 3, 5, 2)
(2, 3, 5, 1)
<class 'list'>
数据统计
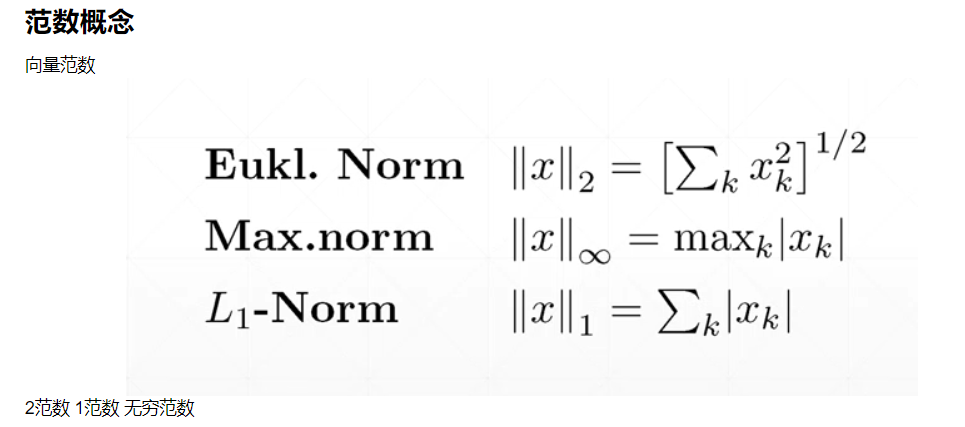
tf.norm(a,ord=,axis=)
在某一维度上计算他们的范数
二范数就是向量的模
a = tf.reshape(tf.range(25),[5,5])
a = tf.cast(a,tf.float32)
print(a)
tf.norm(a,ord=2,axis=1)
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]
[ 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]
[10. 11. 12. 13. 14.]
[15. 16. 17. 18. 19.]
[20. 21. 22. 23. 24.]], shape=(5, 5), dtype=float32)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5,), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([ 5.477226 , 15.9687195, 27.018513 , 38.144463 , 49.29503 ],
dtype=float32)>
tf.reduce_min(a,axis=)
tf.reduce_max(a,axis=)
计算某纬度上的最大值最小值
b = tf.random.normal([3,4])
print(b)
tf.reduce_min(b,axis=0)
[[-0.15871765 -1.0335457 1.6171131 -1.2334267 ]
[-0.24595834 0.37801972 0.17244333 -0.7095063 ]
[ 0.37281558 -0.15079713 -1.5931925 0.48200387]], shape=(3, 4), dtype=float32)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([-0.24595834, -1.0335457 , -1.5931925 , -1.2334267 ], dtype=float32)>
tf.argmin(b,axis=)
tf.argmax(b,axis=)
返还在某纬度上最值得索引 默认按第0个纬度来计算
index_min = tf.argmin(b,axis=1)
index_max = tf.argmax(b,axis=0)
print(index_min)
print(index_max)
tf.Tensor([3 3 2], shape=(3,), dtype=int64)
tf.Tensor([2 1 0 2], shape=(4,), dtype=int64)
tf.equal(a,b)
比较是否相同,返还一个bool类型的tensor
s = tf.constant([0,1,2,3,4])
ss = tf.constant([1,1,3,1,2])
res = tf.equal(s,ss)
print(res)
res_sum = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(res,dtype=tf.int32))
print(res_sum)
tf.Tensor([False True False False False], shape=(5,), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
上述方法可以计算 准确率
# accuracy 计算 预测争取率计算
获得预测值
res = tf.constant([0.04,0.06,0.9,0.01,0.10,0.89],shape=(2,3))
print(res)
# 获得最大值的位置 即结果
pre = tf.cast(tf.argmax(res,axis=1),dtype=tf.int32)
print(pre)
# constant默认是int64
# 这是正确结果
y = tf.constant([1,2])
print(y.numpy())
# 将两个结果进行对比 求和 获得 正确多少个
correct = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(tf.equal(y,pre),dtype=tf.int32))
print(correct.numpy())
# 获得正确率
print(correct / len(y))
tf.Tensor(
[[0.04 0.06 0.9 ]
[0.01 0.1 0.89]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor([2 2], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
[1 2]
1
tf.Tensor(0.5, shape=(), dtype=float64)
tf.unique()
去重操作
返还两个值 一个是 去重后的 不相同数的集合
一个是 原来的集合中各个数在 不相同集合数中的位置
b = tf.constant([1,2,1,2])
b1,b2 = tf.unique(b)
# b1 指的是 合并后的值
print(b1)
# b2 指的是 原值在b1中的位置
print(b2)
tf.Tensor([1 2], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([0 1 0 1], shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
张量排序
tf.sort(a,direction=) 将值进行升降序排列
默认是升序
s = tf.random.shuffle(tf.range(5))
sort_s = tf.sort(s)
sort_ss = tf.sort(s,direction="DESCENDING")
print(sort_s,sort_ss)
tf.Tensor([2 3 4 1 0], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4], shape=(5,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor([4 3 2 1 0], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
tf.argsort(a,direction)
返还排序后 值的 index
sort_index = tf.argsort(s)
print(sort_index)
tf.Tensor([4 3 0 1 2], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
tf.math.top_k(s,n)
返还s的最大值的前n个值的在s中的 索引 和 值
res = tf.math.top_k(s,3)
print(res.indices)
print(res.values)
tf.Tensor([2 1 0], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([4 3 2], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)
填充和复制
tf.pad(a,[...],constant_values=)
填充边框
[]里面有几维 就有多少个[] 分别代表了 两边的填充数
a = tf.range(9)
a = tf.reshape(a,[3,3])
a = tf.pad(a,[[1,1],[0,0]],constant_values=2)
print(a)
# 可以用于图形处理 增加边框
tf.Tensor(
[[2 2 2]
[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]
[2 2 2]], shape=(5, 3), dtype=int32)

tf.tile()
可以用 broadcast_to实现的 就不用tile
a = tf.reshape(tf.range(9),[3,3])
print(a)
# 行纬度 复制一次 列纬度 复制两次
aa = tf.tile(a,[1,2])
print(aa)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 1 2 0 1 2]
[3 4 5 3 4 5]
[6 7 8 6 7 8]], shape=(3, 6), dtype=int32)
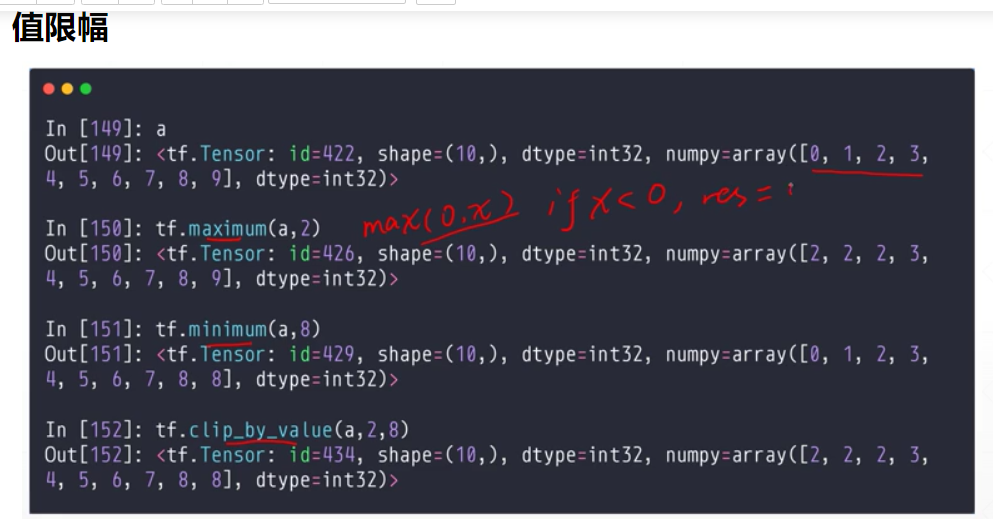
张量限幅
tf.maximum(a,num)
小于num的 变成 num
tf.minimum(a,num)
大于num的 变成num
tf.clip_by_value(a,mim,max)
限制在 min max 间
tf.relu(a) = tf.maximum(a,0)
tf.clip_by_norm(s,num)
num是范数 将s的值 缩放到范数为num
s = tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=10)
ss = tf.norm(s)
sss = tf.clip_by_norm(s,15)
ssss = tf.norm(sss)
print(s)
print(ss)
print(sss)
print(ssss)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 8.890684 9.104048]
[11.712432 9.590533]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(19.775928, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[6.743565 6.9054008]
[8.883855 7.2743993]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(14.999999, shape=(), dtype=float32)
补充操作
tf.where(s)
获得true的索引
tf.gather_nd(s,index)
根据index 获得 s 的值
s = tf.random.normal([3,3])
print(s)
ss = s > 0
print(s)
index_s = tf.where(ss)
print(index_s)
tf.gather_nd(s,index_s)
tf.Tensor(
[[-0.23861103 -1.494727 0.10118695]
[ 0.0751402 -0.68392587 0.09880055]
[-1.2351059 2.4509006 0.95428455]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[False False True]
[ True False True]
[False True True]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)
tf.Tensor(
[[0 2]
[1 0]
[1 2]
[2 1]
[2 2]], shape=(5, 2), dtype=int64)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5,), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([0.10118695, 0.0751402 , 0.09880055, 2.4509006 , 0.95428455],
dtype=float32)>

print(ss)
sss = tf.cast(tf.reshape(tf.range(9),[3,3]),dtype=tf.float32)
# 类型必须一样
tf.where(ss,s,sss)
tf.Tensor(
[[False True True]
[False False True]
[False False True]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=bool)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0. , 0.3419926, 2.702432 ],
[3. , 4. , 1.4972699],
[6. , 7. , 0.55077 ]], dtype=float32)>
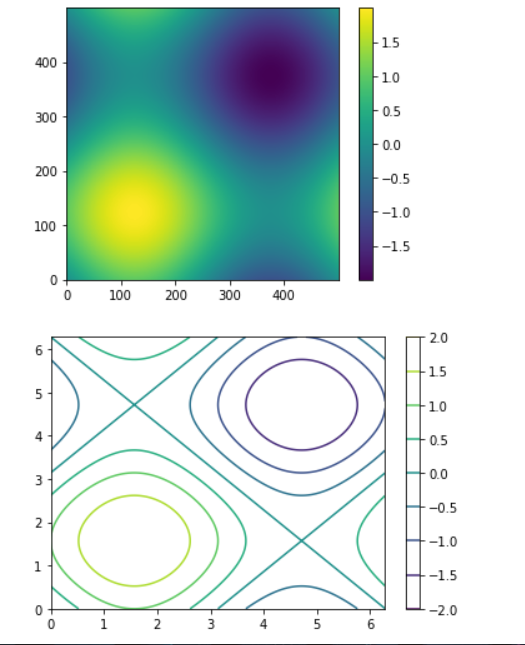
meshgrid 网格生成
tf.meshgrid(x,y)
def func1(x):
z = tf.math.sin(x[...,0])+tf.math.sin(x[...,1])
return z
x = tf.linspace(0.,2*3.14,500)
y = tf.linspace(0.,2*3.14,500)
point_x,point_y = tf.meshgrid(x,y)
# point_x,point_y 都是500*500的矩阵 分别代表了对应位置的 x,y坐标
将两个面合并 成为一个坐标系[500,500,2]
points = tf.stack([point_x,point_y],axis=2)
计算在该位置的函数值
z = func1(points)
print(z.shape)
# 创建一个画布 字符串位名称
plt.figure('plot 2d func value')
# 热图 origin 选择将数组 0,0 放在左上还是左下
# interpolation 插值方法
plt.imshow(z,origin='lower',interpolation='none')
# 添加渐变条
plt.colorbar()
# 创建一个画布
plt.figure('plot 2d func contour')
# 给出坐标 和 值 画出等高线
plt.contour(point_x,point_y,z)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号