YOLOv8-Pose 自定义关键点检测全流程:LabelMe 标注→模型训练→ONNX/RKNN 转换 RK3588 部署
YOLOv8-Pose 模型检测人体17个关键点,想检测其他物体的关键点只能通过训练自己的模型来实现,文章记录训练自定义模型识别指定图形全过程。
一、准备工作
使用 labelme 标注工具可以标注点和一些自定义形状图形。labelme 默认输出的格式是 json 不能直接用来训练 YOLO ,所以数据标注完之后还需写python代码进行一次格式转换。
安装 labelme
pip install labelme
标注数据
如何有多个矩形框需要进行分组,标注时需要填写 groupId 方便后面进行数据格式转换,没有 groupId 数据格式转完犊子了。
除非你是按顺序标注,每四个点标完再画一个矩形框,那么后面可以通过代码按顺序 4+1 item 进行添加 groupId。第一次没经验我就是这么干的 🤣
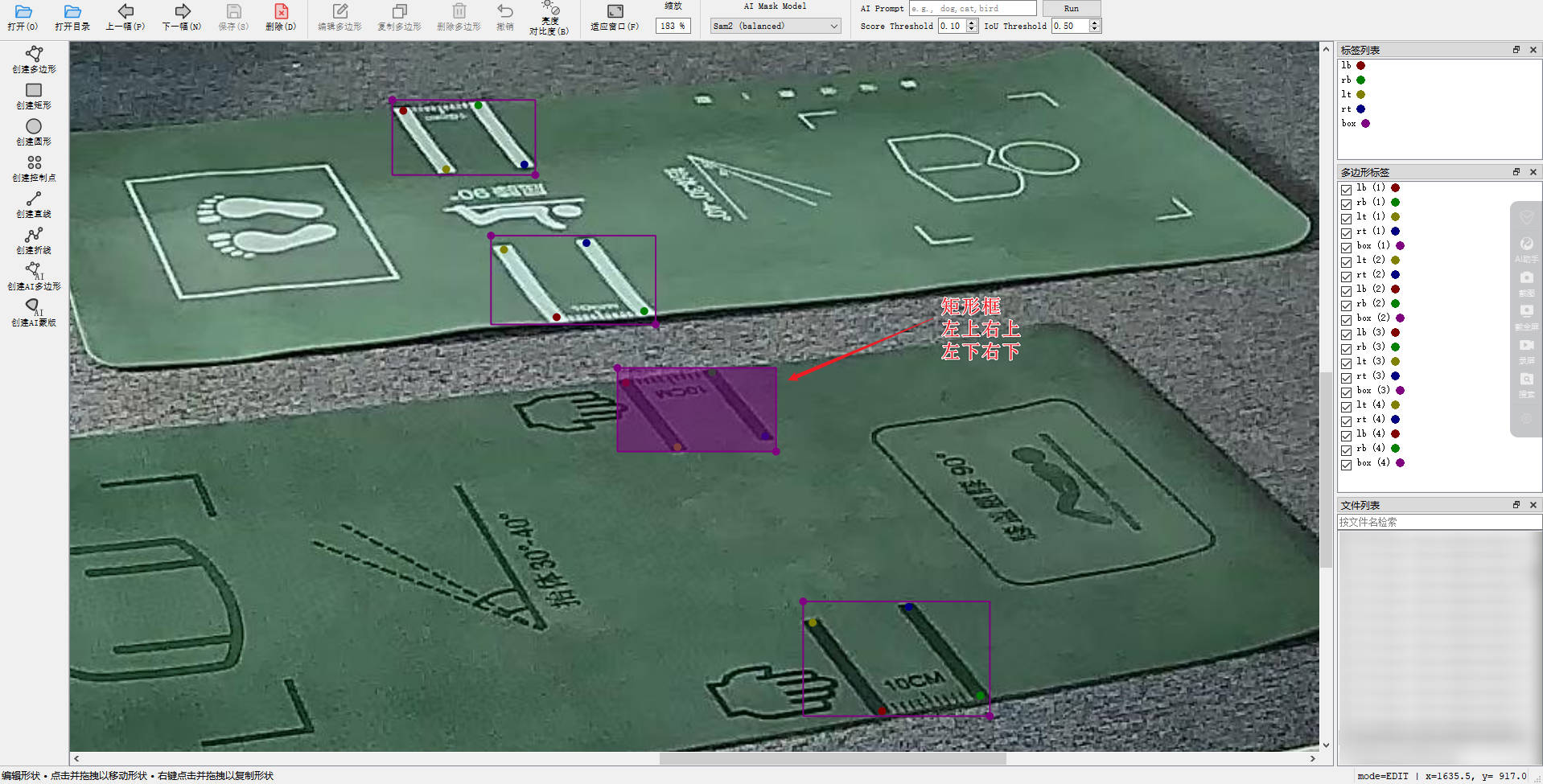
yolov8-pose训练关键点检测必须要有矩形框,再在框里面标注点。
LabelMe 数据格式
shapes 是一个数组包含了你标注的框啊,点啊之类的正常情况是按顺序的。
如果通过代码批量更新或覆盖
JSON文件要包含imageDatabase64图片数据否则labelme打开不对应图片
{
"flags": {},
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAA…………省略",
"imageHeight": 1440,
"imagePath": "001.jpg",
"imageWidth": 2560,
"shapes": [
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 1,
"label": "lb",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1745.3333333333333,
1114.4444444444446
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 1,
"label": "rb",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1813.3333333333333,
1104.6666666666667
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 1,
"label": "lt",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1698.6936936936936,
1052.8828828828828
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 1,
"label": "rt",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1762.4324324324323,
1042.5225225225224
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 1,
"label": "box",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1689.9099099099099,
1039.8198198198197
],
[
1820.09009009009,
1118.198198198198
]
],
"shape_type": "rectangle"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 2,
"label": "lt",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1606.310043668122,
934.410480349345
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 2,
"label": "rt",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1666.5720524017465,
926.5502183406112
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 2,
"label": "lb",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1571.593886462882,
890.3056768558951
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 2,
"label": "rb",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1629.0174672489081,
883.1004366812226
]
],
"shape_type": "point"
},
{
"description": "",
"flags": {},
"group_id": 2,
"label": "box",
"mask": null,
"points": [
[
1566.5720524017465,
880.2620087336244
],
[
1673.1222707423578,
937.6855895196505
]
],
"shape_type": "rectangle"
}
],
"version": "5.10.1"
}
格式转换
labelme_to_yolo_pose.py
import json
from collections import defaultdict
KEYPOINT_ORDER = ["lt", "rt", "lb", "rb"]
NUM_KPTS = len(KEYPOINT_ORDER)
def labelme_to_yolo_pose(json_path, img_w=2560, img_h=1440, class_id=0):
with open(json_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
groups = defaultdict(dict)
boxes = {}
# 1按 group_id 收集数据
for shape in data["shapes"]:
gid = shape["group_id"]
label = shape["label"]
pts = shape["points"]
if shape["shape_type"] == "point":
groups[gid][label] = pts[0]
elif shape["shape_type"] == "rectangle":
boxes[gid] = pts
yolo_lines = []
# 2逐个目标生成一行
for gid, box_pts in boxes.items():
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = box_pts
# bbox
cx = (x1 + x2) / 2 / img_w
cy = (y1 + y2) / 2 / img_h
w = abs(x2 - x1) / img_w
h = abs(y2 - y1) / img_h
line = [class_id, cx, cy, w, h]
# 3关键点
kpts = groups.get(gid, {})
for name in KEYPOINT_ORDER:
if name in kpts:
x, y = kpts[name]
line.extend([x / img_w, y / img_h, 2])
else:
line.extend([0, 0, 0])
yolo_lines.append(" ".join(f"{v:.6f}" if isinstance(v, float) else str(v) for v in line))
return yolo_lines
for i in range(1, 100):
name = f"{i:03d}.json"
print(i)
result = labelme_to_yolo_pose("D:\\xxxxx\\yoga-pose\\"+name,2560,1440)
label_path = f"D:\\xxxxx\\yoga-pose\\{i:03d}.txt"
with open(label_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("\n".join(result))
YOLO-Pose 标签格式
YOLOv8-Pose 每一行:分类 x坐标 y坐标 宽度 高度 是否可见 关键点1x 关键点1y 是否可见
class cx cy w h v kpt1_x kpt1_y v1 kpt2_x kpt2_y v2 ...
- 坐标 全部归一化
v:0= 不可见 / 不存在1= 存在但不可见2= 可见
class cx cy w h
lt_x lt_y 2
rt_x rt_y 2
lb_x lb_y 2
rb_x rb_y 2
源数据:
0 0.501427 0.715411 0.038011 0.080128 0.484976 0.710069 2 0.508413 0.678819 2 0.495793 0.751202 2 0.518179 0.714076 2
0 0.470853 0.600294 0.031851 0.071047 0.464543 0.633146 2 0.485276 0.604033 2 0.456280 0.600294 2 0.472356 0.568510 2
格式化展示:
0 0.501427 0.715411 0.038011 0.080128 0.484976 0.710069 2
0.508413 0.678819 2
0.495793 0.751202 2
0.518179 0.714076 2
0 0.470853 0.600294 0.031851 0.071047 0.464543 0.633146 2
0.485276 0.604033 2
0.456280 0.600294 2
0.472356 0.568510 2
二、训练数据
dataset.yaml
path: /your/dataset/root # 数据集根目录(绝对路径 or 相对路径)
train: images/train
val: images/val
names:
0: box
# -------- pose 关键点配置 --------
kpt_shape: [4, 3] # 4 个关键点,每个 (x, y, v)
flip_idx: [1, 0, 3, 2] # lt <--> rt ,lb <--> rb,左右翻转,否则增强会把点搞乱
字段解释(重点)
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
kpt_shape: [4, 3] |
必须,否则模型不知道你是 4 点 |
flip_idx |
左右翻转时关键点对换关系 |
names |
类别名,pose 也必须有 |
目录结构
- train:训练
- val:验证
我这里验证数据占比 10% 训练数据 90%,数据量不大也就150左右,据说要训练好的上千张才行
dataset/
├── images/
│ ├── train/
│ │ ├── 001.jpg
│ │ └── 002.jpg
│ └── val/
│ └── 101.jpg
│
├── labels/
│ ├── train/
│ │ ├── 001.txt
│ │ └── 002.txt
│ └── val/
│ └── 101.txt
│
└── dataset.yaml
三、安装环境&训练&验证
Ultralytics
最低版本:Python 3.8
pip install ultralytics
训练
在 dataset 目录打开 cmd 执行命令(最小可用):
yolo pose train \
model=yolov8n-pose.pt \
data=dataset.yaml \
imgsz=640 \
epochs=100 \
batch=16
完整训练命令:
yolo task=pose ^
mode=train ^
model=yolov8n-pose.pt ^
data=dataset.yaml ^
epochs=300 ^
imgsz=640 ^
batch=8 ^
device=0 ^
lr0=0.002 ^
lrf=0.01 ^
cos_lr=True ^
degrees=45 ^
translate=0.1 ^
scale=0.6 ^
fliplr=0.5 ^
mosaic=0.0 ^
mixup=0.0 ^
patience=80
参考:使用 Ultralytics YOLO 进行模型训练#训练设置
验证
some_test_images:需要验证的图片目录(多个图片)runs/pose/predict:生成验证结果目录
yolo task=pose mode=predict ^
model=runs/pose/train3/weights/best.pt ^
source=./some_test_images ^
save=True ^
conf=0.3
四、转 ONNX 模型&验证
导出 ONNX
很简单一条命令搞定
yolo export \
model=runs/pose/train/weights/best.pt \
format=onnx \
opset=12 \
simplify \
dynamic=False
| 参数 | 原因 |
|---|---|
opset=12 |
RKNN 最稳(别用 13/17) |
simplify |
减少 ONNX 节点,RKNN 更容易过 |
dynamic=False |
RKNN 不支持动态 shape |
注:导出模型在 runs/pose/train/weights/best.onnx
ONNX 模型推理
from ultralytics import YOLO
IMG_PATH = './001.jpg'
model = YOLO('best.onnx', task='pose')
# 进行推理
results = model(IMG_PATH)
# 打印结果
for r in results:
boxes = r.boxes
keypoints = r.keypoints
print(f"Number of objects detected: {len(boxes)}")
if len(boxes) > 0:
print("Boxes (xyxy):")
print(boxes.xyxy)
print("\nKeypoints (xy):")
print(keypoints.xy)
print("-------------------------------------")
# 保存结果图片
res_img = r.plot()
from cv2 import imwrite
imwrite('result_ultra.jpg', res_img)
print("Ultralytics result saved to result_ultra.jpg")
推理结果:

五、转 RKNN 模型&验证
在导出模型时遇到几个问题:
- 如果开启量化就检测不到结果了,只能使用未量化的模型
Failed to config layer: 'Conv:/model.22/dfl/conv/Conv' using 3Core fallback to single core mode:指定卷积层无法使用 3 核并行计算,降级为单核运行,可能导致模型推理速度下降,推理时确实有点慢。
导出 RKNN
参考瑞芯微 yolov8_pose 导出模型代码修改:
quant_dataset.txt
./images/001.jpg
./images/002.jpg
./images/003.jpg
./images/004.jpg
./images/005.jpg
./images/006.jpg
./images/007.jpg
./images/008.jpg
./images/009.jpg
./images/010.jpg
./images/011.jpg
./images/012.jpg
./images/013.jpg
./images/014.jpg
./images/015.jpg
./images/016.jpg
./images/017.jpg
./images/018.jpg
./images/019.jpg
./images/020.jpg
convert_yolov8_pose_to_rknn.py
import sys
import os
from rknn.api import RKNN
# ================== 配置区 ==================
# 量化数据集(txt,每行一个图片路径)
DATASET_PATH = './quant_dataset.txt'
# 默认输出
DEFAULT_RKNN_PATH = './yoga_pose.rknn'
# 默认是否量化
DEFAULT_QUANT = True
def parse_arg():
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
print("Usage: python3 {} onnx_model_path platform [dtype(optional)] [output_rknn_path(optional)]".format(sys.argv[0]))
print("platform: rk3562, rk3566, rk3568, rk3576, rk3588, rv1126b")
print("dtype: i8 | fp")
exit(1)
model_path = sys.argv[1]
platform = sys.argv[2]
do_quant = DEFAULT_QUANT
if len(sys.argv) > 3:
dtype = sys.argv[3]
if dtype not in ['i8', 'fp']:
print("ERROR: dtype must be 'i8' or 'fp'")
exit(1)
do_quant = (dtype == 'i8')
if len(sys.argv) > 4:
output_path = sys.argv[4]
else:
output_path = DEFAULT_RKNN_PATH
return model_path, platform, do_quant, output_path
if __name__ == '__main__':
model_path, platform, do_quant, output_path = parse_arg()
# Create RKNN object
rknn = RKNN(verbose=True)
# ================== 1. Config ==================
print('--> Config RKNN')
rknn.config(
mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]],
std_values=[[255, 255, 255]],
target_platform=platform,
optimization_level=3
)
print('done')
# ================== 2. Load ONNX ==================
print('--> Loading ONNX model')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model=model_path)
if ret != 0:
print('Load model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# ================== 3. Build ==================
print('--> Building RKNN model')
if do_quant:
print('Quantization: ENABLED')
print('Quant dataset:', DATASET_PATH)
ret = rknn.build(
do_quantization=True,
dataset=DATASET_PATH
)
else:
print('Quantization: DISABLED (FP mode)')
ret = rknn.build(
do_quantization=False
)
if ret != 0:
print('Build model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# ================== 4. Export ==================
print('--> Export RKNN model')
ret = rknn.export_rknn(output_path)
if ret != 0:
print('Export rknn failed!')
exit(ret)
print("RKNN saved to:", output_path)
# Release
rknn.release()
导出命令:
python convert_yolov8_pose_to_rknn.py yoga_pose.onnx rk3588 fp
RKNN 模型推理
yoga_rknn_demo.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
import argparse
import time
from rknn.api import RKNN
# 配置模型参数
CLASSES = ['yoga_mat'] # 类别名称
NUM_KEYPOINTS = 4 # 关键点数量
CONF_THRES = 0.5 # 置信度阈值
NMS_THRES = 0.45 # NMS 阈值
class YOLOv8PoseRKNN:
def __init__(self, model_path, target='rk3588', device_id=None):
# 1. 初始化 RKNN 对象
self.rknn = RKNN(verbose=True)
# 2. 加载模型
print(f"--> Loading RKNN model: {model_path}")
ret = self.rknn.load_rknn(model_path)
if ret != 0:
print(f"Load RKNN model \"{model_path}\" failed!")
exit(ret)
# 3. 初始化运行时环境
# rknn.api 的 init_runtime 需要指定 target (如 rk3588) 和 device_id (如果连接了多个设备)
print(f"--> Init runtime environment (Target: {target}, Device ID: {device_id})")
ret = self.rknn.init_runtime(target=target, device_id=device_id)
if ret != 0:
print("Init runtime environment failed!")
exit(ret)
print("--> Runtime initialized")
def letterbox(self, im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114)):
"""
图片缩放与填充,保持长宽比
"""
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def process_keypoints(self, kpts, dw, dh, ratio):
"""
将关键点坐标映射回原图
"""
# kpts shape: [N, 4, 3] or [N, 4*3] -> [x, y, conf]
kpts = np.array(kpts)
if len(kpts.shape) == 1:
kpts = kpts.reshape(-1, 3) # Reshape to [4, 3]
# 减去 padding
kpts[:, 0] -= dw
kpts[:, 1] -= dh
# 除以缩放比例
kpts[:, 0] /= ratio[0]
kpts[:, 1] /= ratio[1]
return kpts
def post_process(self, outputs, ratio, dwdh):
"""
针对 YOLOv8 标准输出的后处理
假设输出 Shape 为 (1, channels, 8400)
Channels = 4(box) + 1(cls_score) + 4*3(kpts) = 17 (针对你的单类+4点模型)
"""
# rknn.inference 返回的是列表
output = outputs[0]
# 检查是否需要 Transpose
# YOLOv8 默认导出通常是 [1, 17, 8400],需要转置为 [1, 8400, 17] 以便处理
if output.shape[1] < output.shape[2]:
output = np.transpose(output, (0, 2, 1))
prediction = output[0] # [8400, 17]
# 1. Box 处理 (cx, cy, w, h) -> (x1, y1, x2, y2)
boxes = prediction[:, :4]
# 2. Score 处理
# 第4列开始是类别分数
scores = prediction[:, 4:4+len(CLASSES)]
max_scores = np.max(scores, axis=1)
class_ids = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)
# 3. 过滤低置信度
mask = max_scores > CONF_THRES
prediction = prediction[mask]
boxes = boxes[mask]
max_scores = max_scores[mask]
class_ids = class_ids[mask]
if len(prediction) == 0:
return []
# 4. 坐标转换 cxcywh -> xyxy
cx = boxes[:, 0]
cy = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2]
h = boxes[:, 3]
x1 = cx - w / 2
y1 = cy - h / 2
x2 = cx + w / 2
y2 = cy + h / 2
boxes_xyxy = np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=1)
# 5. NMS (非极大值抑制)
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes_xyxy.tolist(), max_scores.tolist(), CONF_THRES, NMS_THRES)
results = []
dw, dh = dwdh
if len(indices) > 0:
indices = indices.flatten()
for i in indices:
# 获取 Box
box = boxes_xyxy[i]
# 还原到原图尺寸
box[0] = (box[0] - dw) / ratio[0]
box[1] = (box[1] - dh) / ratio[1]
box[2] = (box[2] - dw) / ratio[0]
box[3] = (box[3] - dh) / ratio[1]
# 获取 Keypoints
# 关键点数据起始位置 = 4(box) + len(CLASSES)
kpt_start_idx = 4 + len(CLASSES)
raw_kpts = prediction[i, kpt_start_idx:]
# 处理关键点坐标
kpts = self.process_keypoints(raw_kpts, dw, dh, ratio)
results.append({
"class_id": class_ids[i],
"score": max_scores[i],
"box": box, # [x1, y1, x2, y2]
"keypoints": kpts # [[x,y,conf], ...]
})
return results
def run(self, img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img is None:
print(f"Image not found: {img_path}")
return
# 1. 预处理
# YOLOv8 默认输入 640x640,请根据你训练时的 imgsz 修改
input_size = (640, 640)
input_img, ratio, dwdh = self.letterbox(img, input_size)
# 转换为 RGB (OpenCV 是 BGR)
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(input_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 增加 batch 维度 [1, 640, 640, 3]
input_tensor = np.expand_dims(input_img, axis=0)
# 2. 推理
print('--> Running model')
start_time = time.time()
# rknn.inference 接口
outputs = self.rknn.inference(inputs=[input_tensor])
print(f"Inference time: {(time.time() - start_time)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 调试:查看输出形状,确保与 post_process 预期一致
# for i, out in enumerate(outputs):
# print(f"Output[{i}] shape: {out.shape}")
# 3. 后处理
detections = self.post_process(outputs, ratio, dwdh)
# 4. 绘图
for det in detections:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, det['box'])
score = det['score']
cls_id = det['class_id']
kpts = det['keypoints']
# 画框
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
label = f"{CLASSES[cls_id]} {score:.2f}"
cv2.putText(img, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 画关键点 (4个点)
for i, kp in enumerate(kpts):
x, y, conf = kp
if conf > 0.5: # 只画置信度高的点
cv2.circle(img, (int(x), int(y)), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 可选:给点标号
# cv2.putText(img, str(i), (int(x), int(y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255), 1)
save_path = "result_rknn_api.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(save_path, img)
print(f"Result saved to {save_path}")
def release(self):
self.rknn.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='YOLOv8 Pose RKNN Inference (Full API)')
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, required=True, help='Path to .rknn model')
parser.add_argument('--img', type=str, required=True, help='Path to image')
parser.add_argument('--target', type=str, default='rk3588', help='Target platform (e.g., rk3588, rk3566)')
parser.add_argument('--device_id', type=str, default=None, help='Device ID (for ADB connection)')
args = parser.parse_args()
app = YOLOv8PoseRKNN(args.model, target=args.target, device_id=args.device_id)
try:
app.run(args.img)
finally:
app.release()
执行命令:
python yoga_rknn_demo.py --model ./yoga_pose.rknn --img ./001.jpg
RK3588 推理结果:
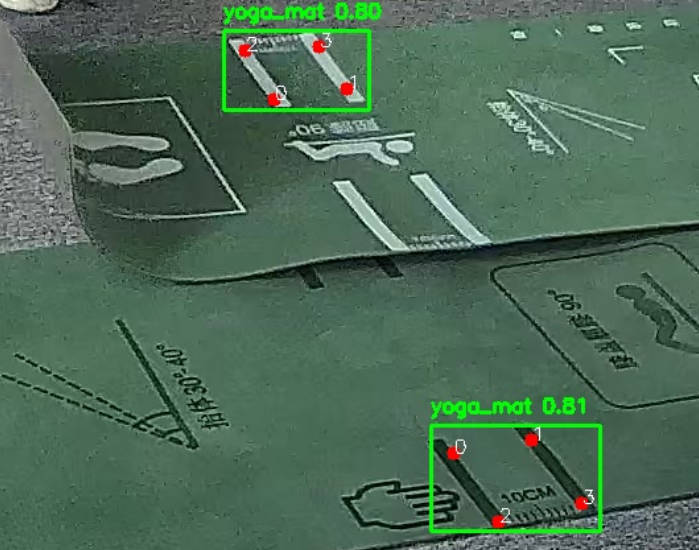
六、总结
在训练自定义模型并运行在 RK3588 盒子上过程中耗时还是比较长的,最开始标注数据,格式没搞清楚来回修改数据格式(JSON)浪费一些时间。还有比较耗时间的是在转 RKNN 模型成功后,验证模型成了最大问题,解析推理数据始终拿不到正确的框和点,这期间用了很多 AI(ChatGPT、GLM、Doubao、Gemini) 工具进行代码生成测试问题特别多,耗时特别长。
最终测试 Google Gemini 完胜,碾压一众AI大模型,基本一次就能给到对的结果,大部分推理验证代码都是 Gemini 生成。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号