解决非Spring Bean访问Spring Bean的问题:实用指南
在非SpringBean类里获取SpringBean,会是什么情况?
case1
先贴出来下面 `SpringContextUtils`,这是一个常见的 Spring 上下文工具类,用于在非 Spring 管理的类中获取 Bean。这个工具类实现了 `ApplicationContextAware` 接口,通过 Spring 容器自动注入 `ApplicationContext`。
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SpringContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringContextUtils.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
//确保在 Spring 容器初始化完成后使用该工具类,否则可能抛出异常(但在容器初始化完成前调用可能导致 NPE)。
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
}
接下来,下面这段代码中,PlainClass 表示一个普通Java类,其 foo1 方法使用到了 SpringContextUtils#getBean。
public class PlainClass {
public void foo1() {
TheOtherBean bean = SpringContextUtils.getBean(TheOtherBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
我们在SpringBean里执行 PlainClass#foo1 是没问题的。
而在非SpringBean中执行 PlainClass#foo1,会抛空指针异常,这是因为在这种情况下,SpringContextUtils未被Spring容器管理,无法获取到applicationContext对象。
java.lang.NullPointerException
at jstudy.redislimit.SpringContextUtils.getBean(SpringContextUtils.java:30)
at jstudy.beantest.PlainClass.foo1(PlainClass.java:12)
at jstudy.beantest.BeanTest.test(BeanTest.java:18)
case2
接着看下面代码中的 PlainClass :
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class PlainClass {
此时,在SpringBean 里执行 PlainClass#foo2 , 输出结果是什么?
是null。也就是说 theOtherBean 对象是null。为什么? 因为Spring启动时,程序先加载的是 PlainClass 类(它不受Spring管理),而此时`TheOtherBean`尚未被注入容器里,自动装配失败,注入的`TheOtherBean`为null。
当然, 我们通常在项目中不会写这种烂代码来“博人眼球”。
细心的同学可以发现,IDE会在 PlainClass 这个非SpringBean里使用的@Autowired注解上给出警告,提示"Autowired members must be defined in valid Spring bean (@Component|@Service|...)",提醒开发者合适地定义Bean以避免这类问题。
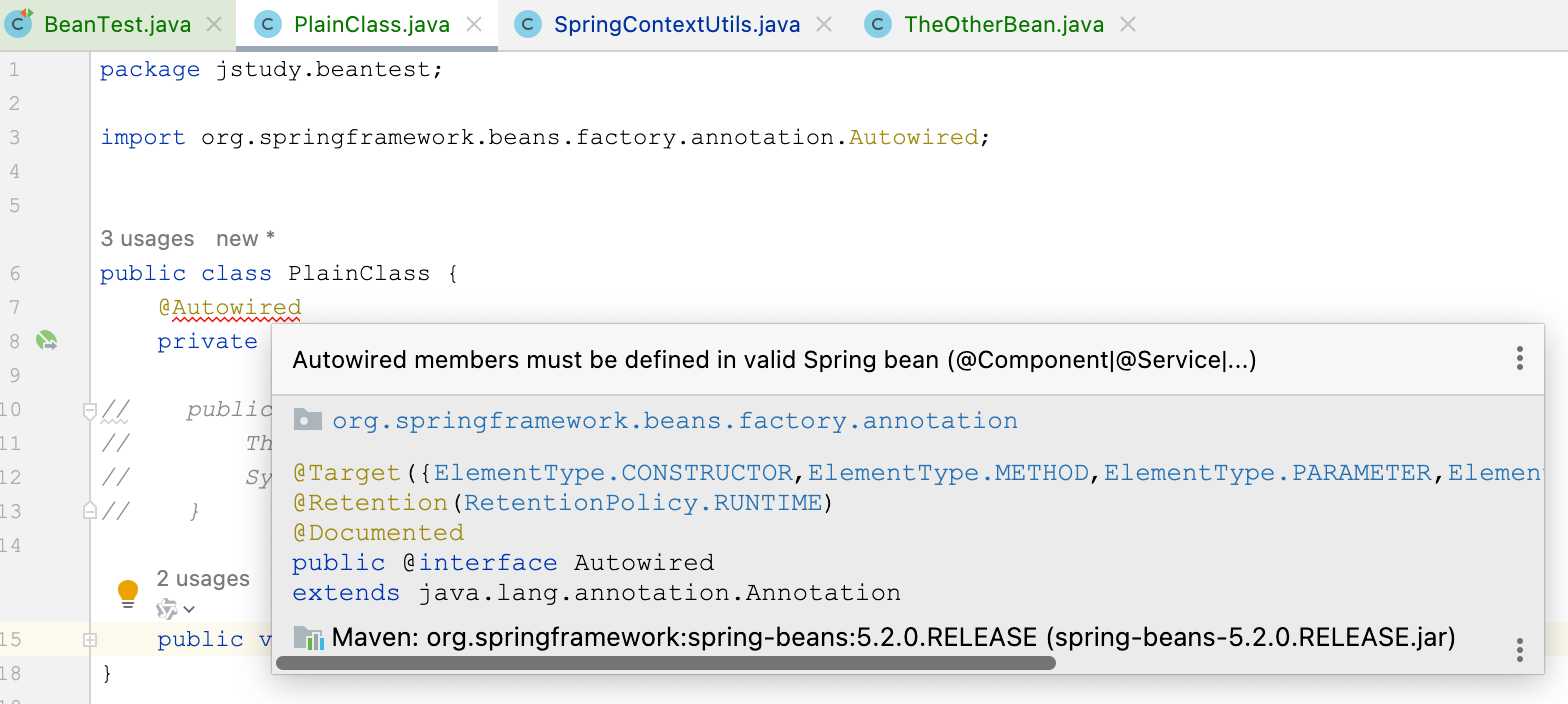
另外,在非SpringBean 里执行 PlainClass#foo2呢?依然是null。
附上我所使用的测试类代码
package jstudy.beantest;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
该测试类`BeanTest`在SpringBoot环境下运行。注释掉 @SpringBootTest 和 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)后,`BeanTest`就是一个非SpringBean(普通Java类)了。
0.0 总结
在非SpringBean类中直接获取SpringBean可能会引发问题,例如上面案例里提到的空指针和自动装配失败。为避免这些问题,建议将需要访问Spring Bean的类也注册为Spring Bean,以确保依赖关系得到正确管理。
当看到一些不好的代码时,会发现我还算优秀;当看到优秀的代码时,也才意识到持续学习的重要!--buguge
本文来自博客园,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/buguge/p/18333846




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号