Python3 数据结构
builtins
list
list.append() list.extend() del list[index] list.insert(index, obj) list.pop([index=-1]) list.remove(obj) list.reverse() list.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) list.clear() list.copy()
示例
>>> list=['a','b','c'] >>> list.append(['d, 'e']) ['a', 'b', 'c', ['d', 'e'] ] >>> list.extend(['d','e','f']) >>> list ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
tuple
set
set.add(obj) set.update(set_obj) set.remove(obj) # set.pop() # 随机移除元素 set.discard(obj) set.union() set.difference() set.difference_update() set.intersection() set.intersection_update() set.symmetric_difference() set.symmetric_difference_update() set.isdisjoint() set.issubset() set.issuperset()
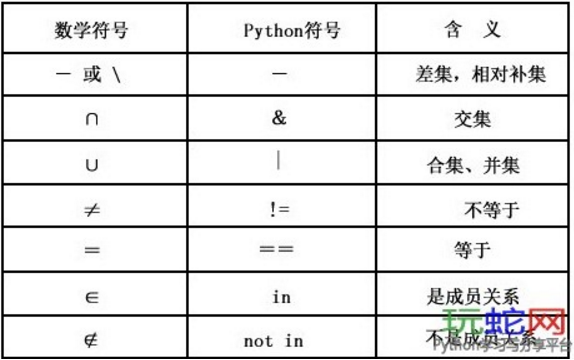
更多的,我们使用set的重载运算符:
dict
dict.clear() dict.fromkeys(seq[, value]) key (not) in dict # 判断是否存在该元素(key) dict[key] = value # 添加新元素(或改写已有元素) dict.update(dict2) dict.keys() # 返回一个迭代器,内容为dict的key元素,等同于直接迭代dict dict.values() dict.items() # 返回包含 key,value 的迭代器 dict.pop(key[,default]) # 删除字典给定键key所对应的值,返回值为被删除的value。若不存在该元素,返回default值。 # dict.popitem() # 随机返回并删除字典中的一对键和值(一般删除末尾对)
示例
# 合并字典(方法之一) dictMerged2 = dict(dict1, **dict2) # 等同于(方法之二): dictMerged = dict1.copy() dictMerged.update(dict2)
str
str.count(sub[, start[, end]]) str.encode(encoding="utf-8", errors="strict") str.format(*args, **kwargs) # s = "this is from {}".format(__file__) str.find(sub[, start[, end]]) # 没有查找到子串,返回-1 str.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) # 没有查找到子串,则报Except str.index(sub[, start[, end]]) str.replace(old, new[, count]) str.join(iterable) str.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) str.splitlines([keepends]) str.strip([chars]) str.lstrip([chars]) str.rstrip([chars]) str.partition(sep) str.expandtabs(tabsize=8) str.zfill(width) str.upper() str.lower() str.islower(), c.isalpha(), c.isdecimal(), c.isdigit(), or c.isnumeric() str.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) str.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) eval(source[, globals[, locals]]) # 将str作为有效表达式并返回结果
bytes / bytearray
fromhex(string) # classmethod encode() # classmethod bytes.count(sub[, start[, end]]) bytes.decode(encoding="utf-8", errors="strict") bytearray.decode(encoding="utf-8", errors="strict") bytes.find(sub[, start[, end]]) bytearray.find(sub[, start[, end]]) bytes.join(iterable) bytearray.join(iterable) bytes.replace(old, new[, count]) bytearray.replace(old, new[, count]) bytes.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) bytearray.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]])
enum
示例
from enum import Enum >>> class Color(Enum): ... RED = 1 ... GREEN = 2 ... BLUE = 3 >>> print(Color.RED)
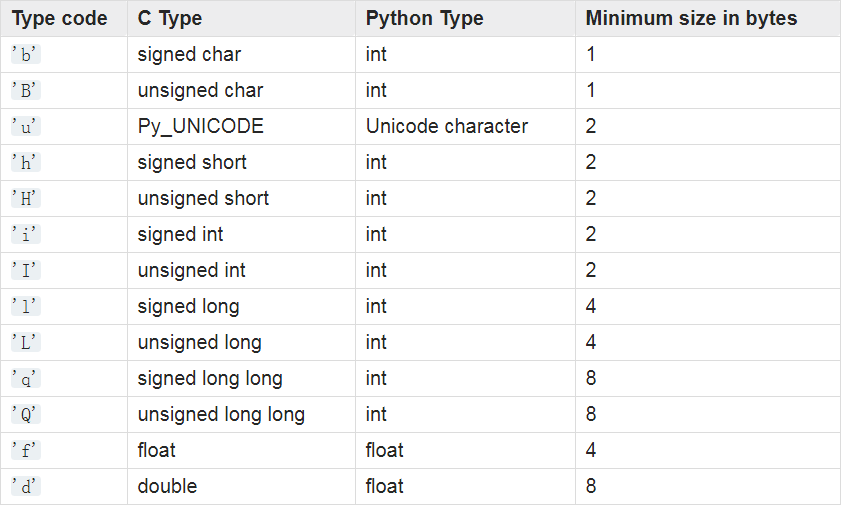
array
array.itemsize
array.typecode
array.array(typecode[, initializer])
array.frombytes(s)
array.fromlist(list)
array.fromstring()
array.fromunicode(s)
array.tobytes()
array.tolist()
array.tostring()
array.tounicode()
array.count(x)
array.append(x)
array.extend(iterable)
array.pop([i])
array.remove(x)
collections
namedtuple
示例
Point = namedtuple('My_Point', ['x', 'y']) >>> p = Point(11, y=22) # p = My_Point(x=11, y=22) >>> p[0] + p[1] # indexable like the plain tuple (11, 22) 33 >>> p.x + p.y # fields also accessible by name 33
OrderedDict
keys()
values()
示例
OrderedDict([('apple', 4), ('banana', 3), ('orange', 2), ('pear', 1)])
OrderedDict(sorted(dict_test.items(), key=lambda t: t[0]))
collections.defaultdict
collections.deque
clear()
copy()
count(x)
append(x)
appendleft(x)
extend(iterable)
extendleft(iterable)
insert(i, x)
index(x[, start[, stop]])
pop()
popleft()
remove(value)
reverse()
collections.Counter
>>> from collections import Counter >>> c = Counter() >>> for ch in 'programming': ... c[ch] = c[ch] + 1 ... >>> c Counter({'g': 2, 'm': 2, 'r': 2, 'a': 1, 'i': 1, 'o': 1, 'n': 1, 'p': 1})


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号