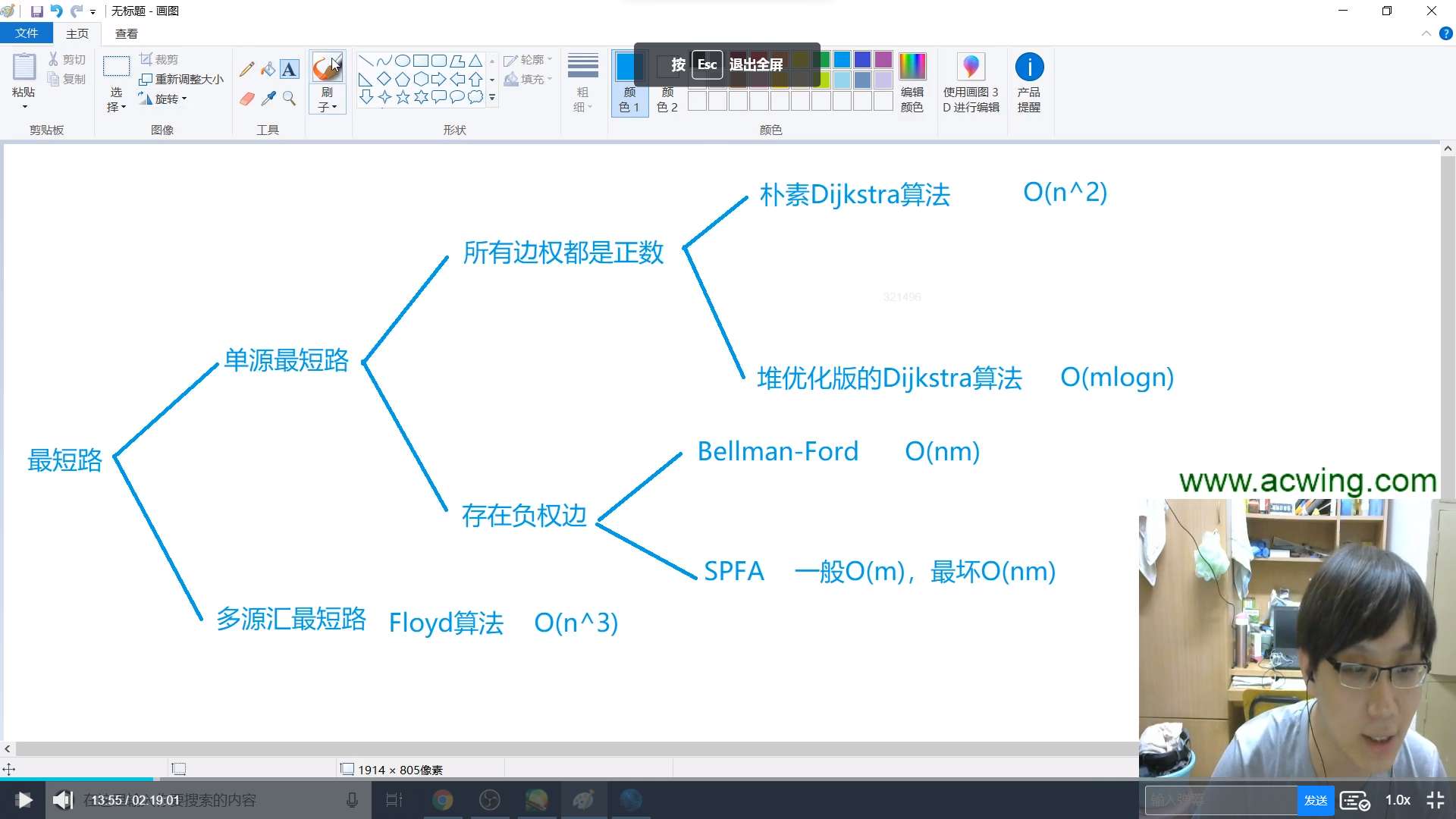
最短路算法模版集合
例题https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1339
朴素dijkstra (邻接表)
dijkstra 正确性来自于贪心 也就是st数组内的数(dist) 必须逐渐变大这样才能保证后面的数更新的时候,当前的第三边dist[t]都是最小值 [详见](https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/94237/)
dist[x]表示 x到start 的最短距离
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2510, M = 6220 * 2;
int h[N], w[M], ne[M], e[M], idx;
int n, m, start, ened;
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int dijkstra()
{
dist[start] = 0;
int k = n;
while (k -- ) // 运行n - 1 次就行 n次一样不错就是多算一遍 可改成 --k
{
int t = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!st[i] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[i]))
t = i;
st[t] = true;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + w[i]);
}
}
return dist[ened];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> start >> ened;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
cout << dijkstra();
return 0;
}
朴素dijkstra 邻接矩阵
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3510;
int g[N][N];
int n, m, start, ened;
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
int dijkstra()
{
dist[start] = 0;
int k = n;
while (k -- )
{
int t = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!st[i] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[i]))
t = i;
st[t] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
dist[i] = min(dist[i], dist[t] + g[t][i]);
}
return dist[ened];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> start >> ened;
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b], c);
g[b][a] = min(g[b][a], c);
}
cout << dijkstra();
return 0;
}
堆优化dijkstra
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 2510, M = 6550 * 2;
int h[N], ne[M], e[M], w[M], idx;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n, m, S, T;
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int dijkstra()
{
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> q;
q.push({0, S});
dist[S] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.top();
q.pop();
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;
if (st[ver]) continue;
st[ver] = true; // 标记已经用这个点更新过了 (此点目前最小)
for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j] = distance + w[i];
q.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
return dist[T];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> S >> T;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
cout << dijkstra();
return 0;
}
spfa
我更新过谁,我再拿被更新的这个更新别人。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2510, M = 6210 * 2;
int h[N], ne[M], e[M], idx, w[M];
int n, m, S, T;
int dist[N];
int q[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int spfa()
{
int tt = 1, hh = 0;
q[hh] = S;
dist[S] = 0;
while (hh != tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
st[t] = false; // 退出队列后还有可能进来
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!st[j]) // 保证队列中这个点只有一个
{
q[tt ++ ] = j;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return dist[T];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> S >> T;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
cout << spfa();
return 0;
}
bellman_ford
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2510, M = 6500 * 2;
int h[N], ne[M], e[M], w[M], idx;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n, m, S, T;
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int bellman_ford()
{
int k = n;
dist[S] = 0;
while (k -- )
{
int backup[N];
memcpy(backup, dist, sizeof dist); // 备份防止连续更新边 , 正常情况下没影响,限制边数时必须有
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = h[i]; j != -1; j = ne[j])
dist[e[j]] = min(dist[e[j]], backup[i] + w[j]);
}
return dist[T];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> S >> T;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
cout << bellman_ford();
return 0;
}
Floyd
原理是动态规划 时间复杂度O(n ^ 3)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2510;
int g[N][N];
int n, m, S, T;
int main()
{
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &S, &T);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = min(c, g[a][b]);
}
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ )
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (i != j) g[i][j] = min(g[i][j], g[i][k] + g[k][j]);
printf("%d", g[S][T]);
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号