心电图
参考自:手把手教你打造一个心电图效果View Android自定义View
动态心电图详见接收数据实时更新的波状曲线图
效果图
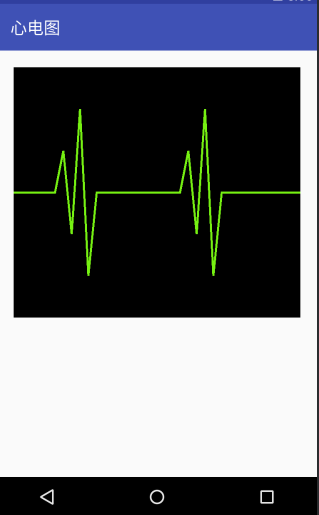
布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="20dp"
tools:context="com.wingsofts.cardiograph.MainActivity">
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#000000" />
<com.wingsofts.cardiograph.PathView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
自定义控件
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
//画笔
protected Paint paint;
//心电图折线
protected Path path;
//自身的大小
private int width, height;
//折现的颜色
private int lineColor = Color.parseColor("#76f112");
public PathView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
paint = new Paint();
path = new Path();
}
private void drawPath(Canvas canvas) {
// 重置path
path.reset();
//用path模拟一个心电图样式
//1.初始位置x=0,y在中间
path.moveTo(0, height / 2);
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//平移
path.lineTo(tmp + 100, height / 2);
//上滑
path.lineTo(tmp + 120, height / 2 - 100);
//下滑
path.lineTo(tmp + 140, height / 2 + 100);
//上滑
path.lineTo(tmp + 160, height / 2 - 200);
//下滑
path.lineTo(tmp + 180, height / 2 + 200);
//回到中间
path.lineTo(tmp + 200, height / 2);
//平滑
path.lineTo(tmp + 300, height / 2);
//x坐标增加到第二次循环开始的地方
tmp = tmp + 300;
}
//设置画笔style
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setColor(lineColor);
paint.setStrokeWidth(5);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
width = w;
height = h;
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
drawPath(canvas);
//x轴滑动速度
scrollBy(1, 0);
//非UI线程下刷新布局,因为UI线程不是线程安全的
postInvalidateDelayed(10);
}
}
activity
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
最重要的就是Path这个类和moveTo()/lineTo()方法
欢迎关注我的微信公众号:安卓圈





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号