[学习笔记]DDPM图片降噪
之前学习了一下流匹配的最简单的demo,前两天学长讲了一下扩散模型的简单应用,就尽快学一下然后把博客写上来。
先贴一下仓库
然后是学长的博客
生成扩散模型漫谈(一):DDPM = 拆楼 + 建楼 - 科学空间|Scientific Spaces
代码也是由学长提供的,强无敌的学长
(一个看起来无比古老的博客)
那么接下来,进入正题,开始打这个boss——扩散模型
0.什么是扩散模型
学长的一个比喻非常形象:拆楼与盖楼。
训练的过程就是把楼给拆了
生成的过程就是把楼搭好喽
这里的拆楼,就是在清晰的图片上加噪声
这里的搭楼,就是把雪花图上的噪声消除。
至于为什么叫扩散,因为它的过程很像把一滴墨滴到水中,扩散完的灰色墨水往回逆推。
反正我觉得这个名字还是比较形象的。
1.扩散模型的理论基础
这个部分学长的博客里讲得非常明白,大概就是利用高斯分布的叠加性。至于没法通过观测获得的那些量,那就利用强大的神经网络来进行拟合。
其次,这大概是我第一次真正接触到U-Net这个东西,本来它只存在于人工智能与机器视觉的课堂上,这下它真的走到了工程里
U-Net形如其名,网络像一个U形,因为直接添加了从浅层到深层的连接。
众所周知,深层的网络会包含更加复杂的特征,感受野较大但无法注意到细节;
浅层的网络会注意到一些细节的信息,比如边缘、角点之类
如果直接用MLP一路算下去,就算还原了图片也只能看到一个平滑的光杆(笑
U-Net开辟了一条直接从浅层网络指向深层网络的路径,很好地解决了这个问题。
实现方法:

1 # 上采样(带跳跃连接) 2 x = self.up1(torch.cat([x, x3], dim=1), t) # [B, 128, 14, 14] 3 # cat:连接矩阵,dim=1表示按列连接,dim=0表示按行连接 4 # 拼接特征,达到连接的效果 5 x = self.up2(torch.cat([x, x2], dim=1), t) # [B, 64, 28, 28] 6 x = self.up3(torch.cat([x, x1], dim=1), t) # [B, 64, 28, 28]
也是比较直白。
2.扩散模型的实现方法
还是直接贴代码吧,我感觉注释挺详细了。
不过扩散模型的数学基础有点小复杂,跟代码对应起来有点困难。
不过基本上都是按照数学推导一步一步来的
ddpm_model.py:

1 import torch 2 import torch.nn as nn 3 import math 4 5 6 class SinusoidalPositionalEmbedding(nn.Module): 7 """时间步的位置编码""" 8 # 具有线性性质,并且不重复 9 10 def __init__(self, dim): 11 super().__init__() 12 self.dim = dim 13 14 def forward(self, time): 15 device = time.device # 获取张量所在的设备,gpu计算步骤 16 half_dim = self.dim // 2 17 emb = math.log(10000) / (half_dim - 1) 18 emb = torch.exp(torch.arange( 19 half_dim, device=device, dtype=torch.float32) * -emb) 20 emb = time[:, None].float() * emb[None, :] 21 emb = torch.cat([emb.sin(), emb.cos()], dim=-1) 22 return emb 23 24 25 class Block(nn.Module): 26 """U-Net的基础块""" 27 28 def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, time_emb_dim, up=False, down=False): 29 super().__init__() 30 self.time_mlp = nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, out_ch) # 简单的线性全连接层 31 if up: # U-Net,上下采样 32 self.conv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_ch, out_ch, 4, 2, 1) # 转置卷积 33 elif down: 34 # stride=2 for downsampling 35 # 简单的卷积层,in out kernel_size stride padding 36 self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, 2, 1) 37 else: 38 self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, padding=1) 39 self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(8, out_ch) # 组归一化,总之就是归一化,作用差不多 40 self.act = nn.SiLU() # sigmoid,你终于出现了 41 42 def forward(self, x, t): 43 # 时间嵌入 44 t_emb = self.time_mlp(t)[:, :, None, None] 45 # 卷积 46 h = self.conv(x) 47 # 添加时间嵌入 48 h = h + t_emb 49 # 妙哉时间嵌入 50 # 时间条件注入:通过广播加法,给整张图打上“时间底色”。 51 # 这不是覆盖特征,而是调节特征,让模型根据当前的时间步 t 来处理图像。 52 53 # 归一化和激活 54 h = self.norm(h) 55 h = self.act(h) 56 return h 57 58 59 class SimpleUNet(nn.Module): 60 """简单的U-Net架构用于DDPM""" 61 62 def __init__(self, image_size=28, in_channels=1, time_emb_dim=32): 63 super().__init__() 64 self.time_emb_dim = time_emb_dim 65 66 # 时间嵌入 67 self.time_mlp = nn.Sequential( # 时间嵌入层:使用 nn.Sequential 封装成一个线性流水线 68 # 作用:将标量时间步 t 转化为高维向量,经过位置编码 -> 线性变换 -> 激活 -> 线性变换 69 SinusoidalPositionalEmbedding(time_emb_dim), 70 nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, time_emb_dim), 71 nn.SiLU(), 72 nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, time_emb_dim) 73 ) 74 75 # 下采样路径 76 self.down1 = Block(in_channels, 64, time_emb_dim) 77 self.down2 = Block(64, 128, time_emb_dim, down=True) 78 self.down3 = Block(128, 256, time_emb_dim, down=True) 79 80 # 中间层 81 self.mid1 = Block(256, 256, time_emb_dim) 82 self.mid2 = Block(256, 256, time_emb_dim) 83 # 中间层 (Bottleneck): 84 # 在最低分辨率(7x7)和最高通道数(256)下处理图像的全局语义信息。 85 # 这里是连接编码器(Encoder)和解码器(Decoder)的桥梁,负责对提取的深层特征进行转换。 86 87 # 上采样路径 88 self.up1 = Block(256 + 256, 128, time_emb_dim, up=True) # 7x7 -> 14x14 89 self.up2 = Block(128 + 128, 64, time_emb_dim, 90 up=True) # 14x14 -> 28x28 91 # 28x28 -> 28x28 (不再上采样) 92 self.up3 = Block(64 + 64, 64, time_emb_dim, up=False) 93 94 # 输出层 95 self.out = nn.Conv2d(64, in_channels, 1) 96 97 def forward(self, x, timestep): 98 """ 99 x: [B, C, H, W] 噪声图像 100 timestep: [B] 时间步 101 """ 102 # 时间嵌入 103 t = self.time_mlp(timestep) 104 105 # 下采样 106 x1 = self.down1(x, t) # [B, 64, 28, 28] 107 x2 = self.down2(x1, t) # [B, 128, 14, 14] 108 x3 = self.down3(x2, t) # [B, 256, 7, 7] 109 110 # 中间层 111 x = self.mid1(x3, t) 112 x = self.mid2(x, t) 113 114 # 上采样(带跳跃连接) 115 x = self.up1(torch.cat([x, x3], dim=1), t) # [B, 128, 14, 14] 116 # cat:连接矩阵,dim=1表示按列连接,dim=0表示按行连接 117 x = self.up2(torch.cat([x, x2], dim=1), t) # [B, 64, 28, 28] 118 x = self.up3(torch.cat([x, x1], dim=1), t) # [B, 64, 28, 28] 119 120 # 输出 121 return self.out(x) 122 123 124 class DiffusionProcess: 125 """扩散过程""" 126 127 def __init__(self, num_timesteps=1000, beta_start=0.0001, beta_end=0.02, device='cuda'): 128 # num_timesteps: 扩散步数 129 # beta_start: beta的起始值 130 # beta_end: beta的结束值 131 self.num_timesteps = num_timesteps 132 self.device = device 133 134 # 线性beta调度 135 self.betas = torch.linspace( 136 beta_start, beta_end, num_timesteps, device=device) 137 # torch.linspace:生成一个等差数列,线性插值 138 self.alphas = 1.0 - self.betas # 保留多少原图信息,alpha=1-beta 139 140 self.alphas_cumprod = torch.cumprod(self.alphas, dim=0) 141 # torch.cumprod:计算一个张量的累积积 142 # 对于输入张量 x,输出 y 的第 i 个元素为: 143 # # y[i] = x[0] × x[1] × ... × x[i] 144 self.alphas_cumprod_prev = torch.cat( 145 [torch.tensor([1.0], device=device), self.alphas_cumprod[:-1]]) 146 # t-1 的alphas_cumprod 147 148 # 用于采样的参数 149 self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod = torch.sqrt(self.alphas_cumprod) 150 self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod = torch.sqrt( 151 1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod) 152 # sqrt(1-alphas_cumprod),数学这一块 153 154 # 用于去噪的参数 155 self.posterior_variance = self.betas * \ 156 (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod) 157 158 def q_sample(self, x_start, t, noise=None): 159 """前向扩散过程:添加噪声""" 160 # x_start: 原始图像 161 if noise is None: 162 noise = torch.randn_like(x_start) 163 # randn_like:生成一个与给定张量相同形状的随机张量,并使用给定张量的数据类型和设备,正态分布 164 165 sqrt_alphas_cumprod_t = self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 166 sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t = self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod[t].view( 167 -1, 1, 1, 1) 168 169 return sqrt_alphas_cumprod_t * x_start + sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t * noise 170 # 按照数学模型加噪声 171 172 def p_sample(self, model, x_t, t): 173 """反向去噪过程:单步采样""" 174 # 预测噪声 175 predicted_noise = model(x_t, t) 176 177 # 计算系数 178 alpha_t = self.alphas[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 179 alpha_cumprod_t = self.alphas_cumprod[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 180 beta_t = self.betas[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 181 182 # 计算x_0的预测值 183 pred_x_start = (x_t - torch.sqrt(1.0 - alpha_cumprod_t) 184 * predicted_noise) / torch.sqrt(alpha_cumprod_t) 185 pred_x_start = torch.clamp(pred_x_start, -1.0, 1.0) 186 # torch.clamp:将张量中的元素限制在给定的区间内 187 # 不同于归一化,更像二值化,将超出范围的值截断为边界值 188 # 先预测一个x0,然后根据这个x0预测x_t,相当于锚点 189 190 # 对于t=0,直接返回预测的x_0 191 if t[0] == 0: 192 return pred_x_start 193 194 # 计算alpha_cumprod_prev 195 alpha_cumprod_prev_t = self.alphas_cumprod_prev[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 196 197 # 后验均值的系数 198 posterior_mean_coef1 = torch.sqrt( 199 alpha_cumprod_prev_t) * beta_t / (1.0 - alpha_cumprod_t) 200 posterior_mean_coef2 = torch.sqrt( 201 alpha_t) * (1.0 - alpha_cumprod_prev_t) / (1.0 - alpha_cumprod_t) 202 203 # 计算后验均值 204 posterior_mean = posterior_mean_coef1 * \ 205 pred_x_start + posterior_mean_coef2 * x_t 206 207 # 计算后验方差 208 posterior_variance = self.posterior_variance[t].view(-1, 1, 1, 1) 209 210 # 采样 211 noise = torch.randn_like(x_t) 212 # 叠加噪声,补充细节:把“平均的模糊”变成“具体的纹理” 213 return posterior_mean + torch.sqrt(posterior_variance) * noise 214 215 def p_sample_loop(self, model, shape, num_samples=1): 216 """完整的反向采样过程""" 217 model.eval() 218 with torch.no_grad(): 219 # 从纯噪声开始 220 x = torch.randn(num_samples, *shape, device=self.device) 221 # torch.randn:生成一个张量,张量的元素从标准正态分布中随机采样 222 223 # 逐步去噪 224 for i in reversed(range(self.num_timesteps)): 225 # reversed:返回一个迭代器,迭代器返回列表或元组中的元素,按从后到前的顺序 226 t = torch.full((num_samples,), i, 227 device=self.device, dtype=torch.long) 228 # torch.full:生成一个张量,张量的元素填充为给定值 229 # torch.long:表示整数 230 x = self.p_sample(model, x, t) 231 # 丢进神经网络,统统丢进神经网络! 232 233 model.train() 234 return x
这个模块定义了U-Net、扩散过程
简单介绍一下各个模块:
class SinusoidalPositionalEmbedding(nn.Module): 这个class在forward里定义了一个时间编码器,总之就是把时间步嵌入到向量里,告诉流匹配模型当前到哪个时间步了
class Block(nn.Module): 这个类定义了U-Net网络的基本构成,U-Net由多个略有不同的Block组成 首先是init,定义了各个层 其次是forward,加入了时间嵌入
class SimpleUNet(nn.Module): 这个类具体实现了U-Net
在Block前,又增加了一些层,一些时间嵌入啊、sigmoid啊、线性层之类的
接着就是具体的采样过程了
class DiffusionProcess: 这个类是整个扩散过程与逆扩散过程的实现
在init中,计算了一些后续要用到的量以便查表(比如数学推导中用到的乘法前缀和,以便查表)
q_sample函数即向清晰的图像中加噪声,不同的时间步有不同的噪声量
p_sample即单步去噪过程
p_sample_loop即多次使用单步降噪,获得最终图片
这个文件大概就是这样
接下来是sample.py

1 import torch 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from ddpm_model import SimpleUNet, DiffusionProcess 5 6 7 def sample_and_visualize( 8 model_path='ddpm_mnist_final.pth', 9 num_samples=16, 10 num_timesteps=1000, 11 device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu', 12 save_path='generated_samples.png' 13 ): 14 """从训练好的模型采样并可视化""" 15 print(f"使用设备: {device}") 16 17 # 加载模型 18 model = SimpleUNet(image_size=28, in_channels=1, 19 time_emb_dim=32).to(device) 20 model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)) 21 model.eval() 22 # 网络初始化 23 24 # 创建扩散过程 25 diffusion = DiffusionProcess(num_timesteps=num_timesteps, device=device) 26 27 print(f"生成 {num_samples} 个样本...") 28 29 # 采样 30 samples = diffusion.p_sample_loop( 31 model, shape=(1, 28, 28), num_samples=num_samples) 32 # 去噪过程 33 samples = samples.cpu() 34 # 把数据搬运到cpu上 35 36 # 反归一化:从[-1, 1]回到[0, 1] 37 samples = (samples + 1.0) / 2.0 38 samples = torch.clamp(samples, 0.0, 1.0) 39 # 先归一化,再截断 40 41 # 可视化 42 grid_size = int(np.sqrt(num_samples)) 43 fig, axes = plt.subplots(grid_size, grid_size, figsize=(10, 10)) 44 axes = axes.flatten() 45 46 for i in range(num_samples): 47 img = samples[i].squeeze().numpy() 48 axes[i].imshow(img, cmap='gray') 49 axes[i].axis('off') 50 51 plt.tight_layout() 52 plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight') 53 print(f"生成的样本已保存到 {save_path}") 54 55 return samples 56 57 58 def sample_with_progress( 59 model_path='ddpm_mnist_final.pth', 60 num_samples=16, 61 num_timesteps=1000, 62 device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu', 63 save_path='generation_progress.png' 64 ): 65 """可视化生成过程(中间步骤)""" 66 print(f"使用设备: {device}") 67 68 # 加载模型 69 model = SimpleUNet(image_size=28, in_channels=1, 70 time_emb_dim=32).to(device) 71 model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)) 72 model.eval() 73 74 # 创建扩散过程 75 diffusion = DiffusionProcess(num_timesteps=num_timesteps, device=device) 76 77 # 从纯噪声开始 78 x = torch.randn(1, 1, 28, 28, device=device) 79 80 # 选择要可视化的时间步 81 timesteps_to_show = [999, 800, 600, 400, 200, 100, 50, 0] 82 images = [] 83 84 with torch.no_grad(): 85 for i in reversed(range(num_timesteps)): 86 t = torch.full((1,), i, device=device, dtype=torch.long) 87 x = diffusion.p_sample(model, x, t) 88 89 if i in timesteps_to_show: 90 img = x.cpu().squeeze().numpy() 91 img = (img + 1.0) / 2.0 92 img = np.clip(img, 0.0, 1.0) 93 images.append((i, img)) 94 95 # 可视化生成过程 96 fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(images), figsize=(15, 3)) 97 for idx, (t, img) in enumerate(images): 98 axes[idx].imshow(img, cmap='gray') 99 axes[idx].set_title(f't={t}') 100 axes[idx].axis('off') 101 102 plt.tight_layout() 103 plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight') 104 print(f"生成过程已保存到 {save_path}") 105 106 107 if __name__ == '__main__': 108 # 生成样本 109 samples = sample_and_visualize( 110 model_path='ddpm_mnist_final.pth', 111 num_samples=64, 112 save_path='generated_samples.png' 113 ) 114 115 # 可视化生成过程 116 sample_with_progress( 117 model_path='ddpm_mnist_final.pth', 118 save_path='generation_progress.png' 119 )
def sample_and_visualize
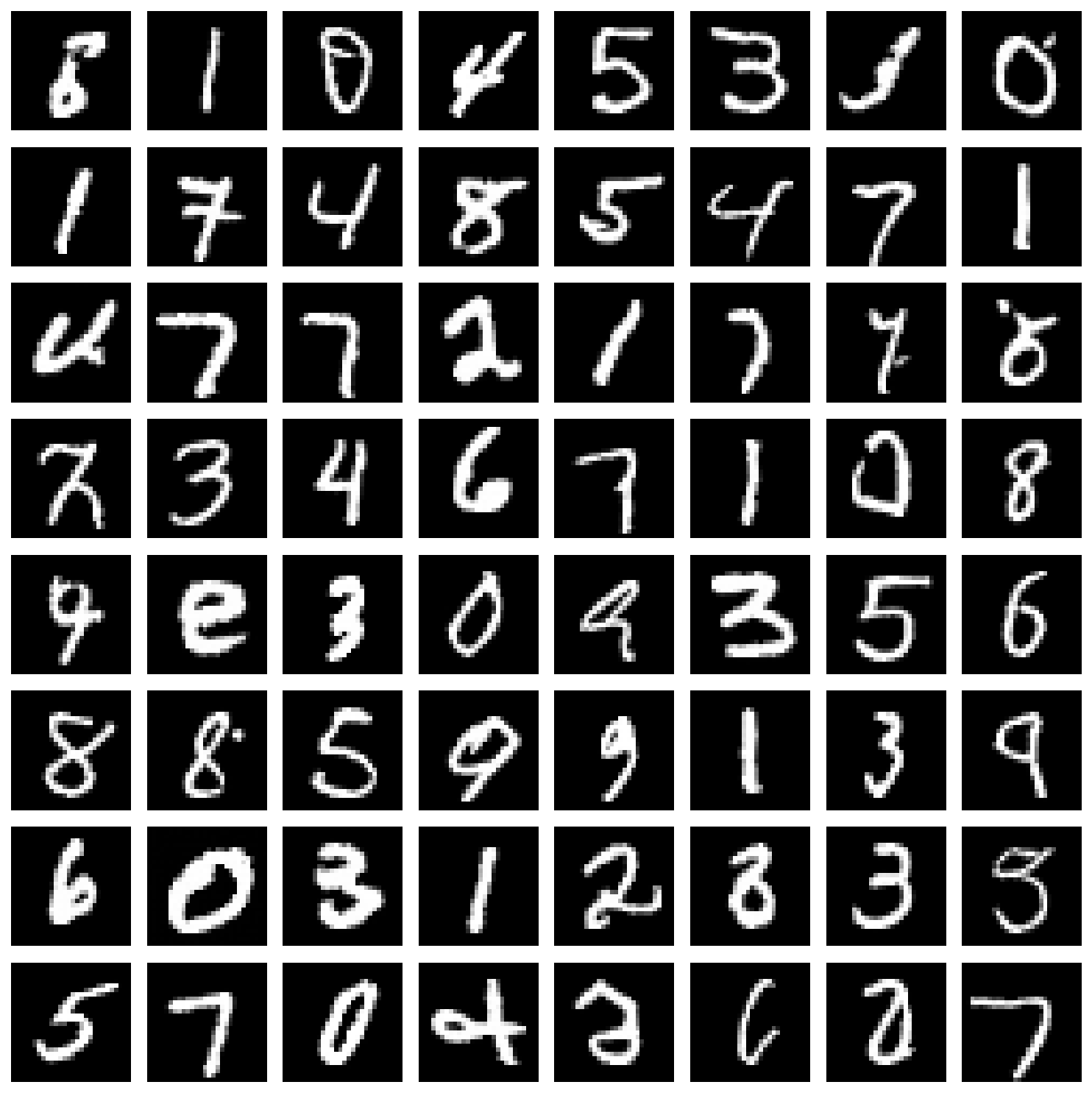
这个函数生成了一批图片,然后一起降噪,并可视化为一个表格(图1所示)
加载模型,生成样本,扩散!
def sample_with_progress
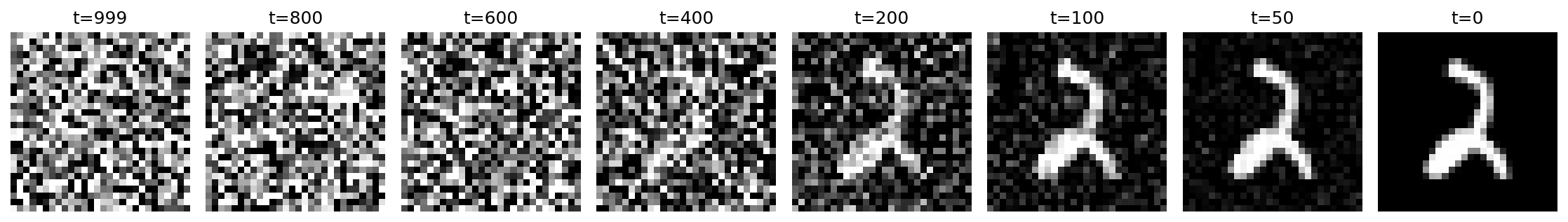
这个函数生成了一张图片,把降噪过程展示了出来(图2所示)
加载模型,生成样本,扩散!
接下来是train.py(其实就没什么好看的了)

1 import torch 2 import torch.nn as nn 3 import torch.optim as optim 4 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 5 from torchvision import datasets, transforms 6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 7 from ddpm_model import SimpleUNet, DiffusionProcess 8 9 10 def train_ddpm( 11 num_epochs=500, 12 batch_size=128, 13 learning_rate=2e-4, 14 num_timesteps=1000, 15 device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' 16 ): 17 """训练DDPM模型生成MNIST数字""" 18 print(f"使用设备: {device}") 19 20 # 数据预处理:归一化到[-1, 1] 21 transform = transforms.Compose([ 22 transforms.ToTensor(), 23 transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # 从[0,1]归一化到[-1,1] 24 ]) 25 26 # 加载MNIST数据集 27 print("加载MNIST数据集...") 28 train_dataset = datasets.MNIST( 29 root='./data', 30 train=True, 31 download=True, 32 transform=transform 33 ) 34 train_loader = DataLoader( 35 train_dataset, 36 batch_size=batch_size, 37 shuffle=True, 38 num_workers=2 39 ) 40 41 # 创建模型和扩散过程 42 model = SimpleUNet(image_size=28, in_channels=1, time_emb_dim=32).to(device) 43 diffusion = DiffusionProcess(num_timesteps=num_timesteps, device=device) 44 45 # 优化器 46 optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) 47 criterion = nn.MSELoss() 48 49 # 训练循环 50 print("开始训练...") 51 losses = [] 52 53 for epoch in range(num_epochs): 54 epoch_loss = 0.0 55 num_batches = 0 56 57 for batch_idx, (images, _) in enumerate(train_loader): 58 images = images.to(device) 59 60 # 随机采样时间步 61 t = torch.randint(0, num_timesteps, (images.shape[0],), device=device) 62 63 # 采样噪声 64 noise = torch.randn_like(images) 65 66 # 前向扩散:添加噪声 67 x_t = diffusion.q_sample(images, t, noise) 68 69 # 预测噪声 70 predicted_noise = model(x_t, t) 71 72 # 计算损失 73 loss = criterion(predicted_noise, noise) 74 75 # 反向传播 76 optimizer.zero_grad() 77 loss.backward() 78 # 梯度裁剪 79 torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 1.0) 80 optimizer.step() 81 82 epoch_loss += loss.item() 83 num_batches += 1 84 85 if batch_idx % 100 == 0: 86 print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Batch [{batch_idx}/{len(train_loader)}], Loss: {loss.item():.6f}") 87 88 avg_loss = epoch_loss / num_batches 89 losses.append(avg_loss) 90 91 print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], 平均损失: {avg_loss:.6f}") 92 93 # 每10个epoch保存一次模型 94 if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0: 95 torch.save(model.state_dict(), f'ddpm_mnist_epoch_{epoch+1}.pth') 96 print(f"模型已保存到 ddpm_mnist_epoch_{epoch+1}.pth") 97 98 # 保存最终模型 99 torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'ddpm_mnist_final.pth') 100 print("最终模型已保存到 ddpm_mnist_final.pth") 101 102 # 绘制损失曲线 103 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) 104 plt.plot(losses) 105 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 106 plt.ylabel('Loss') 107 plt.title('Training Loss') 108 plt.grid(True) 109 plt.savefig('training_loss.png') 110 print("损失曲线已保存到 training_loss.png") 111 112 return model, diffusion 113 114 115 if __name__ == '__main__': 116 model, diffusion = train_ddpm( 117 num_epochs=500, 118 batch_size=128, 119 learning_rate=2e-4, 120 num_timesteps=1000 121 )
3.Q&A
列一些我学习过程中遇到的比较神奇的问题吧,记录一下,也希望能够帮助到一些人入门(坑)
感谢gemini的大力支持没有gemini我死这了
Q1:为什么时间码与前向传播的特征直接就相加了?这样不会导致特征消融或是时间码重复吗?比如两个不同的图片,加上不同的时间码反而相同了?
A1:应该不会,这个时间码更像一种“偏置”,即将整个图片的像素都“变亮”或者“变暗”了固定值。当然,这里是对于提取出的特征的偏执,所以不仅不会重复,还利于广播(反正我是似懂非懂的)
Q2:为什么在单步去噪过程中要直接预测一个x0(即初始图像)呢?
A2:在数学推导里有出现x0,但是我们不知道真正的x0,所以只能用现阶段的模型预测一个,不管它有多离谱,先用着,有比没有强,当作一个锚点来进行指导(依旧似懂非懂,反正工程上存在肯定有它的好处就对了)
翻了一下对着gemini哈气的界面,暂时就找到这两个。那大概就写到这吧
(完)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号