CF2048 VP 记录
C
巧妙的贪心.
最高位为 \(1\) 那么首先整个串要选,接着考虑按位贪心,找到从高到低第一位为 \(0\) 的位置 \(i\),我们希望改这一位,所以串长 \(len\ge n-i+1\);我们不希望改变前缀 \(1\),所以串长 \(len\le n-i+1\). 综上串长只可能为 \(n-i+1\),把这些串拉出来取异或最大值即可. 时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\).
然而上述做法由于要实现一些字符串操作,有人写挂破防了,所以还有一个 \(O(n)\) 的思路.
找出前缀第一个极长全 \(0\) 段 \([l,r]\),我们希望尽可能把前缀 \(0\) 变成 \(1\),根据上面的结论,发现这个只能用前面极长全 \(1\) 段 \([1,l-1]\) 来做. 所以前缀最多能改的 \(0\) 个数为 \(x=\min(l-1,r-l+1)\),选择的子串为 \([l-x,l-x+(n-i+1)-1]\).
还需要特判全 \(1\) 串.
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e3 + 10;
int T, n; char s[maxn];
void solve() {
cin >> (s + 1); n = strlen(s + 1); int cnt1 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cnt1 += s[i] == '1';
cout << "1 " << n << " "; if(cnt1 == n) {cout << "1 1\n"; return;}
int l = 1, r;
while(s[l] == '1') l++; r = l;
while(s[r + 1] == '0' && r + 1 <= n) r++;
int x = min(l - 1, r - l + 1);
cout << l - x << " " << l - x + (n - l + 1) - 1 << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> T; while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
D
D<C.
考虑 \(a_1\) 的排名,若所有 \(b_i\le a_1\) 则 \(a_1\) 必然并列第一. 除此之外,\(a_i\) 排名比 \(a_1\) 靠前当且仅当存在 \(b_i\) 满足 \(a_1<b_i\le a_i\),此时 \(b_i\) 对排名的贡献是这样 \(a_i\) 的个数 \(+1\),设为 \(ans_i\). 一场比赛的贡献就是所有题目 \(ans_i\) 的最大值. 并列第一有 \(ans_i=1\).
考虑计算不同划分方式 \(k\) 的答案,先对 \(ans_i\) 从小到大排序,一个贪心的想法是划分为 \([1,k],[k+1,2k],\cdots\),这个容易用扰动法证明. 所以可以直接调和级数统计答案,时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\).
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
int T, n, m, a[maxn], b[maxn];
long long ans[maxn];
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> b[i], ans[i] = a[1] >= b[i];
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) if(!ans[i]) ans[i] = n - (lower_bound(a + 1, a + n + 1, b[i]) - a) + 2;
sort(ans + 1, ans + m + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) for(int j = i + i; j <= m; j += i) ans[i] += ans[j];
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == m];
}
int main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> T; while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
E
意义不明.
要求总边数为 \(2nm\),由于不能成环,所以我们希望用每种颜色把 \(2n+m\) 个点连成树,即边数至多为 \(n(2n+m-1)\). 解得 \(m\le 2n-1\). 先拿这个必要条件判一下.
考虑对于 \(m=2n-1\) 的进行构造,那么其他情况限制更松,肯定可以沿用相同的构造. 由于右部点度数为 \(2n\),令每种颜色连两条边,再考虑在左部点怎么选两个点,发现每次循环位移一位,连相邻两点即可. 下面是 \(n=2,m=3\) 的一个例子.
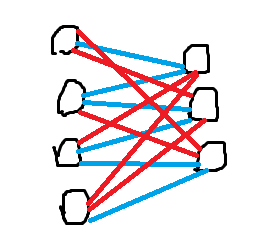
此时输出即为:
1 2 2
1 1 2
2 1 1
2 2 1
归纳一下,发现对于左部点编号为 \(i\),右部点编号为 \(j\),颜色为:
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int T, n, m;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
if(m > 2 * n - 1) {cout << "NO\n"; return;}
cout << "YES\n";
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cout << ((i + j) % (2 * n)) / 2 + 1 << " \n"[j == m];
}
}
}
int main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> T; while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
F
DP 好题.
G
组合计数好题. 有时间回来补.
H
鬼题.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号