周记2
这个周做的题很杂,有DP,也有线段树。
。。。第一天(想奋斗DP)
Luogu P1220 关路灯
题目描述
某一村庄在一条路线上安装了 \(n\) 盏路灯,每盏灯的功率有大有小(即同一段时间内消耗的电量有多有少)。老张就住在这条路中间某一路灯旁,他有一项工作就是每天早上天亮时一盏一盏地关掉这些路灯。
为了给村里节省电费,老张记录下了每盏路灯的位置和功率,他每次关灯时也都是尽快地去关,但是老张不知道怎样去关灯才能够最节省电。他每天都是在天亮时首先关掉自己所处位置的路灯,然后可以向左也可以向右去关灯。开始他以为先算一下左边路灯的总功率再算一下右边路灯的总功率,然后选择先关掉功率大的一边,再回过头来关掉另一边的路灯,而事实并非如此,因为在关的过程中适当地调头有可能会更省一些。
现在已知老张走的速度为 \(1m/s\),每个路灯的位置(是一个整数,即距路线起点的距离,单位:\(m\))、功率(\(W\)),老张关灯所用的时间很短而可以忽略不计。
请你为老张编一程序来安排关灯的顺序,使从老张开始关灯时刻算起所有灯消耗电最少(灯关掉后便不再消耗电了)。
输入格式
第一行是两个数字 \(n\)(表示路灯的总数)和 \(c\)(老张所处位置的路灯号);
接下来 \(n\) 行,每行两个数据,表示第 \(1\) 盏到第 \(n\) 盏路灯的位置和功率。数据保证路灯位置单调递增。
输出格式
一个数据,即最少的功耗(单位:\(J\),\(1J=1W\times s\))。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
5 3
2 10
3 20
5 20
6 30
8 10
输出 #1
270
说明/提示
样例解释
此时关灯顺序为 3 4 2 1 5。
数据范围
\(1\le n\le50\),\(1\le c\le n\),\(1\le W_i \le 100\)。
这里我们设 \(dp[l][r][0/1]\) 表示已经关完了 \(l\sim r\) ,当前停留在 \(l/r\) ,消耗的最小电量是多少。
所以,转移式就显而易见(看代码)。
点击查看代码
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
const int N = 60;
int n, c;
int p[N], sum[N];
int dp[N][N][2];
int calc(int i, int j, int l, int r)
{
return (p[j] - p[i]) * (sum[l] + sum[n] - sum[r - 1]);
}
int main()
{
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof(dp));
cin >> n >> c;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int a;
cin >> p[i] >> a;
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a;
}
dp[c][c][0] = dp[c][c][1] = 0;
for (int j = c; j <= n; ++j)
for (int i = j - 1; i >= 1; --i)
{
dp[i][j][0] = std::min(dp[i + 1][j][0] + calc(i, i + 1, i, j + 1), dp[i + 1][j][1] + calc(i, j, i, j + 1));
dp[i][j][1] = std::min(dp[i][j - 1][1] + calc(j - 1, j, i - 1, j), dp[i][j - 1][0] + calc(i, j, i - 1, j));
}
cout << std::min(dp[1][n][0], dp[1][n][1]) << '\n';
return 0;
}
第二天(被诱导着去奋斗线段树了):
Luogu P5522 [yLOI2019] 棠梨煎雪
题目背景
岁岁花藻檐下共将棠梨煎雪,
自总角至你我某日辗转天边。
天淡天青,宿雨沾襟,
一年一会信笺却只见寥寥数言。
——银临《棠梨煎雪》
题目描述
扶苏正在听《棠梨煎雪》的时候,@spitfirekindergarten 发来一道 IOI2018 集训队作业题:我切了这集训队题,辣鸡扶苏快过来做题。扶苏定睛一看,这不 s* 题嘛,写了一发交上去才发现自己看错题目了。但是写完的代码不能浪费,于是就有了这道题。
歌词中的主人公与她的朋友一年会有一次互相写信给对方,一共通信了 \(m\) 年。为了简化问题,我们认为她们每封信的内容都是一条二进制码,并且所有二进制码的长度都是 \(n\)。即每封信的内容都是一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串,这个字符串只含字符 0 或 1。
这天她拿出了朋友写给她的所有信件,其中第 \(i\) 年的写的信件编号为 \(i\)。由于信件保存时间过久,上面有一些字符已经模糊不清,我们将这样的位置记为 ?,? 字符可以被解释为 0 或 1。由于她的朋友也是人,符合人类的本质,所以朋友在一段连续的时间中书写的内容可能是相同的。现在她想问问你,对于一段连续的年份区间 \([l,r]\) 中的所有信件,假如朋友在这段时间展示了人类的本质,所写的是同一句话,那么这一句话一共有多少种可能的组成。也即一共有多少字符串 \(S\),满足在这个区间内的所有信件的内容都可能是 \(S\)。
一个长度为 \(n\) 的只含 0,1,? 的字符串 \(A\) 可能是一个字符串 \(B\) 当且仅当 \(B\) 满足如下条件:
- \(B\) 的长度也是 \(n\) 。
- \(B\) 中只含字符
0,1。 - \(A\) 中所有为
0的位置在 \(B\) 中也是0。 - \(A\) 中所有为
1的位置在 \(B\) 中也是1。 - \(A\) 中为
?的位置在 \(B\) 中可以为0也可以是1。
同时她可能会突然发现看错了某年的信的内容,于是她可能会把某一年的信的内容修改为一个别的只含 0,1,? 的长度为 \(n\) 的字符串。
输入格式
每个输入文件中都有且仅有一组测试数据。
输入数据第一行为三个用空格隔开的整数,分别代表代表字符串长度 \(n\),字符串个数 \(m\) 和操作次数 \(q\)。
下面 \(m\) 行,每行是一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串,第 \((i + 1)\) 行的字符串 \(s_i\) 代表第 \(i\) 年信的内容。
下面 \(q\) 行,每行的第一个数字是操作编号 \(opt\)。
- 如果 \(opt=0\),那么后面接两个整数 \([l,~r]\),代表一次查询操作。
- 如果 \(opt=1\),那么后面接一个整数 \(pos\),在一个空格后会有一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串 \(t\),代表将第 \(pos\) 个字符串修改为新的字符串 \(t\)。
输出格式
为了避免输出过大,请你输出一行一个数代表所有查询的答案异或和对 \(0\) 取异或的结果。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
3 3 5
010
0?0
1?0
0 1 2
0 2 3
1 3 0??
0 2 3
0 1 3
输出 #1
2
说明/提示
样例 1 解释
- 对于第一次询问,只有串
010符合要求。 - 对于第二次询问,由于第二个串的第一位为
0,第三个串的第一位为1,故没有串符合要求。 - 修改后将第三个串修改为
0??。 - 对于第四次询问,有两个串符合要求,分别为
000和010。 - 对于第五次询问,只有
010符合要求。
故答案为 \(1,0,2,1\),他们的异或和再异或 \(0\) 的值为 \(2\)。
数据规模与约定
本题采用多测试点捆绑测试,共有 7 个子任务。
| 子任务编号 | $m = $ | $q = $ | $n = $ | 子任务分数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(1\) | \(1\) | \(0\) | \(1\) | \(5\) |
| \(2\) | \(102\) | \(102\) | \(10\) | \(10\) |
| \(3\) | \(1003\) | \(1003\) | \(10\) | \(15\) |
| \(4\) | \(1004\) | \(10004\) | \(30\) | \(15\) |
| \(5\) | \(100005\) | \(500005\) | \(1\) | \(15\) |
| \(6\) | \(100006\) | \(50006\) | \(30\) | \(10\) |
| \(7\) | \(100007\) | \(1000007\) | \(30\) | \(30\) |
对于全部的测试点,保证:
- \(1 \leq m \leq 10^5 + 7\),\(0 \leq q \leq 10^6 + 7\),\(1 \leq n \leq 30\)。
- \(0 \leq opt \leq 1\),\(1 \leq pos \leq m\),\(1 \leq l \leq r \leq m\)。
- \(s_i, t\) 的长度均为 \(n\) 且只含有字符
0,1,?。 - 输入字符串的总长度不超过 \(5 \times 10^6\)。数据在 Linux 下生成,即换行符不含
\r。
提示
- 请注意常数因子对程序效率造成的影响。
- 请注意数据读入对程序效率造成的影响。
- 请注意输入的问号为嘤文问号,即其 ASCII 值为 \(63\)
注: 为减少错误做法的通过率,时限于 2020 年 7 月由 2000ms 改为 1500ms
这道题一开始想的字符串 \(+\) 线段树。
代码(就线段树的 \(+\) 运算符需要大概看一看):
点击查看代码
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
const int N = 1e5 + 7;
int n, m, q;
struct Node
{
string s;
bool f;
Node() : s(""), f(true) {}
void init(string str)
{
f = true;
s = str;
}
friend Node operator+(const Node &a, const Node &b)
{
Node ret;
ret.f = a.f && b.f;
if (!ret.f)
return ret;
ret.s = a.s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (a.s[i] != b.s[i] && a.s[i] != '?' && b.s[i] != '?')
{
ret.f = false;
return ret;
}
if (a.s[i] == '?' && b.s[i] != '?')
ret.s[i] = b.s[i];
else if (a.s[i] != '?' && b.s[i] == '?')
ret.s[i] = a.s[i];
else if (a.s[i] == '?' && b.s[i] == '?')
ret.s[i] = '?';
}
return ret;
}
}z[N << 2];
string s[N];
void build(int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
z[rt].init(s[l]);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
z[rt] = z[rt << 1] + z[rt << 1 | 1];
}
void modify(int l, int r, int rt, int p, string s)
{
if (l == r)
{
z[rt].init(s);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m)
modify(lson, p, s);
else
modify(rson, p, s);
z[rt] = z[rt << 1] + z[rt << 1 | 1];
}
Node query(int l, int r, int rt, int nowl, int nowr)
{
if (nowl <= l && r <= nowr)
return z[rt];
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
Node left, right;
bool has_left = false, has_right = false;
if (nowl <= m)
{
left = query(lson, nowl, nowr);
has_left = true;
}
if (nowr > m)
{
right = query(rson, nowl, nowr);
has_right = true;
}
if (has_left && has_right)
return left + right;
else if (has_left)
return left;
else
return right;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
cin >> s[i];
s[i] = ' ' + s[i];
}
build(1, m, 1);
int ans = 0;
while (q--)
{
int opt;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 0)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
Node p = query(1, m, 1, l, r);
if (!p.f)
{
ans ^= 0;
continue;
}
int now = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (p.s[i] == '?')
now *= 2;
ans ^= now;
}
else
{
int p;
string noww;
cin >> p >> noww;
noww = ' ' + noww;
modify(1, m, 1, p, noww);
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
复杂度是什么呢?是 \(\mathcal O(mq\log n)\) 的。
貌似过不了(\(70pts\))。
我们考虑二进制。
我们用 \(x\) 表示当前节点的每一位是否确定,\(y\) 表示如果确定,值是多少。
于是便优化到了 \(\mathcal O(q\log n)\)(注意看 \(+\) 运算符重载中的位运算符号,一定不要把 & 写成了 &&)。
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
const int N = 1e5 + 7;
int n, m, q;
struct Node
{
int x, y;
bool f;
Node() {}
void init(int x, int y)
{
f = true;
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
friend Node operator+(const Node &a, const Node &b)
{
Node ret;
ret.x = a.x | b.x;
ret.y = a.y | b.y;
if (((a.x & b.x) & (a.y ^ b.y)) || (!a.f) || (!b.f))
ret.f = false;
else
ret.f = true;
return ret;
}
}z[N << 2];
int x[N], y[N];
void build(int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
z[rt].init(x[l], y[l]);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
z[rt] = z[rt << 1] + z[rt << 1 | 1];
}
void modify(int l, int r, int rt, int p, int x, int y)
{
if (l == r)
{
z[rt].init(x, y);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m)
modify(lson, p, x, y);
else
modify(rson, p, x, y);
z[rt] = z[rt << 1] + z[rt << 1 | 1];
}
Node query(int l, int r, int rt, int nowl, int nowr)
{
if (nowl <= l && r <= nowr)
return z[rt];
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (nowl <= m)
{
if (nowr > m)
return query(lson, nowl, nowr) + query(rson, nowl, nowr);
else
return query(lson, nowl, nowr);
}
else
return query(rson, nowl, nowr);
}
#define root 1, m, 1
char noww[40];
char s[N][40];
void readin(int& x)
{
x = 0;
char c = getchar();
int f = 1;
while (c < '0' || c > '9')
{
if (c == '-')
f = -f;
c = getchar();
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
{
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
c = getchar();
}
x = x * f;
}
int main()
{
readin(n), readin(m), readin(q);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
cin >> (s[i] + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
if (s[i][j] != '?')
{
x[i] |= (1 << (j - 1));
y[i] |= ((s[i][j] - '0') << (j - 1));
}
}
}
// for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
// cout << s[i] << '\n';
build(root);
int ans = 0;
while (q--)
{
int opt;
readin(opt);
if (opt == 0)
{
int l, r;
readin(l), readin(r);
int now = 1;
Node p = query(root, l, r);
if (p.f == 0)
{
ans ^= 0;
continue;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!(p.x & (1 << (i - 1))))
now <<= 1;
ans ^= now;
}
else
{
int p;
readin(p), cin >> (noww + 1);
int x, y;
x = y = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (noww[i] != '?')
{
x |= (1 << (i - 1));
y |= ((noww[i] - '0') << (i - 1));
}
}
modify(root, p, x, y);
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
...
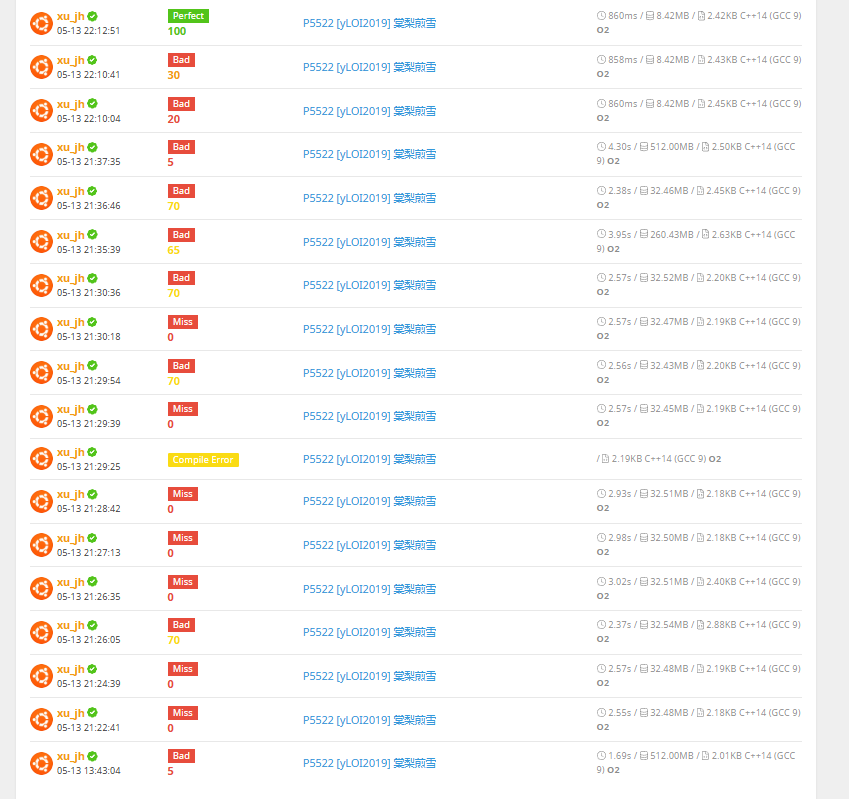
众所周知,扶苏出的题对我们的思维能力和代码能力的考察很多。
第 \(n\) 天(不知为何,又开始图论):
Luogu P4568 [JLOI2011] 飞行路线
题目描述
Alice 和 Bob 现在要乘飞机旅行,他们选择了一家相对便宜的航空公司。该航空公司一共在 \(n\) 个城市设有业务,设这些城市分别标记为 \(0\) 到 \(n-1\),一共有 \(m\) 种航线,每种航线连接两个城市,并且航线有一定的价格。
Alice 和 Bob 现在要从一个城市沿着航线到达另一个城市,途中可以进行转机。航空公司对他们这次旅行也推出优惠,他们可以免费在最多 \(k\) 种航线上搭乘飞机。那么 Alice 和 Bob 这次出行最少花费多少?
输入格式
第一行三个整数 \(n,m,k\),分别表示城市数,航线数和免费乘坐次数。
接下来一行两个整数 \(s,t\),分别表示他们出行的起点城市编号和终点城市编号。
接下来 \(m\) 行,每行三个整数 \(a,b,c\),表示存在一种航线,能从城市 \(a\) 到达城市 \(b\),或从城市 \(b\) 到达城市 \(a\),价格为 \(c\)。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数,为最少花费。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
5 6 1
0 4
0 1 5
1 2 5
2 3 5
3 4 5
2 3 3
0 2 100
输出 #1
8
说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于 \(30\%\) 的数据,\(2 \le n \le 50\),\(1 \le m \le 300\),\(k=0\)。
对于 \(50\%\) 的数据,\(2 \le n \le 600\),\(1 \le m \le 6\times10^3\),\(0 \le k \le 1\)。
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,\(2 \le n \le 10^4\),\(1 \le m \le 5\times 10^4\),\(0 \le k \le 10\),\(0\le s,t,a,b < n\),\(a\ne b\),\(0\le c\le 10^3\)。
另外存在一组 hack 数据。
这不就是分层图跑最短路的板子吗。
点击查看代码
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define pii std::pair<int, int>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
const int N = 1.1e5 + 10;
int dist[N];
std::priority_queue<pii, std::vector<pii>, std::greater<pii>> q;
std::vector<pii> e[N];
int main()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
int s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
for (int j = 0; j <= k; ++j)
{
e[j * n + u].push_back({j * n + v, w});
e[j * n + v].push_back({j * n + u, w});
if (j < k)
{
e[j * n + u].push_back({(j + 1) * n + v, 0});
e[j * n + v].push_back({(j + 1) * n + u, 0});
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i)
{
dist[i * n + s] = 0;
q.push({0, i * n + s});
}
while (!q.empty())
{
auto [val, now] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (dist[now] != val)
continue;
for (auto [to, w] : e[now])
{
if (dist[to] > dist[now] + w)
{
dist[to] = dist[now] + w;
q.push({dist[to], to});
}
}
}
int ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i)
{
ans = std::min(ans, dist[i * n + t]);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
然后,又开始颓主席树。
Luogu P1533 可怜的狗狗
题目描述
小卡家有 \(n\) 只狗,由于品种、年龄不同,每一只狗都有一个不同的漂亮值。漂亮值与漂亮的程度成反比(漂亮值越低越漂亮),吃饭时,狗狗们会按顺序站成一排等着主人给食物。
可是嘉嘉真的很懒,他才不肯喂这么多狗呢,这多浪费时间啊,于是他每次就只给第 \(i\) 只到第 \(j\) 只狗中第 \(k\) 漂亮的狗狗喂食(好狠心的人啊)。而且为了保证某一只狗狗不会被喂太多次,他喂的每个区间 \([i,j]\) 不互相包含。
输入格式
第一行输入两个数 \(n,m\), \(m\) 表示嘉嘉喂食的次数
第二行 \(n\) 个整数,表示第 \(i\) 只狗的漂亮值为 \(a_i\)。
接下来 \(m\) 行,每行 \(3\) 个整数 \(i,j,k\),表示询问这次喂食喂第 \(i\) 到第 \(j\) 只狗中第 \(k\) 漂亮的狗的漂亮值。
输出格式
\(m\) 行,每行一个整数,表示每一次喂的那只狗漂亮值为多少。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
7 2
1 5 2 6 3 7 4
1 5 3
2 7 1
输出 #1
3
2
说明/提示
\(1\le n \le 3\times 10^5 ,1\le m \le5\times10^4,0\le a_i<2^{31}\),且 \(a_i\) 互不相同。
哈,主席树板子。
但是。。。
不加离散化根本过不了,用纯 map 离散化也过不了。
所以导致了:
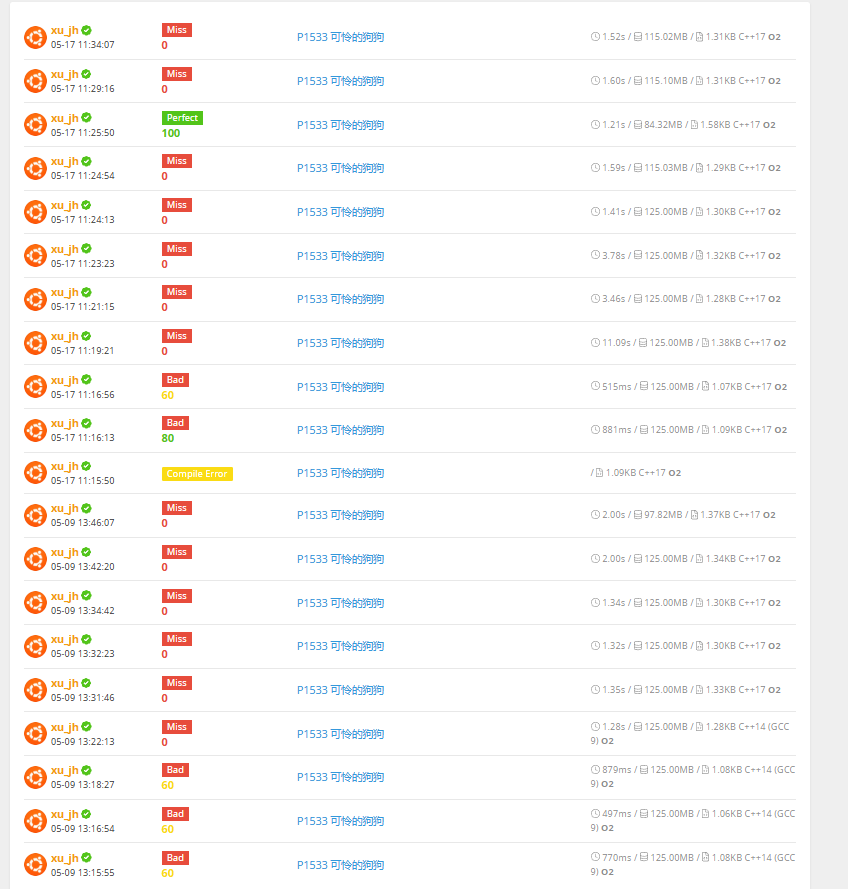

但。。。我仍不太懂为什么不加离散化不行。
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::map;
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
struct Node {
int l, r, sum;
} z[N * 30];
int cnt;
int a[N], b[N];
int root[N];
map<int, int> ma;
void update(int x) {
z[x].sum = z[z[x].l].sum + z[z[x].r].sum;
}
int modify(int l, int r, int rt, int p, int k) {
int q = ++cnt;
z[q] = z[rt];
if (l == r) {
z[q].sum += k;
return q;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m)
z[q].l = modify(l, m, z[q].l, p, k);
else
z[q].r = modify(m + 1, r, z[q].r, p, k);
update(q);
return q;
}
int query(int x1, int x2, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l == r)
return l;
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
int left_sum = z[z[x2].l].sum - z[z[x1].l].sum;
if (left_sum >= k)
return query(z[x1].l, z[x2].l, l, m, k);
else
return query(z[x1].r, z[x2].r, m + 1, r, k - left_sum);
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> a[i];
b[i] = a[i];
}
std::sort(b + 1, b + n + 1);
int tot = std::unique(b + 1, b + n + 1) - b - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i)
ma[b[i]] = i;
int maxv = tot;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
root[i] = modify(1, maxv, root[i - 1], ma[a[i]], 1);
while (m--) {
int x, y, k;
cin >> x >> y >> k;
int pos = query(root[x - 1], root[y], 1, maxv, k);
cout << b[pos] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
总结:这个周就是在跟各种题打游击战。。。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号