Ros2 学习日志
Node
节点是 Ros2 控制机器人的底层部分。
通过节点间的通讯,来实现机器人的不同功能并封装,实现功能包。
New_Node
class my_node : public rclcpp :: Node {
// 使用类继承的方法定义一个新节点类,rclcpp :: Node 是 Ros2 里已经给我们提供好的一个类
public:
// 构造函数,有一个参数为节点名称
Niluo_Node (std :: string name) : Node (name) {
name = "niluo";
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "大家好,我是 %s", name.c_str ());
// this 指代当前类,get_logger 表示获取一个与 “特定实体(通常是节点)绑定的日志器实例”
// 通过获取该日志来保证日志输出的节点级一致性。
}
private: // empty
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
/*
argc,argv 是 mian 函数的命令行参数载体。
argc:代表启动程序时传入的参数总数量
argv:储存了具体运行参数。
有例:./my_node --ros-args -r __node:=new_talker
则有 argc = 4(因为参数有 ./my_node、--ros-args、-r、__node:=new_talker,共 4 个);
argv[0] = "./my_node"(程序路径);
argv[1] = "--ros-args"(ROS2 的命令行参数标识);
argv[2] = "-r"(ROS2 参数重映射的标识);
argv[3] = "__node:=new_talker"(将节点名重命名为 new_talker)。
*/
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto node = std :: make_shared <my_node> ("node");
// 使用 make_shared 共享指针定义一个节点
rclcpp :: spin (node);
// 让任务保持运行,知道检测到有 ctrl+c 输入
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
// 关闭任务
return 0;
}
顺便在这里记录一些编译相关指令。
ros2 pkg create [the name of the package] --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp
// 用 ros2 建包;ament_cmake 是一种常见类型;并且声明对 rclcpp 已有功能包的依赖
colcon build --packages-select [the name of the package]
// 查询某个目录进行指定编译
colcon build
// 编译工作空间下的所有文件
rm -rf build install log
// 删除当前工作空间下的编译环境(可用于处理环境污染,清空工作空间)
source install/setup.bash
// 用于加载编译环境变量
ros2 run [the name of the package] [the name of the code]
// 执行某个功能包下的特定任务代码。
以及典型文件结构。
. // 工作空间
└── src // 源文件
└── my_node // 一个功能包
├── CMakeLists.txt // CMake 编译助手
├── include
│ └── my_node
├── package.xml // 建包助手
└── src
└── my_node.cpp // 代码源文件
5 directories, 3 files
其中 CMakeLists.txt 和 package.xml 有他们特殊的语法结构,掌握以下基础部分即可。
这两部分结构往往会在报错提示里提醒你,无需过于在意。
add_executable (node src/my_node.cpp) // 结合源代码文件可执行节点文件
ament_target_dependencies (node rclcpp) // 为 node(示例节点)添加 rclcpp 功能包依赖
install (TARGETS
my_node
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
// 表示安装可执行文件 my_node
<depend>rclcpp</depend> // 申明依赖
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
Topic
创建一个社区话题,创作者发布作品,粉丝接受作品。作品具有统一格式,也就是 ros2 定义的消息接口。
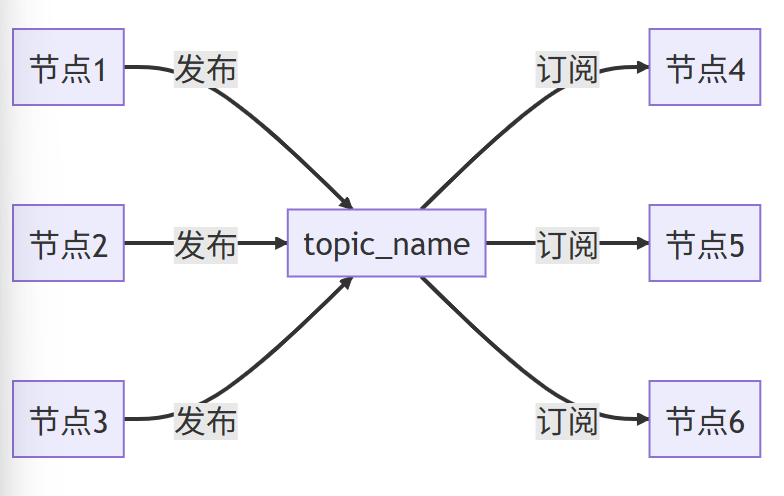
Niluo_Node
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp" // 消息接口包头文件,调用前需声明依赖
class Niluo_Node : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
Niluo_Node (std :: string name) : Node (name) {
name = "niluo";
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "大家好,我是 %s", name.c_str ());
// 打个招呼吧
publisher_ = this -> create_publisher <std_msgs :: msg :: String> ("mingyue", 10);
// 创建发布者,这里是一个 msg 接口包里自带的 String 类型接口,话题名字为 mingyue
timer_ = this -> create_wall_timer (
std :: chrono :: milliseconds (5000),
std :: bind (&Niluo_Node :: timer_callback, this)
);
// 创建定时器,5000ms 为周期,定时发布
// bind 的作用是捆绑,在传参传入回调函数时需要捆绑一个指针。
}
private:
void timer_callback () {
// 定时器回调函数
static int Tot = 1;
std_msgs :: msg :: String message;
message.data = "我上了第 " + std :: to_string (Tot++) + " 节工程设计";
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "%s", message.data.c_str ());
// 日志打印,始终牢记日志和节点的相关性
publisher_ -> publish (message);
// 使用内置函数发布消息
}
rclcpp :: TimerBase :: SharedPtr timer_;
// 声名定时器指针
rclcpp :: Publisher <std_msgs :: msg :: String> :: SharedPtr publisher_;
// 声明话题发布者指针
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto node = std :: make_shared <Niluo_Node> ("Niluo_Node");
rclcpp :: spin (node);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
Student_Node
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp"
class Student_Node : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
// 构造函数,有一个参数为节点名称
Student_Node (std :: string name) : Node (name) {
name = "waya";
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "大家好,我是 %s", name.c_str ());
subscribe_ = this -> create_subscription <std_msgs :: msg :: String> (
"mingyue",
10,
std :: bind (&Student_Node :: receive_callback, this, std :: placeholders :: _1)
);
// 订阅名为 mingyue 的 string 类型话题,且绑定一个回调函数。
// 其中的数字 10 表示 qos,指消息缓存长度(最多可以缓存十条消息)
}
private:
void receive_callback (const std_msgs :: msg :: String :: SharedPtr msg) {
// 收到话题数据的回调函数,可以在这里对收到的话题信息进行一些处理
}
rclcpp :: Subscription <std_msgs :: msg :: String> :: SharedPtr subscribe_;
// 声明话题订阅者指针
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto node = std :: make_shared <Student_Node> ("Student_Node");
rclcpp :: spin (node);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
Service
一个服务端提供服务,多个客户端享受服务,这或许是大部分应用程序的使用模式。
注意到上一部分的 Topic 是单向的通信方式,我们无法得知在消息给出后,接收端做出了怎样的行为,又有怎样的反馈。
而 Service 就是用来构建这样的请求-反馈机制
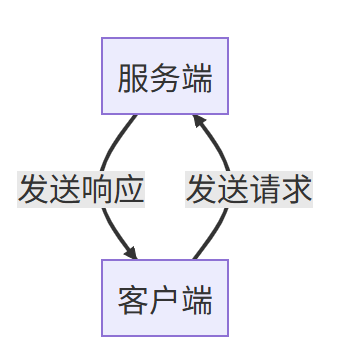
在这里使用了一个自定义 srv 类型接口,以如下结构进行编写。在编译后调用方式就和 ros2 自带接口一样。
└── lr_interfaces // 接口功能包
├── CMakeLists.txt // CMake 编译助手
├── package.xml // 建包助手
└── srv
└── Climb.srv // 接口定义文件
float64 target_height
---
float64 current_height
int32 days
用分割线隔开 Request 和 Response 两种信息。
Service
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/srv/climb.hpp" // 声明我们的自定义接口
using std :: placeholders :: _1;
using std :: placeholders :: _2;
// 提前定义占位符
class CarService : public rclcpp :: Node {
// ros2 的大部分功能都是基于节点实现的,故而都需要先定义节点的继承类
public:
CarService () : Node ("car_service") {
service_ = this -> create_service <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb> (
"car_climb",
std :: bind (&CarService :: handle_service, this, _1, _2)
);
// 创建一个服务端,名字叫 car_climb
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Car Climb Service is ready.");
}
private:
rclcpp :: Service <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb> :: SharedPtr service_;
// 声明一个服务端
void handle_service (
const std :: shared_ptr <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb :: Request> request,
std :: shared_ptr <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb :: Response> response) {
// 处理收到的服务请求,传入参数为请求、回应两个类型
// 后面是机器人运动逻辑
double target = request -> target_height, current = 0;
int days = 0;
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Received target height: %.2f", target);
while (current < target) {
current += 3.0;
days++;
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Day %d: Current height = %.2f", days, current);
}
response -> days = days;
response -> current_height = current;
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Climb completed in %d days to reach height %.2f", days, current);
}
};
int main (int argc, char ** argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
rclcpp :: spin (std :: make_shared <CarService> ());
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
Client
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/srv/climb.hpp"
#include <chrono>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std :: chrono_literals;
class CarClient : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
CarClient () : Node ("car_client") {
client_ = this -> create_client <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb> ("car_climb");
// 创建一个客户端
while (!client_ -> wait_for_service (1s)) {
// 需要等待服务端上线再进行后续使用
if (!rclcpp :: ok ()) {
// 服务端出现问题,这个 ok 会返回 false,此时服务过程中断
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Client interrupted while waiting for service. Exiting.");
return ;
}
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Service not available, waiting again...");
}
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Service is available.");
}
void send_request (double target_height) {
// 发送一个请求
auto request = std :: make_shared <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb :: Request> ();
request -> target_height = target_height;
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Sending request with target height: %.2f", target_height);
auto result_future = client_ -> async_send_request (
request,
std :: bind (&CarClient :: response_callback, this, std :: placeholders :: _1)
);
/*
简单区分一下同步发送和异步发送,表格嵌于代码后
*/
rclcpp :: spin_until_future_complete (this -> get_node_base_interface (), result_future);
// 挂起直到任务完成
}
private:
rclcpp :: Client <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb> :: SharedPtr client_;
void response_callback (rclcpp :: Client <lr_interfaces :: srv :: Climb> :: SharedFuture future) {
auto response = future.get ();
RCLCPP_INFO (
this -> get_logger (),
"Climb completed in %d days, reached height %.2f",
response -> days, response -> current_height
);
// 收取服务端的回复,从异步发送的 future 中调取
}
};
int main (int argc, char ** argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto node = std :: make_shared <CarClient> ();
double target_height;
std :: cout << "Enter target height for the car to climb: ";
std :: cin >> target_height;
node -> send_request (target_height);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
| 维度 | 同步发送 | 异步发送 |
|---|---|---|
| 阻塞性 | 会阻塞当前线程(代码“卡”在发送处) | 不阻塞当前线程(发送后直接走后续逻辑) |
| 执行流程 | 发送 → 等结果 → 执行后续代码 | 发送 → 直接执行后续代码 → 结果回来后再处理 |
| 结果获取 | 直接拿到最终结果(比如服务响应) | 先拿到“未决结果(future)”,后续再取结果 |
| 适用场景 | 需要立即用结果的场景(比如依赖响应做下一步操作) | 不着急要结果、不想卡线程的场景(比如高频率任务、UI 线程) |
Action
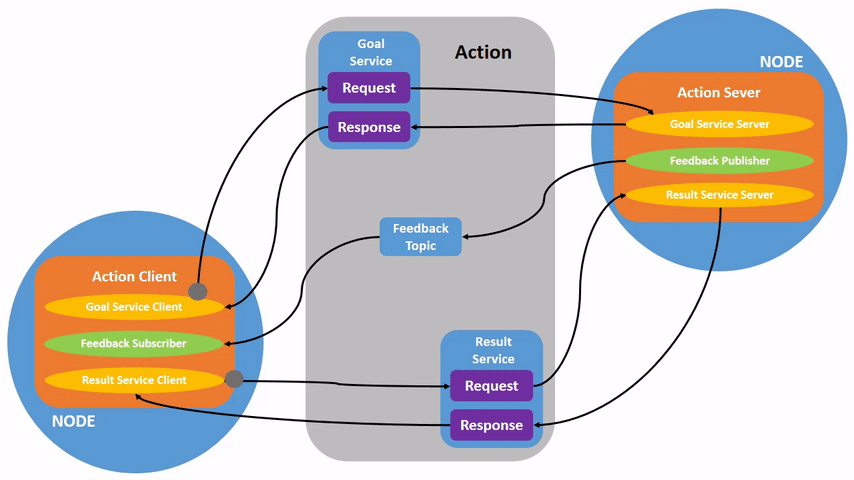
Robot_Action
#include "Robot/robot.h"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/action/move.hpp"
#include <mutex> // 用于线程安全地保护共享变量。
#include <thread> // 用于创建独立线程,实现并行执行动作。
#include <memory> // 用于智能指针
#include <atomic> // 提供原子变量(?)适合跨线程控制标志,避免竞争条件。
class Action : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
using move_robot = lr_interfaces :: action :: Move;
using GoalHandleMove = rclcpp_action :: ServerGoalHandle <move_robot>;
// 表示一个 Goal 的句柄,用于操作当前目标,比如取消、发布反馈、成功/失败等。
Action (std :: string name) : Node (name) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Action %s Node has been started", name.c_str ());
using std :: placeholders :: _1;
using std :: placeholders :: _2;
robot_ = std :: make_shared <Robot> ();
// 初始化一个 Robot 智能指针,保证全局只有一个 Robot 对象,状态会在抢占或取消时保持当前位置。
this -> action_server_ = rclcpp_action :: create_server <move_robot> (
this,
"move_robot",
std :: bind (&Action :: handle_goal, this, _1, _2),
std :: bind (&Action :: handle_cancel, this, _1),
std :: bind (&Action :: handle_accepted, this, _1)
);
}
// 析构函数,确保资源清理(将停止当前执行线程)
~ Action () {
std :: lock_guard <std :: mutex> lock (goal_mutex_);
// lock_guard:自动加锁并在作用域结束解锁,保护 active_ctx_。
// 这是 C++ 提供的一个线程同步工具,用来保护共享资源,防止多个线程同时访问导致的数据竞争。
if (active_ctx_) {
// 设定停止标志以通知执行线程退出
active_ctx_ -> stop_flag -> store (true);
active_ctx_.reset ();
}
}
private:
rclcpp_action :: Server <move_robot> :: SharedPtr action_server_;
std :: mutex goal_mutex_; // 作用在当前域里的互斥锁,保护 active_ctx_
// 使用 ExecutionContext 存放 handle + stop_flag
struct ExecutionContext {
std :: shared_ptr <GoalHandleMove> handle;
std :: shared_ptr <std :: atomic_bool> stop_flag;
/*
原子变量是一种多线程安全的变量类型。任何对原子变量的读写操作都是原子操作,即:
不可分割:操作不会被线程切换打断。
立即可见:写操作对其他线程立刻可见。
相比于互斥锁,原子变量是针对于单个变量的。
*/
};
std :: shared_ptr <ExecutionContext> active_ctx_;
std :: shared_ptr <std :: thread> execution_thread_;
// 记录当前执行线程(保持但不强制 join)。
// join:阻塞主线程直到分线程运行完毕。通常是用于防止主线程提前结束。
std :: shared_ptr <Robot> robot_;
// 声明智能指针。
rclcpp_action :: GoalResponse handle_goal (
const rclcpp_action :: GoalUUID & uuid,
std :: shared_ptr <const move_robot :: Goal> goal) {
// 当客户端发送目标时调用。
// GoalResponse::ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE:接受并执行 Goal。
// uuid 是 Goal 唯一 ID,可以用来区分不同请求。
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Received goal request with target position (%.2f, %.2f)", goal -> target_position.x, goal -> target_position.y);
(void)uuid;
return rclcpp_action :: GoalResponse :: ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE;
}
rclcpp_action :: CancelResponse handle_cancel (
const std :: shared_ptr <GoalHandleMove> goal_handle) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Received request to cancel goal");
// 当客户端请求取消 Goal 时调用。
// 使用 ExecutionContext 检查是否是当前活跃的 goal。
std :: lock_guard <std :: mutex> lock (goal_mutex_);
if (active_ctx_ && active_ctx_ -> handle && active_ctx_ -> handle -> get_goal_id () == goal_handle -> get_goal_id ()) {
// 标记停止,这样执行线程会检测到并处理取消
active_ctx_ -> stop_flag -> store (true);
return rclcpp_action :: CancelResponse :: ACCEPT;
}
return rclcpp_action :: CancelResponse :: REJECT;
}
// execute_move 接受 ExecutionContext,让一个 flag 绑定 handle
void execute_move (std :: shared_ptr <ExecutionContext> ctx) {
auto robot = robot_;
// 不再创建新的 Robot,继承使用全局 Robot,但不修改。
auto goal_handle = ctx -> handle;
const auto goal = goal_handle -> get_goal ();
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Executing goal to move to (%.2f, %.2f)", goal -> target_position.x, goal -> target_position.y);
auto result = std :: make_shared <move_robot :: Result> ();
rclcpp :: Rate rate = rclcpp :: Rate (2); // 控制循环频率
robot -> set_goal (goal -> target_position);
while (rclcpp :: ok () && !robot -> close_goal ()) {
// 先检查是否该线程被要求停止(即被抢断)
if (ctx -> stop_flag -> load ()) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal preempted. Stopping this goal's execution.");
result -> final_position = robot -> get_current_pos ();
goal_handle -> abort (result);
return ;
}
// 检查是否被客户端取消
if (goal_handle -> is_canceling ()) {
robot -> stop ();
result -> final_position = robot -> get_current_pos ();
result -> total_time_sec = robot -> get_tim ();
goal_handle -> canceled (result);
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal canceled");
return ;
}
robot -> move_step ();
auto feedback = std :: make_shared <move_robot :: Feedback> ();
feedback -> current_position = robot -> get_current_pos ();
feedback -> current_velocity = robot -> get_current_vel ();
feedback -> distance_to_target = robot -> get_dist ();
goal_handle -> publish_feedback (feedback);
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Publish Feedback");
rate.sleep ();
}
// 完成前再次检查 stop_flag(防止刚完成时被抢断)
if (ctx -> stop_flag -> load ()) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal completed but was preempted. Aborting.");
result -> final_position = robot -> get_current_pos ();
goal_handle -> abort (result);
return ;
}
result -> final_position = robot -> get_current_pos ();
goal_handle -> succeed (result);
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal succeeded");
// 清理当前活跃上下文(如果仍是该上下文)
std :: lock_guard <std :: mutex> lock (goal_mutex_);
if (active_ctx_ && active_ctx_ -> handle == goal_handle)
active_ctx_.reset ();
}
void handle_accepted (const std :: shared_ptr <GoalHandleMove> goal_handle) {
// 当 Goal 被接受时调用。
// 如果已有活跃 Goal,则抢占(设置 stop_flag)。
std :: lock_guard <std :: mutex> lock (goal_mutex_);
if (active_ctx_) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Preempting old goal for new goal");
active_ctx_ -> stop_flag -> store (true);
}
auto ctx = std :: make_shared <ExecutionContext> ();
ctx -> handle = goal_handle;
ctx -> stop_flag = std :: make_shared <std :: atomic_bool> (false);
active_ctx_ = ctx;
std :: thread ([this, ctx] () {
this -> execute_move (ctx);
}).detach (); // detach 让线程独立运行,不需要 join。
}
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto action_server = std :: make_shared <Action> ("Action_Robot");
rclcpp :: spin (action_server);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
/*
source install/setup.bash
ros2 action send_goal /move_robot lr_interfaces/action/Move "{target_position: {x: -10.0, y: -10.0}}"
ros2 action send_goal /move_robot lr_interfaces/action/Move "{target_position: {x: 20.0, y: 20.0}}"
*/
Robot_Control
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/action/move.hpp"
class Control : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
using move_robot = lr_interfaces :: action :: Move;
using GoalHandleMove = rclcpp_action :: ClientGoalHandle <move_robot>;
Control (
std :: string name,
const rclcpp :: NodeOptions& node_opt = rclcpp :: NodeOptions ()) : Node (name, node_opt) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Control %s Node has been started", name.c_str ());
this -> client_ptr = rclcpp_action :: create_client <move_robot> (this, "move_robot");
this -> timer = this -> create_wall_timer (
std :: chrono :: milliseconds (500),
std :: bind (&Control :: send_goal, this)
);
}
void send_goal () {
using namespace std :: placeholders;
this -> timer -> cancel ();
if (!this -> client_ptr -> wait_for_action_server (std :: chrono :: seconds (10))) {
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Action server not available after waiting");
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return;
}
auto goal_msg = move_robot :: Goal ();
goal_msg.target_position.x = 10.0;
goal_msg.target_position.y = 10.0;
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Sending goal request to move to (%.2f, %.2f)", goal_msg.target_position.x, goal_msg.target_position.y);
auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action :: Client <move_robot> :: SendGoalOptions ();
send_goal_options.goal_response_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: goal_response_callback, this, _1);
send_goal_options.feedback_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: feedback_callback, this, _1, _2);
send_goal_options.result_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: result_callback, this, _1);
this -> client_ptr -> async_send_goal (goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
private:
rclcpp_action :: Client <move_robot> :: SharedPtr client_ptr;
rclcpp :: TimerBase :: SharedPtr timer;
void goal_response_callback (const GoalHandleMove :: SharedPtr goal_handle) {
if (!goal_handle)
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was rejected by server");
else
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal accepted by server, waiting for result");
}
void feedback_callback (
GoalHandleMove :: SharedPtr,
const std :: shared_ptr <const move_robot :: Feedback> feedback) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Current Position: (%.2f, %.2f), Current Velocity: (%.2f, %.2f), Distance to Target: %.2f",
feedback -> current_position.x,
feedback -> current_position.y,
feedback -> current_velocity.x,
feedback -> current_velocity.y,
feedback -> distance_to_target
);
}
void result_callback (const GoalHandleMove :: WrappedResult & result) {
switch (result.code) {
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: SUCCEEDED:
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal succeeded!");
break;
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: ABORTED:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was aborted");
return;
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: CANCELED:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was canceled");
return;
default:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Unknown result code");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Final Position: (%.2f, %.2f), Total Time: %.2f sec",
result.result -> final_position.x,
result.result -> final_position.y,
result.result -> total_time_sec
);
}
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto control_node = std :: make_shared <Control> ("Control_Robot");
rclcpp :: spin (control_node);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}
Robot.h
/*
copyright
*/
#ifndef EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#define EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/action/move.hpp"
class Robot {
public:
using move_robot = lr_interfaces :: action :: Move;
Robot () = default;
~Robot () = default;
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point move_step ();
bool set_goal (geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point dist);
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point get_current_pos ();
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Vector3 get_current_vel ();
float get_dist ();
float get_tim ();
int get_status ();
bool close_goal ();
void stop ();
void init_tim ();
private:
// PID
struct {
float Kp = 2.0;
float Ki = 0.0;
float Kd = 0.8;
float dt = 0.1;
float max_speed = 5.0;
float I_max = 20.0;
float integral_x = 0.0, integral_y = 0.0;
float prev_error_x = 0.0, prev_error_y = 0.0;
} pid_;
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point current_position {}
, goal_position {}
, step {};
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Vector3 current_velocity {};
float distance_to_target {0.0}
, total_step {0.0};
std :: atomic <bool> cancel_flag {false};
};
#endif // EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
Robot
#include "Robot/robot.h"
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point Robot :: move_step () {
float error_x = goal_position.x - current_position.x;
float error_y = goal_position.y - current_position.y;
float derivative_x = (error_x - pid_.prev_error_x) / pid_.dt;
float derivative_y = (error_y - pid_.prev_error_y) / pid_.dt;
pid_.prev_error_x = error_x;
pid_.prev_error_y = error_y;
float provisional_x = pid_.Kp * error_x + pid_.Kd * derivative_x;
float provisional_y = pid_.Kp * error_y + pid_.Kd * derivative_y;
if (fabs (provisional_x) < pid_.max_speed)
pid_.integral_x += error_x * pid_.dt;
if (fabs (provisional_y) < pid_.max_speed)
pid_.integral_y += error_y * pid_.dt;
if (pid_.integral_x > pid_.I_max)
pid_.integral_x = pid_.I_max;
if (pid_.integral_x < -pid_.I_max)
pid_.integral_x = -pid_.I_max;
if (pid_.integral_y > pid_.I_max)
pid_.integral_y = pid_.I_max;
if (pid_.integral_y < -pid_.I_max)
pid_.integral_y = -pid_.I_max;
float control_x = pid_.Kp * error_x + pid_.Ki * pid_.integral_x + pid_.Kd * derivative_x;
float control_y = pid_.Kp * error_y + pid_.Ki * pid_.integral_y + pid_.Kd * derivative_y;
if (fabs (control_x) > pid_.max_speed)
control_x = (control_x > 0 ? pid_.max_speed : -pid_.max_speed);
if (fabs (control_y) > pid_.max_speed)
control_y = (control_y > 0 ? pid_.max_speed : -pid_.max_speed);
current_position.x += control_x * pid_.dt;
current_position.y += control_y * pid_.dt;
current_velocity.x = control_x;
current_velocity.y = control_y;
distance_to_target = std :: sqrt (error_x * error_x + error_y * error_y);
total_step++;
std :: cout
<< "Robot moving to ("
<< current_position.x << ", "
<< current_position.y << "), vel = ("
<< current_velocity.x << ","
<< current_velocity.y << ")"
<< std :: endl;
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point step;
step.x = control_x * pid_.dt;
step.y = control_y * pid_.dt;
return step;
}
bool Robot :: set_goal (geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point dist) {
goal_position = dist;
if (close_goal ())
return false;
return true;
}
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Point Robot :: get_current_pos () { return current_position; }
geometry_msgs :: msg :: Vector3 Robot :: get_current_vel () { return current_velocity; }
void Robot :: init_tim () { total_step = 0; }
float Robot :: get_tim () { return total_step; }
float Robot :: get_dist () { return distance_to_target; }
bool Robot :: close_goal () {
float distance = sqrt (pow (goal_position.x - current_position.x, 2) + pow (goal_position.y - current_position.y, 2));
if (distance < 0.1)
return true;
return false;
}
void Robot :: stop () {
std :: cout << "Robot has stopped at (" << current_position.x << ", " << current_position.y << ")" << std :: endl;
}
Parameter
其实就是让我们的节点绑定上特定参数。
可以在节点任务里进行调用,也可以外部修改这个参数。
Parameter
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "lr_interfaces/action/move.hpp"
using std :: placeholders :: _1;
using std :: placeholders :: _2;
class Control : public rclcpp :: Node {
public:
using move_robot = lr_interfaces :: action :: Move;
using GoalHandleMove = rclcpp_action :: ClientGoalHandle <move_robot>;
Control (
std :: string name,
const rclcpp :: NodeOptions& node_opt = rclcpp :: NodeOptions ()) : Node (name, node_opt) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Control %s Node has been started", name.c_str ());
this -> client_ptr = rclcpp_action :: create_client <move_robot> (this, "move_robot");
this -> timer = this -> create_wall_timer (
std :: chrono :: milliseconds (500),
std :: bind (&Control :: init_goal, this)
);
this -> update_timer = this -> create_wall_timer (
std :: chrono :: milliseconds (50),
std :: bind (&Control :: Check, this)
);
// 声明中间参数 next_target
this -> declare_parameter ("next_target.x", 10.0);
this -> declare_parameter ("next_target.y", 10.0);
// 参数变更回调
param_callback_handle_ =
this -> add_on_set_parameters_callback (
std :: bind (&Control :: param_callback, this, std :: placeholders :: _1)
);
}
void init_goal () {
this -> timer -> cancel ();
if (!this -> client_ptr -> wait_for_action_server (std :: chrono :: seconds (10))) {
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Action server not available after waiting");
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return;
}
send_goal ();
}
void send_goal () {
auto goal_msg = move_robot :: Goal ();
goal_msg.target_position.x = this -> get_parameter ("next_target.x").as_double ();
goal_msg.target_position.y = this -> get_parameter ("next_target.y").as_double ();
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (),
"Sending goal request to move to (%.2f, %.2f)",
goal_msg.target_position.x, goal_msg.target_position.y
);
auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action :: Client <move_robot> :: SendGoalOptions ();
send_goal_options.goal_response_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: goal_response_callback, this, _1);
send_goal_options.feedback_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: feedback_callback, this, _1, _2);
send_goal_options.result_callback = std :: bind (&Control :: result_callback, this, _1);
this -> client_ptr -> async_send_goal (goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
private:
bool updated_x_ = false;
bool updated_y_ = false;
rcl_interfaces :: msg :: SetParametersResult
param_callback (const std :: vector <rclcpp :: Parameter> ¶ms) {
for (auto &p : params) {
if (p.get_name () == "next_target.x")
updated_x_ = true;
if (p.get_name () == "next_target.y")
updated_y_ = true;
}
rcl_interfaces :: msg :: SetParametersResult result;
result.successful = true;
return result;
}
// 用一个定时器一直刷,看是否参数完整更新
void Check () {
if (updated_x_ && updated_y_) {
this -> send_goal ();
updated_x_ = false, updated_y_ = false;
}
return ;
}
rclcpp_action :: Client <move_robot> :: SharedPtr client_ptr;
rclcpp :: TimerBase :: SharedPtr timer;
rclcpp :: TimerBase :: SharedPtr update_timer;
OnSetParametersCallbackHandle::SharedPtr param_callback_handle_;
void goal_response_callback (const GoalHandleMove :: SharedPtr goal_handle) {
if (!goal_handle)
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was rejected by server");
else
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal accepted by server, waiting for result");
}
void feedback_callback (
GoalHandleMove :: SharedPtr,
const std :: shared_ptr <const move_robot :: Feedback> feedback) {
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Current Position: (%.2f, %.2f), Current Velocity: (%.2f, %.2f), Distance to Target: %.2f",
feedback -> current_position.x,
feedback -> current_position.y,
feedback -> current_velocity.x,
feedback -> current_velocity.y,
feedback -> distance_to_target
);
}
void result_callback (const GoalHandleMove :: WrappedResult & result) {
switch (result.code) {
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: SUCCEEDED:
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Goal succeeded!");
break;
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: ABORTED:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was aborted");
return;
case rclcpp_action :: ResultCode :: CANCELED:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Goal was canceled");
return;
default:
RCLCPP_ERROR (this -> get_logger (), "Unknown result code");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO (this -> get_logger (), "Final Position: (%.2f, %.2f), Total Steps: %.0f Steps.",
result.result -> final_position.x,
result.result -> final_position.y,
result.result -> total_time_sec
);
}
};
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp :: init (argc, argv);
auto control_node = std :: make_shared <Control> ("Control_Robot");
rclcpp :: spin (control_node);
rclcpp :: shutdown ();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号