Probabilistic Roadmaps (PRM)
Probabilistic Roadmaps (PRM)
Tune the Number of Nodes
Tune the Connection Distance
load exampleMaps.mat
map = binaryOccupancyMap(simpleMap,2);
rngState = rng; % 控制rand、randi和randn使用的随机数生成器。获取当前生成器的状态
prm = mobileRobotPRM(map,100);
startLocation = [2 1];
endLocation = [12 10];
% path = findpath(prm,startLocation,endLocation);
% show(prm)
rng(rngState); % 还原生成器的状态,以便生产相同的值
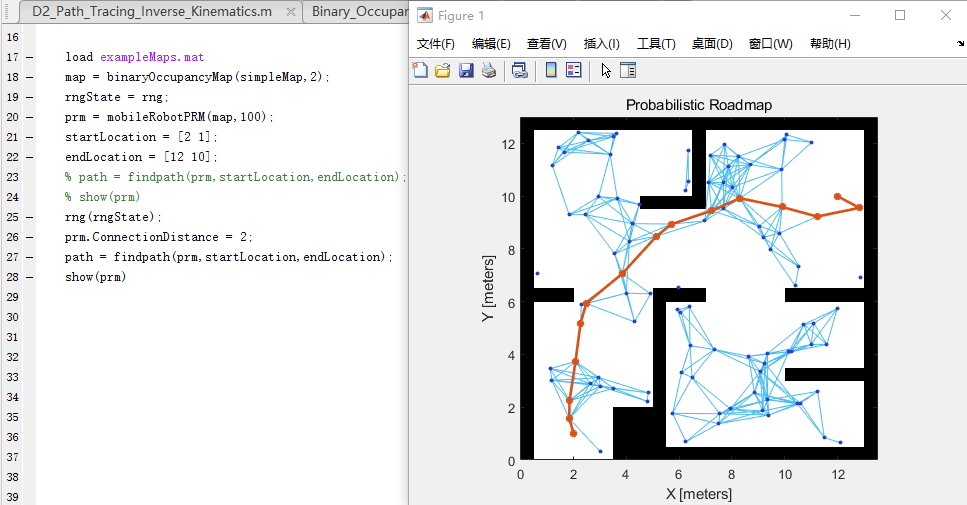
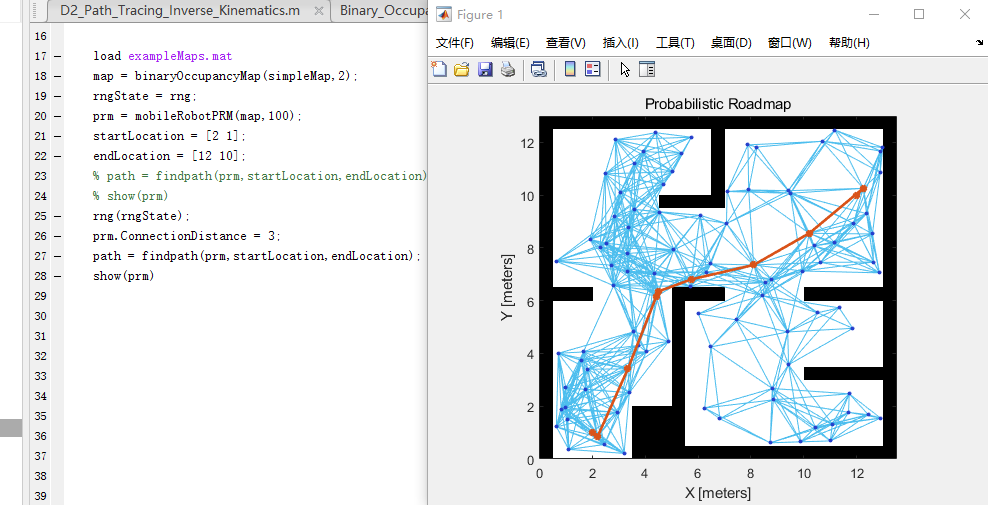
prm.ConnectionDistance = 2;
path = findpath(prm,startLocation,endLocation);
show(prm)
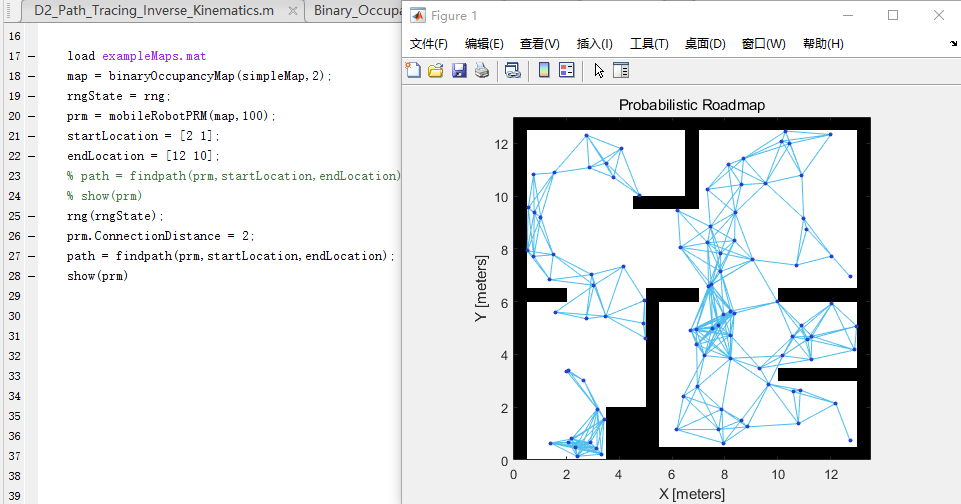
Use the ConnectionDistance property on the PRM object to tune the algorithm.
ConnectionDistance是路线图中连接的点距离的上阈值。每个节点都连接到此连接距离内的所有节点,这些节点之间没有任何障碍。通过降低连接距离,可以限制连接的数量,从而减少计算时间并简化映射。然而,较低的距离限制了找到完全无障碍路径的可用路径的数量。对于具有大量障碍的复杂映射,具有较低连接距离的节点数量越多,找到解决方案的机会就越大。
Create or Update PRM
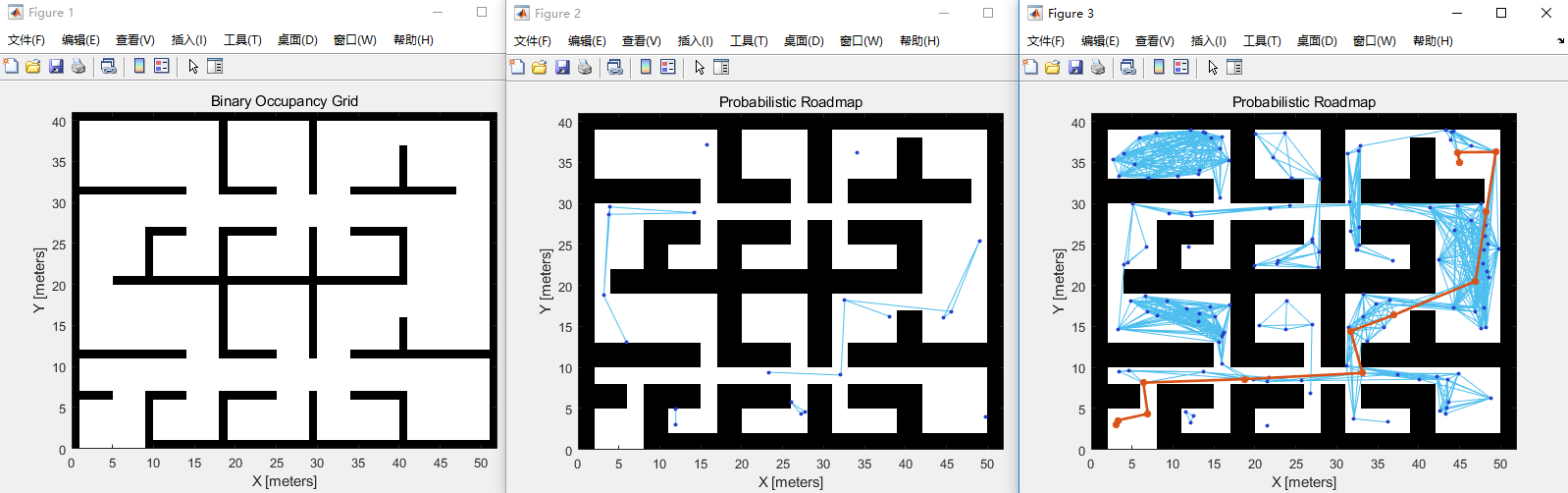
当使用mobileRobotPRM对象并修改属性时,每次新的函数调用,对象都会触发来重新放置并计算路线图的点及其连接。因为重新计算映射可能需要大量的计算,所以可以通过调用具有不同起始和结束位置的findpath来重用相同的路线图。
% % 导入用于规划路径的示例映射
load exampleMaps.mat
map = binaryOccupancyMap(complexMap,1);
% % 定义机器人的尺寸并根据机器人尺寸膨胀地图
robotRadius = 0.2;
mapInflated = copy(map);
inflate(mapInflated, robotRadius);
% % 构造PRM并设置参数
prm.Map = mapInflated;
prm.NumNodes = 20;
prm.ConnectionDistance = 15;
% % 在建立的PRM上寻找可行路径
startLocation = [3 3];
endLocation = [45 35];
path = findpath(prm, startLocation, endLocation);
while isempty(path)
% No feasible path found yet, increase the number of nodes
prm.NumNodes = prm.NumNodes + 10;
% Use the |update| function to re-create the PRM roadmap with the changed
% attribute
update(prm);
% Search for a feasible path with the updated PRM
path = findpath(prm, startLocation, endLocation);
end
show(prm)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号