5月凸轮剑魔做题记录
前言
水哥来给我们讲课前,hfu 说这次让他给我们讲一点稍微基础的图论,想听的就在机房听,不想听的就在隔壁去听 DX 给 SCOI 讲 ds。我犹豫了一会决定还是听图论,结果难爆了,听一上午下来只想出来 eps 个题。我:不是说好的图论基础吗???
以下内容按笔者做题顺序展开。
Make Adjacent
牛逼题,挂一个半年前写的题解。
Bytehattan
一个比较套路的题。就是看到网格图就要注意它有对偶图,在原图的操作等于对偶图上对应位置的逆操作。于是我们把每次删边的过程看成在对偶图上加边的过程,当对偶图上两个点形成环的时候说明原图上两点不连通。这个过程用并查集维护即可。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-24 15:02:51
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-24 15:15:55
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e6 + 5;
int n, q, ff[N], m;
bool las = true;
inline int fd(int x){return ff[x] ^ x ? fd(ff[x]) : x;}
inline bool mrg(int u, int v){if((u = fd(u)) == (v = fd(v)))return false; return ff[u] = v, true;}
signed main(){
cin >> n >> q; --n; m = n * n + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)ff[i] = i;
for(int i = 1, a, b, c, d, u, v; i <= q; ++i){
char s1, s2; cin >> a >> b >> s1 >> c >> d >> s2;
if(! las)swap(a, c), swap(b, d), swap(s1, s2);
u = (max(a, b) == n + 1) ? m : (a - 1) * n + b;
if(s1 == 'N')v = a == 1 ? m : (a - 2) * n + b;
else v = b == 1 ? m : (a - 1) * n + b - 1;
puts((las = mrg(u, v)) ? "TAK" : "NIE");
}
return 0;
}
Canvas
为数不多想出来的题。
注意到有私人覆盖操作,于是倒序考虑。考虑一组 \((1,1)\) 一定最后放,\((2,2)\) 一定最先放。所以我们需要确定的东西其实是形如 \((1,2)\) 的二元组的顺序。考虑如果一个位置 \(x\) 已经放了 \(2\),那么后面在 \(x\) 放 \(1\) 一定不会对其造成影响,于是就可以操作在 \(x\) 的 \((1,2)\),这样的操作方式有一定的传递性。所以我们进行图论建模,考虑把每个操作看成一条边,然后拓扑排序解决此题。
具体的,我们对于每个 \((u,1,v,2)\) 的操作,当成 \(u\) 向 \(v\) 连边,对原图缩点。对于所有 \((u,2,v,2)\) 的 \(u\) 和 \(v\) 如果其入度为零那么我们就可以从这个点作为起点开始做,可以发现一个位置可以操作只需要这个点已经为 \(2\) 即可,所以从一个点作为起点我们直接 \(\text{dfs}\) 即可,并不需要拓扑排序。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-24 16:58:38
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-24 17:30:12
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, top, tim, dfn[N], low[N], col[N], st[N], in[N];
#define pii pair < int , int >
vector < pii > e[N];
int ans[N], cnt, res, tot, bg[N], bcnt;
int l[N], r[N], x[N], y[N], sum[N];
bool vs[N];
void init(){
top = tim = cnt = res = tot = bcnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)dfn[i] = low[i] = in[i] = col[i] = sum[i] = 0, e[i].clear();
}
void tar(int u){
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++tim; vs[st[++top] = u] = true;
for(pii i : e[u]){
int v = i.first;
if(! dfn[v])tar(v), low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
else if(vs[v])low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if(low[u] ^ dfn[u])return;
++tot;
while(st[top] ^ u)vs[st[top]] = false, col[st[top--]] = tot;
vs[u] = false; col[u] = tot; --top;
}
void dfs(int u){
vs[u] = true;
for(pii i : e[u]){
ans[++cnt] = i.second;
if(! vs[i.first])dfs(i.first);
}
}
signed main(){
int T = rd();
while(T--){
n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
l[i] = rd(), x[i] = rd(), r[i] = rd(), y[i] = rd();
if(x[i] + y[i] == 3){
if(x[i] ^ 1)swap(l[i], r[i]), swap(x[i], y[i]);
e[l[i]].push_back(make_pair(r[i], i));
}
if(x[i] + y[i] == 4)bg[++bcnt] = l[i], bg[++bcnt] = r[i], ans[++cnt] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(! dfn[i])tar(i);
for(int u = 1, v; u <= n; ++u)for(pii j : e[u])if(col[u] ^ col[v = j.first])++in[col[v]];
for(int i = 1; i <= bcnt; ++i)if(! in[col[bg[i]]] and ! vs[bg[i]])dfs(bg[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(! in[col[i]] and ! vs[i])dfs(i);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)if(x[i] + y[i] == 2)ans[++cnt] = i;
for(int i = cnt; i; --i)sum[l[ans[i]]] = x[ans[i]], sum[r[ans[i]]] = y[ans[i]];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)res += sum[i]; printf("%d\n", res);
for(int i = cnt; i; --i)printf("%d%c", ans[i], i ^ 1 ? ' ' : '\n');
init();
}
return 0;
}
C0mp0nents
困难题。
考虑所有 \(i\equiv x\pmod k\) 才可能互相贡献答案,于是我们将点分类并对每一类按照除以 \(k\) 的商排序,然后忽略无意义的边。接下来我们对每一类分别计算答案。考虑所有数同时除以 \(k\) 之后就变成了若干个连续且公差为一的等差数列,所以我们只考虑 \(k=1\) 的情况。
假设我们现在要求 \(s=1\) 时的答案。我们发现如果 \([1,i]\) 的所有点都能变成 \(1\) 说明每个 \(x\in[1,i)\) 都向后至少连了一条边到 \((x,i]\),原因是如果我们想让 \(i\) 变成 \(1\),就要经历 \(i\rightarrow i-1\rightarrow\dots\rightarrow1\) 的过程。所以 \(i\) 一定和 \(i-1\) 有连边;\(i-2\) 一定有边连到 \(\{i-1,i\}\) 中,以此类推。
拓展到一般情况,如果 \([l,r]\) 能够变成 \(s\),那么:
- 每个 \(x\in(s,r)\) 都向后至少连了一条边到 \((x,r]\);
- 每个 \(x\in(l,s)\) 都向前至少连了一条边到 \([l,x)\);
- \([l,r]\) 是一个连通块。
我们可以先处理前两个限制,对于最后一个判断是否有边从 \(s\) 的前面连向后面即可。现在具体讲一下怎么处理前面两个东西,首先可以发现这两个东西本质相同所以只考虑第一个的处理,第二个类比即可。
现在说第一个限制的处理方式。因为我们的 \(s\) 在不停地向右移动,所以对区间的限制在不断变少,所以区间的右端点在单调递增。这启发我们线性处理。这里有一个比较显然但是很关键的性质,就是假设对 \(i\) 满足条件的最大 \(r\) 记做 \(rp_i\),有 \(rp_i=rp_{i+1}\) 或 \(i\)。证明考虑如果当前点 \(i\) 向区间 \((i,rp_{i+1}]\) 存在连边则有 \(rp_i=rp_{i+1}\),否则就是 \(rp_i=i\)。于是我们就可以倒着扫一遍序列即可。
最后我们还需要判断区间之间是否有边。我们转换视角,考虑每条边对哪一段区间有贡献。对于一条边 \((u,v),u<v\),如果存在 \(i\) 满足 \(lp_i\le u<i<v\le rp_i\) 即合法。考虑到 \(lp_i,rp_i\) 都具有单调性所以合法的点一定是一段连续的区间。现在考虑求这段区间。因为二维的限制不好处理所以我们把它变成两个一维限制扫一遍即可。最后处理出对哪些区间有贡献后需要做一些区间加以及单点查,这个可以差分实现。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-25 19:47:13
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-25 20:16:20
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5, M = 1e6 + 5, S = 1 << 25;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, k, a[N], pos[N], d[N];
int l[N], r[N], lp[N], rp[N], pr[N], sf[N];
int hd[N], cnt, tot;
struct edge{int nxt, to;}e[M << 1];
inline void add(int u, int v){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v}; hd[u] = cnt;}
int ans[N];
void solve(int rr){
tot = n / k + (n % k >= rr); lp[1] = 1; rp[tot] = tot; sf[0] = 0; pr[tot + 1] = tot + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i)pos[a[i] = i * k - k + rr] = i, d[i] = 0;
for(int u = 1; u <= tot; ++u){
l[u] = 0, r[u] = tot + 1;
for(int i = hd[a[u]], v; i; i = e[i].nxt)if((v = pos[e[i].to]) < u)l[u] = max(l[u], v); else r[u] = min(r[u], v);
}
for(int i = 2; i <= tot; ++i){lp[i] = lp[i - 1]; if(l[i - 1] < lp[i] and lp[i] ^ i - 1)lp[i] = i - 1;}
for(int i = tot - 1; i; --i){rp[i] = rp[i + 1]; if(rp[i] < r[i + 1] and rp[i] ^ i + 1)rp[i] = i + 1;}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i)for(sf[i] = sf[i - 1]; sf[i] < tot and lp[sf[i] + 1] <= i; ++sf[i]);
for(int i = tot; i; --i)for(pr[i] = pr[i + 1]; pr[i] > 1 and i <= rp[pr[i] - 1]; --pr[i]);
for(int u = 1; u <= tot; ++u)for(int i = hd[a[u]], v; i; i = e[i].nxt)if(u < (v = pos[e[i].to])){
int bg = max(u + 1, pr[v]), ed = min(v - 1, sf[u]);
if(bg <= ed)++d[bg], --d[ed + 1];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i){
d[i] += d[i - 1];
if(l[i] < lp[i] and rp[i] < r[i])lp[i] = rp[i] = i;
else if(! d[i])if(l[i] < lp[i])lp[i] = i; else if(rp[i] < r[i])rp[i] = i;
ans[a[i]] = rp[i] - lp[i] + 1;
}
}
signed main(){
n = rd(), m = rd(), k = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i){
u = rd(), v = rd();
if(u % k == v % k)add(u, v), add(v, u);
}
for(int rr = 1; rr <= k; ++rr)solve(rr);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cout << ans[i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
CF1956F
题目显然要求连通块个数。
设 \(lp_i=[i-r_i,i-l_i],rp_i=[i+l_i,i+r_i]\),若 \(i\ge j\),则有 \(i+l_i>j-l_j\),所以 \(rp_i\cap lp_i=\emptyset\)。我们就可以用 \((rp_i\cap lp_j)\cup(rp_j\cap lp_i)\) 描述两个点之间的连边情况。于是我们可以很自然地想到从 \(i\) 向区间连边。但是这样会有问题!可能存在两个点只通过 \(lp_i\cap lp_j\) 或者 \(rp_i\cap rp_j\) 的条件但是依然有连边,所以我们需要删除一些点。
在进行连边前我们可以处理出所有 \(lp_i,rp_i\),对于一个虚点 \(x\),若同时有 \(\exists i,\exists j,x\in lp_i,x\in rp_j\) 则当前点可以保留。这样就能解决上述情况。
因为有点向区间连边所以考虑线段树优化建图,但是太麻烦了,因为我们只用判断连通块个数所以我们只需要将点向区间左端点连边然后在连通区间内的点即可。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-25 21:39:12
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-25 22:00:04
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e6 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, a[N], b[N], ff[N], l[N], r[N], pr[N], sf[N], d[N], res, tot;
inline int fd(int x){return x ^ ff[x] ? ff[x] = fd(ff[x]) : x;}
inline void upd(int i, int x, int y){if(x <= y)++d[x], --d[y], ff[fd(i)] = fd(n + x);}
signed main(){
int T = rd();
while(T--){
n = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
l[i] = rd(), r[i] = rd(); ff[i] = i;
++a[max(1, i - r[i])]; --a[max(1, i - l[i] + 1)];
++b[min(n, i + l[i])]; --b[min(n, i + r[i] + 1)];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
a[i] += a[i - 1]; b[i] += b[i - 1];
if(a[i] and b[i])pr[i] = sf[i] = ++tot, ff[n + tot] = n + tot; else pr[i] = tot;
}
sf[n + 1] = n * 2 + 5;
for(int i = n; i; --i)if(! sf[i])sf[i] = sf[i + 1];
for(int i = 1, x, y; i <= n; ++i){
x = sf[max(1, i - r[i])]; y = pr[max(0, i - l[i])]; upd(i, x, y);
x = sf[min(n + 1, i + l[i])]; y = pr[min(n, i + r[i])]; upd(i, x, y);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i){d[i] += d[i - 1]; if(d[i])ff[fd(n + i)] = fd(n + i + 1);}
for(int i = 1; i <= n + tot; ++i)res += ff[i] == i;
cout << res << endl; res = tot = 0; n = n * 2 + 2;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)a[i] = b[i] = sf[i] = d[i] = 0;
}
return 0;
}
CF1967D
对置换建图,然后你就建出一个基环森林,考虑每一次变化当成在图上跳父亲。因为最小化每个位置最多跳跃次数所以二分答案。设每个数初始为 \(a_i\),最后为 \(b_i\),对于每个数 \(a_i\),我们看它在 \(mid\) 次内能跳到的大于等于 \(b_i\) 且尽量小的数即可。但是这样写貌似要用到一些高级数据结构而且时间复杂度上天。考虑值域很小,所以直接枚举具体跳到哪个数即可。时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\)。
虽然这是一颗基环树,但是全都是有向边所以直接断环即可。跳多少步相当于要看终点是否为起点的祖先且深度差是否小于限制。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-26 08:24:24
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-26 08:59:34
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, hd[N], cnt, ff[N], fa[N], a[N];
int lp[N], rp[N], tim, dep[N], cir[N];
struct edge{int nxt, to;}e[N];
inline void add(int u, int v){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v}; hd[u] = cnt;}
inline void init(){
cnt = tim = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)hd[i] = cir[i] = dep[i] = 0;
}
inline int fd(int x){return x ^ ff[x] ? ff[x] = fd(ff[x]) : x;}
inline bool mrg(int x, int y){return x = fd(x), y = fd(y), x ^ y and (ff[x] = y, true);}
inline bool sub(int x, int y){return lp[x] <= lp[y] and lp[y] <= rp[x];}
void dfs(int u){
lp[u] = ++tim;
for(int i = hd[u], v; i; i = e[i].nxt)dep[v = e[i].to] = dep[u] + 1, dfs(v);
rp[u] = tim;
}
inline int dis(int x, int y){
if(fd(x) ^ fd(y))return inf;
if(sub(y, x))return dep[x] - dep[y];
if(sub(y, fa[cir[fd(x)]]))return dep[x] + 1 + dep[fa[cir[fd(x)]]] - dep[y];
return inf;
}
bool chk(int d){
int i = 1, j = 1;
for(; i <= n and j <= m; ++i)for(; j <= m and dis(a[i], j) > d; ++j);
return j <= m;
}
void solve(){
n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)a[i] = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)fa[i] = rd(), ff[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)if(! mrg(i, fa[i]))cir[fd(i)] = i; else add(fa[i], i);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)if(ff[i] == i)dfs(cir[i]);
// for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)printf("dep[%d] = %d\n", i, dep[i]);
int l = 0, r = m, res = - 1;
while(l <= r){
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(chk(mid))res = mid, r = mid - 1; else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << res << endl; init();
}
signed main(){
int T = rd();
while(T--)solve();
return 0;
}
邮箱题
个人感觉可以评黑。
懒得整理了直接挂机房同学的博客,其实是我给他讲的,然后因为他把我想讲的基本给讲清楚了所以我懒得写了()
大概口胡一下。
首先可以把图拆成一些置换环,然后经典断环成链,答案转换成求一个点向后最远走到哪里和一个点所在强连通分量大小。考虑从后往前算答案。
在链上我们维护可以走通的区间和强连通分量,考虑区间由若干强连通分量构成且这些东西全部是连续的。然后对于新加入链的一个点 \(i\),考虑它能和什么东西合并。首先如果有 \((i,i+1)\) 那么区间会拓展,然后考虑如果能合并这个区间的强连通分量就把中间的全部合并,所以对每个区间预处理可达最靠右的点。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-26 11:15:45
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-26 12:05:08
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e6 + 5, S = 1 << 25;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, k[N];
int ans1[N], ans2[N];
bool vs[N];
int tot, cyc[N], pr[N], id[N], ma[N];
vector < int > g[N];
struct dsu{
int ff[N];
inline int fd(int x){return x ^ ff[x] ? ff[x] = fd(ff[x]) : x;}
inline void mrg(int x, int y){ff[fd(y)] = fd(x);}
}lian, huan;
void solve(int pos){
while(! vs[pos])vs[pos] = true, cyc[++tot] = pos, id[pos] = tot, pos = k[pos];
for(int i = tot * 2; i; --i){
lian.ff[i] = huan.ff[i] = i; pr[i] = ma[i] = 0;
int u = cyc[i > tot ? i - tot : i];
for(int v : g[u])if(id[v]){
v = id[v]; v += tot * (v + tot < i); v -= tot * (v > i);
pr[i] = max(pr[i], v); v += tot * (v < i);
if(v <= tot * 2)ma[lian.fd(v)] = max(ma[lian.fd(v)], huan.fd(v));
}
while(true){
for(int p1 = huan.fd(i), p2 = lian.fd(i); p1 < ma[p2]; p1 = huan.fd(i))huan.mrg(p1 + 1, p1);
int p1 = huan.fd(i), p2 = lian.fd(i); ma[p2] = 0;
if(p2 == tot * 2 or p1 ^ p2 or pr[p2 + 1] < i)break;
lian.mrg(p2 + 1, p2);
}
ans1[u] = min(tot, lian.fd(i) - i + 1); ans2[u] = min(tot, huan.fd(i) - i + 1);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i)id[cyc[i]] = 0; tot = 0;
}
signed main(){
int T = rd();
while(T--){
n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)vector < int > ().swap(g[i]), vs[i] = false, k[i] = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i)u = rd(), v = rd(), g[v].push_back(u);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(! vs[i])solve(i);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)printf("%d %d\n", ans1[i], ans2[i]);
}
return 0;
}
CF429E
好题!非常牛逼的凸轮剑魔!
考虑一种颜色权值为 1 另一种为 -1,我们需要满足最后所有位置值在 \([-1,1]\) 之间。首先离散化,然后对于被偶数区间覆盖的点满足权值等于 0,否则就为 1/-1。考虑给被奇数区间覆盖的点补一个虚空区间,然后当成偶数的做。实际上我们要做的就是跑欧拉回路,对于一条边,如果我们顺着走就染一种颜色,否则就另一种。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-26 14:45:13
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-26 14:53:56
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, a[N], l[N], r[N], hd[N], cnt = 1, tot, d[N];
bool col[N], vs[N];
struct edge{int nxt, to, id; bool o;}e[N << 1];
inline void add(int u, int v, int i){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v, i, 0}; hd[u] = cnt;}
void dfs(int u){
vs[u] = true;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = hd[u] = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].to; if(e[i].o)continue;
e[i].o = e[i ^ 1].o = true;
col[e[i].id] = u < v;
dfs(v);
}
}
signed main(){
n = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)l[i] = a[++tot] = rd(), r[i] = a[++tot] = rd() + 1;
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + tot); tot = unique(a + 1, a + 1 + tot) - a - 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
l[i] = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + tot, l[i]) - a;
r[i] = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + tot, r[i]) - a;
++d[l[i]]; --d[r[i]];
add(l[i], r[i], i); add(r[i], l[i], i);
}
for(int i = 1, s = 0; i <= tot; ++i){s += d[i]; if(s & 1)add(i, i + 1, n + 1), add(i + 1, i, n + 1);}
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i)if(! vs[i])dfs(i);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cout << col[i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
CF241E
唉这不是差分约束吗?秒了拜拜。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-26 15:30:23
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-26 15:51:23
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 1005, M = 5005, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, hd[N], cnt, tot;
int pr[N], d[N], apr[N], ans[M];
struct Edge{int u, v, id;}E[M];
vector < int > g[2][N];
struct edge{int nxt, to, w;}e[M << 1];
inline void add(int u, int v, int w){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v, w}; hd[u] = cnt;}
bool tg[N], vs[2][N], vis[N], ok;
void dfs(int u, bool typ){vs[typ][u] = true; for(int v : g[typ][u])if(! vs[typ][v])dfs(v, typ);}
void spfa(){
queue < int > q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(tg[i])vis[i] = true, d[i] = inf, q.push(i);
while(! q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].to, w = e[i].w;
if(d[u] + w < d[v]){
d[v] = d[u] + w; apr[v] = apr[u] + 1; pr[v] = u;
if(apr[v] > tot)return puts("No"), ok = true, void();
if(! vis[v])q.push(v), vis[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
signed main(){
n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i)u = rd(), v = rd(), E[i] = {u, v, i}, g[0][u].push_back(v), g[1][v].push_back(u);
dfs(1, 0); dfs(n, 1); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(vs[0][i] and vs[1][i])tg[i] = true, ++tot;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int u = E[i].u, v = E[i].v;
if(tg[u] and tg[v])add(u, v, - 1), add(v, u, 2);
else ans[i] = 1;
}
spfa();
if(ok)return 0;
puts("Yes");
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)printf("%d\n", ans[i] ? ans[i] : d[E[i].u] - d[E[i].v]);
return 0;
}
CF843D
有点厉害的技巧题。
发现 q 很小,然后我们可以先做一遍 dij。每次都会给一些边+1,好困难啊!难不成要重新跑一遍 dij 了?
我们可以定义一个增量数组 \(\Delta_i\) 表示 \(i\) 的距离增量。我们定义新图边权为 \(d_u+w(u,v)-d_v\),我们在新图上走出来的东西就是增量距离 \(\Delta\)。考虑 dij 不现实,所以我们就用一个桶维护边权进行更新即可。注意有点小卡常,如果你像我一样常熟小就当我没说。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-27 09:40:59
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-27 10:17:44
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, q, hd[N], cnt;
ll d[N], dt[N];
struct edge{int nxt, to; ll w;}e[N];
inline void add(int u, int v, ll w){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v, w}, hd[u] = cnt;}
bool vs[N];
#define pii pair < ll , int >
queue < int > b[N];
void dij(){
priority_queue < pii > q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)d[i] = INF;
q.push(make_pair(d[1] = 0, 1));
while(! q.empty()){
int u = q.top().second; q.pop();
if(vs[u])continue; vs[u] = 1;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].to; ll w = e[i].w;
if(d[v] > d[u] + w)q.push(make_pair(- (d[v] = d[u] + w), v));
}
}
}
void bfs(int lim){
ll up = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= up; ++i)while(! b[i].empty()){
int u = b[i].front(); b[i].pop(); if(dt[u] < i)continue;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].to; ll w = d[u] - d[v] + e[i].w;
if(dt[v] > dt[u] + w){
dt[v] = dt[u] + w;
if(dt[v] <= min(lim, n - 1))up = max(up, dt[v]), b[dt[v]].push(v);
}
}
}
}
signed main(){
n = rd(), m = rd(); q = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v, w; i <= m; ++i)u = rd(), v = rd(), w = rd(), add(u, v, w);
dij();
for(int i = 1, o, x; i <= q; ++i){
o = rd(), x = rd();
if(o == 1)printf("%lld\n", d[x] == INF ? - 1 : d[x]);
else{
for(int j = 1; j <= x; ++j)++e[rd()].w;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)dt[i] = INF;
dt[1] = 0; b[0].push(1); bfs(x);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)d[i] = min(INF, d[i] + dt[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
ARC144E
牛逼题。
先拆点。
注意从 1/n 到一个点如果有多条路径就有可能产生限制,不看那些可以填任意数的点,我们发现路径上固定数值的点权和的差一定是答案的倍数。所以拆点后我们可以先跑一棵树出来,对于非树边我们会得到一个环,这个时候就会出现两条路径,我们就求一下 \(\gcd\) 即可。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-26 18:14:01
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-26 22:26:07
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 6e5 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 1e9 + 7, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m, dep[N];
ll a[N], f[N], res;
vector < int > g[2][N];
bool vs[2][N], tg[N], vis[N];
int hd[N], cnt;
struct edge{int nxt, to; ll w;}e[N << 1];
inline void add(int u, int v, ll w){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v, w}, hd[u] = cnt;}
struct Edge{int u, v;}E[N];
inline ll gcd(ll x, ll y){return y ? gcd(y, x % y) : x;}
void dfs1(int u, bool typ){vs[typ][u] = true; for(int v : g[typ][u])if(! vs[typ][v])dfs1(v, typ);}
void dfs2(int u){
tg[u] = true;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt){
int v = e[i].to; ll w = e[i].w;
if(! tg[v])dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, f[v] = f[u] + w, dfs2(v);
else if(dep[v] < dep[u])res = gcd(res, abs(f[u] - f[v] + w));
}
}
signed main(){
n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i)u = rd(), v = rd(), E[i] = {u, v}, g[0][u].push_back(v), g[1][v].push_back(u);
dfs1(1, 0), dfs1(n, 1); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(vs[0][i] and vs[1][i])vis[i] = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)a[i] = rd();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(~ a[i] and vis[i])add(i, i + n, a[i]), add(i + n, i, - a[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int u = E[i].u, v = E[i].v;
if(vis[u] and vis[v])add(u + n, v, 0), add(v, u + n, 0);
}
add(1, n * 2, 0); add(n * 2, 1, 0);
for(int i = 1, j; i <= n * 2; ++i)if(vis[(j = i > n ? i - n : i)] and ! tg[i])dfs2(i);
cout << (res ? res : - 1);
return 0;
}
AGC035E
艰难依旧坚持。感觉有意思的题。
首先如果 \(K\) 为偶数就说明不能连续选连续选 \(K\over2\) 个数。这个直接 dp 然后奇偶答案合并一下即可。
关键在 \(K\) 为奇数的时候。我把图画一下(盗一张图):
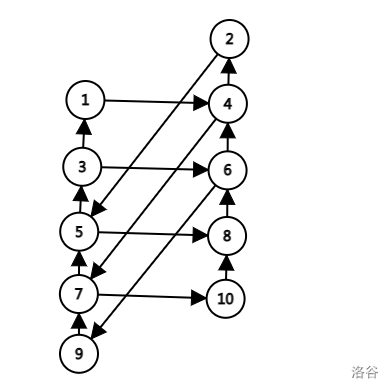
注意到环的大小都是 \(K+2\) 的,并且如果要成为环必须是从左边的链走到右边,所以我们需要在 dp 中记录左边的最长链。
我们考虑从上到下一层一层地 dp,设 \(f_{p,i,j}\) 表示到第 \(p\) 层,右边最长链为 \(i\) 左边为 \(j\) 的方案数。每次往下一层讨论选点的情况。
- 两个点都不选,显然有:
- 左边选右边不选,右边最长链变成零,左边最长链加一。但是注意如果左边最长链本来是 0 的话,+1 后就到了右侧导致一层选了两个点不成立,所以不能更新。转移显然。
- 左边不选右边选,转移显然。
- 都选,右边的最长链一定是 +1,考虑左边的最长链有两种选择方式,既可以直接 +1,又可以选择连上右边的最长链,所以有:
注意转移的限制,因为并不是每一层两边都有点。最后答案就是枚举最后左右两边的最长链长度即可。时间复杂度 \(O(nk^2)\) 或者 \(O(n^2k)\)。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-27 08:32:56
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-27 08:54:05
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 155, S = 1 << 25, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
void fileio(const string &s){
freopen((s + ".in").c_str(), "r", stdin);
freopen((s + ".out").c_str(), "w", stdout);
}
int p;
inline int Add(int x, int y){return x - p + y >= 0 ? x - p + y : x + y;}
inline int Sub(int x, int y){return x < y ? x - y + p : x - y;}
inline int Mul(int x, int y){return 1ll * x * y % p;}
inline int Mo(ll x){return (x % p + p) % p;}
inline int qmi(int x, int y){int res = 1; for(; y; y >>= 1, x = Mul(x, x))if(y & 1)res = Mul(res, x); return res;}
inline void exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y){if(! b)return x = 1, y = 0, void(); exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); y -= a / b * x;}
inline int Inv(int q){ll x, y; exgcd(q, p, x, y); return Mo(x);}
inline void upd(int &x, int y){x = Add(x, y);}
int n, k;
int f[N][N], g[N][N][N], res;
void solve1(){
int m = n + k >> 1; g[0][0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j <= n; ++j)for(int q = 0; q < k + 2; ++q)upd(g[i][0][0], g[i - 1][j][q]);
if(i * 2 >= k + 1)for(int j = 0; j <= n; ++j){
for(int q = 1; q < k + 2; ++q)upd(g[i][0][q + 1], g[i - 1][j][q]);
upd(g[i][0][0], g[i - 1][j][0]);
}
if(i * 2 <= n)for(int j = 0; j <= n; ++j)for(int q = 0; q < k + 2; ++q)upd(g[i][j + 1][0], g[i - 1][j][q]);
if(i * 2 <= n and i * 2 >= k + 1)for(int j = 0; j <= n and j <= k; ++j)for(int q = 0; q < k + 2; ++q)
upd(g[i][j + 1][max(q + 1, j + 2)], g[i - 1][j][q]);
}
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i)for(int j = 0; j < k + 2; ++j)upd(res, g[m][i][j]);
}
void solve2(){
int s1 = 0, s2 = 0; k >>= 1; f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= (n + 1 >> 1); ++i)for(int j = 0; j <= k; ++j){
upd(f[i][0], f[i - 1][j]);
if(j)upd(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i)upd(s1, f[n >> 1][i]), upd(s2, f[n + 1 >> 1][i]);
res = Mul(s1, s2);
}
const string FileName = "";
signed main(){
// fileio(FileName);
n = rd(), k = rd(), p = rd();
if(k & 1)solve1(); else solve2();
cout << res;
return 0;
}
ARC153F
不好评价这道题。首先容斥。然后考虑两种颜色肯定好算,现在要算有三种颜色但是不合法的东西。
我们考虑一个点双。如果点双大小为 3 我们染三种颜色其实是不合法的,所以我们可以统计到答案里面。现在考虑这个点双连的有其他点。如果只有一个点连出去,我们称其为关键点,那么只要让连出去的东西颜色都与关键点相邻的边颜色不同即可。如果连出去了两个或三个部分,那么一定会得到合法的路径,所以我们不能对此统计。
总结一下,只有当这种点双在圆方树的叶子上才能统计答案。
我们继续考虑特殊的点双。如果大小为 4,边数为 5/6,我们先确定一个三元环,那么剩下的边就根据三元环上的边的颜色也确定了下来。并且这种东西不能有边连出去,否则肯定会有合法的路径。
考虑一般的情况,我们把一个点双统一为一种颜色,然后从这个点双连出去的一些子树只要里面颜色相同外面不需要考虑乱填即可。
点击查看代码
/*
* @Author: Nekopedia
* @Date: 2025-05-28 12:31:20
* @Last Modified by: Nekopedia
* @Last Modified time: 2025-05-28 12:47:23
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define gc() (p1 == p2 and (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, S, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5, S = 1 << 25, p = 998244353, inf = 2e9;
const ll INF = 2e18;
char buf[S], *p1, *p2;
inline ll rd(){
ll x = 0, f = 1; char c = gc();
while(! isdigit(c)){if(c == '-')f = - f; c = gc();}
while(isdigit(c)){x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = gc();}
return x * f;
}
void fileio(const string &s){
freopen((s + ".in").c_str(), "r", stdin);
freopen((s + ".out").c_str(), "w", stdout);
}
inline int Add(int x, int y){return x - p + y >= 0 ? x - p + y : x + y;}
inline int Sub(int x, int y){return x < y ? x - y + p : x - y;}
inline int Mul(int x, int y){return 1ll * x * y % p;}
inline int Mo(ll x){return (x % p + p) % p;}
inline int qmi(int x, int y){int res = 1; for(; y; y >>= 1, x = Mul(x, x))if(y & 1)res = Mul(res, x); return res;}
inline void exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y){if(! b)return x = 1, y = 0, void(); exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); y -= a / b * x;}
inline int Inv(int q){ll x, y; exgcd(q, p, x, y); return Mo(x);}
int n, m, hd[N], cnt, tot, dg[N];
int dfn[N], low[N], tim, st[N], top;
vector < int > g[N];
struct edge{int nxt, to;}e[N << 1];
inline void add(int u, int v){e[++cnt] = {hd[u], v}; hd[u] = cnt; ++dg[u];}
void tar(int u){
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++tim; st[++top] = u;
for(int v : g[u])if(! dfn[v]){
tar(v); low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
if(dfn[u] == low[v]){
++tot;
while(st[top] ^ v)add(st[top], tot), add(tot, st[top--]);
add(tot, v); add(v, tot); --top;
add(tot, u); add(u, tot);
}
}
else low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
int ans, pw2[N], pw3[N];
inline int calc(int x){return Add(pw3[x], Sub(3, Mul(3, pw2[x])));}
const string FileName = "";
signed main(){
// fileio(FileName);
tot = n = rd(), m = rd();
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i)u = rd(), v = rd(), g[u].push_back(v), g[v].push_back(u);
tar(1); pw2[0] = pw3[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)pw2[i] = Mul(pw2[i - 1], 2), pw3[i] = Mul(pw3[i - 1], 3);
if(n == 4 and m > 4 and tot == n + 1)ans = 6;
for(int u = n + 1; u <= tot; ++u)if(dg[u] == 3){
int res = 0;
for(int i = hd[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt)res += dg[e[i].to] > 1;
if(res < 2)ans += 6;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(dg[i] > 2)ans = Add(ans, calc(dg[i]));
cout << Sub(calc(m), ans);
return 0;
}
后记
凸轮剑魔恐怖如斯,下来我还要多花一些时间整理总结一下。并且这种类型的题需要多见一些花样,我还有很多事要做......


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号