Linux 使用技巧总结(二)
Git
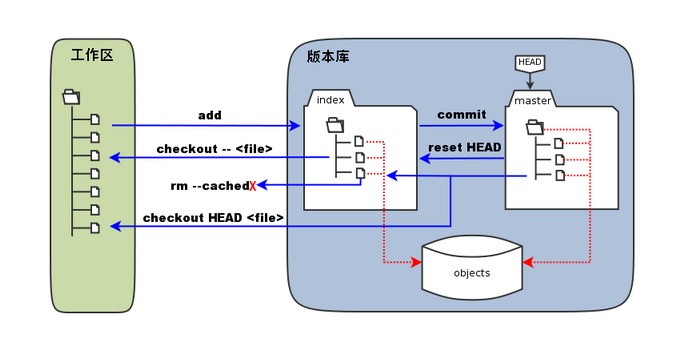
git --help #best way to review in a short time
git config --global user.name "jcp22" #change user name to "jcp22"
git config --global user.email "jcp22@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn" #change user's email to "..."
git init git-test
git status #show the files that not added(or not committed)
git add * #add all files
git commit -m "I've modified ..." #commit with message("I've...")
# HEAD(in your computer); master(the main branch); truck
git branch #show current branch
git branch March26 #create a new branch
git switch March26 #switch branch to March26
git merge March26 #add files from branch "March26" to current position(branch)
git branch -d March26 #delete a merged branch(-D for unmerged branch)
git log #show modify log
git log --graph --oneline --all #show the log more human readably
git checkout ec723b2 ./
git reset --hard ec723b2 #change HEAD to version ec723b2(hash)
git diff # show the uncommitted content
注意本地会随着 branch 的 switch 而变化。
关联远程仓库:(SSH方法)
远程仓库:类似github,gitlab(THU)
配置密钥:ls ~/.ssh 里面查看是否已经有密钥(如 ed25519),如果没有就 ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -a 100 生成密钥。
然后复制 ed25519.pub 中的公钥,粘到github/gitlab的settings/SSH Keys中。
将一个本地的git仓库关联上远程仓库:git remote add <name> <url>,其中远程仓库名 name 通常为 origin,url为仓库url,如:git@github.com:jiazp/hello-git.git。
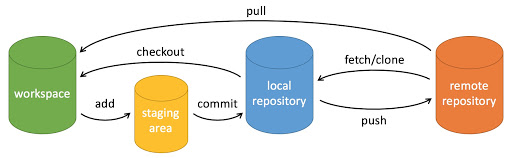
推送 git push -u origin master(-u 远程;master 是一个分支)(git push -u 似乎可以自动将 origin 推送到 master)(似乎 -u 都不需要加)
获取:先检查更新 git remote update,再获取到本地 git pull。还有种操作是 git fetch,它和 git pull 的区别:
git fetch updates your remote-tracking branches under refs/remotes/<remote>/.
This operation is safe to run at any time
since it never changes any of your local branches under refs/heads.
git pull brings a local branch up-to-date with its remote version,
while also updating your other remote-tracking branches.
分支查看和切换:git branch 查看;git checkout -b <branch-name> 切换(没有则新建)
查看远程仓库其他分支:git branch [-r|--remote] 或者和本地的一起显示:git branch [-a|--all]
拉取和推送远程仓库其他分支:直接 clone 默认拉取远程主分支。git checkout -b gemv origin/gemv 可以拉取远程的 gemv 分支到本地 gemv 分支。git push -u origin stage-2 会将本地的 stage-2 分支推送到远程的 stage-2 分支。其中 -u 是 --set-upstream 的缩写,作用是推送到上游。
删除远程仓库分支:git push -d origin <branch>。
更多有关 Remote Branches:可以使用 git ls-remote <remote> 或 git remote show <remote> 来获取 remote branches 信息,其中 <remote> 是远程仓库的“名字”,通常为 origin。很不错的文档,图文并茂,例子丰富,兼讲原理。
克隆仓库:git clone <url>,会自动关联远程仓库(origin)
tag:项目做的很大的时候可能会用到tag,表示不同版本。不过clone下来的大项目经常涉及到tag。git tag 或 git tag -l 查看所有tag;git tag -a v0.3 -m "blabla" 创建tag;git show 显示当前 tag 详细信息;git show v1.1 显示指定的 v1.1 tag 的信息。
stash:需要暂时存储当前修改但不 commit 的一种选择吧。git stash 命令。先 git add *,然后 git stash -m "blabla" (或者 git stash save 'blabla')存下来当前暂存区(staging area)内容。这时候工作区和暂存区就清空了,我们可以checkout到别的版本下干活。之后 git stash pop 取出最近一次储藏的结果并弹栈。多次储藏可以 git stash list 查看储藏记录列表;git stash apply stash@{index} 取出储藏;git stash drop stash@{index} 删除储藏。
github 的 Fork:把仓库复制成自己的一个仓库,然后就可以在上面搞事情了。比如正常人要给 NVIDIA 或 Microsoft 的 github 上pull东西是不允许的,一般都是 Fork 然后 Pullrequest。
.gitignore:github doc. must in your repository's root directory. example:
*.log
*.sql
*.sqlite
这样会自动忽略这三类文件。
patch:patch意为“补丁”,当我们对项目做了一点小修改后,可以生成一个仅包含修改信息的 .patch 文件,然后 email 给管理者让他打上 patch。使用方法:(首先要 fork 后 clone 之类的)首先 checkout 到要做修改的 commit 版本,然后进行一些修改,然后 git format-patch -l edd9....3d97b,其中 -1 意思应该是生成和前面一个版本的比对 .patch 文件,这样会得到一个 .patch 文件。有了这个文件就可以让别人在对应 commit 版本(可能只要不冲突的版本就行)下 git apply xx.patch 就能修改。详见下图

git rebase 与冲突处理:如果我在本地从版本 A 做修改到了版本 B,lsr 从 A 修改到了 C,并且 lsr 还把 C push 到了远端。这时候我需要把 C 拉下来并与 B 做合并。这时候会提示需要 git rebase。对 rebase 的理解。只需要执行命令 git rebase,这时候就会提示让我处理冲突。建议用 VSCode 处理冲突。有的不需要处理(如只有我动过的文件),有的需要处理,可以选择冲突的块要自己的还是要 lsr 的,抑或是整个都要 lsr 的。处理好后 git add * 加 git rebase --continue。注意这时候 HEAD 指针会指向“基”(这里是 C),并显示 B 是在 C 基础上改过的。这样就需要 reset 到 B,并 push 上去。
checkout vs. reset(待进一步学习):改变 git 显示的版本(HEAD) 有两种做法,一种是 git checkout <hash>,这样就会提示 detached HEAD,这个时候只能看,没办法 git push 之类的操作。另一种做法是 git reset --hard <hash>,这样就会把 HEAD 移动到 <hash>。似乎说会把 <hash> 后面所有的改动都删掉,不过 reset 后可以 git push。
修改 git commit message 默认编辑器:git config --global core.editor "vim" 可以将默认编辑器设置为 vim。如果只想在某个仓库修改,可以去掉 --global
放弃本地的修改而恢复到原来的commit: git checkout -- <file-name>: To discard changes to a specific (uncommitted) file. git checkout -- .: To discard all uncommitted changes in your working directory.
git submodules: git submodule add git@github.com:chaconinc/DbConnector to add a submodule.
After cloning a repository with submodules, initialize and update them with: git submodule update --init --recursive.
Update: git submodule foreach git pull
Commit Submodule Changes: If you make changes to a submodule, commit those changes within the submodule directory first, then update the main repository:
git commit -am "Updated submodule" # In the submodule directory
cd ../main-repo
git add <submodule-directory>
git commit -m "Updated submodule reference"
对 git 原理的理解
git rebase: e.g. A -> B -> C -> D(branchA), A -> B -> E -> F(branchB). and you (branchA)> git rebase branchB, then git will add C and D one by one after F. You should solve the conflicts one by one. After solving, you may run git rebase --continue according to the hints.
git merge: (branchA)> git merge branchB: git will find the changed files by branchB but not changed by branchA, and change them. If a file is changed by both branchA and branchB, the merging will fail(conflict), and git will mark the difference between change of branchA and change of branchB. If no conflict, git will help you commit it as "merge". Or you should fix the conflicts (modify the conflicted files directly) and commit manually.
git fetch: modify origin/main but not main.
git pull: git fetch + git merge(merge origin/main to main).
fast-forward merge: If branchA has no other commits except those of branchB, then git will mark branchA directly to the commit version of branchB, and won't make another commit. e.g. A -> B(main) -> C -> D(feature). Then we can make a fast-forward merge from feature in main.
Set merge --no-ff to disable it.
If there are files modified but not committed: if the merge is not relevant to it(branchB didn't modify it), good; if is, you should make commit first.
conda 版本管理
咕咕咕
注意 conda 管理的话就会产生好多环境,需要识别哪个东西在那个环境的。提示:sudo 的时候不会进入 conda 环境,因此如果想要用 sudoer 身份执行某一特定环境的代码(如 scapy)的时候需要把 sudo 换成 sudo env PATH=...:$PATH,如可以使用 sudo env PATH=/home/jiazp/miniconda3/bin/python:$PATH scapy(要在bash中) 来让 scapy 有更高权限。
Proxy, 端口转发, ladder relative(仍需了解学习相关常识)
p=搞研究, q=fq, r=违法, ((p->q) ^ (q->r)) -> (p->r)
(不挂梯子真不好搞研究)纯属经验,完全不懂,内部原理仍需学习,仅记录方法。
之前在 wallesspku 搞了个翻的方法,以下基于 *** 。
General 里面打开 System Proxy,然后在 Proxies 里面选个能用的就好。
- 关于 Linux 上的 *** for Windows
wallesspku 上有一些资源。这种东西变化很多,说不准啥时候就没了,得实时查找。
- 额外添加需要翻的网站
背景:WallPKU 里面已经有了绝大多数用得到的网站,但也有如 huggingface.co 等没加进去的需要手动加。
方法:在 Profile 里面找到 WallessPKU.yaml,右键选 edit,找到里面的 rules,照猫画虎把 huggingface.co 加进去,用 DOMAIN-SUFFIX 和 \U0001F9F1 GFW(模仿 youtube 的写法)
- 端口转发
背景:本机能翻,但虚拟机和服务器还不行。
方法:每次用之前需要先在 *** 上面打开 Allow LAN(据说不建议一直开?),然后(最好)在 Windows 本地上打开 ssh -p 44322 jiazhaopeng@166.111.68.163 -R localhost:7890:localhost:7890,其中 -R 表示从本地转发到服务器上(对应地,-L 表示从服务器转发到本地上),把本地的 localhost:7890 转发到服务器的 localhost:7890。然后在 nico0 上就可以使了。如果想要在 nico3 上使用,那么还需要再套一层:ssh nico3 -R local......(同上),把端口转发到 nico3 上(当然不能直接这么干,因为 ssh nico3 需要在 nico3 上有任务。
可以在 .ssh/config 里面配置:
Host i1
HostName e1.sc.team
User jiazhaopeng
ProxyJump nico
RemoteForward 12333 localhost:12333
RemoteForward 9874 localhost:9874
对于 GitHub,需要在虚拟机或服务器上的 ~/.ssh/config 里面添加配置(注意关掉梯子以后要注释掉 ProxyCommand 那一行)
Host github.com
Hostname ssh.github.com
Port 443
ProxyCommand nc -X connect -x localhost:7890 %h %p
其中 7890 是 *** 里面 General 中 Port 上面写的编号。其他的直接写上去即可。
对于 HTTP 和 HTTPS,需要如下:
jiazhaopeng@nico0:~$ export HTTP_PROXY=http://localhost:7890
jiazhaopeng@nico0:~$ export HTTPS_PROXY=http://localhost:7890
remark: 可以直接写成个脚本每次 source 一下:
export http_proxy=http://localhost:12333
export https_proxy=http://localhost:12333
export all_proxy=socks5://127.0.0.1:12333
curl https://www.google.com
- 常识
ping 不走代理,可以用 curl 来测试:curl https://www.google.com(需要全名)。
- Feb. 25, 2024 updated:
在新笔记本上试过可行的方法:首先要用管理员身份打开 ***,然后(可能需要 install 一下Service Mode),打开 Mixin(同时启用 http 和 socks 代理) 和 System Proxy,把 Port 改为 12333(防止扫荡),在 Proxies 里面选一个能用的服务器。如果想要让 linux 也能用,还需要打开 Allow LAN(并在linux 里面设置一堆配置)
比如要想在 windows 里面手动配置代理,需要 SET https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:12333,然后就可以使用 curl https://www.google.com 了。(对应 http 也一样)。linux 的命令为 export https_proxy=http://183.172.77.20:12333,其中 183.172.77.20 为广域网 ip,可以在 windows 的 cmd 中用 ipconfig 命令得到,其中的 IPv4 地址 即为所求;12333 是 *** 的 port。注意这个 ip 地址每次开机可能会变,所以每次重启需要重新配置。
如果想要在服务器上连代理,也需要 export http_proxy=http://183.172.77.20:12333 之类的。如果想 git clone,需要在 ~/.ssh/config 里面设置(见上)。因为这里没有端口转发,所以可以直接把 localhost:7890 改成 183.172.77.20:12333。
小常识: github 用 http clone 下来的项目只能看不能改,要想该必须用 ssh
- proxychains4
郭神推荐的,说是可以惩治那些死活不用代理的命令,强制让他们用代理。linux 中安装 sudo apt install proxychains4。
方便起见,可以重命名:首先 which proxchains4 确定位置;然后 sudo ln -s /usr/bin/proxychains /usr/bin/p4 创建链接。
可以 sudo nano /etc/proxychains4.conf 查看和修改配置文件。需要修改如下两点:1. 找到并开启 quiet_mode(不然可能会输出一堆东西)2. 在最后 [ProxyList] 下面修改为 http 183.172.77.20 12333,注释掉 socks 那行。注意重启后检查更新 ip 地址。
使用方法:p4 command 如 p4 curl https://www.google.com
nc,网络相关
gugugu
Apache(HTTP server)
(记住 HTTP server 是固定在 80 端口)
Windows 上的安装教程。这个教程挺详细,直接包养到会在本地开启 HTTP server 本地访问。注意可能需要 net start Apache2.4 来启动。
netstat -na 显示所有端口情况。
telnet 命令可以检查能不能连接某一端口,例如 telnet 127.0.0.1 80。
在 Windows Defender 防火墙(可以在控制面板中找到。trick:控制面板“显示大图标”能看到更多选项)-高级设置中可以设置入站、出站规则。添加端口。(似乎 apache 会自动把端口添加好。实在不行手动添加个TCP 80 端口:防火墙开端口教程)。如果实在搞不定防火墙可以索性把防火墙关了(反正 Linux 本身也没有防火墙也没怎么着)。还搞不定就用手机热点直接连接。
一些基于 Linux 的小工具
thu-cloud-dl
打包下载清华云盘的文件夹
tldr
sudo apt install tldr,然后 tldr -u 加载,完事以后就可以 tldr <command> 查命令的简短版 manual 了。(如果说 /home/train/.local/share/tldr: createDirectory: does not exist (No such file or directory) 那就建一个 /home/train/.local/share/tldr,tldr会把 github 上面的东西 clone 进这个文件里面)
fish
更 friendly 的 shell: fish(friendly interface shell),更好使些。
设置 fish 为默认 shell:chsh -s /usr/bin/fish。
使用 bash 命令打开 bash。
fish 可以 history 来查看 shell 输入的历史。
注意 fish 并不 和 POSIX sh 兼容,所以无法运行 bash 脚本,需要 bash 切换到 bash 运行。
others
wget, curl:向网站发送、接收信息。
xdg-open: 打开各种文件
extensions: 里面可以选择装 gnome 的各种插件,比如 Caffeine, OpenWeather 就挺好玩的
双系统
看的这个:装双系统 知乎。还可以参考科服资料:Windows + Linux(Ubuntu) 双系统安装教程
不知道怎么做的U盘,因为是 gsy 帮我整的。记得挂载 / 和 /home
按照这个知乎教程安装可能不会把启动用的 grub(?) 装到 ubuntu 的 efi 上,而和 win 的 efi 装到一起。这样如果 win 更新,可能会把 linux 的给抹掉。所以建议装到不同的位置。可以使用 fdisk:Linux 下管理磁盘分区的利器 来查看分区情况,用 mount & umount 之类的东西来修改?(还是找科服吧)
Ubuntu 安装搜狗输入法
看这个,注意安装最后那两个依赖。
跟教程的时候让更新需要更新;如果没有用就 kill fcitx 后 fcitx start 看看能不能成功启动,有可能会提示原因。我这次修复就需要在一个可以开机自启的地方(如 /etc/environment,or /etc/profile)添加:
(在/etc/environment)
GTK_IM_MODULE=fcitx
QT_IM_MODULE=fcitx
XMODIFIERS=@im=fcitx
SLURM 任务管理与 MPI, OpenMP 并行计算
(不是特别符合本文主题,但经常用,就放这里吧,记录一些问题和思考)
slurm
一个 HPC 场景常用的资源调度器。参考 pku hpc guide
sbatch
sbatch 的各个参数:可以通过 sbatch --help 查询。
Sbatch 脚本并不会帮你主动启动多个进程,只是会给你划分硬件资源,你(例如用 mpirun)使用的资源不可以超过给你划分的硬件资源。当然,sbatch 还会设定一些环境变量指导分配进程,例如设定 #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=2 和 #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=3 可以设定每个节点最多启动的进程数,同时授权使用多于进程数的核心;此时如果 mpirun -n 4 ... 就会自动把这四个进程分配到两个节点上。
MPI
消息传递并行模型。参考翟老师高性能计算导论课件。
mpirun:具体参数可以通过 mpirun --help 查询。mpirun 会根据你设定的进程数和映射方式启动多进程。intelmpi 可以用 machinefile,openmpi 可以用 hostfile,格式相似但略有不同,参考官方文档。
OpenMP
共享内存并行模型。参考翟老师高性能计算导论课件。
进程绑定
参考 高性能计算导论实验文档。部分信息过时或有 typo,需要配合各工具文档使用。
MPI+OpenMP 混合程序进程绑定
建议使用 wrapper + numactl工具 进行细粒度进程绑定。下面是一个例子:(参考哥廷根大学超算文档, 以 OpenMPI 为例)
比如我们有一个简单的 MPI+OpenMP 混合程序:
// hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <omp.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Initialize the MPI environment
MPI_Init(NULL, NULL);
// Get the number of processes
int world_size;
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_size);
// Get the rank of the process
int world_rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_rank);
// Get the name of the processor
char processor_name[MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME];
int name_len;
MPI_Get_processor_name(processor_name, &name_len);
int nthreads, tid;
// Fork a team of threads giving them their own copies of variables
#pragma omp parallel private(nthreads, tid)
{
// Obtain thread number
tid = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("Hello World from thread = %d, processor %s, rank %d out of %d processors\n", tid, processor_name, world_rank, world_size);
// Only primary thread does this
if (tid == 0)
{
nthreads = omp_get_num_threads();
printf("Number of threads = %d\n", nthreads);
}
} // All threads join primary thread
// Finalize the MPI environment.
MPI_Finalize();
}
我们可以通过 mpicc -fopenmp -o hello hello.c 来编译得到可执行文件 hello。
为了在 slurm 上运行这一程序,我们写一个 run-wrapper.sh 来通过 wrapper 指定进程映射:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=mpiomp-test
#SBATCH --output=mpiomp.out
#SBATCH --error=mpiomp.err
#SBATCH --time=02:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=LONG
#SBATCH --nodes=2
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=2
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=3
export MAPBY="--bind-to none --report-bindings ./wrapper.sh"
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=3
export OMP_PROC_BIND=spread
export OMP_PLACES=threads
mpirun -n 4 ${MAPBY} ./hello
注意这里需要 mpirun --bind-to none 来避免干扰。当然这里 nodes 数量和 ntasks-per-node 数量可以更大,只要够用就行。mpirun 实际上会让每一个进程执行一下 wrapper.sh,由它来手动为每一个进程指定核心:
#!/bin/bash
# local id within its node
LOCAL_RANK=$OMPI_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_RANK # for OpenMPI
# LOCAL_RANK=$MPI_LOCALRANKID # for Intel MPI
# LOCAL_RANK=$SLURM_LOCALID # for SLURM
# num of processes within a node
LOCAL_SIZE=$OMPI_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_SIZE # for OpenMPI
# LOCAL_SIZE=$MPI_LOCALNRANKS # for Intel MPI
# LOCAL_SIZE=$SLURM_TASKS_PER_NODE # for SLURM
# calculate binding parameters
CORES_PER_PROCESS=$OMP_NUM_THREADS
CORE_START=$(($LOCAL_RANK * $CORES_PER_PROCESS))
CORE_END=$((($LOCAL_RANK + 1) * $CORES_PER_PROCESS - 1))
CORES=$(seq -s, $CORE_START 1 $CORE_END) # e.g. 3,4,5
# execute command with specific cores
echo "Process $LOCAL_RANK on $(hostname) bound to core $CORES"
exec numactl -C "$CORES" $@
上面这个 wrapper.sh 通过 mpirun 设定的环境变量来计算,通过 numactl -C 来指定这个进程具体用哪些核.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号