BLOG-2
BOLG-2
前言
难度
- 题目集四的1,3两题较为简单,第2题是在三角形的基础上又衍生出来的四边形,难度较高。
- 题目集五难度也较高,说是五边形的作业,在我看来更像是多边形的作业,因为写了多边形的父类。
- 期中考试的题目较为简单,用于检测对基础的掌握程度。
题量
- 题目集四和题目集五的题量都较大,期中考试的题量较小。
知识点
- 4-7-1使用到了Pattern类和Matcher类
String s = sc.nextLine();
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
while(!s.equals("end")) {
int sum = 0;
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(s);
while( matcher.find()) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(0) ) ;
sum += num;
}
System.out.println(sum);
s = sc.nextLine();
}可以很好的用于检测和提取字段中匹配正则表达式的字段。
- 4-7-2使用到父类
class Polygon {};
class Quadrangle extends Polygon{};
class Triangle extends Polygon{);
类内部细节可见源码提高了代码的复用性。
- 5-7-1计算多边形的面积时使用鞋带定理
// 计算多边形的面积
double calculateArea() {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
double num1 = 0;
double num2 = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % listPoint.size();
num1 += listPoint.get(i).getx() * listPoint.get(k).gety();
num2 += listPoint.get(i).gety() * listPoint.get(k).getx();
}
double area = Math.abs((num1 - num2) / 2);
return area;
} - 5-7-2在计算多边形重叠面积时,先求出两个多边形的交点,然后分别得到多边形的互相在其内部的点,组成的一个构成多边形的点的有序数组。
// 返回重写排序的数组
ArrayList<Point> listReorder( ArrayList<Point> list){
Point core = this.calculateCore();
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
double num = 0;
double min = 0;
int flag = 0;
while(list.size() != 0) {
min = Math.atan2(list.get(0).gety() - core.gety(), list.get(0).getx()- core.getx());//此时点是无序的,还需对其进行排序
for( int i=1 ; i < list.size() ; i++) {
num = Math.atan2(list.get(i).gety()- core.gety(), list.get(i).getx()- core.getx());
if( min > num ) {
flag = i;
min = num ;
}
}
ps.add(list.get(flag));
list.remove(flag);
flag = 0;
}
return ps;
}// 得到两多边形重叠部分的面积
double getOverlapArea( Polygon polygon) {
if( this.judgeIsContain(polygon) || this.judgeIsInside(polygon) || this.judgeCompletelyCoincide(polygon)) {
return Math.min( this.calculateArea() , polygon.calculateArea());
}
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.addAll(this.calculatePolygonIntersection(polygon));
points.addAll(this.getPointInSide(polygon));
points.addAll(polygon.getPointInSide(this));
points = this.deleteRepeatPoint(points);
points = this.listReorder(points);
Polygon p = new Polygon(points);
return p.calculateArea();
}
设计与分析
-
4-7-1识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式)
背景简介:
“蛟龙号”载人深潜器是我国首台自主设计、自主集成研制的作业型深海载人潜水器,设计最大下潜深度为7000米级,也是目前世界上下潜能力最强的作业型载人潜水器。“蛟龙号”可在占世界海洋面积99.8%的广阔海域中使用,对于我国开发利用深海的资源有着重要的意义。
中国是继美、法、俄、日之后世界上第五个掌握大深度载人深潜技术的国家。在全球载人潜水器中,“蛟龙号”属于第一梯队。目前全世界投入使用的各类载人潜水器约90艘,其中下潜深度超过1000米的仅有12艘,更深的潜水器数量更少,目前拥有6000米以上深度载人潜水器的国家包括中国、美国、日本、法国和俄罗斯。除中国外,其他4国的作业型载人潜水器最大工作深度为日本深潜器的6527米,因此“蛟龙号”载人潜水器在西太平洋的马里亚纳海沟海试成功到达7020米海底,创造了作业类载人潜水器新的世界纪录。
从2009年至2012年,蛟龙号接连取得1000米级、3000米级、5000米级和7000米级海试成功。下潜至7000米,说明蛟龙号载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一。
2012年6月27日11时47分,中国“蛟龙”再次刷新“中国深度”——下潜7062米。6月3日,“蛟龙”出征以来,已经连续书写了5个“中国深度”新纪录:6月15日,6671米;6月19日,6965米;6月22日,6963米;6月24日,7020米;6月27日,7062米。下潜至7000米,标志着我国具备了载人到达全球99%以上海洋深处进行作业的能力,标志着“蛟龙”载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一,标志着中国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平。
‘蛟龙’号是我国载人深潜发展历程中的一个重要里程碑。它不只是一个深海装备,更代表了一种精神,一种不畏艰险、赶超世界的精神,它是中华民族进军深海的号角。
了解蛟龙号”载人深潜器“的骄人业绩,为我国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平而自豪,小伙伴们与祖国同呼吸、共命运,一定要学好科学文化知识、提高个人能力,增强创新意识,做事精益求精,立科技报国之志!
请编写程序,实现如下功能:读入关于蛟龙号载人潜水器探测数据的多行字符串,从给定的信息找出数字字符,输出每行的数字之和。
提示 若输入为“2012年2月”,则该行的输出为:2014。若干个连续的数字字符作为一个整体,以十进制形式相加。
输入格式:
读入关于蛟龙号载人潜水器探测数据的多行字符串,每行字符不超过80个字符。
以"end"结束。
输出格式:
与输入行相对应的各个整数之和。
- 源码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main{
public static void main( String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
while(!s.equals("end")) {
int sum = 0;
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(s);
while( matcher.find()) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(0) ) ;
sum += num;
}
System.out.println(sum);
s = sc.nextLine();
}
}
}
- 源码分析
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
while(!s.equals("end")) {
int sum = 0;
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(s);
while( matcher.find()) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(0) ) ;
sum += num;
}
Pattern类提供一个正则表达式pattern,Matcher类用于匹配给的字符中符合pattern结构的字符串并且存放到group(0)中。
-
4-7-2点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。 以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。 选项包括: 1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral" 3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral" 4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。 后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s: 1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。 2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y 5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
- 源码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {
/*
* 用于判断输入是否合法 合法就返回一个数组 不合法就返回空
*/
private void isLegal(String string) {
if (!string.matches(
"^[1-5][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}}
// 判断点数量是否正确
private void pointsNum(int len, String[] str) {
if (str[0].matches("[123]")) {
if (str.length != 9) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
} else if (len == 4) {
if (str.length != 13) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
} else if (len == 5) {
if (str.length != 11) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}// 返回不含重复对象的数组
private ArrayList<Point> reallyPoint(Point[] points) {
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
ps.add(points[0]);
if (!ps.contains(points[1])) {
ps.add(points[1]);
}
if (!ps.contains(points[2])) {
ps.add(points[2]);
}
if (!ps.contains(points[3])) {
ps.add(points[3]);
}
return ps;
}// 判断点是否重合
private void pointsCoincide(int len, String[] str) {
ArrayList<Point> set1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
set1.add(point1);
set1.add(point2);
set1.add(point3);
set1.add(point4);
Point[] points = set1.toArray(new Point[set1.size()]);
ArrayList<Point> set = this.reallyPoint(points);
// System.out.println(set.size()); System.out.println(set);
if (len == 4 && point1.isCoincide(point2)) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
if (str[0].matches("[13]")) {
if (set.size() != 4) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}private void play(int len, String[] str) {
if (len == 1) {
this.play1(str);
} else if (len == 2) {
this.play2(str);
} else if (len == 3) {
this.play3(str);
} else if (len == 4) {
this.play4(str);
} else if (len == 5) {
this.play5(str);
}}
// 5:-60,40 -40,60 -40,40 -40,0 -80,40
// 5:20,40 0,60 0,40 0,0 40,40
private void play5(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle(points);
if (q.judegeIsQuadriangle()) {
if (q.judgePointInEdges(point1)) {
System.out.println("on the quadrilateral");
} else if (q.judgePointInSide(point1)) {
System.out.println("in the quadrilateral");
} else {
System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral");
}
} else if (q.judgeIsTriangle()) {
ArrayList<Point> p = q.realPolygon();
Triangle t = new Triangle(p);
if (t.judgePointInEdges(point1)) {
System.out.println("on the triangle");
} else if (t.judgePointInSide(point1)) {
System.out.println("in the triangle");
} else {
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
} else {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}}
private void play4(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
Point point6 = new Point(str[11], str[12]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
points.add(point6);
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle(points);
Line l = new Line(point1, point2);
if (q.judegeIsQuadriangle()) {
if (q.judgeLineIsCoincide(l)) {
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
return;
}
System.out.print(q.calculateIntersectionCount(l));if (q.calculateIntersectionCount(l) == 2) {
System.out.print(" ");
print(q.calculateCutArea(l));
System.out.print(" ");
print(q.calculateArea() - q.calculateCutArea(l));
}
} else if (q.judgeIsTriangle()) {
ArrayList<Point> p = q.realPolygon();
Triangle t = new Triangle(p);
if (t.judgeLineIsCoincide(l)) {
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
return;
}
System.out.print(t.calculateIntersectionCount(l));
if (t.calculateIntersectionCount(l) == 2) {
System.out.print(" ");
print(t.calculateCutArea(l));
System.out.print(" ");
print(t.calculateArea() - t.calculateCutArea(l));
}
} else {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}}
private void play3(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point1);
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle(points);
if (q.judgeIsPolygon()) {
System.out.print(q.judgePolygonType());
System.out.print(" ");
print(q.calculatePerimeter());
System.out.print(" ");
print(q.calculateArea());
} else {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
}private void play2(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point1);
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle(points);
if (q.judegeIsQuadriangle()) {
System.out.println(q.judgeQuadriangleIsRhombic() + " " + q.judgeQuadriangleIssRectangular() + " "
+ q.judgeQuadriangleIssSquare());
} else {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}}
private void play1(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point1);
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle(points);
System.out.println(q.judegeIsQuadriangle() + " " + q.judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle());
}private void print(double num) {
if (num * 1000 % 1 != 0) {
System.out.printf("%.3f", num);
} else {
System.out.print(num);
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String string = sc.nextLine();
test.isLegal(string); // 判断输入合法性
String[] str = string.split(",| |:");
int len = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
test.pointsNum(len, str); // 判断点的数量是否正确
test.pointsCoincide(len, str); // 判断点是否重合
test.play(len, str);
}}
class Polygon {
private ArrayList<Point> pointList = new ArrayList<Point>();
public ArrayList<Point> getPointList() {
return pointList;
}public Polygon() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}public Polygon(ArrayList<Point> pointList) {
super();
this.pointList = pointList;
}
// 判断能否构成多边形,能返回true
boolean judgeIsPolygon() {
ArrayList<Line> list = this.getLineList();
int k = 0;
int count = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 2 ) % list.size();
for( int j = 0 ; j < list.size() - 3; j++) {
if( list.get(i).judgeIntersectionIsInLine(list.get(k))) {
count ++;
}
k = (k + 1) % list.size();
}
}
return count == 0;
}
// 删除多边形冗余的点,只留下真正构成多边形的点,以动态数组返回
ArrayList<Point> realPolygon(){
ArrayList<Point> list = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> list1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
list1.add(this.pointList.get(0));
for(int i = 0; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) { //先删除重复的点
if( !list1.contains( pointList.get(i) ) ) {
list1.add(pointList.get(i));
}
}
int k1 = 0;
int k2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { // 在删除在一条线上的点的中间那个
k1 = (i - 1 + list1.size()) % list1.size();
k2 = (i + 1 + list1.size()) % list1.size();
Line l = new Line( list1.get(k1),list1.get(k2));
if( !l.judgePointInLine( list1.get(i) ) && !list.contains( list1.get(i) )) {
list.add( list1.get(i));
}
}
return list;
}// 由多边形的点生成多边形相邻两点构成的对角线,返回对角线的动态数组
ArrayList<Line> getAdjacentLineList() {
ArrayList<Line> list = new ArrayList<Line>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
int k1 = 0;
int k2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k1 = (i - 1 + listPoint.size()) % listPoint.size();
k2 = (i + 1 + listPoint.size()) % listPoint.size();
Line l = new Line(listPoint.get(k1), listPoint.get(k2));
list.add(l);
}
return list;
}// 由多边形的点生成多边形的边,返回边的动态数组
ArrayList<Line> getLineList() {
ArrayList<Line> list = new ArrayList<Line>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % listPoint.size();
Line l = new Line(listPoint.get(i), listPoint.get(k));
list.add(l);
}
return list;
}// 判断多边形的点是否重合 有重合的点返回true
boolean pointIsCoincide() {
ArrayList<Point> list = new ArrayList<Point>();
list.add(this.pointList.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) {
if (list.contains(pointList.get(i))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}// 计算多边形的周长
double calculatePerimeter() {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
double circle = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
circle += listLine.get(i).calculateLineLength();
}
return circle;
}// 计算多边形的面积
double calculateArea() {
double num1 = 0;
double num2 = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % this.pointList.size();
num1 += this.pointList.get(i).getx() * this.pointList.get(k).gety();
num2 += this.pointList.get(i).gety() * this.pointList.get(k).getx();
}
double area = Math.abs((num1 - num2) / 2);
return area;
}// 当交点是2个时,求线切割多边形后的面积,返回面积小的部分
double calculateCutArea(Line line) {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint2 = new ArrayList<Point>();
for (int i = 0; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) {
if (line.judgePointInLineRight(this.pointList.get(i))) {
listPoint1.add(this.pointList.get(i));
listPoint2.add(this.pointList.get(i));
}
}
listPoint1.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(0));
listPoint1.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(1));
listPoint2.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(1));
listPoint2.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(0));
Polygon p1 = new Polygon(listPoint1);
Polygon p2 = new Polygon(listPoint2);
double area = 0;
if( p1.judgeIsPolygon()) {
area = p1.calculateArea();
}else {
area = p2.calculateArea();
}
return Math.min(area, this.calculateArea() - area);
}// 计算直线与多边形交点
ArrayList<Point> calculateIntersection(Line line) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point point;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
point = listLine.get(i).calculateIntersection(line);
if (listLine.get(i).judgePointInLine(point) && !listPoint.contains(point)) {
listPoint.add(point);
}
}
return listPoint;
}// 计算直线与多边形交点数量
int calculateIntersectionCount(Line line) {
return this.calculateIntersection(line).size();
}// 判断点是否在多边形的边上 若在返回true
boolean judgePointInEdges(Point point) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
if (listLine.get(i).judgePointInLine(point))
return true;
}
return false;
}// 判断点是否在多边形内部
boolean judgePointInSide(Point point) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = new ArrayList<Point>();
listPoint.add(point);
listPoint.add(listLine.get(i).getPoint1());
listPoint.add(listLine.get(i).getPoint2());
Polygon p = new Polygon(listPoint);
sum += p.calculateArea();
}
return !this.judgePointInEdges(point) && sum == this.calculateArea();
}// 判断线是否与多边形某边重合, 重合返回true
boolean judgeLineIsCoincide(Line line) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
if (listLine.get(i).isCoincide(line)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}// 判断多边形的类型,凸多边形返回true
boolean judgePolygonType() {
ArrayList<Line> list = this.getAdjacentLineList();
int count = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % list.size();
if (list.get(i).judgeIntersectionIsInLine(list.get(k))) {
count++;
}
}
return count == list.size();
}}
class Quadrangle extends Polygon{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private Point point3;
private Point point4;public Quadrangle(ArrayList<Point> points) {
super(points);
this.point1 = points.get(0);
this.point2 = points.get(1);
this.point3 = points.get(2);
this.point4 = points.get(3);
}
// 判断是否是四边形 (即四个点能否构成四边形) ,判断结果输出true/false
boolean judegeIsQuadriangle() {
return this.judgeIsPolygon() && this.realPolygon().size() == 4;
}// 判断四个点在无法构成四边形的情况下,能否构成三角形
boolean judgeIsTriangle() {
return this.judgeIsPolygon() && this.realPolygon().size() == 3 ;
}
// 判断是否平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false
boolean judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line34 = new Line(point3, point4);
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line34.calculateLineLength() && line12.judgeParallel(line34) && this.judgeIsPolygon();
}// 判断是否是菱形
boolean judgeQuadriangleIsRhombic() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line23 = new Line(point2, point3);
return judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() && line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength();
}// 判断是否是矩形,
boolean judgeQuadriangleIssRectangular() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line23 = new Line(point2, point3);
return judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() && line12.judgeIsPerpendicular(line23);
}// 判断是否是正方形,
boolean judgeQuadriangleIssSquare() {
return judgeQuadriangleIsRhombic() && judgeQuadriangleIssRectangular();
}
}
class Triangle extends Polygon{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private Point point3;
// 构造函数
public Triangle(ArrayList<Point> points) {
super(points);
this.point1 = points.get(0);
this.point2 = points.get(1);
this.point3 = points.get(2);
}
//判断三角形是否等腰
boolean isIsoscelesTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line13.calculateLineLength() || line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() || line13.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() ;
}
//判断三角形是否等边
boolean isRegularTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line13.calculateLineLength() && line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() ;
}
// 计算三角形的重心
Point calculateCore() {
double x = ( point1.getx() + point2.getx() + point3.getx() ) / 3;
double y = ( point1.gety() + point2.gety() + point3.gety() ) / 3;
Point p = new Point(x,y);
return p;
}
// 判断是否为钝角三角形
boolean isObtuseTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a > b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b > a + c ;
}else {
return c > b + a ;
}
}
// 判断是否为直角三角形
boolean isRightTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a == b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b == a + c ;
}else {
return c == b + a ;
}
}
// 判断是否为锐角三角形
boolean isAcuteTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a < b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b < a + c ;
}else {
return c < b + a ;
}
}
}
class Line {private Point point1;
private Point point2;
// 构造函数
public Line(Point point1, Point point2) {
super();
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
}
// 得到点一
Point getPoint1() {
return this.point1;
}
// 得到点二
Point getPoint2() {
return this.point2;
}
// 得到x的系数A
double getA() {
return point1.gety()-point2.gety();
}
// 得到y的系数B
double getB() {
return point2.getx()-point1.getx();
}
// 得到常数C
double getC() {
return point1.getx() * point2.gety() - point2.getx() * point1.gety();
}
// 得到直线的斜率K
double getK() {
return (point1.gety()-point2.gety())/(point1.getx()-point2.getx());
}
// 计算点到直线的距离
double calculateDistance( Point point) {
double a = Math.abs( this.getA()*point.getx() + this.getB()*point.gety() + this.getC());
double b = Math.sqrt(this.getA() * this.getA() + this.getB()*this.getB());
return a/b;
}
/* 判断三点是否共线
* 或者判断点是否在直线上
*/
boolean judgePointOnLine( Point point ){
return this.getA()*point.getx()+this.getB()*point.gety()+this.getC() == 0;
}
// 判断两直线是否平行 平行返回true
boolean judgeParallel( Line line ) {
if(this.getB() != 0 && line.getB() !=0)
return this.getK() == line.getK() ;
else if(this.getB() == 0 && line.getB() ==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
/*判断两直线是否垂直
* 采用向量法,避免对斜率是否存在的讨论
*/
boolean judgeIsPerpendicular(Line line) {
double x1 = this.point1.getx()-this.point2.getx();
double y1 = this.point1.gety()-this.point2.gety();
double x2 = line.point1.getx()-line.point2.getx();
double y2 = line.point1.gety()-line.point2.gety();
return x1*x2 + y1*y2 == 0;
}
// 计算线与线的交点
Point calculateIntersection( Line line) {
double x = (line.getC()*this.getB()-this.getC()*line.getB())/(this.getA()*line.getB()-line.getA()*this.getB());
double y = (line.getC()*this.getA()-this.getC()*line.getA())/(line.getA()*this.getB()-this.getA()*line.getB());
if(x==0) {
x=0;
}
if(y==0) {
y=0;
}
Point point = new Point(x,y);
return point;
}
// 判断直线上的点是否在某一线段的内部,包括端点 (若不想包含端点删掉 = 号即可)
boolean PointBetweenLine ( Point point ) {
if( point.getx() <= Math.max( this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx() ) && point.getx() >= Math.min( this.point1.getx() , this.point2.getx() ) && point.gety() <= Math.max( this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety() ) && point.gety() >= Math.min( this.point1.gety() , this.point2.gety() ))
return true;
else
return false;
}
// 判断点是否在某一线段内部包括端点
boolean judgePointInLine ( Point point ) {
return this.judgePointOnLine(point) && this.PointBetweenLine(point);
}
// 判断两线段是否有交点 有为true
boolean judgeIntersectionIsInLine( Line line) {
return this.judgePointInLine(this.calculateIntersection(line)) && line.PointBetweenLine(line.calculateIntersection(this));
}
// 计算线的长度
double calculateLineLength() {
return this.point1.calculateDistance(this.point2);
}
// 计算线的长度的平方
double calculateLineLength2() {
return this.point1.calculateDistance2(this.point2);
}
//判断两直线是否重合 重合返回true
boolean isCoincide( Line line) {
return this.judgeParallel(line) && line.judgePointOnLine(point1);
}
// 判断两直线是否有交点,且交点是否在后面传参的线段内
boolean judgeIntersectionIsInLaterLine( Line line) {
return !this.judgeParallel(line) && line.judgePointInLine( this.calculateIntersection(line) ) ;
}
// 判断点是否在直线的同一侧
boolean judgePointInLineRight( Point point ) {
return this.getA()*point.getx() + this.getB()*point.gety() + this.getC() >=0;
}
}
class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
// 构造函数
public Point(String stringx, String stringy) {
this.x = Double.parseDouble(stringx) ;
this.y = Double.parseDouble(stringy) ;
}
// 构造函数
public Point(double x, double y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
//得到点的x坐标
double getx() {
return this.x;
}
//得到点的y坐标
double gety() {
return this.y;
}
//计算两点的距离
double calculateDistance( Point point) {
double num = (this.x - point.x)*(this.x - point.x) + (this.y - point.y)*(this.y - point.y);
return Math.sqrt(num);
}
//计算两点的距离的平方
double calculateDistance2( Point point) {
return (this.x - point.x)*(this.x - point.x) + (this.y - point.y)*(this.y - point.y);
}
//判断两点是否重合 重合返回true
boolean isCoincide( Point point) {
return this.x==point.x&&this.y==point.y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Point other = (Point) obj;
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
}
- 源码分析
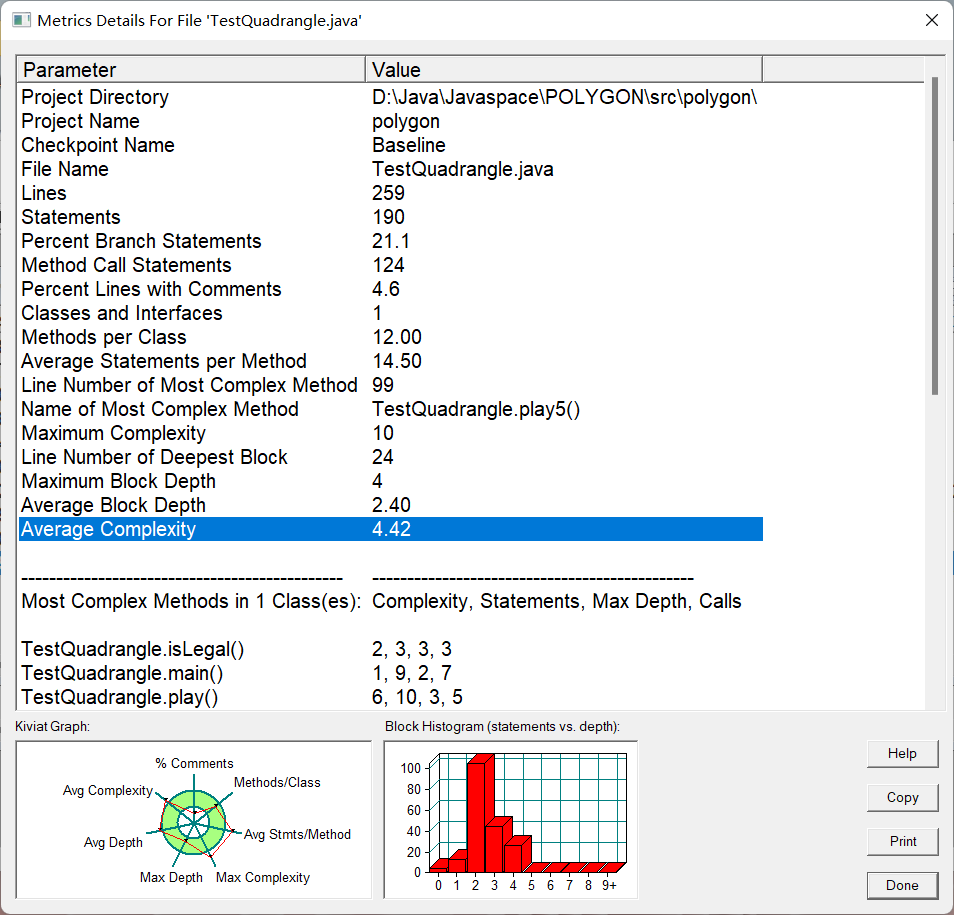
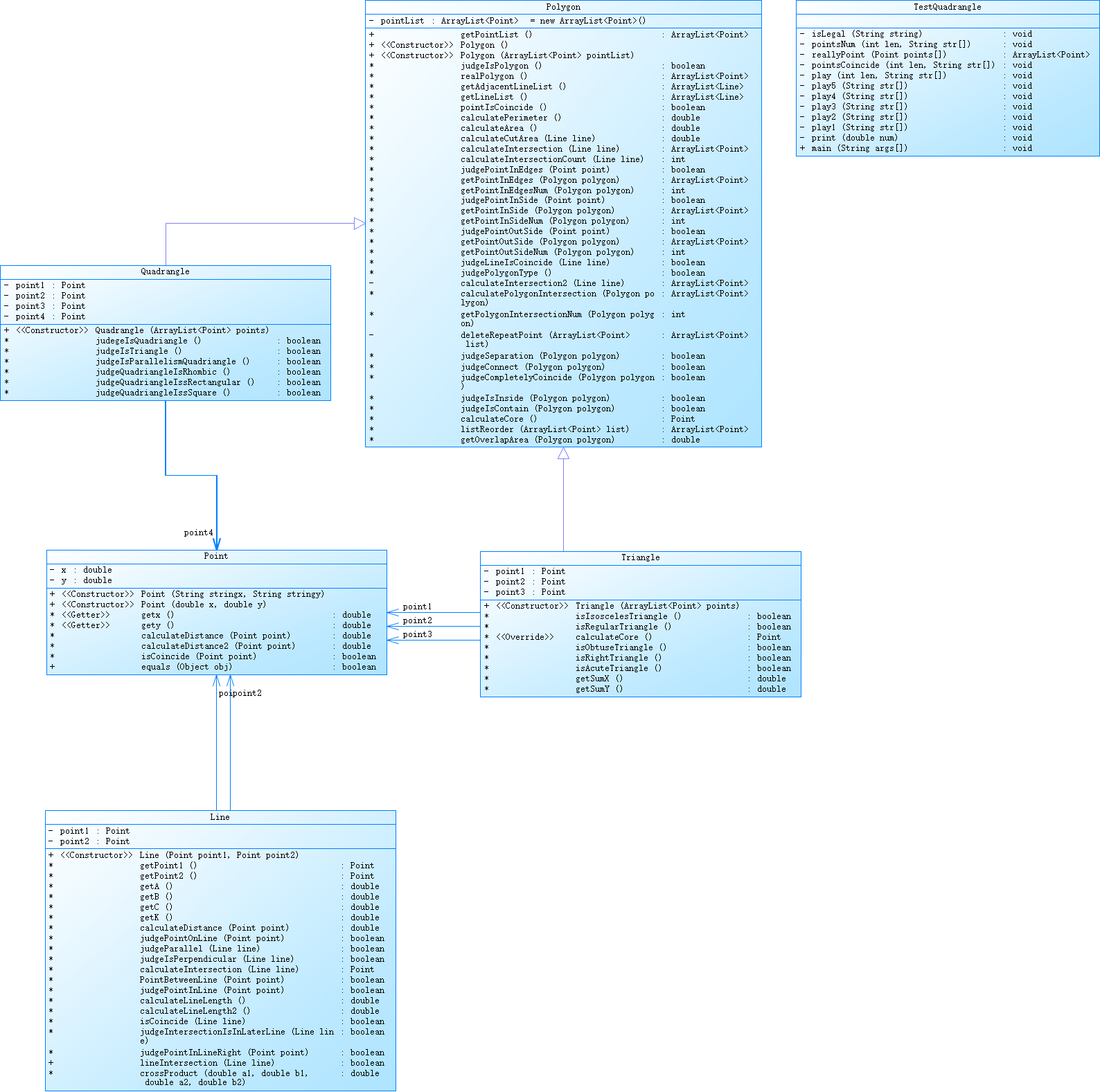
题目难度较大,上面的源码也不是我的最初版本,最初版本是没有父类Polygon的,已经找不到开始的代码了,是在老师上课讲解了父类之后加上去的父类。
并且有了三角形的铺垫后,代码的圈复杂度明显减小了,只有4.42.
-
4-7-3 设计一个银行业务类
编写一个银行业务类BankBusiness,具有以下属性和方法: (1)公有、静态的属性:银行名称bankName,初始值为“中国银行”。 (2)私有属性:账户名name、密码password、账户余额balance。 (3)银行对用户到来的欢迎(welcome)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“中国银行欢迎您的到来!”,其中“中国银行”自动使用bankName的值。 (4)银行对用户离开的提醒(welcomeNext)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!” (5)带参数的构造方法,完成开户操作。需要账户名name、密码password信息,同时让账户余额为0。 (6)用户的存款(deposit)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息),密码不对时无法存款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确、完成用户存款操作后,要提示用户的账户余额,例如“您的余额有1000.0元。”。 (7)用户的取款(withdraw)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息)。密码不对时无法取款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确但余额不足时提示“您的余额不足!”;密码正确且余额充足时扣除交易额并提示用户的账户余额,例如“请取走钞票,您的余额还有500.0元。”。 编写一个测试类Main,在main方法中,先后执行以下操作: (1)调用BankBusiness类的welcome()方法。 (2)接收键盘输入的用户名、密码信息作为参数,调用BankBusiness类带参数的构造方法,从而创建一个BankBusiness类的对象account。 (3)调用account的存款方法,输入正确的密码,存入若干元。密码及存款金额从键盘输入。 (4)调用account的取款方法,输入错误的密码,试图取款若干元。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。 (5)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额大于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。 (6)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额小于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。 (7)调用BankBusiness类的welcomeNext()方法。 输入格式: 输入开户需要的姓名、密码 输入正确密码、存款金额 输入错误密码、取款金额 输入正确密码、大于余额的取款金额 输入正确密码、小于余额的取款金额 输出格式: 中国银行(银行名称)欢迎您的到来! 您的余额有多少元。 您的密码错误! 您的余额不足! 请取走钞票,您的余额还有多少元。 请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!
源码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main{
public static void main( String[] args){
BankBusiness.welcome();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
BankBusiness account = new BankBusiness(sc.next(),sc.next());
account.deposit(sc.next(), sc.nextDouble());
account.withdraw(sc.next(), sc.nextDouble());
account.withdraw(sc.next(), sc.nextDouble());
account.withdraw(sc.next(), sc.nextDouble());
BankBusiness.welcomeNext();
}
}
class BankBusiness {
public static String bankName = "中国银行" ;
private String name ;
private String password ;
private double balance ;
public static void welcome () {
System.out.println(bankName+"欢迎您的到来!");
}
public static void welcomeNext () {
System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
}
public BankBusiness(String name, String password) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
this.balance = 0;
}
public void deposit(String password,double money) {
if( ! this.password.equals(password) ) {
System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}else {
this.balance += money;
System.out.println("您的余额有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
}
public void withdraw(String password,double money) {
if( ! this.password.equals(password) ) {
System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}else if(this.balance >= money){
this.balance -= money;
System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有"+this.balance+"元。");
}else {
System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
}
}
}
- 源码分析
这个题目较为简单,只有一个Main类和银行类,就不对其进行分析了。
-
5-7-1 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1 和 5-7-2 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
两个题目都是五边形,我写代码是放一起写的,就把两个题目放一起了。
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。 以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。 选项包括: 1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。 2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon" 3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部
分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内
部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s: 1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。 2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y 输入格式: 基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。 输出格式: 基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。 异常情况输出: 如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。 如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。 注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
- 源码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {
/*
* 用于判断输入是否合法 合法就返回一个数组 不合法就返回空
*/
private void isLegal(String string) {
if(!string.matches("^[1-6][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")){System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}}
// 判断点数量是否正确
private void pointsNum(int len, String[] str) {
if (str[0].matches("[12]")) {
if (str.length != 11) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
} else if (len == 3) {
if (str.length != 15) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}else if (len == 4 || len ==5) {
if (str.length != 21) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}else if (len == 6) {
if (str.length != 13) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}// 判断点是否重合
private void pointsCoincide(int len, String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
if (len == 3 && point1.isCoincide(point2)) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}//
private String findType(Polygon polygon) {
if(polygon.realPolygon().size() == 5)
return "pentagon";
if(polygon.realPolygon().size() == 4)
return "quadrilateral";
return "triangle";
}
private void play(int len, String[] str) {
if (len == 1) {
this.play1(str);
} else if (len == 2) {
this.play2(str);
} else if (len == 3) {
this.play3(str);
} else if(len == 4) {
this.play4(str);
} else if( len ==5) {
this.play5( str);;
} else if(len == 6) {
this.play6(str);
}}
private void play6(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
Point point6 = new Point(str[11], str[12]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
points.add(point6);
Polygon po = new Polygon(points);
if(po.judgePointInSide(point1)) {
System.out.println("in the "+this.findType(po));
}else if(po.judgePointInEdges(point1)) {
System.out.println("on the "+this.findType(po));
}else {
System.out.println("outof the "+this.findType(po));
}
}
private void play5(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
Point point6 = new Point(str[11], str[12]);
Point point7 = new Point(str[13], str[14]);
Point point8 = new Point(str[15], str[16]);
Point point9 = new Point(str[17], str[18]);
Point point10 = new Point(str[19], str[20]);
ArrayList<Point> points1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
points1.add(point1);
points1.add(point2);
points1.add(point3);
points1.add(point4);
points1.add(point5);
ArrayList<Point> points2 = new ArrayList<Point>();
points2.add(point6);
points2.add(point7);
points2.add(point8);
points2.add(point9);
points2.add(point10);
Polygon po1 = new Polygon(points1);
Polygon po2 = new Polygon(points2);
this.print(po1.getOverlapArea(po2));
}
private void play4(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
Point point6 = new Point(str[11], str[12]);
Point point7 = new Point(str[13], str[14]);
Point point8 = new Point(str[15], str[16]);
Point point9 = new Point(str[17], str[18]);
Point point10 = new Point(str[19], str[20]);
ArrayList<Point> points1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
points1.add(point1);
points1.add(point2);
points1.add(point3);
points1.add(point4);
points1.add(point5);
ArrayList<Point> points2 = new ArrayList<Point>();
points2.add(point6);
points2.add(point7);
points2.add(point8);
points2.add(point9);
points2.add(point10);
Polygon po1 = new Polygon(points1);
Polygon po2 = new Polygon(points2);
// System.out.println( po1.getPolygonIntersectionNum(po2));
if(po1.judgeSeparation(po2)) {
System.out.println("no overlapping area between the previous "+findType(po1)+" and the following "+findType(po2));
}
else if(po1.judgeConnect(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is connected to the following "+findType(po2));
}
//4:35,25 25,15 35,5 45,10 45,20
else if(po1.judgeCompletelyCoincide(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" coincides with the following "+findType(po2));
}
// the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
else if(po1.judgeIsInside(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is inside the following "+findType(po2));
}else if(po1.judgeIsContain(po2)) {
// the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" contains the following "+findType(po2));
}else {
// 4:0,0 6,0 8,0 7,3 6,6 4,0 6,0 8,0 12,0 7,3
//the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is interlaced with the following "+findType(po2));
}
}
private void play3(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
Point point6 = new Point(str[11], str[12]);
Point point7 = new Point(str[13], str[14]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
points.add(point6);
points.add(point7);
Pentagon pe = new Pentagon(points);
Line l = new Line(point1,point2);
if( pe.judgeLineIsCoincide(l)) {
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
System.exit(0);
}
if (pe.judgeIsPolygon()) {
System.out.print( pe.calculateIntersectionCount(l) );
if (pe.calculateIntersectionCount(l) == 2) {
System.out.print(" ");
print(pe.calculateCutArea(l));
System.out.print(" ");
print(pe.calculateArea() - pe.calculateCutArea(l));
}
} else {
System.out.println("not a polygon");
}
}private void play2(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point1);
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
Pentagon pe = new Pentagon(points);
if (pe.judgeIsPentagon()) {
System.out.print(pe.judgePolygonType());
if(pe.judgePolygonType()) {
System.out.print(" ");
print(pe.calculatePerimeter());
System.out.print(" ");
print(pe.calculateArea());
}
} else {
System.out.println("not a pentagon");
}}
private void play1(String[] str) {
Point point1 = new Point(str[1], str[2]);
Point point2 = new Point(str[3], str[4]);
Point point3 = new Point(str[5], str[6]);
Point point4 = new Point(str[7], str[8]);
Point point5 = new Point(str[9], str[10]);
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.add(point1);
points.add(point2);
points.add(point3);
points.add(point4);
points.add(point5);
Pentagon pe = new Pentagon(points);
System.out.println(pe.judgeIsPentagon());
}private void print(double num) {
if (num * 1000 % 1 != 0) {
System.out.printf("%.3f", num);
} else {
System.out.print(num);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String string = sc.nextLine();
test.isLegal(string); // 判断输入合法性
String[] str = string.split(",| |:");
int len = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
test.pointsNum(len, str); // 判断点的数量是否正确
test.pointsCoincide(len, str); // 判断点是否重合
test.play(len, str);
}
//3:6,0 6,6 0,0 6,0 8,0 8,3 8,6}
class Polygon {
private ArrayList<Point> pointList = new ArrayList<Point>();public ArrayList<Point> getPointList() {
return pointList;
}public Polygon() {
}public Polygon(ArrayList<Point> pointList) {
super();
this.pointList = pointList;
}// 判断能否构成多边形,能返回true
boolean judgeIsPolygon() {
ArrayList<Line> list = this.getLineList();
int k = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % list.size();
for (int j = 0; j < list.size() - 3; j++) {
k = (k + 1) % list.size();
if (list.get(i).lineIntersection(list.get(k))) {
count++;
}}
}
return count == 0;
}// 删除多边形冗余的点,只留下真正构成多边形的点,以动态数组返回
ArrayList<Point> realPolygon() {
ArrayList<Point> list = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> list1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
list1.add(this.pointList.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) { // 先删除重复的点
if (!list1.contains(pointList.get(i))) {
list1.add(pointList.get(i));
}
}
int k1 = 0;
int k2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { // 在删除在一条线上的点的中间那个
k1 = (i - 1 + list1.size()) % list1.size();
k2 = (i + 1 + list1.size()) % list1.size();
Line l = new Line(list1.get(k1), list1.get(k2));
if (!l.judgePointInLine(list1.get(i))) {
list.add(list1.get(i));
}}
return list;}
// 由多边形的点生成多边形相邻两点构成的对角线,返回对角线的动态数组
ArrayList<Line> getAdjacentLineList() {
ArrayList<Line> list = new ArrayList<Line>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
int k1 = 0;
int k2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k1 = (i - 1 + listPoint.size()) % listPoint.size();
k2 = (i + 1 + listPoint.size()) % listPoint.size();
Line l = new Line(listPoint.get(k1), listPoint.get(k2));
list.add(l);
}
return list;
}// 由多边形的点生成多边形的边,返回边的动态数组
ArrayList<Line> getLineList() {
ArrayList<Line> list = new ArrayList<Line>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % listPoint.size();
Line l = new Line(listPoint.get(i), listPoint.get(k));
list.add(l);
}
return list;
}// 判断多边形的点是否重合 有重合的点返回true
boolean pointIsCoincide() {
ArrayList<Point> list = new ArrayList<Point>();
list.add(this.pointList.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) {
if (list.contains(pointList.get(i))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}// 计算多边形的周长
double calculatePerimeter() {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
double circle = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
circle += listLine.get(i).calculateLineLength();
}
return circle;
}// 计算多边形的面积
double calculateArea() {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();
double num1 = 0;
double num2 = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % listPoint.size();
num1 += listPoint.get(i).getx() * listPoint.get(k).gety();
num2 += listPoint.get(i).gety() * listPoint.get(k).getx();
}
double area = Math.abs((num1 - num2) / 2);
return area;
}// 当交点是2个时,求线切割多边形后的面积,返回面积小的部分
double calculateCutArea(Line line) {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint2 = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = this.realPolygon();for (int i = 0; i < listPoint.size(); i++) {
if (line.judgePointInLineRight(listPoint.get(i))) {
listPoint1.add(listPoint.get(i));
listPoint2.add(listPoint.get(i));
}
}
listPoint1.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(0));
listPoint1.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(1));
listPoint2.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(1));
listPoint2.add(this.calculateIntersection(line).get(0));
Polygon p1 = new Polygon(listPoint1);
Polygon p2 = new Polygon(listPoint2);
double area = 0;
if (p1.judgeIsPolygon()) {
area = p1.calculateArea();
} else {
area = p2.calculateArea();
}return Math.min(area, this.calculateArea() - area);
}// 计算直线与多边形交点
ArrayList<Point> calculateIntersection(Line line) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point point;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
point = listLine.get(i).calculateIntersection(line);
if (listLine.get(i).judgePointInLine(point) && !listPoint.contains(point)) {
listPoint.add(point);
}
}
return listPoint;
}// 计算直线与多边形交点数量
int calculateIntersectionCount(Line line) {
return this.calculateIntersection(line).size();
}// 判断点是否在多边形的边上 若在返回true
boolean judgePointInEdges(Point point) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
if (listLine.get(i).judgePointInLine(point))
return true;
}
return false;
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 边上的点。
ArrayList<Point> getPointInEdges(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> points = this.realPolygon();
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
if (polygon.judgePointInEdges(points.get(i))) {
ps.add(points.get(i));
}
}
return ps;
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 边上的点的数量
int getPointInEdgesNum(Polygon polygon) {
return this.getPointInEdges(polygon).size();
}// 判断点是否在多边形内部
boolean judgePointInSide(Point point) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = new ArrayList<Point>();
listPoint.add(point);
listPoint.add(listLine.get(i).getPoint1());
listPoint.add(listLine.get(i).getPoint2());
Polygon p = new Polygon(listPoint);
sum += p.calculateArea();
}
return !this.judgePointInEdges(point) && sum == this.calculateArea();
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 内部的点
ArrayList<Point> getPointInSide(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> points = this.realPolygon();
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
if (polygon.judgePointInSide(points.get(i))) {
ps.add(points.get(i));
}
}
return ps;
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 内部的点的数量
int getPointInSideNum(Polygon polygon) {
return this.getPointInSide(polygon).size();
}// 判断点是否在多边形外部
boolean judgePointOutSide(Point point) {
return !this.judgePointInSide(point) && !this.judgePointInEdges(point);
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 外部点
ArrayList<Point> getPointOutSide(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Point> points = this.realPolygon();
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
if (polygon.judgePointOutSide(points.get(i))) {
ps.add(points.get(i));
}
}
return ps;
}// 输出前一个多边形在后一个多边形 外部的点的数量
int getPointOutSideNum(Polygon polygon) {
return this.getPointOutSide(polygon).size();
}// 判断线是否与多边形某边重合, 重合返回true
boolean judgeLineIsCoincide(Line line) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
if (listLine.get(i).isCoincide(line)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}// 判断多边形的类型,凸多边形返回true
boolean judgePolygonType() {
ArrayList<Line> list = this.getAdjacentLineList();
int count = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
k = (i + 1) % list.size();
if (list.get(i).lineIntersection(list.get(k))) {
count++;
}
}
return count == list.size();
}// 计算线段与多边形交点
private ArrayList<Point> calculateIntersection2(Line line) {
ArrayList<Line> listLine = this.getLineList();
ArrayList<Point> listPoint = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point point;
for (int i = 0; i < listLine.size(); i++) {
point = listLine.get(i).calculateIntersection(line);
if (listLine.get(i).judgePointInLine(point) && line.judgePointInLine(point) && !listPoint.contains(point)) {
listPoint.add(point);
}
}
return listPoint;
}// 计算两个多边形之间的交点
ArrayList<Point> calculatePolygonIntersection(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
ArrayList<Line> list1 = this.getLineList();
ArrayList<Point> ps;
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
ps = polygon.calculateIntersection2(list1.get(i));
points.addAll(ps);
}return this.deleteRepeatPoint(points);
}// 得到两个多边形之间的交点数量
int getPolygonIntersectionNum(Polygon polygon) {
return this.calculatePolygonIntersection(polygon).size();
}// 使arraylist中不含重复元素
private ArrayList<Point> deleteRepeatPoint(ArrayList<Point> list) {
ArrayList<Point> p = new ArrayList<Point>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (!p.contains(list.get(i))) {
p.add(list.get(i));
}
}
return p;
}/*
* 判断两个多边形的关系 判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
* 两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合)3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错
* 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
*/
// 判断分离
boolean judgeSeparation(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> list1 = this.realPolygon();
ArrayList<Point> list2 = polygon.realPolygon();
Polygon p1 = new Polygon(list1);
Polygon p2 = new Polygon(list2);
if (p1.getPolygonIntersectionNum(p2) == 0 && p1.judgePointOutSide(p2.pointList.get(0))
&& p2.judgePointOutSide(p1.pointList.get(0)))
return true;
else
return false;
}// 判断连接
boolean judgeConnect(Polygon polygon) {
ArrayList<Point> list1 = this.getPointInEdges(polygon);
ArrayList<Point> list2 = polygon.getPointInEdges(this);
list1.addAll(list2);
ArrayList<Point> list = this.deleteRepeatPoint(list1);
if (list.size() <= 2 && this.getPointOutSideNum(polygon) != 0 && polygon.getPointOutSideNum(this) != 0
&& this.getPointInSideNum(polygon) == 0 && polygon.getPointInSideNum(this) == 0
&& this.getPolygonIntersectionNum(polygon) == list.size()) {
return true;
}
return false;}
// 判断完全重合
boolean judgeCompletelyCoincide(Polygon polygon) {
if (this.getPointInEdgesNum(polygon) == this.realPolygon().size()
&& this.calculateArea() == polygon.calculateArea())
return true;
return false;
}// 判断被包含
boolean judgeIsInside(Polygon polygon) {
if (this.getPointOutSideNum(polygon) == 0 && this.calculateArea() != polygon.calculateArea())
return true;
return false;
}// 判断包含
boolean judgeIsContain(Polygon polygon) {
if (this.getPointInSideNum(polygon) == 0 && this.calculateArea() != polygon.calculateArea() && polygon.getPointOutSideNum(this) == 0 )
return true;
return false;
}
// 计算多边形的重心
Point calculateCore() {
ArrayList<Point> list = this.realPolygon();
ArrayList<Triangle> listTri = new ArrayList<Triangle>();
double a = 0 ;
double b = 0 ;
for( int i=1 ; i+1 < list.size(); i++) { // 将n多边形分为n-2个三角形
ArrayList<Point> l = new ArrayList<Point>();
l.add(list.get(0));
l.add(list.get(i));
l.add(list.get(i+1));
Triangle t = new Triangle(l);
listTri.add(t);
}
for( int i=0 ; i< listTri.size(); i++) {
a += listTri.get(i).getSumX() * listTri.get(i).calculateArea();
b += listTri.get(i).getSumY() * listTri.get(i).calculateArea();
}
return new Point( a/(3*this.calculateArea()),b/(3*this.calculateArea()) );
}
// 返回重写排序的数组
ArrayList<Point> listReorder( ArrayList<Point> list){
Point core = this.calculateCore();
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>();
double num = 0;
double min = 0;
int flag = 0;
while(list.size() != 0) {
min = Math.atan2(list.get(0).gety() - core.gety(), list.get(0).getx()- core.getx());
for( int i=1 ; i < list.size() ; i++) {
num = Math.atan2(list.get(i).gety()- core.gety(), list.get(i).getx()- core.getx());
if( min > num ) {
flag = i;
min = num ;
}
}
ps.add(list.get(flag));
list.remove(flag);
flag = 0;
}
return ps;
}
// 得到两多边形重叠部分的面积
double getOverlapArea( Polygon polygon) {
if( this.judgeIsContain(polygon) || this.judgeIsInside(polygon) || this.judgeCompletelyCoincide(polygon)) {
return Math.min( this.calculateArea() , polygon.calculateArea());
}
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>();
points.addAll(this.calculatePolygonIntersection(polygon));
points.addAll(this.getPointInSide(polygon));
points.addAll(polygon.getPointInSide(this));
points = this.deleteRepeatPoint(points);
points = this.listReorder(points);
Polygon p = new Polygon(points);
return p.calculateArea();
}
}class Pentagon extends Polygon{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private Point point3;
private Point point4;
private Point point5;
public Pentagon(ArrayList<Point> points) {
super(points);
this.point1 = points.get(0);
this.point2 = points.get(1);
this.point3 = points.get(2);
this.point4 = points.get(3);
this.point5 = points.get(4);
}public boolean judgeIsPentagon() {
return this.judgeIsPolygon() && this.realPolygon().size() == 5;
}
}class Quadrangle extends Polygon{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private Point point3;
private Point point4;public Quadrangle(ArrayList<Point> points) {
super(points);
this.point1 = points.get(0);
this.point2 = points.get(1);
this.point3 = points.get(2);
this.point4 = points.get(3);
}
// 判断是否是四边形 (即四个点能否构成四边形) ,判断结果输出true/false
boolean judegeIsQuadriangle() {
return this.judgeIsPolygon() && this.realPolygon().size() == 4;
}// 判断四个点在无法构成四边形的情况下,能否构成三角形
boolean judgeIsTriangle() {
return this.judgeIsPolygon() && this.realPolygon().size() == 3 ;
}
// 判断是否平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false
boolean judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line34 = new Line(point3, point4);
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line34.calculateLineLength() && line12.judgeParallel(line34) && this.judgeIsPolygon();
}// 判断是否是菱形
boolean judgeQuadriangleIsRhombic() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line23 = new Line(point2, point3);
return judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() && line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength();
}// 判断是否是矩形,
boolean judgeQuadriangleIssRectangular() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1, point2);
Line line23 = new Line(point2, point3);
return judgeIsParallelismQuadriangle() && line12.judgeIsPerpendicular(line23);
}// 判断是否是正方形,
boolean judgeQuadriangleIssSquare() {
return judgeQuadriangleIsRhombic() && judgeQuadriangleIssRectangular();
}
}class Triangle extends Polygon{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private Point point3;
// 构造函数
public Triangle(ArrayList<Point> points) {
super(points);
this.point1 = points.get(0);
this.point2 = points.get(1);
this.point3 = points.get(2);
}
//判断三角形是否等腰
boolean isIsoscelesTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line13.calculateLineLength() || line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() || line13.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() ;
}
//判断三角形是否等边
boolean isRegularTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
return line12.calculateLineLength() == line13.calculateLineLength() && line12.calculateLineLength() == line23.calculateLineLength() ;
}
// 计算三角形的重心
Point calculateCore() {
double x = ( point1.getx() + point2.getx() + point3.getx() ) / 3;
double y = ( point1.gety() + point2.gety() + point3.gety() ) / 3;
Point p = new Point(x,y);
return p;
}
// 判断是否为钝角三角形
boolean isObtuseTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a > b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b > a + c ;
}else {
return c > b + a ;
}
}
// 判断是否为直角三角形
boolean isRightTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a == b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b == a + c ;
}else {
return c == b + a ;
}
}
// 判断是否为锐角三角形
boolean isAcuteTriangle() {
Line line12 = new Line(point1,point2 ); // 点一 与 点二 构成
Line line13 = new Line(point1,point3 );; // 点一 与 点三 构成
Line line23 = new Line(point2,point3 );; // 点二 与 点三 构成
double a = line12.calculateLineLength2() ;
double b = line13.calculateLineLength2() ;
double c = line23.calculateLineLength2() ;
if(a > b && a > c ) {
return a < b + c ;
}else if(b > a && b > c ) {
return b < a + c ;
}else {
return c < b + a ;
}
}
// 计算三角形三个点x值总和
double getSumX() {
return point1.getx()+point2.getx()+point3.getx();
}
// 计算三角形三个点y值总和
double getSumY() {
return point1.gety()+point2.gety()+point3.gety();
}
}class Line {
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
// 构造函数
public Line(Point point1, Point point2) {
super();
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
}
// 得到点一
Point getPoint1() {
return this.point1;
}
// 得到点二
Point getPoint2() {
return this.point2;
}
// 得到x的系数A
double getA() {
return point1.gety()-point2.gety();
}
// 得到y的系数B
double getB() {
return point2.getx()-point1.getx();
}
// 得到常数C
double getC() {
return point1.getx() * point2.gety() - point2.getx() * point1.gety();
}
// 得到直线的斜率K
double getK() {
return (point1.gety()-point2.gety())/(point1.getx()-point2.getx());
}
// 计算点到直线的距离
double calculateDistance( Point point) {
double a = Math.abs( this.getA()*point.getx() + this.getB()*point.gety() + this.getC());
double b = Math.sqrt(this.getA() * this.getA() + this.getB()*this.getB());
return a/b;
}
/* 判断三点是否共线
* 或者判断点是否在直线上
*/
boolean judgePointOnLine( Point point ){
return Math.abs(this.getA()*point.getx()+this.getB()*point.gety()+this.getC() )< 0.0000001;
}
// 判断两直线是否平行 平行返回true
boolean judgeParallel( Line line ) {
if(this.getB() != 0 && line.getB() !=0)
return this.getK() == line.getK() ;
else if(this.getB() == 0 && line.getB() ==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
/*判断两直线是否垂直
* 采用向量法,避免对斜率是否存在的讨论
*/
boolean judgeIsPerpendicular(Line line) {
double x1 = this.point1.getx()-this.point2.getx();
double y1 = this.point1.gety()-this.point2.gety();
double x2 = line.point1.getx()-line.point2.getx();
double y2 = line.point1.gety()-line.point2.gety();
return x1*x2 + y1*y2 == 0;
}
// 计算线与线的交点
Point calculateIntersection( Line line) {
double x = (line.getC()*this.getB()-this.getC()*line.getB())/(this.getA()*line.getB()-line.getA()*this.getB());
double y = (line.getC()*this.getA()-this.getC()*line.getA())/(line.getA()*this.getB()-this.getA()*line.getB());
if(x==0) {
x=0;
}
if(y==0) {
y=0;
}
Point point = new Point(x,y);
return point;
}
// 判断直线上的点是否在某一线段的内部,包括端点 (若不想包含端点删掉 = 号即可)
boolean PointBetweenLine ( Point point ) {
if( point.getx() <= Math.max( this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx() ) && point.getx() >= Math.min( this.point1.getx() , this.point2.getx() ) && point.gety() <= Math.max( this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety() ) && point.gety() >= Math.min( this.point1.gety() , this.point2.gety() ))
return true;
else
return false;
}
// 判断点是否在某一线段内部包括端点
boolean judgePointInLine ( Point point ) {
return this.judgePointOnLine(point) && this.PointBetweenLine(point);
}
// 计算线的长度
double calculateLineLength() {
return this.point1.calculateDistance(this.point2);
}
// 计算线的长度的平方
double calculateLineLength2() {
return this.point1.calculateDistance2(this.point2);
}
//判断两直线是否重合 重合返回true
boolean isCoincide( Line line) {
return this.judgeParallel(line) && line.judgePointOnLine(point1);
}
// 判断两直线是否有交点,且交点是否在后面传参的线段内
boolean judgeIntersectionIsInLaterLine( Line line) {
return !this.judgeParallel(line) && line.judgePointInLine( this.calculateIntersection(line) ) ;
}
// 判断点是否在直线的同一侧
boolean judgePointInLineRight( Point point ) {
return this.getA()*point.getx() + this.getB()*point.gety() + this.getC() >=0;
}
// 判断两线段有没有交点
public boolean lineIntersection(Line line) {
if (Math.max(this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx()) < Math.min(line.point1.getx(), line.point2.getx())
|| Math.min(this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx()) > Math.max(line.point1.getx(), line.point2.getx())
|| Math.max(this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety()) < Math.min(line.point1.gety(), line.point2.gety())
|| Math.min(this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety()) > Math.max(line.point1.gety(), line.point2.gety())) {
return false;
}
if (crossProduct(this.point1.getx() - line.point1.getx(), this.point1.gety() - line.point1.gety(), line.point1.getx() - line.point2.getx(), line.point1.gety() - line.point2.gety())
* crossProduct(this.point2.getx() - line.point1.getx(), this.point2.gety() - line.point1.gety(), line.point1.getx() - line.point2.getx(), line.point1.gety() - line.point2.gety()) > 0) {
return false;
}
if (crossProduct(line.point1.getx() - this.point1.getx(), line.point1.gety() - this.point1.gety(), this.point1.getx() - this.point2.getx(), this.point1.gety() - this.point2.gety())
* crossProduct(line.point2.getx() - this.point1.getx(), line.point2.gety() - this.point1.gety(), this.point1.getx() - this.point2.getx(), this.point1.gety() - this.point2.gety()) > 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}double crossProduct(double a1, double b1, double a2, double b2) {
return a1 * b2 - b1 * a2;
}
}
class Point {private double x;
private double y;// 构造函数
public Point(String stringx, String stringy) {
this.x = Double.parseDouble(stringx);
this.y = Double.parseDouble(stringy);
}// 构造函数
public Point(double x, double y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}// 得到点的x坐标
double getx() {
return this.x;
}// 得到点的y坐标
double gety() {
return this.y;
}// 计算两点的距离
double calculateDistance(Point point) {
double num = (this.x - point.x) * (this.x - point.x) + (this.y - point.y) * (this.y - point.y);
return Math.sqrt(num);
}// 计算两点的距离的平方
double calculateDistance2(Point point) {
return (this.x - point.x) * (this.x - point.x) + (this.y - point.y) * (this.y - point.y);
}// 判断两点是否重合 重合返回true
boolean isCoincide(Point point) {
return this.x == point.x && this.y == point.y;
}@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Point other = (Point) obj;
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}}
![复制代码]()
- 源码分析
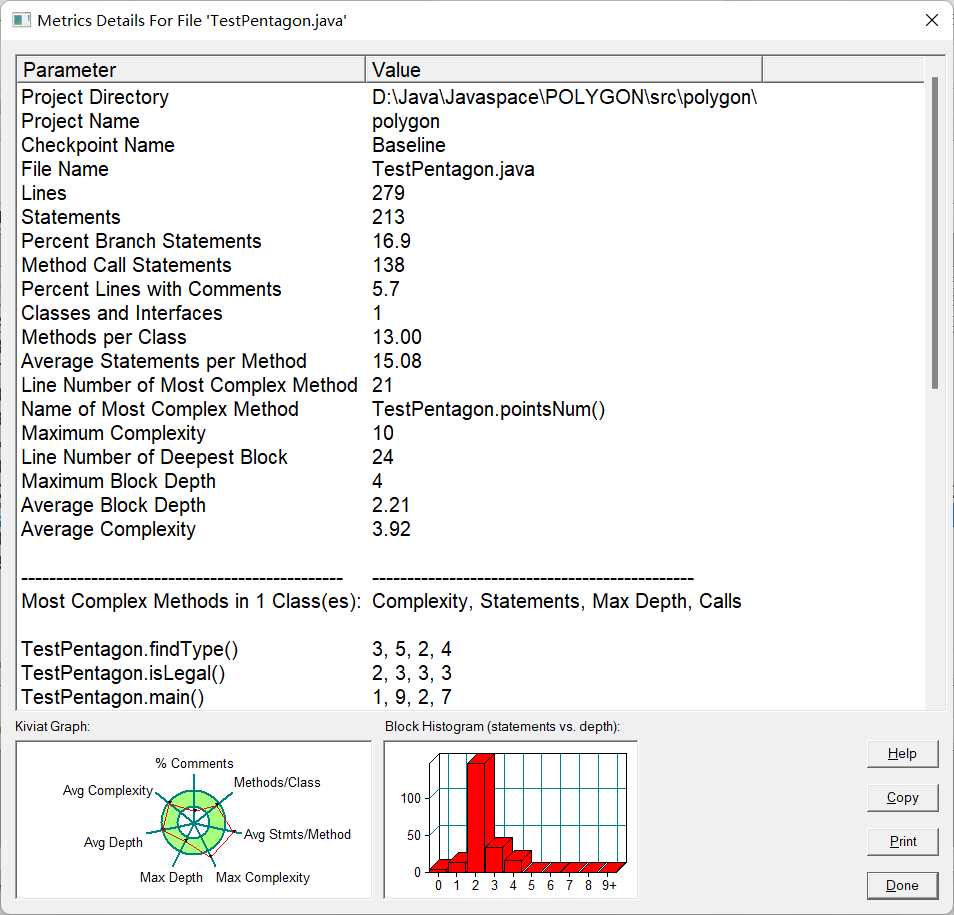
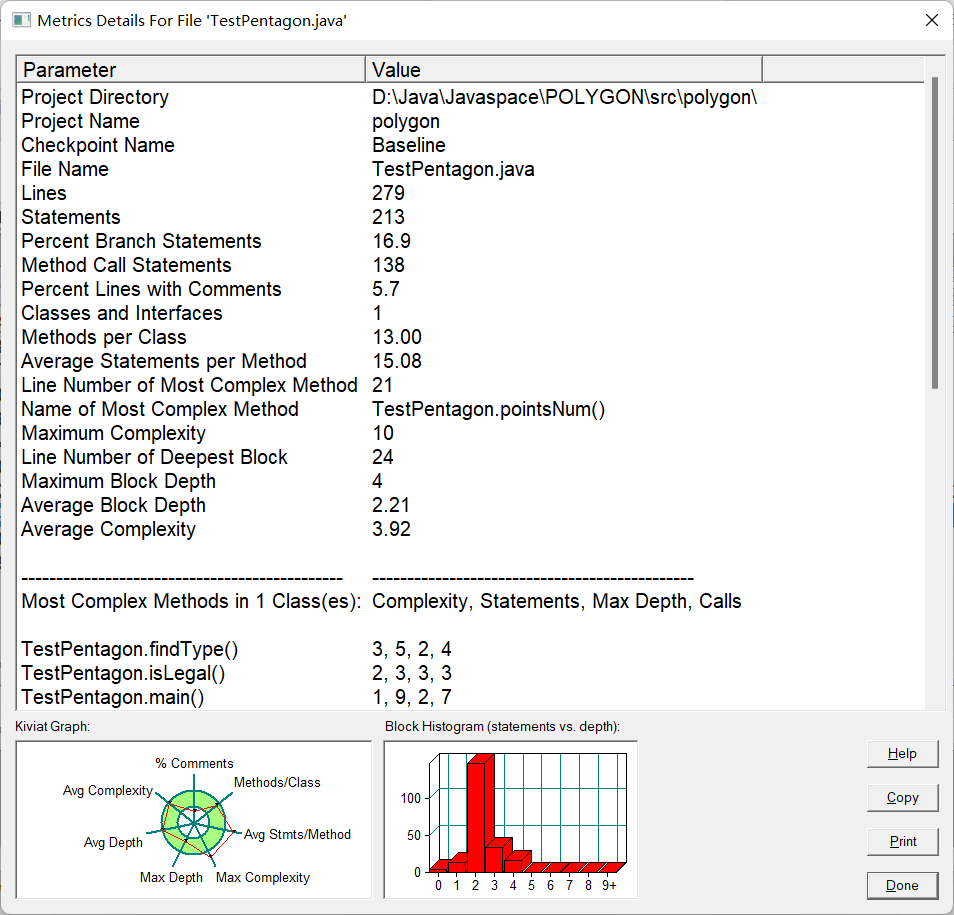
在编写五边形的代码时,我完完全全是在编写多边形,在我的五边形类里面只有一个构造函数,一切的功能都是在五边形中完成的。而且圈复杂度也只有3.92.
期中考试7-1 点与线(类设计)
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
- 源码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double startx = sc.nextDouble(); double starty = sc.nextDouble(); double endx = sc.nextDouble(); double endy = sc.nextDouble(); String color = sc.next(); if(startx > 0 && startx<=200 && starty > 0 && starty<=200 &&endx > 0 && endx<=200 &&endy > 0 && endy<=200 ) { Point point1 = new Point(startx,starty); Point point2 = new Point(endx,endy); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,color); line.display(); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Point { private double x; private double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",x,y); } } class Line { private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public void setcolor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double num = (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY()); return Math.sqrt(num); } public void display() { System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f",this.getDistance()); } }
- 源码分析
没什么好分析,和前面的作业一样,还是简化版。
期中考试7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:The Plane's color is:颜色
在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
- 源码
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double startx = sc.nextDouble(); double starty = sc.nextDouble(); double endx = sc.nextDouble(); double endy = sc.nextDouble(); String color = sc.next(); if(startx > 0 && startx<=200 && starty > 0 && starty<=200 &&endx > 0 && endx<=200 &&endy > 0 && endy<=200 ) { Element point1 = new Point(startx,starty); Element point2 = new Point(endx,endy); Point point3 = new Point(startx,starty); Point point4 = new Point(endx,endy); Element line = new Line(point3,point4,color); Element plane = new Plane(color); point1.display(); point2.display(); line.display(); plane.display(); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } abstract class Element { public abstract void display(); } class Plane extends Element { private String color; public Plane() { } public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public void setcolor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public void setcolor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double num = (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY()); return Math.sqrt(num); } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n",this.getDistance()); } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } @Override public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",x,y); } }
- 源码分析
使用到了抽象类。但总体代码简单。
abstract class Element { public abstract void display(); }
期中考试7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) 增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下: 1:向容器中增加Point对象 2:向容器中增加Line对象 3:向容器中增加Plane对象 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作 0:输入结束
- 源码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>(); GeometryObject g = new GeometryObject(list); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = -1; choice = sc.nextInt(); while (choice != 0) { switch (choice) { case 1: { double x = sc.nextDouble(); double y = sc.nextDouble(); Element point1 = new Point(x, y); g.getList().add(point1); break; } case 2: { double startx = sc.nextDouble(); double starty = sc.nextDouble(); double endx = sc.nextDouble(); double endy = sc.nextDouble(); String color = sc.next(); Point point3 = new Point(startx, starty); Point point4 = new Point(endx, endy); Element line = new Line(point3, point4, color); g.getList().add(line); break; } case 3: { String color = sc.next(); Element plane = new Plane(color); g.getList().add(plane);break; } case 4: { int a = sc.nextInt(); if (a > 0 && a <= list.size()) g.remove(a); break; } } choice = sc.nextInt(); } for (Element e : g.getList()) { e.display(); } /* * double endx = sc.nextDouble(); double endy = sc.nextDouble(); String color = * sc.next(); if(startx > 0 && startx<=200 && starty > 0 && starty<=200 &&endx > * 0 && endx<=200 &&endy > 0 && endy<=200 ) { Element point1 = new * Point(startx,starty); Element point2 = new Point(endx,endy); Point point3 = * new Point(startx,starty); Point point4 = new Point(endx,endy); Element line = * new Line(point3,point4,color); Element plane = new Plane(color); * point1.display(); point2.display(); line.display(); plane.display(); }else { * System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } */ } } class GeometryObject { private ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>(); public GeometryObject(ArrayList<Element> list) { super(); this.list = list; } public void add(Element element) { this.list.add(element); } public void remove(int index) { this.list.remove(index-1); } public ArrayList<Element> getList(){ return this.list; } } class Plane extends Element { private String color; public Plane() { } public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public void setcolor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public void setcolor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double num = (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY()); return Math.sqrt(num); } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n",this.getDistance()); } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } @Override public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",x,y); } } abstract class Element { public abstract void display(); }
- 源码分析
ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>();
踩坑心得
- 4-7-2中Line类判断两线段有无交点,建议使用向量来做,使用其他的可能存在误差,导致测试点过不去的情况
// 判断两线段有没有交点
public boolean lineIntersection(Line line) {
if (Math.max(this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx()) < Math.min(line.point1.getx(), line.point2.getx())
|| Math.min(this.point1.getx(), this.point2.getx()) > Math.max(line.point1.getx(), line.point2.getx())
|| Math.max(this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety()) < Math.min(line.point1.gety(), line.point2.gety())
|| Math.min(this.point1.gety(), this.point2.gety()) > Math.max(line.point1.gety(), line.point2.gety())) {
return false;
}
if (crossProduct(this.point1.getx() - line.point1.getx(), this.point1.gety() - line.point1.gety(), line.point1.getx() - line.point2.getx(), line.point1.gety() - line.point2.gety())
* crossProduct(this.point2.getx() - line.point1.getx(), this.point2.gety() - line.point1.gety(), line.point1.getx() - line.point2.getx(), line.point1.gety() - line.point2.gety()) > 0) {
return false;
}
if (crossProduct(line.point1.getx() - this.point1.getx(), line.point1.gety() - this.point1.gety(), this.point1.getx() - this.point2.getx(), this.point1.gety() - this.point2.gety())
* crossProduct(line.point2.getx() - this.point1.getx(), line.point2.gety() - this.point1.gety(), this.point1.getx() - this.point2.getx(), this.point1.gety() - this.point2.gety()) > 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
double crossProduct(double a1, double b1, double a2, double b2) {
return a1 * b2 - b1 * a2;
}
4-7-2 Line类中判断点在直线上。不要直接判断==0,而是给它一个很小的范围,比如0.000001等,因为double转化二进制是会存在误差的。
* 或者判断点是否在直线上
*/
boolean judgePointOnLine( Point point ){
return Math.abs(this.getA()*point.getx()+this.getB()*point.gety()+this.getC() )< 0.0000001;
}
- 5-7-2 判断两多边形的关系,对于交错的类型比较复杂,难以判断。可以先将重合,包含,连接,被包含等关系给判断好了以后,直接使用else来判断是否交错。
if(po1.judgeSeparation(po2)) {
System.out.println("no overlapping area between the previous "+findType(po1)+" and the following "+findType(po2));
}
else if(po1.judgeConnect(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is connected to the following "+findType(po2));
}
//4:35,25 25,15 35,5 45,10 45,20
else if(po1.judgeCompletelyCoincide(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" coincides with the following "+findType(po2));
}
// the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
else if(po1.judgeIsInside(po2)) {
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is inside the following "+findType(po2));
}else if(po1.judgeIsContain(po2)) {
// the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" contains the following "+findType(po2));
}else {
// 4:0,0 6,0 8,0 7,3 6,6 4,0 6,0 8,0 12,0 7,3
//the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
System.out.println("the previous "+findType(po1)+" is interlaced with the following "+findType(po2));
}
改进建议
- 可以单独写一个输入判断类和一个输出类来控制输入输出,而不是一股脑全放在Main类中。
- 可以将一些方法中 if 括号里面的判断语句单独写一个 private 类型的方法来判断,提高代码的可读性。
- 在构造函数中不是只可以有基础的语句,也可以在期中调用其他方法,比如多边形中得到真正构成多边形的点的代码,可以放入构造函数中,省的以后每一步都要调用个那个方法。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号