个人项目
一、github项目地址:https://github.com/Micro-sun/first-java-project
二、实现的功能:
- -c 返回文件 file.c 的字符数
- -w 返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
- -l 返回文件 file.c 的行数
- -x 通过图形界面展现文件的信息
三、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning | 60 | 120 |
| · Estimate | 600 | 800 |
| Development | 120 | 360 |
| · Analysis | 360 | 240 |
| · Design Spec | 120 | 90 |
| · Design Review | 80 | 100 |
| · Coding Standard | 60 | 90 |
| · Design | 100 | 120 |
| · Coding | 360 | 400 |
| · Code Review | 90 | 100 |
| · Test | 160 | 200 |
| Reporting | 140 | 200 |
| Test Report | 60 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | 30 | 30 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 |
四、解题思路
1、分析题目,题目使用-c/-w/-l输入后选择所需的模块函数进行,选取,进入函数之后在输入路径。
2、-c在每个类中的函数用BufferedReader方法读取文件中的字符数,然后在加以分析;使用正则表达式,结合pattern类和matcher类判别是否匹配字符串中的每一个字符,使用while判别。
3、-w在每个类中的函数用BufferedReader方法读取文件中的字符数,然后在加以分析;用readline()结合while的方法读取获取字符串的每一行字符串,使用切割字符串成为一个字符串数组,当字符串没有时则读取切割完成,最后使用length获取数组长度即字符串中单词数量。
4、-l在每个类中的函数用BufferedReader方法读取文件中的字符数,然后在加以分析;每读取一行则变量加一,读取完成之后就输出变量。
5、文件的读取,为了避免读取文件的时候出现错误,从而使用了try{}cacth{}finaly{}结构块。或在创建方法的时候使用throws IOException。读取错误时候抛出错误提示。
6、文件路径输入与用户交互选择处理:使用scanner与用户在终端交互,而可视化图形则使用文本框与用户交互数据。
7、图形化可视化处理:使用了JFrame容器,并且时直接在main文件里创建了一个方法来执行图形化,其中要引入awt的java包,处理文本框,按钮,监听事件等。
8、处理包管理:使用java编辑器简易处理,编写main函数执行。
五、运行测试
测试文件
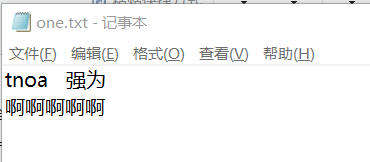
(1)非图形:
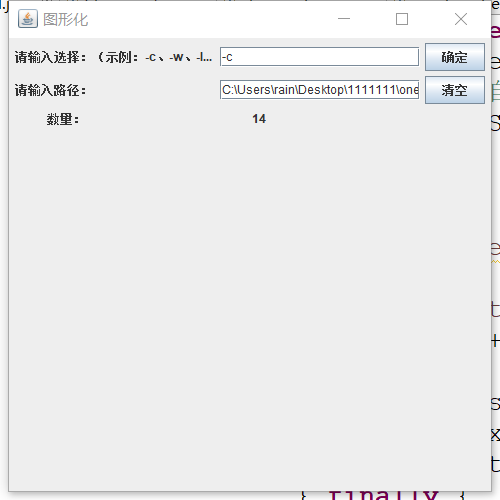
1、-c 检测文件中字符数(输入选择-c,然后输入文件one.txt路径,终端输出数量number:14)
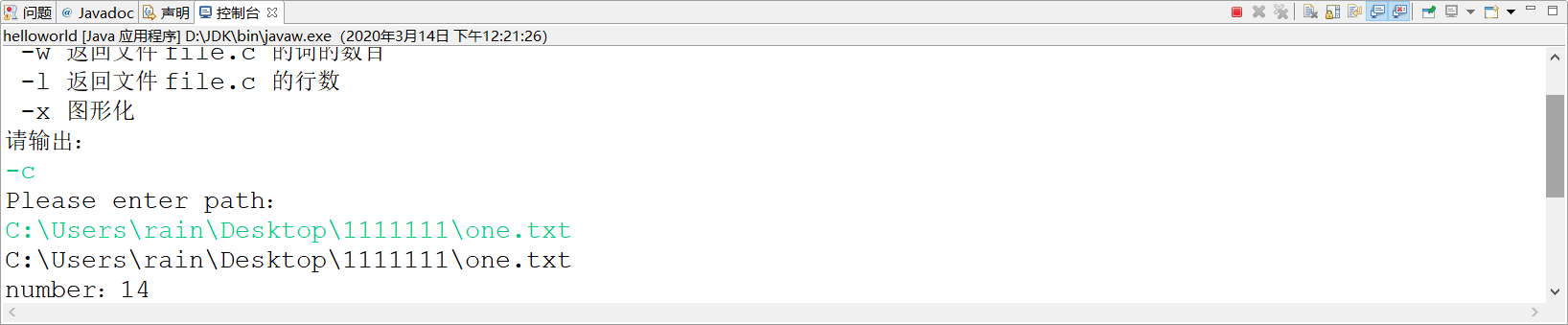
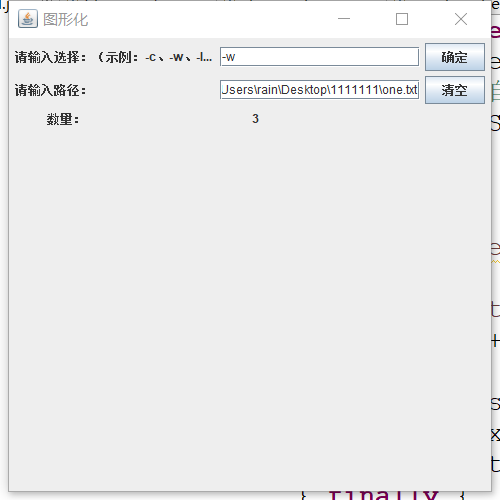
2、-w检测文件单词数量(输入选择-w,然后输入文件one.txt路径,终端输出数量number:3)
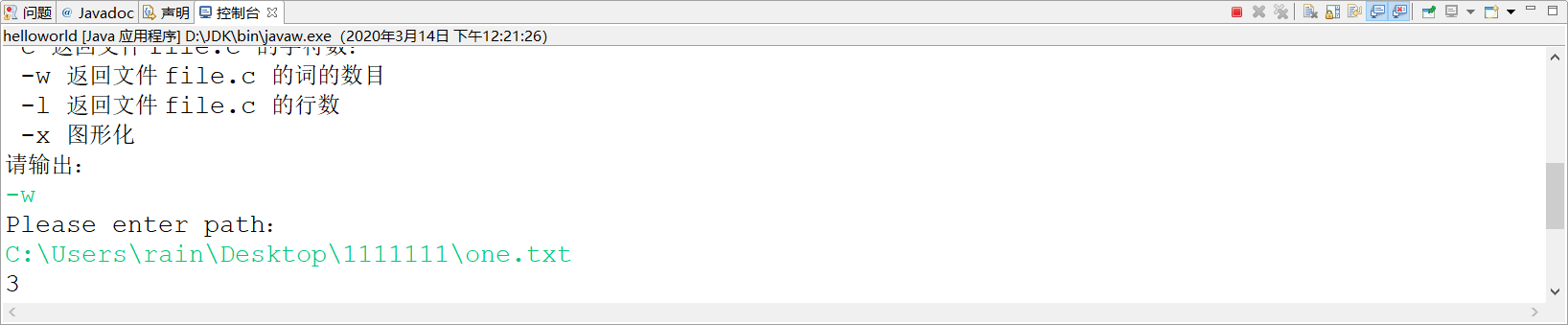
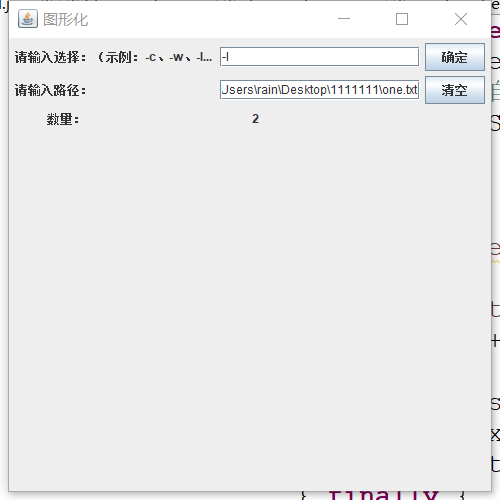
3、-l检测文件单词数量(输入选择-w,然后输入文件one.txt路径,终端输出数量line number:2)
4、图形化检测测试结果。
六、主要代码
String R ="."; charnumber() throws IOException { System.out.println("Please enter path:"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String path=input.nextLine(); System.out.println(path); BufferedReader file =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); int charcount=0; String w; Pattern p =Pattern.compile(R); while((w=file.readLine()) != null) { Matcher m =p.matcher(w); while(m.find()){ //找到对应字符时字符数+1 charcount ++;} } System.out.println("number:"+charcount); file.close();
以上为选择-c检测字符串的代码。-c在每个类中的函数用BufferedReader方法读取文件中的字符数,然后在加以分析;使用正则表达式,结合pattern类和matcher类判别是否匹配字符串中的每一个字符,使用while判别。
linenumber() throws IOException { System.out.println("Please enter path:"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String path=input.nextLine(); int line = 0; BufferedReader file =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); try { String tempString = null; while ((tempString = file.readLine()) != null) { line++; } file.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (file != null) { try { file.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } }
以上为选择-l检测行数的代码。每读取一行则变量加一,读取完成之后就输出变量。
String reg = " +"; String[] arr ; int wordnumber=0; wordnumber() throws IOException { System.out.println("Please enter path:"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String path=input.nextLine(); BufferedReader file =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); try { String tempString = null; while ((tempString = file.readLine()) != null) { arr = tempString.split(reg); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) { wordnumber++; } // System.out.println(tempString); } file.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (file != null) { try { file.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } System.out.println("number:"+wordnumber); }
以上为选择-w检测word单词数代码。使用切割字符串成为一个字符串数组,当字符串没有时则读取切割完成,最后使用length获取数组长度即字符串中单词数量。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ while(true) { System.out.println("输入显示:"); System.out.println("-c 返回文件 file.c 的字符数:"); System.out.println(" -w 返回文件 file.c 的词的数目 "); System.out.println(" -l 返回文件 file.c 的行数"); System.out.println(" -x 图形化"); System.out.println("请输出:"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); //从键盘上输入指令并执行 String commend=input.nextLine(); switch (commend) { case "-c": charnumber ch = new charnumber(); break; case "-l": linenumber line = new linenumber(); break; case "-w": wordnumber word = new wordnumber(); break; case "-x": shape(); break; } } }
以上为main函数代码,选择不同输入则执行不同类或方法。
private static void shape() { //定义一个窗体对象f,窗体名称为"一个简单窗口" JFrame f = new JFrame("图形化"); f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); f.setBounds(100,100,500,500); // f.setResizable(false); Container c=f.getContentPane(); c.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); JLabel l=new JLabel("请输入选择:(示例:-c、-w、-l)"); l.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(l); JTextField jt=new JTextField(); jt.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(jt); JButton btnone=new JButton("确定"); btnone.setBounds(0,0,10,10); c.add(btnone); JLabel path=new JLabel("请输入路径:"); path.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(path); JTextField pathtext=new JTextField(); pathtext.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(pathtext); JButton btntwo=new JButton("清空"); btntwo.setBounds(0,0,10,10); c.add(btntwo); JLabel ansertext=new JLabel("数量:"); ansertext.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(ansertext); JTextField answer=new JTextField(); answer.setPreferredSize(new Dimension (200,20)); c.add(answer); f.setVisible(true); btnone.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ switch (jt.getText()) { case "-c": c(); break; case "-l": l(); break; case "-w": w(); break; } }
创建一个私有方法,实现执行图形化。
七、项目小结
1、因为刚布置项目来实现的时候是没有了解过java的,所以只能在两个星期内通过自学,在完成显目deadline这个期限内边学习java边开始做这个项目,所以总体来说还是比较吃力地。
2、之前是刚刚接触过C,慢慢的便了解了java的类,继承,对象等等,然后也上手了,有不懂的就差找了菜鸟教程这些网站上找知识点,也有看视屏,查博客,解决了很多坑,用了长时间来做这一个项目。
3、用了很长时间完成了项目的基本功能之后才开始试着取实现图形化这一个功能,发现也挺不容易的,终于在deadline前实现了。
4、这个项目让我积累了之前没有的项目经验,让我增强了自学能力,之前没有这种可以自学然后做项目的意识,这次的作业真的让喔明白了许多!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号