Spark 高级:RDD 使用
Spark 提供了数据的核心抽象,称为弹性分布式数据集 (RDD)。此数据集的全部或部分可以缓存在内存中,并在多次计算期间重复使用。RDD实际上是一个分布在多个节点上的数据集。
RDD的主要特点如下:
- RDD是不可变的,但它可以转换为新的RDD进行操作。
- RDD 已分区。RDD 由许多分区组成,每个分区对应一个要执行的任务(该分区将在 3.4 节中详细解释)。
- 在RDD上运行相当于在RDD的每个分区上运行。
- RDD有一系列计算分区的函数,称为运算符(运算符将在3.3节中详细解释)。
- RDD S之间有依赖关系,可以实现流水线,避免中间数据的存储。
1、测试数据说明
知名电影推荐数据集:MovieLen官网 https://grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/
在这里,选择小数据集进行测试。编写逻辑后,可以再次尝试大型数据集。
数据集中有三个文件:
- 电影.dat
- 收视率.dat
- 用户.dat
收视率.dat
这是一份电影评级文件,字段如下:
UserID::MovieID::Rating::Timestamp user ID::film ID::score::time stamp 1::1193::5::978300760 1::661::3::978302109 1::914::3::978301968 1::3408::4::978300275
- 每个用户至少 20 个评分
- 成绩:1-5分
电影.dat
它是一个电影文件,字段如下:
MovieID::Title::Genres film ID::Movie name::Film type 1::Toy Story (1995)::Animation|Children's|Comedy 2::Jumanji (1995)::Adventure|Children's|Fantasy 3::Grumpier Old Men (1995)::Comedy|Romance
胶片类型如下:
Action get some action Adventure adventure Animation cartoon Children's Children's Comedy comedy Crime Crime Documentary documentary Drama Theatre Fantasy fantasy Film-Noir Black film Horror terror Musical musical play Mystery Answer Romance romantic Sci-Fi science fiction Thriller Thriller War Warfare Western occident
用户.dat
用户文件,相关字段如下:
UserID::Gender::Age::Occupation::Zip-code user ID::Gender::Age::occupation::Zip code 1::F::1::10::48067 2::M::56::16::70072 3::M::25::15::55117
年龄表示一个范围:
1: "1-18" 18: "18-24" 25: "25-34" 35: "35-44" 45: "45-49" 50: "50-55" 56: "56+"
职业是一个枚举编号,对应的关系是:
0: "other" or not specified ""Other" or unspecified 1: "academic/educator" "scholar/"Educator" 2: "artist" ""Artist" 3: "clerical/admin" "Clerk/"Administrator" 4: "college/grad student" "college student/"Graduate students" 5: "customer service" ""Customer service" 6: "doctor/health care" "doctor/"Health care" 7: "executive/managerial" "implement/"Management" 8: "farmer" ""Farmers" 9: "homemaker" ""Housewife" 10: "K-12 student" "K-12 "Student" 11: "lawyer" ""Lawyer" 12: "programmer" ""Programmer" 13: "retired" ""Retirement" 14: "sales/marketing" ""Sales and marketing" 15: "scientist" ""Scientists" 16: "self-employed" ""Self employed person" 17: "technician/engineer" "technician/"Engineer" 18: "tradesman/craftsman" "businessman/"Craftsman" 19: "unemployed" "Unemployment " 20: "writer" ""Writer"
2、RDD使用练习
1. 获得电影评价前10名
- 首先,对数据进行分割,得到电影ID的出现情况
- 然后根据电影 ID 进行聚合
- 通过更改电影 ID 和出现次数将出现次数更改为关键位置
- 最后,根据出现次数进行排序
- 打印出前十个匹配项
object MovieLen {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR)
val dataPath = "/home/ffzs/data/ml-1m"
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setAppName("movieLen")
conf.setMaster("local[*]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val ratingsRdd = sc.textFile(f"$dataPath/ratings.dat")
// The number of film reviews ranked top 10
ratingsRdd.map(_.split("::")) // Segmentation data
.map(_(1) -> 1) // Get key value of ID - > 1
.reduceByKey(_+_) // Aggregate the movie id to calculate the number of times each movie appears
.map(it => (it._2, it._1)) // Adjust the key value position to sort the occurrence times
.sortByKey(false) // Sort occurrences
.take(10) // Get the first 10 values
.foreach(println)
}
}
结果输出:
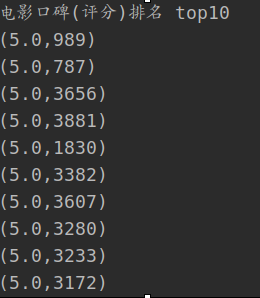
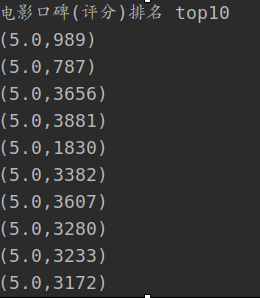
2. 口碑 top10
- 通过电影ID汇总电影的总分和总访问量
- 然后平均每部电影
- 最后,对输出 top10 进行排序
println("Film reputation(score)ranking top10")
ratingsRdd.map(_.split("::"))
.map(it => (it(1), (it(2).toDouble, 1))) // The score is converted to double type to facilitate division calculation
.reduceByKey((x,y) => (x._1 + y._1, x._2 + y._2)) // Aggregate the total score and total viewing times of the film
.map(it => ((it._2._1/it._2._2), it._1)) // The average score of comments is obtained from the total score and the total number of times
.sortByKey(false) // Sort through the average score of comments
.take(10) // Get top10
.foreach(println)
输出结果:
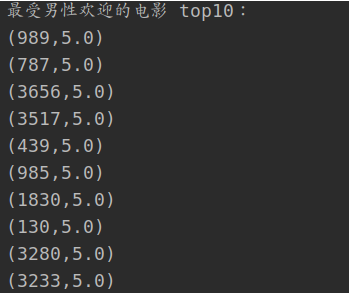
3.男性口碑最高的十大电影
- 加入分数和用户性别
- 然后根据性别进行数据筛选
- 最后根据上面的口碑逻辑评选前10名
val gender = "M"
val genderMap:Map[String, String] = Map("M"->"Male", "F"->"female sex")
println(f"Most popular ${genderMap(gender)}Welcome movie top10: ")
ratingsRdd.map(_.split("::"))
.map(x => (x(0), (x(0), x(1), x(2))))
.join( // join the score and user gender according to the user ID
usersRdd.map(_.split("::"))
.map(x=> x(0)->x(1))
)
.filter(_._2._2.equals(gender)) // Screen out the corresponding gender
.map(it => (it._2._1._2, (it._2._1._3.toDouble, 1))) // Find the average score to sort
.reduceByKey((x,y) => (x._1+y._1, x._2+y._2))
.map(it => (it._2._1/it._2._2, it._1))
.sortByKey(ascending = false)
.map(it => it._2->it._1)
.take(10)
.foreach(println)
输出结果为:
4.分数根据时间排序两次
- 通过分数和时间构建二级排序处理类。分数和时间均按降序排列
- 通过排序类对键进行排序
- 然后输出每行数据
class SecondSortKey(val first:Int, val second:Int) extends Ordered[SecondSortKey] with Serializable {
override def compare(that: SecondSortKey): Int = {
if (this.first != that.first) {
this.first-that.first
}
else{
this.second-that.second
}
}
}
ratingsRdd.map(line => { val row = line.split("::") ((new SecondSortKey(row(2).toInt, row(3).toInt)), line) }) .sortByKey(false) .map(_._2) .take(10) .foreach(println) }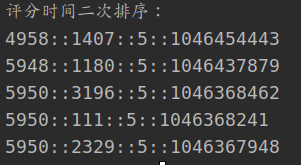
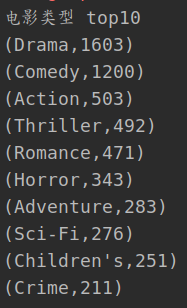
5.Film 类型 top10
- 电影中的电影类型按平面图分割
- 然后计算每种类型的出现次数
- 输出最后一次排序后的前 10 个
println("Film type top10")
movieRdd.map(_.split("::")(2))
.flatMap(_.split("\\|"))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_+_)
.map(it => (it._2, it._1))
.sortByKey(ascending = false)
.map(it=> it._2->it._1)
.take(10)
.foreach(println)
输出:
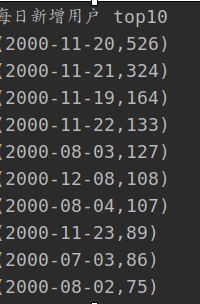
6. 每日新用户
- 首先将时间戳转换为日期
- 然后,通过用户ID分组得到每个组中的最小日期,即用户新日期
- 然后聚合日期
- 最后,对输出进行排序
println("Daily new users top10")
val sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd")
ratingsRdd.map(_.split("::"))
.map(it => (it(0), it(3).toLong*1000))
.map(it => (it._1, sdf.format(it._2)))
.groupByKey()
.map(it => (it._2.min, 1))
.reduceByKey(_+_)
.map(it => it._2 -> it._1)
.sortByKey(ascending = false)
.map(it => it._2 -> it._1)
.take(10)
.foreach(println)
输出结果为:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号