[Javascript] Babel转译原理
概述
编译与转译
编译(Compile):通常是 高级语言 → 机器码/字节码,比如 C → 汇编。
转译(Transpile):通常是 一种语言的源代码 → 另一种语言的源代码,保持抽象层级接近。
前端中常见的转译操作,如下:
- ES6 -> ES5
- TS -> JS
- SASS -> CSS
代码转译示例
Babel库是目前非常流行的 Javascript Transpiler,即JS转译器。
// ES6
let foo = 123
// ES5
var foo = 123
Babel转译演示
- 安装
npm install @babel/core @babel/cli @babel/preset-env
- 创建babel.config.json
{
"presets": [
"@babel/preset-env"
],
"plugins": []
}
- babel转译
babel src --out-dir dist
- plugins使用
{
"presets": [],
"plugins": [
"@babel/plugin-transform-block-scoping"
]
}
转译的原理
核心步骤
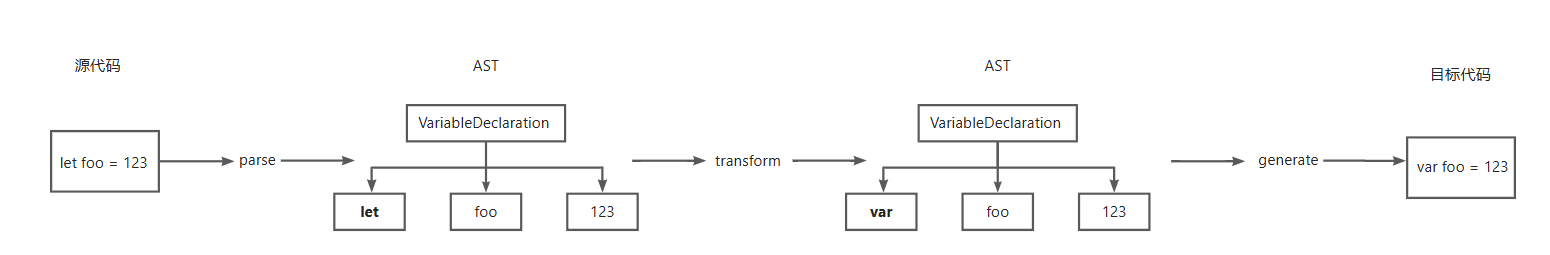
- parse:通过 parser 把源码转成抽象语法树(AST)
- transform:遍历 AST,调用各种 transform 插件对 AST 进行增删改
- generate:把转换后的 AST 输出成目标代码
可视化工具
AST explorer 是一个 AST 可视化工具,通过它可以查看各种编程语言代码解析后的 AST 结构,帮助开发者更直观地观察代码与 AST 节点树具体节点的对应关系。
parse详解
通过 parser 把源码转成抽象语法树(AST)
- 词法分析
- 语法分析
词法分析
将整个代码字符串分割成最小语法单元数组。这些词法单元(tokens)包括数字,标点符号,运算符等,这些词法单元之间都是独立的。
// 源代码
let foo = 123
// 词法分析转换后
const tokens = [
{
"type": { "label": "name" }, "value": "let", "start": 0, "end": 3
},
{
"type": { "label": "name" }, "value": "foo", "start": 4, "end": 7
},
{
"type": { "label": "=" }, "value": "=", "start": 8, "end": 9 },
{
"type": { "label": "num" }, "value": 123, "start": 10, "end": 13
},
{
"type": { "label": "eof" }, "start": 13, "end": 13
}
]
注:可视化工具查看分割的tokens集合。
利用状态机,简单实现词法分析:
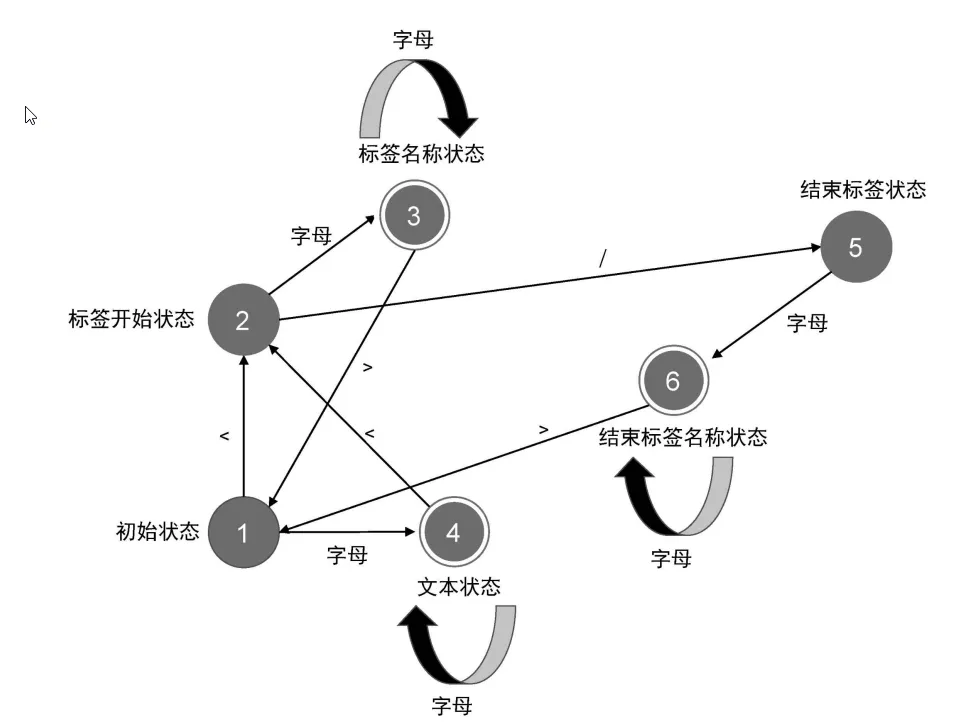
const code = `let foo = 123`;
const TokenState = {
START: 0,
NAME: 1,
EQUAL: 2,
NUMBER: 3,
EOF: 4
};
function tokenizer(code) {
const tokens = [];
let state = TokenState.START;
let buffer = "";
let tokenStart = 0;
function pushToken(type, value, start, end) {
const tok = {
type: { label: type },
start,
end
};
if (value !== undefined) {
tok.value = value;
}
tokens.push(tok);
}
for (let i = 0; i <= code.length; i++) {
const char = code[i] ?? ""; // 最后一轮给空字符
switch (state) {
case TokenState.START:
if (/[a-zA-Z_$]/.test(char)) {
state = TokenState.NAME;
buffer = char;
tokenStart = i;
} else if (/[0-9]/.test(char)) {
state = TokenState.NUMBER;
buffer = char;
tokenStart = i;
} else if (char === "=") {
pushToken("=", "=", i, i + 1);
} else if (/\s/.test(char)) {
// ignore 空格
} else if (char === "") {
state = TokenState.EOF;
pushToken("eof", undefined, i, i);
}
break;
case TokenState.NAME:
if (/[a-zA-Z0-9_$]/.test(char)) {
buffer += char;
} else {
pushToken("name", buffer, tokenStart, i);
buffer = "";
state = TokenState.START;
i--; // 回退一位重新处理
}
break;
case TokenState.NUMBER:
if (/[0-9]/.test(char)) {
buffer += char;
} else {
pushToken("num", Number(buffer), tokenStart, i);
buffer = "";
state = TokenState.START;
i--;
}
break;
}
}
return tokens;
}
const ret = tokenizer(code);
console.log(ret);
语法分析
将词法分析出来的 tokens 按照不同的语法结构如声明语句、赋值表达式等转化成有语法含义的抽象语法树结构。

AST 是对源码的抽象,字面量、标识符、表达式、语句、模块语法、class 语法都有各自的 AST。
- Literal:字面量
- Identifer:标识符
- statement:语句
- Declaration:声明
- Expression:表达式
- Class:类
- Modules:模块
- 其他
- program:整个程序的节点
- directives:指令,例如:"use strict"
- comments:注释
const tokens = [
{ type: { label: 'name' }, start: 0, end: 3, value: 'let' },
{ type: { label: 'name' }, start: 4, end: 7, value: 'foo' },
{ type: { label: '=' }, start: 8, end: 9, value: '=' },
{ type: { label: 'num' }, start: 10, end: 13, value: 123 },
{ type: { label: 'eof' }, start: 13, end: 13 }
]
const AST = {
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"start": 4,
"end": 12,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 4,
"end": 7,
"name": "foo"
},
"init": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"start": 10,
"end": 13,
"value": 123
}
}
],
"kind": "let"
}
]
}
如何处理复杂的语法分析呢,代码如下:
if (true) {
if (true) {
let foo = 123
}
}
const tokens = [
{ type: { label: 'if' }, start: 0, end: 2, value: 'if' },
{ type: { label: '(' }, start: 3, end: 4 },
{ type: { label: 'true' }, start: 4, end: 8, value: 'true' },
{ type: { label: ')' }, start: 8, end: 9 },
{ type: { label: '{' }, start: 10, end: 11 },
{ type: { label: 'if' }, start: 14, end: 16, value: 'if' },
{ type: { label: '(' }, start: 17, end: 18 },
{ type: { label: 'true' }, start: 18, end: 22, value: 'true' },
{ type: { label: ')' }, start: 22, end: 23 },
{ type: { label: '{' }, start: 24, end: 25 },
...
{ type: { label: '}' }, start: 46, end: 47 },
{ type: { label: '}' }, start: 48, end: 49 }
]
let str = `
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<ul>
<li>123</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
`;
let vdom = {
type: "element",
tag: "div",
children: [
{
type: "element",
tag: "ul",
children: [
{
type: "element",
tag: "li",
children: [
{
type: "element",
tag: "ul",
children: [
{
type: "element",
tag: "li",
children: [
{
type: "text",
content: "123",
},
],
},
],
},
],
},
],
},
],
};
function templateToAst(str) {
str = str.trim(); // 去掉头尾空格
const stack = []; // 栈结构
let currentParent = null; // 当前父节点
let root = null;
// 正则表达式
const startTag = /^<([a-zA-Z0-9\-]+)>/;
const endTag = /^<\/([a-zA-Z0-9\-]+)>/;
const textReg = /^([^<]+)/;
while (str) {
if (str.startsWith("</")) {
// 结束标签
const match = str.match(endTag);
if (match) {
stack.pop();
currentParent = stack[stack.length - 1];
str = str.slice(match[0].length);
}
} else if (str.startsWith("<")) {
// 开始标签
const match = str.match(startTag);
if (match) {
const element = {
type: "element",
tag: match[1],
children: [],
};
if (!root) {
root = element;
}
if (currentParent) {
currentParent.children.push(element);
}
stack.push(element);
currentParent = element;
str = str.slice(match[0].length);
}
} else {
// 文本内容
const match = str.match(textReg);
if (match) {
const text = match[1].trim();
if (text) {
currentParent.children.push({
type: "text",
content: text,
});
}
str = str.slice(match[0].length);
}
}
str = str.trim(); // 持续清除空格
}
return root;
}
const ret = templateToAst(str);
console.log(JSON.stringify(ret, null, 2));
transform详解
对AST对象进行遍历,遍历的过程中处理到不同的 AST 节点会调用注册的相应的 visitor 函数,visitor 函数里可以对 AST 节点进行增删改,返回新的 AST。
- traverser 遍历(深度优先遍历)
- transformer 转换
const AST = {
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"start": 4,
"end": 12,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 4,
"end": 7,
"name": "foo"
},
"init": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"start": 10,
"end": 13,
"value": 123
}
}
],
"kind": "let"
}
]
}
function traverser(ast, visitor) {
function traverseArray(array, parent) {
array.forEach((child) => {
traverseNode(child, parent);
});
}
function traverseNode(node, parent) {
if (!node) return;
const path = {
node,
parent,
replaceWith(newNode) {
if (!parent) throw new Error("Cannot replace root node");
// 替换逻辑:根据 parent 的类型找到该 node
for (let key in parent) {
if (Array.isArray(parent[key])) {
const idx = parent[key].indexOf(node);
if (idx > -1) {
parent[key][idx] = newNode;
return;
}
} else if (parent[key] === node) {
parent[key] = newNode;
return;
}
}
},
remove() {
if (!parent) throw new Error("Cannot remove root node");
for (let key in parent) {
if (Array.isArray(parent[key])) {
const idx = parent[key].indexOf(node);
if (idx > -1) {
parent[key].splice(idx, 1);
return;
}
} else if (parent[key] === node) {
parent[key] = null;
return;
}
}
}
};
const visitorFn = visitor[node.type];
if (visitorFn) {
visitorFn(path);
}
switch (node.type) {
case "Program":
traverseArray(node.body, node);
break;
case "VariableDeclaration":
traverseArray(node.declarations, node);
break;
case "VariableDeclarator":
traverseNode(node.id, node);
traverseNode(node.init, node);
break;
case "Identifier":
case "NumericLiteral":
// 叶子节点
break;
default:
throw new TypeError(`Unknown node type: ${node.type}`);
}
}
traverseNode(ast, null);
}
traverser(AST, {
VariableDeclaration(path) {
console.log("VariableDeclaration:", path.node.kind);
},
Identifier(path) {
console.log("Identifier:", path.node.name);
}
});
generate详解
AST 根节点进行递归的字符串拼接,就可以生成目标代码的字符串。
const AST = {
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 13,
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"start": 4,
"end": 12,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 4,
"end": 7,
"name": "foo"
},
"init": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"start": 10,
"end": 13,
"value": 123
}
}
],
"kind": "let"
}
]
}
function traverser(ast, visitor) {
function traverseArray(array, parent) {
array.forEach((child) => {
traverseNode(child, parent);
});
}
function traverseNode(node, parent) {
if (!node) return;
const path = {
node,
parent,
replaceWith(newNode) {
if (!parent) throw new Error("Cannot replace root node");
// 替换逻辑:根据 parent 的类型找到该 node
for (let key in parent) {
if (Array.isArray(parent[key])) {
const idx = parent[key].indexOf(node);
if (idx > -1) {
parent[key][idx] = newNode;
return;
}
} else if (parent[key] === node) {
parent[key] = newNode;
return;
}
}
},
remove() {
if (!parent) throw new Error("Cannot remove root node");
for (let key in parent) {
if (Array.isArray(parent[key])) {
const idx = parent[key].indexOf(node);
if (idx > -1) {
parent[key].splice(idx, 1);
return;
}
} else if (parent[key] === node) {
parent[key] = null;
return;
}
}
}
};
const visitorFn = visitor[node.type];
if (visitorFn) {
visitorFn(path);
}
switch (node.type) {
case "Program":
traverseArray(node.body, node);
break;
case "VariableDeclaration":
traverseArray(node.declarations, node);
break;
case "VariableDeclarator":
traverseNode(node.id, node);
traverseNode(node.init, node);
break;
case "Identifier":
case "NumericLiteral":
// 叶子节点
break;
default:
throw new TypeError(`Unknown node type: ${node.type}`);
}
}
traverseNode(ast, null);
}
traverser(AST, {
VariableDeclaration(path) {
path.node.kind = 'var'
},
Identifier(path) {
path.node.name = 'bar'
}
});
// 递归
function generator(node) {
switch (node.type) {
case "Program":
return node.body.map(generator).join("\n");
case "VariableDeclaration":
return (
node.kind +
" " +
node.declarations.map(generator).join(", ") +
";"
);
case "VariableDeclarator":
return generator(node.id) + " = " + generator(node.init);
case "Identifier":
return node.name;
case "NumericLiteral":
return node.value;
default:
throw new TypeError("Unknown node type: " + node.type);
}
}
const ret = generator(AST)
console.log(ret) // var bar = 123; 最后把字符串写入到文件中
自定义Babel插件
// my-plugin.js
module.exports = ({ types: t }) => {
return {
name: "myPlugin",
visitor: {
VariableDeclaration(path) {
path.node.kind = "var";
},
Identifier(path) {
path.node.name = "bar";
},
},
};
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号