[GenAI] MCP
前置知识
stdio
这是 MCP 中的通信方式。
进程:执行一个应用程序,就会启动一个进程,操作系统会为其分配内存空间、系统资源。
应用程序执行完毕后,系统分配给进程的资源就会被回收。
进程之间是可以通信的。那这里有一个最基本的要求:进程不能结束。如何让进程不结束?
想想微信、QQ启动后为啥不结束?
因为要监听。

这里也同样,只要进程处于监听状态,就不会结束。
// 监听输入
process.stdin.on("data", () => {});
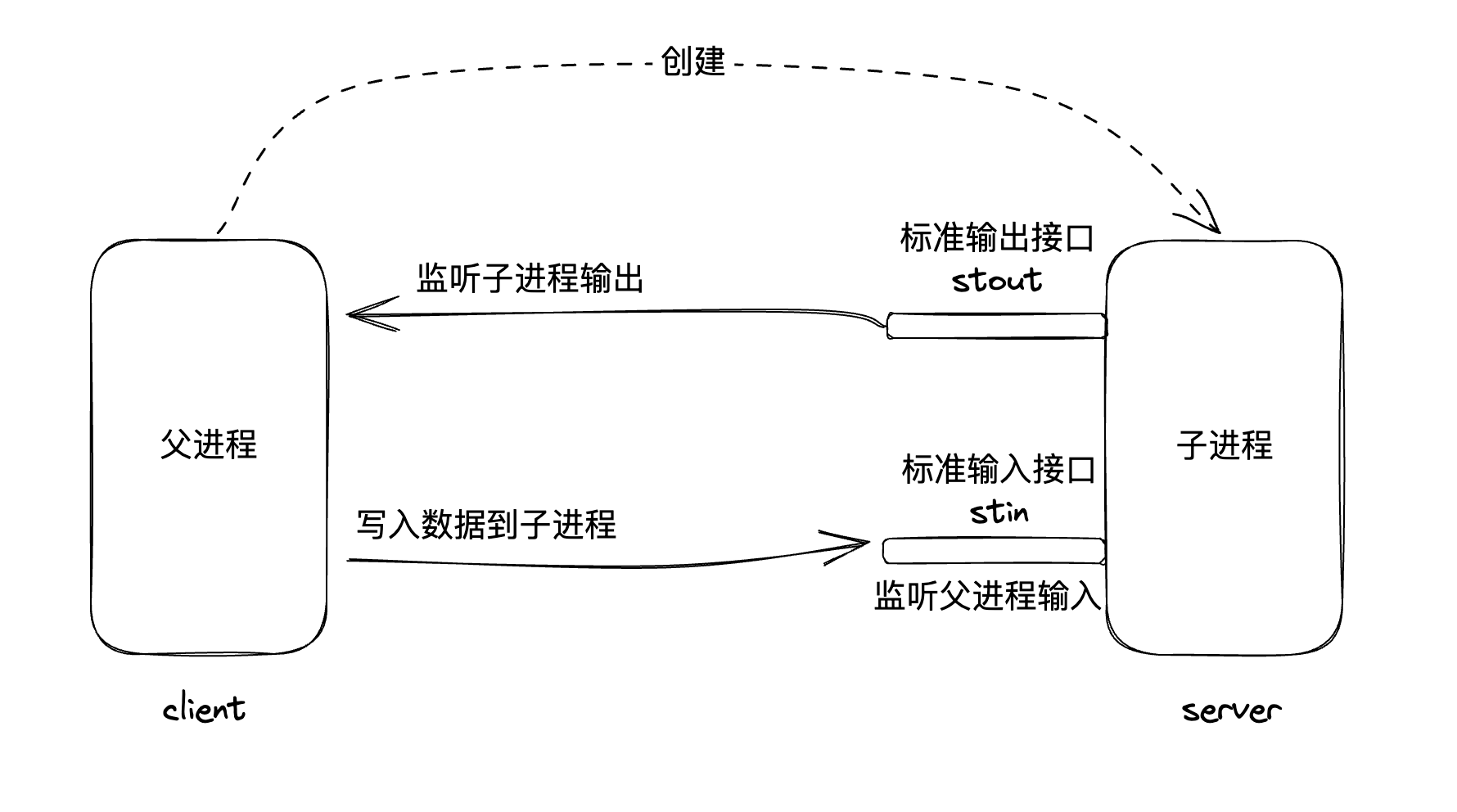
除此之外,一个进程还可以启动另一个进程,这在操作系统中是非常常见和常用的行为,被称之为父子进程模型。
控制台其实也是一个应用程序,启动后也会有进程。因此下面的代码:
node index.js
控制台就是父进程,node程序就是子进程。

🙋 让终端和 node 程序进行通信,该如何进行通信?
stdio: standard input and output 标准输入输出
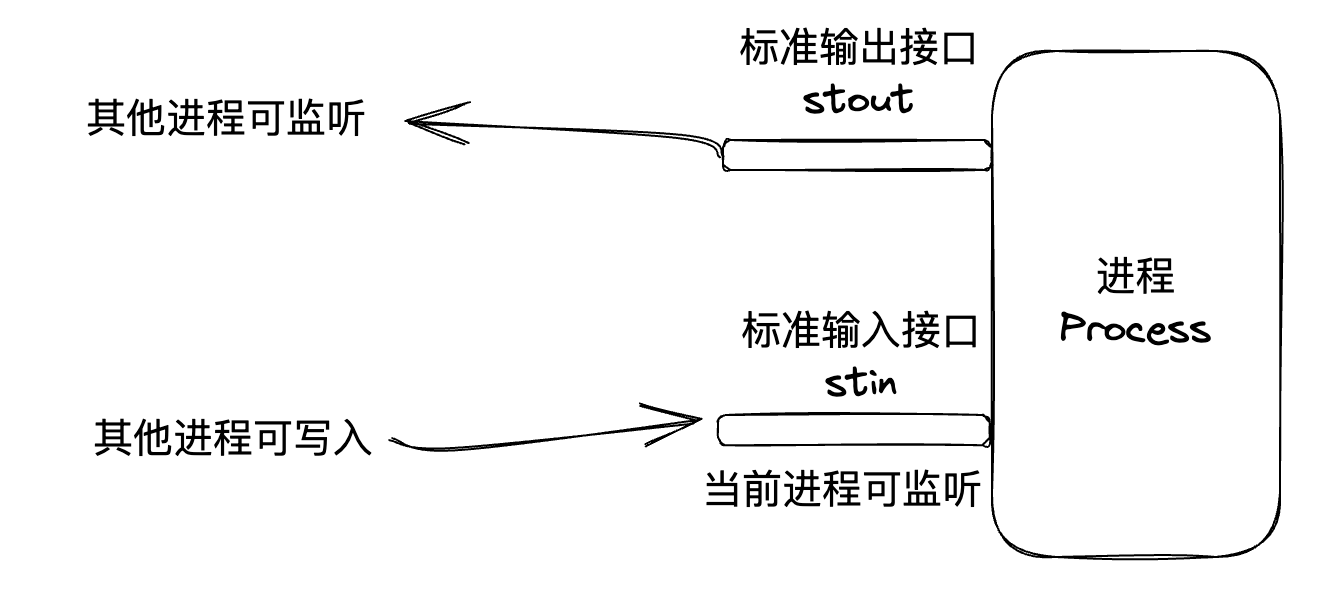
每一个进程启动后,都会留出两个对外通信的接口:
- 标准输入接口:standard in
- 标准输出接口:standard output
上面进程监听输入和对外输出的图,就可以变成这样:
结合前面父子模型的知识:
练习
终端和 node 进程通信
/// client.js
const { spawn } = require("child_process");
// 启动 server.js 子进程
const serverProcess = spawn("node", ["server.js"]);
// 监听服务端的响应
serverProcess.stdout.on("data", (data) => {
process.stdin.write(data.toString());
});
// 发送几条测试消息
const messages = ["生命有意义吗?", "宇宙有尽头吗?", "再见!"];
messages.forEach((msg, index) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`-->${msg}`);
serverProcess.stdin.write(msg);
}, index * 1000); // 每秒发一条
});
///server.js
process.stdin.setEncoding("utf8"); // 设置字符编码
// 处于监听状态,监听其它进程给我的消息
process.stdin.on("data", (data) => {
const response = `AI: ${data
.replace(/[??吗]/g, "")
.replace(/我/g, "你")
.replace(/你/g, "我")}\n`;
process.stdout.write(response); // 向父进程输出信息
});
如下图:

- 一个进程可以启动另外一个进程
- 进程之间可以通信
stdio通信高效、简洁,但仅适用于本地进程间通信
stdio:通信方式
通信格式
通信涉及到数据传输,数据传输的格式有多种:
- xml
- json
- 字符串
JSON-RPC2.0
英语全称为 JSON Remote Procedure Call,JSON 远程函数调用。
通过一个 JSON 远程的调用不在本地的函数。
request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "sum", // 我要调用的函数
"params": { // 函数的参数
"a": 5,
"b": 6
},
"id": 1 // 请求的id,回头该请求对应的响应的id会和这个id相同
}
response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": 11, // 函数的调用结果
"id": 1
}
练习
实现基于 JSON-RPC 的通信
///server.js
const utils = require("./utils.js"); // { sum:f, createFile: f}
process.stdin.on("data", (data) => {
const req = JSON.parse(data);
const funcName = req.method; // sum
const params = req.params; // { "a": 11, "b": 22 }
const result = utils[funcName](params); // 调用对应的方法
// 封装成一个 JSON-RPC2.0 格式的响应
const res = {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
result,
id: req.id,
};
process.stdout.write(JSON.stringify(res) + "\n"); // 给父进程发送消息
});
/// utils.js
const fs = require("fs");
module.exports = {
// 第一个工具
sum({ a, b }) {
return a + b;
},
// 写入文件
createFile({ filename, content }) {
try {
fs.writeFileSync(filename, content);
return true;
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
return false;
}
},
};
test:
{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "sum", "params": { "a": 11, "b": 22 }, "id": 1 }
{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "createFile", "params": { "filename": "/Users/jie/desktop/渡一MCP.txt", "content": "Hello, 渡一MCP!" }, "id": 2 }
初识MCP
MCP是一套 标准协议, 它规定了 应用程序 之间 如何通信
如何通信:
- 通信方式
- stdio: 推荐,高效、简洁、本地
- http: 可远程
- StreamHTTP
- SSE
- 通信格式: 基于JSON-RPC的进一步规范(和上面的例子稍微还有一些不同)
基本规范
1. 初始化 initialize
两个应用程序要开始通信,首先需要初始化
request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize", // 固定为 initialize,不能变,属于 MCP
"params": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05", // MCP协议的版本
"capabilities": { // MCP客户端的能力
"roots": {
"listChanged": true
},
"sampling": {},
"elicitation": {}
},
"clientInfo": { // 告知服务器客户端的信息
"name": "ExampleClient",
"title": "Example Client Display Name",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}
response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05", // 协议版本号
"capabilities": {
"logging": {},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": true
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": true,
"listChanged": true
},
"tools": {
"listChanged": true
}
},
"serverInfo": { // 服务端信息
"name": "ExampleServer",
"title": "Example Server Display Name",
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"instructions": "Optional instructions for the client"
}
}
2. 发现工具 tools/list
服务器有哪些工具函数可以供客户端调用
request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/list", // 固定的方法名
}
response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
// tools对应的是一个数组,因为你会有多个工具(函数)
"tools": [
{
"name": "get_weather", // 函数名
"title": "Weather Information Provider",
"description": "Get current weather information for a location", // 函数的描述
// 函数接收的参数
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City name or zip code"
},
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
}
}
3. 工具调用 tools/call
request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "tools/call", // 调用工具,也是固定的
"params": {
"name": "get_weather", // 工具名,对应工具发现中的name
"arguments": { // 工具参数,需要和工具发现中的结构一致
"location": "New York"
}
}
}
response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"content": [{ // 函数结果需要放到content字段中,如果有多个,使用数组
// 函数结果的类型
// 支持的类型: https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/server/tools#tool-result
"type": "text",
"text": "72°F"
}]
}
}
工具返回的类型有 多种
基于 JSON-RPC2.0 做了进一步的约定,例如 tools/list、tools/call
练习
实现遵循 MCP 协议的服务器
///server.js
const protocal = require("./protocal.js");
const tools = require("./tools.js");
process.stdin.on("data", (data) => {
const req = JSON.parse(data);
let result;
if (req.method === "tools/call") {
// 代表调用工具
result = tools[req.params.name](req.params.arguments);
} else if (req.method in protocal) {
result = protocal[req.method](req.params);
} else {
return;
}
// 将这个结果封装成符合JSON-RPC2.0的格式
const res = {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
result,
id: req.id,
};
process.stdout.write(JSON.stringify(res) + "\n");
});
///porotocal.s
module.exports = {
initialize() {
return {
protocolVersion: "2024-11-05",
capabilities: {
logging: {},
prompts: {
listChanged: true,
},
resources: {
subscribe: true,
listChanged: true,
},
tools: {
listChanged: true,
},
},
serverInfo: {
name: "ExampleServer",
title: "Example Server Display Name",
version: "1.0.0",
},
instructions: "Optional instructions for the client",
};
},
"tools/list"() {
return {
tools: [
{
name: "sum",
title: "两数求和",
description: "得到两个数的和",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
a: {
type: "number",
description: "第一个数",
},
b: {
type: "number",
description: "第二个数",
},
},
required: ["a", "b"],
},
},
{
name: "createFile",
title: "创建文件",
description: "在指定目录下创建一个文件",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
filename: {
type: "string",
description: "文件名",
},
content: {
type: "string",
description: "文件内容",
},
},
required: ["filename", "content"],
},
},
],
};
},
};
///tools.js
const fs = require("fs");
module.exports = {
sum({ a, b }) {
// 这里返回结果的时候,结果的格式要符合MCP协议的格式
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `两数求和结果:${a + b}`,
},
],
};
},
createFile({ filename, content }) {
try {
fs.writeFileSync(filename, content);
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `文件创建成功!`,
},
],
};
} catch (err) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: err.message || "文件创建失败!",
},
],
};
}
},
};
test:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"initialize","params":{"protocolVersion":"2024-11-05","capabilities":{"roots":{"listChanged":true},"sampling":{},"elicitation":{}},"clientInfo":{"name":"ExampleClient","title":"Example Client Display Name","version":"1.0.0"}}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"tools/list"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":2,"method":"tools/call","params":{"name":"sum","arguments":{"a":1, "b":2}}}
{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 2, "method": "tools/call", "params": { "name" :"createFile", "arguments":{"filename": "/Users/jie/desktop/渡一MCP2.txt", "content": "Hello, 渡一MCP2!"}}}
调试工具
服务器目录下,直接运行
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
官方SDK
非业务代码,一般就会封装出来。
使用@modelcontextprotocol/sdk可以更方便的开发MCP Server
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
练习
使用官方SDK实现 MCP 服务器
帮我节省很多的事情,让我们的精力专注于业务代码
///package.json
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./src/server.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^1.15.1",
"zod": "^3.25.76"
}
///server.js
import { McpServer } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import { z } from "zod";
import fs from "fs";
// 创建一个MCP Server的实例
const server = new McpServer({
name: "my mcp server",
version: "0.1.0",
});
// 专注你的业务代码,你这个服务器上面有哪些工具
server.registerTool(
"sum", // 函数名
{
title: "两数求和",
description: "得到两个数的和",
inputSchema: {
a: z.number().describe("第一个数"), // number类型
b: z.number().describe("第二个数"), // number类型
},
},
({ a, b }) => ({
// 正常的函数逻辑 ....
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `两数求和结果:${a + b}`,
},
],
})
);
server.registerTool(
"createFile",
{
title: "创建文件",
description: "在指定目录下创建一个文件",
inputSchema: {
filename: z.string().describe("文件名"),
content: z.string().describe("文件内容"),
},
},
({ filename, content }) => {
try {
fs.writeFileSync(filename, content);
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: `文件创建成功!`,
},
],
};
} catch (err) {
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: err.message || "文件创建失败!",
},
],
};
}
}
);
const transport = new StdioServerTransport(); // 创建一个 stdio 通信通道
server.connect(transport); // 进行连接
对接AI应用
什么是AI应用程序?
所有能与大模型交互的应用都可以看作是AI应用程序
常见的AI应用程序:
-
ChatGPT:AI应用
- GPT:模型
-
DeepSeek Chat Page
-
Claude Desktop
-
VSCode
-
Cursor
-
...
凡是支持 MCP 协议的 AI 应用,就可以充当客户端,连接 MCP 服务器。
- Claude Desktop
支持MCP协议,可充当MCP客户端
https://claude.ai/download - Cursor
支持MCP协议,可充当MCP客户端
https://cursor.com/cn
整个流程如下图:
用户和 AI 应用进行交互,AI 应用背后调用的是大模型。

但是有些事情,大模型办不到。

此时可以通过 MCP 服务器扩宽大模型的能力边界。
🤔 工具是谁调用,大模型调用么?
不是大模型调用,大模型只接收 输入 和 输出。
所以大模型会回复:我需要调用 XXX 工具。

然后 AI 应用调用工具,将工具调用结果返回给大模型。

With cursor
{
"mcpServers": {
"my mcp server": {
"command": "/usr/local/bin/node",
"args": ["/Users/zhentianwan/Downloads/use-sdk/src/server.js"]
}
}
}
-EOF-


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号