vgg16网络及pytorch神经网络
一、基于tensorflow的vgg16:识别猫狗数据集
1 import os, shutil 2 current_dir = (r"E:\人工智能\猫狗数据集\dogs-vs-cats") # 当前目录 3 current_dir[0] 4 base_dir = current_dir[0] + ':/人工智能/cats_dogs_small' 5 os.mkdir(base_dir) # 创建目录 6 # 分别创建训练集、验证集和测试集的目录 7 8 train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,"train") 9 os.mkdir(train_dir) 10 validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,"validation") 11 os.mkdir(validation_dir) 12 test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,"test") 13 os.mkdir(test_dir) 14 15 # 猫、狗的训练、验证、测试图像目录 16 train_cats_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, "cats") 17 os.mkdir(train_cats_dir) 18 train_dogs_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, "dogs") 19 os.mkdir(train_dogs_dir) 20 21 validation_cats_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, "cats") 22 os.mkdir(validation_cats_dir) 23 validation_dogs_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, "dogs") 24 os.mkdir(validation_dogs_dir) 25 26 test_cats_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, "cats") 27 os.mkdir(test_cats_dir) 28 test_dogs_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, "dogs") 29 os.mkdir(test_dogs_dir)
1 # 1000张当做训练集train 2 fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)] 3 for fname in fnames: 4 # 源目录文件 5 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":/人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 6 # 目标目录 7 dst = os.path.join(train_cats_dir, fname) 8 shutil.copyfile(src, dst) 9 10 # 500张当做验证集valiation 11 fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000,1500)] 12 for fname in fnames: 13 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 14 dst = os.path.join(validation_cats_dir, fname) 15 shutil.copyfile(src, dst) 16 17 # 500张当做测试集test 18 fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500,2000)] 19 for fname in fnames: 20 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":/人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 21 dst = os.path.join(test_cats_dir, fname) 22 shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
1 # 针对dog的3个同样操作 2 3 # 1、1000张当做训练集train 4 fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)] 5 for fname in fnames: 6 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":/人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 7 dst = os.path.join(train_dogs_dir, fname) 8 shutil.copyfile(src, dst) 9 10 # 2、500张当做验证集valiation 11 fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000,1500)] 12 for fname in fnames: 13 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":/人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 14 dst = os.path.join(validation_dogs_dir, fname) 15 shutil.copyfile(src, dst) 16 17 # 3、500张当做测试集test 18 fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500,2000)] 19 for fname in fnames: 20 src = os.path.join(current_dir[0] + ":/人工智能/猫狗数据集/dogs-vs-cats/train", fname) 21 dst = os.path.join(test_dogs_dir, fname) 22 shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
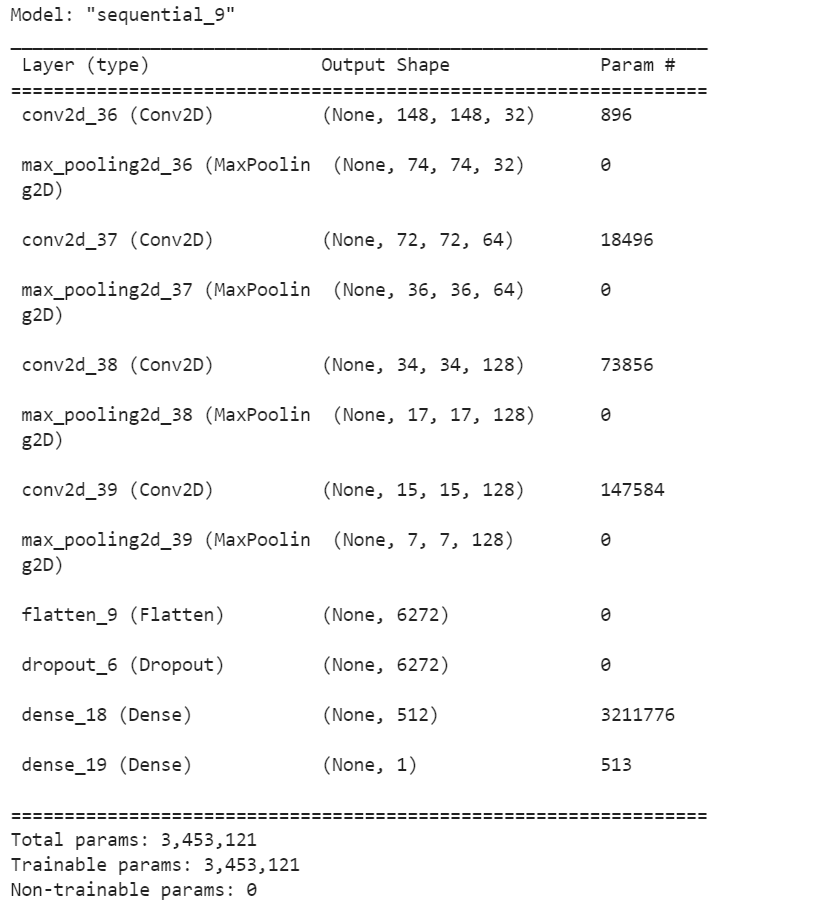
1 #构建神经网络 2 import tensorflow as tf 3 from keras import layers 4 from keras import models 5 6 model = models.Sequential() 7 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32,(3,3),activation="relu", 8 input_shape=(150,150,3))) 9 model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2))) 10 11 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64,(3,3),activation="relu")) 12 model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2))) 13 14 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128,(3,3),activation="relu")) 15 model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2))) 16 17 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128,(3,3),activation="relu")) 18 model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2))) 19 20 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten()) 21 22 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)) 23 24 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation="relu")) 25 model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")) 26 27 model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", 28 optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4), 29 metrics=["acc"]) 30 31 model.summary()
1 from tensorflow.keras import optimizers 2 3 model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", 4 optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4), 5 metrics=["acc"]) 6 def generator(): 7 i=0 8 while True: 9 i += 1 10 yield i 11 for item in generator(): 12 print(item) 13 if item>4: 14 break 15 16 from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator 17 18 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) # 进行缩放 19 test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) # 进行缩放 20 21 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( 22 train_dir, # 待处理的目录 23 target_size=(150,150), # 图像大小设置 24 batch_size=20, 25 class_mode="binary" # 损失函数是binary_crossentropy 所以使用二进制标签 26 ) 27 28 validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory( 29 validation_dir, # 待处理的目录 30 target_size=(150,150), # 图像大小设置 31 batch_size=20, 32 class_mode="binary" # 损失函数是binary_crossentropy 所以使用二进制标签 33 )

1 for data_batch, labels_batch in train_generator: 2 print(data_batch.shape) 3 print(labels_batch.shape) 4 break

1 history = model.fit_generator( 2 train_generator, # 第一个参数必须是Python生成器 3 steps_per_epoch=100, # 2000 / 20 4 epochs=10, # 迭代次数 5 validation_data=validation_generator, # 待验证的数据集 6 validation_steps=50 7 )
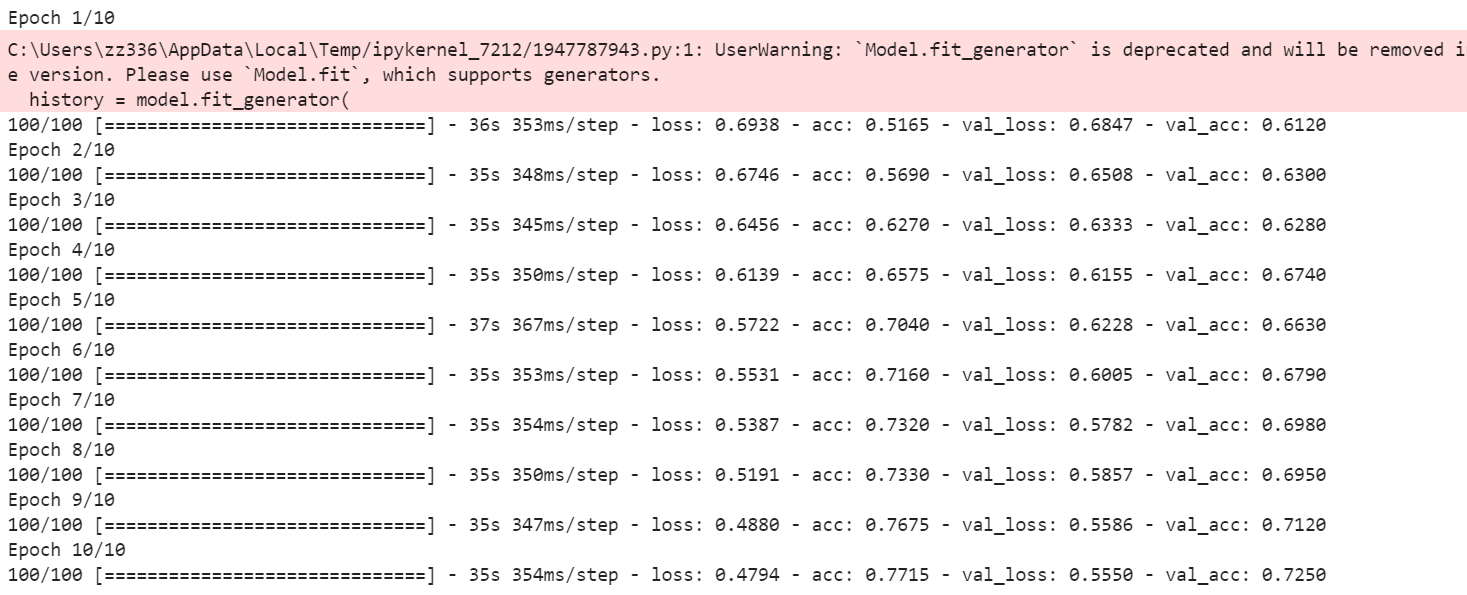
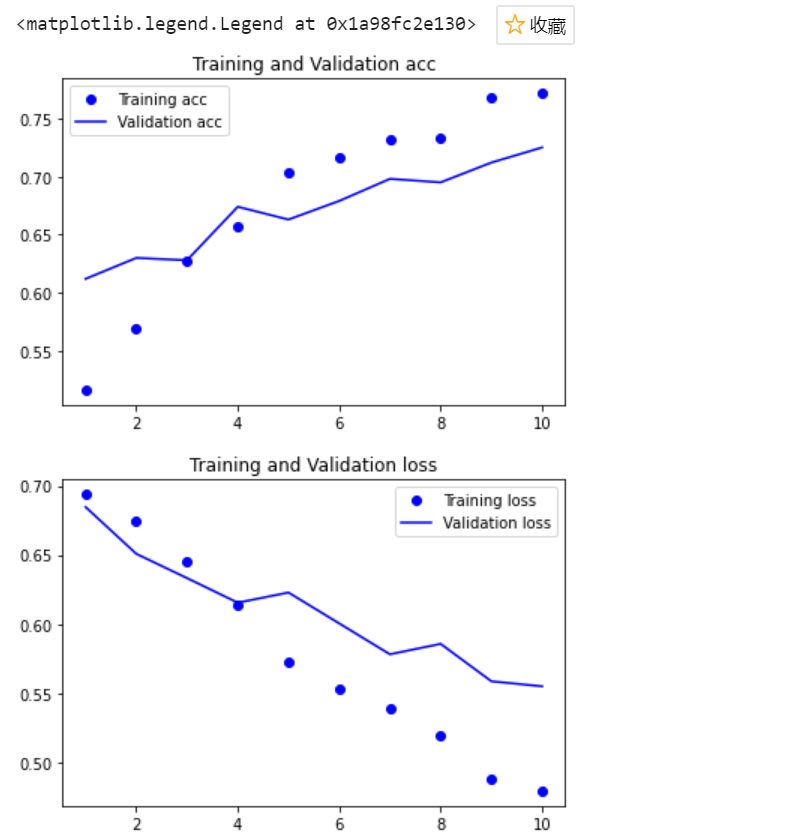
1 # 保存模型 2 model.save("cats_and_dogs_small.h5") 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 %matplotlib inline 5 history_dict = history.history # 字典形式 6 for key, _ in history_dict.items(): 7 print(key) 8 9 acc = history_dict["acc"] 10 val_acc = history_dict["val_acc"] 11 12 loss = history_dict["loss"] 13 val_loss = history_dict["val_loss"]

1 acc = history_dict["acc"] 2 val_acc = history_dict["val_acc"] 3 4 loss = history_dict["loss"] 5 val_loss = history_dict["val_loss"] 6 7 epochs = range(1, len(acc)+1) 8 9 # acc 10 plt.plot(epochs, acc, "bo", label="Training acc") 11 plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, "b", label="Validation acc") 12 plt.title("Training and Validation acc") 13 plt.legend() 14 15 plt.figure() 16 17 # loss 18 plt.plot(epochs, loss, "bo", label="Training loss") 19 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, "b", label="Validation loss") 20 plt.title("Training and Validation loss") 21 plt.legend()
1 #设置数据增强 2 datagen = ImageDataGenerator( 3 rotation_range=40, # 0-180的角度值 4 width_shift_range=0.2, # 水平和垂直方向的范围;相对于总宽度或者高度的比例 5 height_shift_range=0.2, 6 shear_range=0.2, # 随机错切变换的角度 7 zoom_range=0.2, # 图像随机缩放的角度 8 horizontal_flip=True, # 随机将一半图像进行水平翻转 9 fill_mode="nearest" # 用于填充新创建像素的方法 10 ) 11 #显示增强后图像 12 from keras.preprocessing import image 13 fnames = [os.path.join(train_cats_dir,fname) for fname in os.listdir(train_cats_dir)] 14 img_path = fnames[3] 15 # 读取图片并调整大小 16 img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(150,150)) 17 # 转成数组 18 x = image.img_to_array(img) 19 20 # shape转成(1,150,150,3) 21 x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape) 22 23 i = 0 24 for batch in datagen.flow(x, batch_size=1): # 生成随机变换后的图像批量 25 plt.figure() 26 imgplot = plt.imshow(image.array_to_img(batch[0])) 27 i += 1 28 if i % 4 == 0: 29 break # 循环是无限,需要在某个时刻终止 30 plt.show()
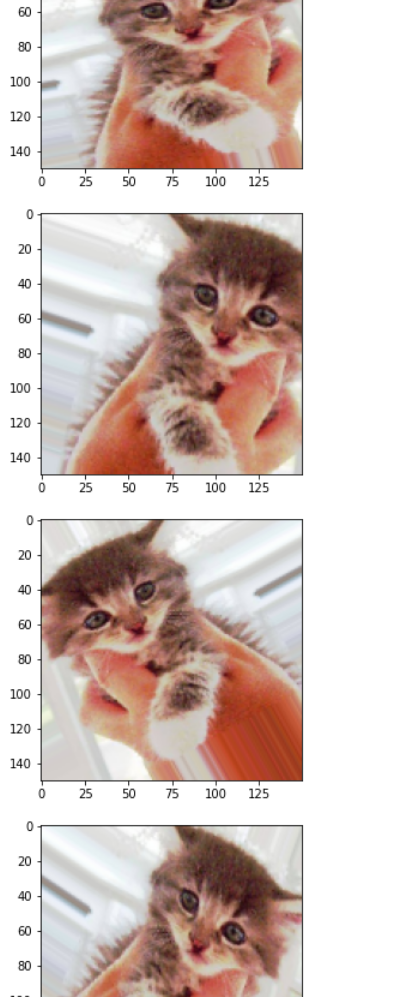

1 # 训练数据的增强 2 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator( 3 rescale=1. / 255, 4 rotation_range=40, 5 width_shift_range=0.2, 6 height_shift_range=0.2, 7 shear_range=0.2, 8 zoom_range=0.2, 9 horizontal_flip=True 10 ) 11 12 # 不能增强验证数据 13 test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1.0 / 255) 14 15 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( 16 train_dir, # 目标目录 17 target_size=(150,150), # 大小调整 18 batch_size=32, 19 class_mode="binary" 20 ) 21 22 validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory( 23 validation_dir, 24 target_size=(150,150), 25 batch_size=32, 26 class_mode="binary" 27 ) 28 29 # 优化:报错有修改 30 history = model.fit_generator( 31 train_generator, 32 # 原文 steps_per_epoch=100, 33 steps_per_epoch=63, # steps_per_epoch=2000/32≈63 取上限 34 epochs=100, 35 validation_data=validation_generator, 36 # 原文 validation_steps=50 37 validation_steps=32 # validation_steps=1000/32≈32 38 )
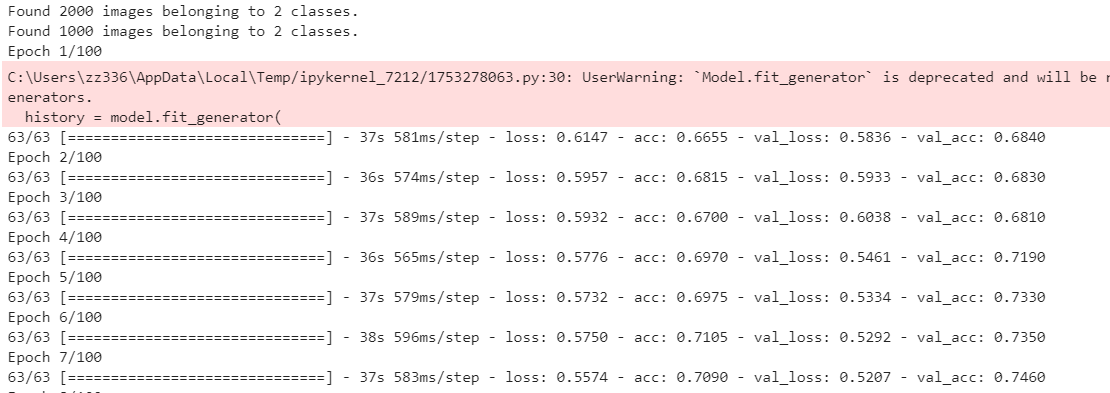

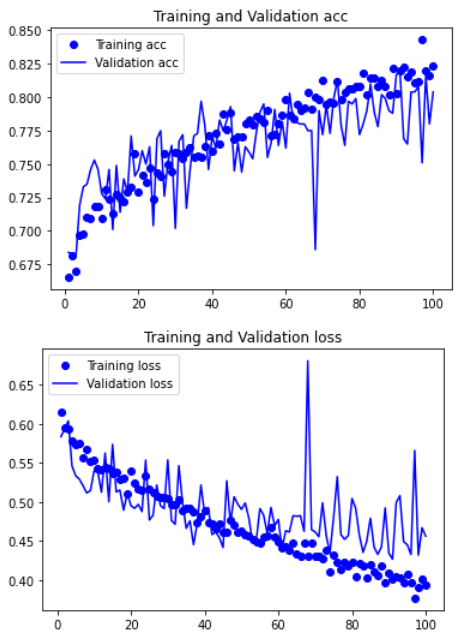
1 # 保存模型 2 model.save("cats_and_dogs_small_2.h5") 3 4 history_dict = history.history # 字典形式 5 6 acc = history_dict["acc"] 7 val_acc = history_dict["val_acc"] 8 loss = history_dict["loss"] 9 val_loss = history_dict["val_loss"]
1 epochs = range(1, len(acc)+1) 2 3 # acc 4 plt.plot(epochs, acc, "bo", label="Training acc") 5 plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, "b", label="Validation acc") 6 plt.title("Training and Validation acc") 7 plt.legend() 8 9 plt.figure() 10 11 # loss 12 plt.plot(epochs, loss, "bo", label="Training loss") 13 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, "b", label="Validation loss") 14 plt.title("Training and Validation loss") 15 plt.legend() 16 17 plt.show()
二、pytorch神经网络
1 #定义神经网络 2 import torch 3 import torch.nn as nn 4 import torch.nn.functional as F 5 6 7 class Net(nn.Module): 8 9 def __init__(self): 10 super(Net, self).__init__() 11 # 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution 12 # kernel 13 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5) 14 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) 15 # an affine operation: y = Wx + b 16 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) 17 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84) 18 self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) 19 20 def forward(self, x): 21 # Max pooling over a (2, 2) window 22 x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2)) 23 # If the size is a square you can only specify a single number 24 x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2) 25 x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x)) 26 x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) 27 x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) 28 x = self.fc3(x) 29 return x 30 31 def num_flat_features(self, x): 32 size = x.size()[1:] # all dimensions except the batch dimension 33 num_features = 1 34 for s in size: 35 num_features *= s 36 return num_features 37 38 39 net = Net() 40 print(net)

1 #一个模型可训练的参数可以通过调用 net.parameters() 返回 2 params = list(net.parameters()) 3 print(len(params)) 4 print(params[0].size()) # conv1's .weight
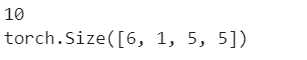
1 #尝试随机生成一个 32x32 的输入 2 input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32) 3 out = net(input) 4 print(out)
![]()
1 #把所有参数梯度缓存器置零,用随机的梯度来反向传播 2 net.zero_grad() 3 out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10)) 4 #损失函数 5 output = net(input) 6 target = torch.randn(10) # a dummy target, for example 7 target = target.view(1, -1) # make it the same shape as output 8 criterion = nn.MSELoss() 9 10 loss = criterion(output, target) 11 print(loss)
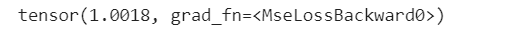
1 print(loss.grad_fn) # MSELoss 2 print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0]) # Linear 3 print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0].next_functions[0][0]) # ReLU

1 #反向传播 2 net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters 3 4 print('conv1.bias.grad before backward') 5 print(net.conv1.bias.grad) 6 7 loss.backward() 8 9 print('conv1.bias.grad after backward') 10 print(net.conv1.bias.grad)

1 #更新神经网络的参数 2 #weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient 随机梯度下降 3 learning_rate = 0.01 4 for f in net.parameters(): 5 f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate) 6 7 import torch.optim as optim 8 9 # create your optimizer 10 optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) 11 12 # in your training loop: 13 optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers 14 output = net(input) 15 loss = criterion(output, target) 16 loss.backward() 17 optimizer.step() # Does the update




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号