TRAC-IK机器人运动学求解器
TRAC-IK和Orocos KDL类似,也是一种基于数值解的机器人运动学求解器,但是在算法层面上进行了很多改进(Specifically, KDL’s convergence algorithms are based on Newton’s method, which does not work well in the presence of joint limits — common for many robotic platforms. TRAC-IK concurrently runs two IK implementations. One is a simple extension to KDL’s Newton-based convergence algorithm that detects and mitigates local minima due to joint limits by random jumps. The second is an SQP (Sequential Quadratic Programming) nonlinear optimization approach which uses quasi-Newton methods that better handle joint limits. By default, the IK search returns immediately when either of these algorithms converges to an answer ),相比KDL求解效率(成功率和计算时间)高了很多。
下面在Ubuntu16.04中安装TRAC-IK(之前已经安装过ROS Kinetic):
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-trac-ik
按照ROS教程新建一个名为ik_test的Package,并创建urdf文件夹用于存放机器人URDF描述文件,创建launch文件夹存放launch文件:

参考trac_ik_examples修改package.xml以及CMakeLists.txt文件,添加TRAC-IK以及KDL的支持。编写一个简单的robot.urdf文件,joint1为与基座link0相连的基关节,joint3为末端关节:

<robot name="test_robot"> <link name="link0" /> <link name="link1" /> <link name="link2" /> <link name="link3" /> <joint name="joint1" type="continuous"> <parent link="link0"/> <child link="link1"/> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> <joint name="joint2" type="continuous"> <parent link="link1"/> <child link="link2"/> <origin xyz="0 0 1" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> <joint name="joint3" type="continuous"> <parent link="link2"/> <child link="link3"/> <origin xyz="0 0 1" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> </robot>
TRAC-IK求解机器人逆运动学函数为CartToJnt:
int CartToJnt(const KDL::JntArray &q_init, const KDL::Frame &p_in, KDL::JntArray &q_out, const KDL::Twist& bounds=KDL::Twist::Zero());
第一个参数q_init为关节的初始值,p_in为输入的末端Frame,q_out为求解输出的关节值。基本用法如下:
#include <trac_ik/trac_ik.hpp> TRAC_IK::TRAC_IK ik_solver(KDL::Chain chain, KDL::JntArray lower_joint_limits, KDL::JntArray upper_joint_limits, double timeout_in_secs=0.005, double error=1e-5, TRAC_IK::SolveType type=TRAC_IK::Speed); % OR TRAC_IK::TRAC_IK ik_solver(string base_link, string tip_link, string URDF_param="/robot_description", double timeout_in_secs=0.005, double error=1e-5, TRAC_IK::SolveType type=TRAC_IK::Speed); % NOTE: The last arguments to the constructors are optional. % The type can be one of the following: % Speed: returns very quickly the first solution found % Distance: runs for the full timeout_in_secs, then returns the solution that minimizes SSE from the seed % Manip1: runs for full timeout, returns solution that maximizes sqrt(det(J*J^T)) % Manip2: runs for full timeout, returns solution that minimizes cond(J) = |J|*|J^-1| int rc = ik_solver.CartToJnt(KDL::JntArray joint_seed, KDL::Frame desired_end_effector_pose, KDL::JntArray& return_joints, KDL::Twist tolerances); % NOTE: CartToJnt succeeded if rc >=0 % NOTE: tolerances on the end effector pose are optional, and if not % provided, then by default are 0. If given, the ABS() of the % values will be used to set tolerances at -tol..0..+tol for each of % the 6 Cartesian dimensions of the end effector pose.
下面是一个简单的测试程序,先通过KDL计算正解,然后使用TRAC-IK反算逆解:

#include "ros/ros.h" #include <trac_ik/trac_ik.hpp> #include <kdl/chainiksolverpos_nr_jl.hpp> #include <kdl/chain.hpp> #include <kdl/chainfksolver.hpp> #include <kdl/chainfksolverpos_recursive.hpp> #include <kdl/frames_io.hpp> using namespace KDL; int main(int argc, char **argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "ik_test"); ros::NodeHandle nh("~"); int num_samples; std::string chain_start, chain_end, urdf_param; double timeout; const double error = 1e-5; nh.param("chain_start", chain_start, std::string("")); nh.param("chain_end", chain_end, std::string("")); if (chain_start=="" || chain_end=="") { ROS_FATAL("Missing chain info in launch file"); exit (-1); } nh.param("timeout", timeout, 0.005); nh.param("urdf_param", urdf_param, std::string("/robot_description")); if (num_samples < 1) num_samples = 1; TRAC_IK::TRAC_IK ik_solver(chain_start, chain_end, urdf_param, timeout, error, TRAC_IK::Speed); KDL::Chain chain; bool valid = ik_solver.getKDLChain(chain); if (!valid) { ROS_ERROR("There was no valid KDL chain found"); return -1; } // Set up KDL IK KDL::ChainFkSolverPos_recursive fk_solver(chain); // Forward kin. solver based on kinematic chain // Create joint array unsigned int nj = chain.getNrOfJoints(); ROS_INFO ("Using %d joints",nj); KDL::JntArray jointpositions = JntArray(nj); // Assign some values to the joint positions for(unsigned int i=0;i<nj;i++){ float myinput; printf ("Enter the position of joint %i: ",i); scanf ("%e",&myinput); jointpositions(i)=(double)myinput; } // Create the frame that will contain the results KDL::Frame cartpos; // Calculate forward position kinematics bool kinematics_status; kinematics_status = fk_solver.JntToCart(jointpositions,cartpos); Vector p = cartpos.p; // Origin of the Frame Rotation M = cartpos.M; // Orientation of the Frame double roll, pitch, yaw; M.GetRPY(roll,pitch,yaw); if(kinematics_status>=0){ printf("%s \n","KDL FK Succes"); std::cout <<"Origin: " << p(0) << "," << p(1) << "," << p(2) << std::endl; std::cout <<"RPY: " << roll << "," << pitch << "," << yaw << std::endl; }else{ printf("%s \n","Error: could not calculate forward kinematics :("); } KDL::JntArray joint_seed(nj); KDL::SetToZero(joint_seed); KDL::JntArray result(joint_seed); int rc=ik_solver.CartToJnt(joint_seed,cartpos,result); if(rc < 0) printf("%s \n","Error: could not calculate forward kinematics :("); else{ printf("%s \n","TRAC IK Succes"); for(unsigned int i = 0; i < nj; i++) std::cout << result(i) << " "; } return 0; }
test.launch文件如下:

<?xml version="1.0"?> <launch> <arg name="chain_start" default="link0" /> <arg name="chain_end" default="link3" /> <arg name="timeout" default="0.005" /> <param name="robot_description" textfile="$(find ik_test)/urdf/robot.urdf" /> <node name="ik_test" pkg="ik_test" type="ik_test" output="screen"> <param name="chain_start" value="$(arg chain_start)"/> <param name="chain_end" value="$(arg chain_end)"/> <param name="timeout" value="$(arg timeout)"/> <param name="urdf_param" value="/robot_description"/> </node> </launch>
使用catkin_make编译成功,并设置环境后,运行该程序
roslaunch ik_test test.launch
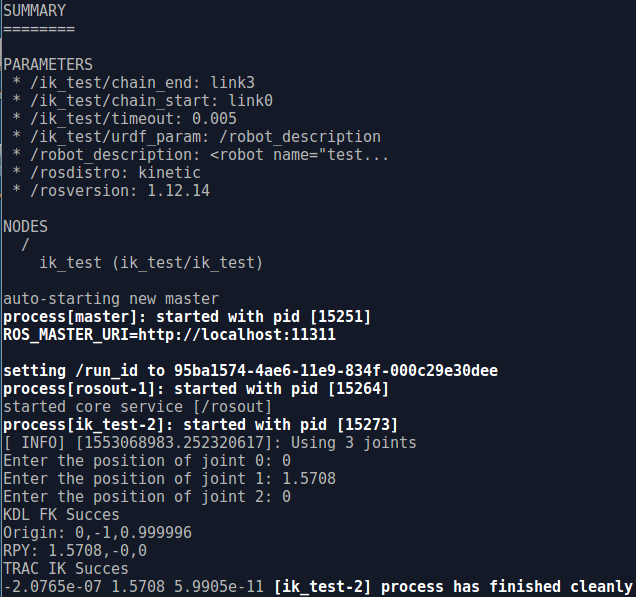
通过键盘分别输入三个关节值:0,1.5708(90°),0 运动学正逆解计算结果如下图所示:
接下来使用7自由的的Franka panda机器人进行正逆解计算测试。
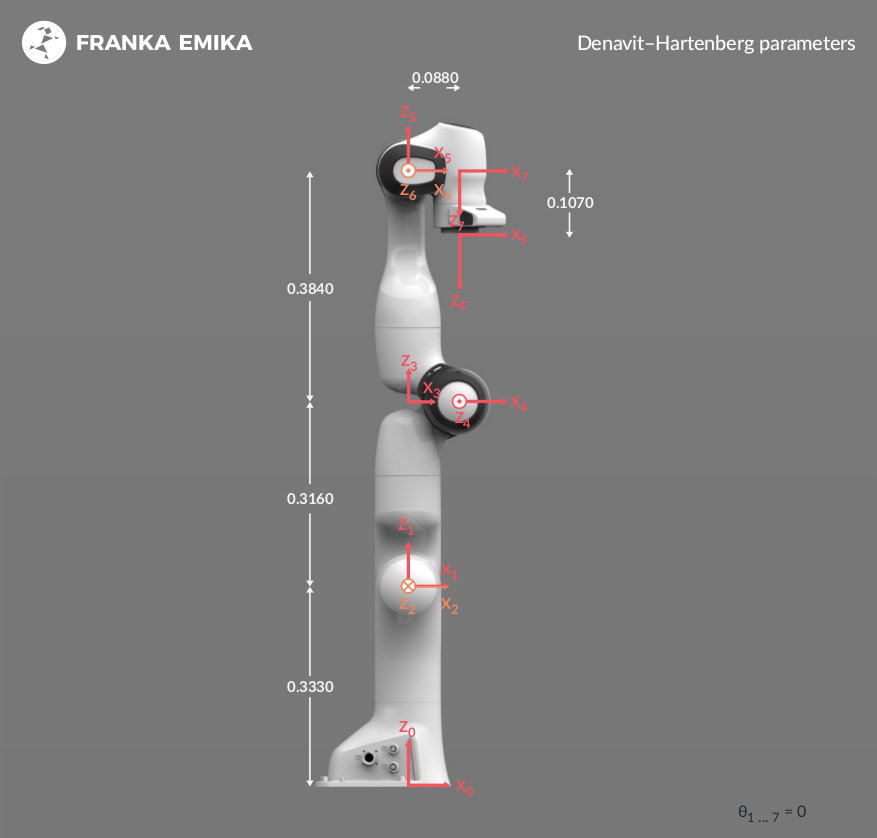
franka_description中包含Franka机器人的URDF文件,编写panda_test.launch,设置基关节为panda_link0,末端关节(法兰盘)为panda_link8。因此,正逆解计算都是以机器人法兰中心为基准。

<?xml version="1.0"?> <launch> <arg name="chain_start" default="panda_link0" /> <arg name="chain_end" default="panda_link8" /> <arg name="timeout" default="0.005" /> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py '$(find franka_description)/robots/panda_arm.urdf.xacro'" /> <node name="ik_test" pkg="ik_test" type="ik_test" output="screen"> <param name="chain_start" value="$(arg chain_start)"/> <param name="chain_end" value="$(arg chain_end)"/> <param name="timeout" value="$(arg timeout)"/> <param name="urdf_param" value="/robot_description"/> </node> </launch>
test.cpp中计算逆解前使用getKDLLimits函数得到机器人关节运动范围,并设定关节初始值在上下限的正中间。

#include "ros/ros.h" #include <trac_ik/trac_ik.hpp> #include <kdl/chainiksolverpos_nr_jl.hpp> #include <kdl/chain.hpp> #include <kdl/chainfksolver.hpp> #include <kdl/chainfksolverpos_recursive.hpp> #include <kdl/frames_io.hpp> using namespace KDL; int main(int argc, char **argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "ik_test"); ros::NodeHandle nh("~"); int num_samples; std::string chain_start, chain_end, urdf_param; double timeout; const double error = 1e-6; nh.param("chain_start", chain_start, std::string("")); nh.param("chain_end", chain_end, std::string("")); if (chain_start=="" || chain_end=="") { ROS_FATAL("Missing chain info in launch file"); exit (-1); } nh.param("timeout", timeout, 0.005); nh.param("urdf_param", urdf_param, std::string("/robot_description")); if (num_samples < 1) num_samples = 1; TRAC_IK::TRAC_IK ik_solver(chain_start, chain_end, urdf_param, timeout, error, TRAC_IK::Distance); KDL::Chain chain; bool valid = ik_solver.getKDLChain(chain); if (!valid) { ROS_ERROR("There was no valid KDL chain found"); return -1; } KDL::JntArray ll, ul; //lower joint limits, upper joint limits valid = ik_solver.getKDLLimits(ll,ul); if (!valid) ROS_INFO("There were no valid KDL joint limits found"); // Set up KDL IK KDL::ChainFkSolverPos_recursive fk_solver(chain); // Forward kin. solver based on kinematic chain // Create joint array unsigned int nj = chain.getNrOfJoints(); ROS_INFO ("Using %d joints",nj); KDL::JntArray jointpositions = JntArray(nj); // Assign some values to the joint positions for(unsigned int i=0;i<nj;i++){ float myinput; printf ("Enter the position of joint %i: ",i); scanf ("%e",&myinput); jointpositions(i)=(double)myinput; } // Create the frame that will contain the results KDL::Frame cartpos; // Calculate forward position kinematics bool kinematics_status; kinematics_status = fk_solver.JntToCart(jointpositions,cartpos); Vector p = cartpos.p; // Origin of the Frame Rotation M = cartpos.M; // Orientation of the Frame double roll, pitch, yaw; M.GetRPY(roll,pitch,yaw); if(kinematics_status>=0){ printf("%s \n","KDL FK Succes"); std::cout <<"Origin: " << p(0) << "," << p(1) << "," << p(2) << std::endl; std::cout <<"RPY: " << roll << "," << pitch << "," << yaw << std::endl; }else{ printf("%s \n","Error: could not calculate forward kinematics :("); } KDL::JntArray joint_seed(nj); //KDL::SetToZero(joint_seed); for (uint j=0; j<joint_seed.data.size(); j++) joint_seed(j) = (ll(j)+ul(j))/2.0; KDL::JntArray result(joint_seed); int rc=ik_solver.CartToJnt(joint_seed,cartpos,result); if(rc < 0) printf("%s \n","Error: could not calculate inverse kinematics :("); else{ printf("%s \n","TRAC IK Succes"); for(unsigned int i = 0; i < nj; i++) std::cout << result(i) << " "; } return 0; }
为了验证TRAC-IK计算结果,使用libfranka中的echo_robot_state先输出机器人当前状态。O_T_EE是末端执行器(这里没有安装末端执行器,因此就是以法兰中心为基准)在机器人基坐标系中的位置姿态矩阵(按列优先存储),q为关节角度。

"O_T_EE": [0.722009,-0.690627,-0.0416898,0,-0.691463,-0.72236,-0.00866381,0,-0.0241316,0.0350823,-0.999093,0,0.371908,0.00215211,0.428567,1], "O_T_EE_d": [0.722007,-0.690631,-0.041642,0,-0.691467,-0.722355,-0.00871983,0,-0.0240581,0.0350898,-0.999095,0,0.371922,0.00215033,0.428596,1], "F_T_EE": [1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1], "EE_T_K": [1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1], "elbow": [-0.0168831,-1], "elbow_d": [-0.0168889,-1], "q": [0.0180582,-0.537152,-0.0168831,-2.60095,0.0297504,2.03967,0.753258], "dq": [-0.00051007,-0.000212418,0.00125443,0.000394549,-2.9871e-05,0.000278746,0.000261954], ...
开启测试程序,输入上面的关节值,输出如下:

KDL正解计算的值与O_T_EE一致。根据Franka机器人的DH参数表,可以写出从法兰到基座的变换矩阵:

将正解输入与逆解输出的关节值分别代入变换矩阵中,可以发现理论计算与O_T_EE和KDL正解结果一致。

由于7自由度机械臂有无数组逆解,因此一般要根据某种优化原则,选取其中一组。对于Franka机械臂,可使用TRAC-IK得到逆解后进行关节空间中的轨迹规划,实现类似于“movej”的功能。
参考:
API reference of the Kinematics and Dynamics Library




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号