工作中最常用的5种本地缓存
前言
今天和大家聊聊一个几乎所有Java开发者都会用到,但很多人对其理解不够深入的技术——本地缓存。
有些小伙伴在工作中可能遇到过这样的场景:系统性能测试时,发现某个接口响应时间越来越长,一查发现是数据库查询太频繁。
加了Redis分布式缓存后有所改善,但网络IO的开销依然存在,特别是对时效性要求高的数据。
这时候,本地缓存的价值就凸显出来了。
本地缓存是什么?
简单说就是将数据存储在应用进程的内存中,实现数据的快速访问。
它的访问速度通常是纳秒级,而分布式缓存(如Redis)是毫秒级,数据库查询更是毫秒到秒级。
01 为什么需要本地缓存?
在深入具体方案前,我们先搞清楚本地缓存的核心价值。
来看一个没有缓存的场景:
// 没有缓存的用户查询服务
@Service
public class CategoryServiceWithoutCache {
@Autowired
private CategoryMapper categoryMapper;
public Category getCategoryById(Long categoryId) {
// 每次调用都直接查询数据库
return categoryMapper.selectById(categoryId);
}
// 假设这个接口每秒被调用1000次
// 数据库就要承受1000QPS的压力
}
这种设计的问题很明显:
- 数据库压力大:每次请求都要查询数据库
- 响应时间长:数据库查询通常需要几毫秒到几十毫秒
- 系统可扩展性差:数据库成为单点瓶颈
引入本地缓存后,情况会大大改善:
// 使用本地缓存的用户查询服务
@Service
public class CategoryServiceWithCache {
@Autowired
private CategoryMapper categoryMapper;
// 使用ConcurrentHashMap作为本地缓存
private final Map<Long, Category> categoryCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public Category getCategoryById(Long categoryId) {
// 1. 先查缓存
Category category = categoryCache.get(categoryId);
if (category != null) {
return category; // 缓存命中,直接返回
}
// 2. 缓存未命中,查询数据库
category = categoryMapper.selectById(categoryId);
if (category != null) {
// 3. 将数据放入缓存
categoryCache.put(categoryId, category);
}
return category;
}
}
这样改造后,对于同一个分类的多次查询,只有第一次会访问数据库,后续查询都直接返回缓存数据,性能提升几个数量级。
但是,简单的ConcurrentHashMap只是本地缓存的最基础形态。
在实际生产中,我们需要考虑更多问题:内存管理、过期策略、缓存淘汰、并发控制等。
这就是各种本地缓存框架存在的意义。
02 本地缓存核心要素
在介绍具体方案前,我们先了解一个优秀本地缓存应该具备的特性:
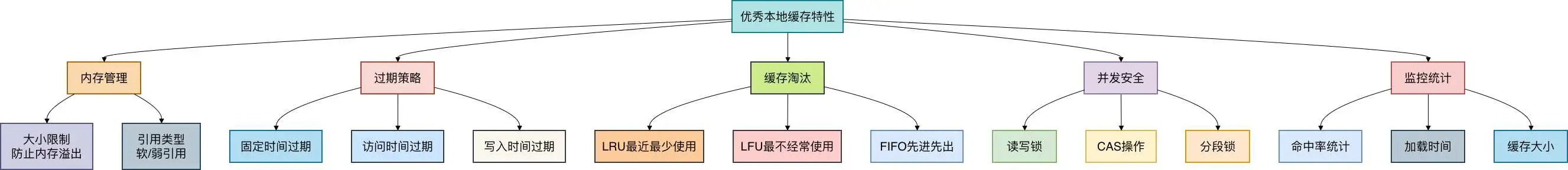
理解了这些核心要素,我们就能更好地评估各种缓存方案。
现在,让我们深入分析5种最常用的本地缓存方案。
03 方案一:ConcurrentHashMap
原理与特点
ConcurrentHashMap是JDK自发的线程安全的哈希表,它通过分段锁技术实现高并发访问。
作为缓存使用时,它是最简单、最轻量级的选择。
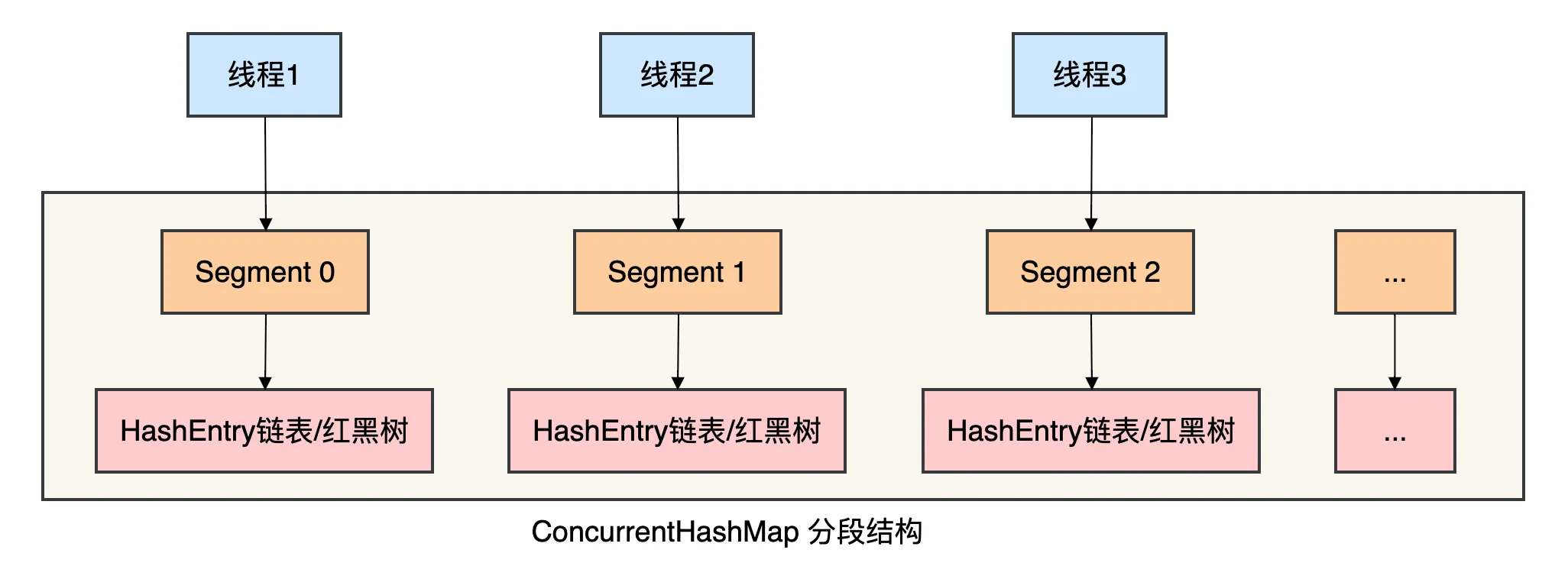
核心机制:
- 分段锁:将整个Map分成多个Segment,每个Segment独立加锁
- 并发度:默认16个Segment,可支持16个线程并发写
- Java 8优化:在Java 8中改为使用
synchronized+CAS+红黑树,性能更好
实战代码示例
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 基于ConcurrentHashMap的简易本地缓存
* 特点:简单、轻量、无过期策略
*/
public class ConcurrentHashMapCache<K, V> {
// 核心缓存存储
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> cache;
// 可选的缓存加载器
private final CacheLoader<K, V> loader;
public ConcurrentHashMapCache() {
this.cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
this.loader = null;
}
public ConcurrentHashMapCache(CacheLoader<K, V> loader) {
this.cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
this.loader = loader;
}
/**
* 获取缓存值
* 如果不存在且配置了loader,则加载数据
*/
public V get(K key) {
V value = cache.get(key);
if (value == null && loader != null) {
// 双重检查锁,防止并发加载
synchronized (this) {
value = cache.get(key);
if (value == null) {
value = loader.load(key);
if (value != null) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
}
}
}
return value;
}
/**
* 放入缓存
*/
public void put(K key, V value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
/**
* 移除缓存
*/
public V remove(K key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
/**
* 清空缓存
*/
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
/**
* 获取缓存大小
*/
public int size() {
return cache.size();
}
/**
* 判断是否包含key
*/
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
return cache.containsKey(key);
}
/**
* 缓存加载器接口
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CacheLoader<K, V> {
V load(K key);
}
}
/**
* 使用示例:用户信息缓存
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceWithConcurrentHashMap {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
// 使用自定义的ConcurrentHashMap缓存
private final ConcurrentHashMapCache<Long, User> userCache;
public UserServiceWithConcurrentHashMap() {
// 初始化缓存,配置缓存加载器
userCache = new ConcurrentHashMapCache<>(userId -> {
// 当缓存不存在时,调用此方法加载数据
System.out.println("缓存未命中,从数据库加载用户: " + userId);
return userMapper.selectById(userId);
});
}
/**
* 获取用户信息(带缓存)
*/
public User getUserById(Long userId) {
return userCache.get(userId);
}
/**
* 更新用户信息(同时更新缓存)
*/
public void updateUser(User user) {
// 1. 更新数据库
userMapper.updateById(user);
// 2. 更新缓存
userCache.put(user.getId(), user);
}
/**
* 删除用户(同时删除缓存)
*/
public void deleteUser(Long userId) {
// 1. 删除数据库记录
userMapper.deleteById(userId);
// 2. 删除缓存
userCache.remove(userId);
}
/**
* 批量获取用户(优化N+1查询)
*/
public Map<Long, User> getUsersByIds(List<Long> userIds) {
Map<Long, User> result = new HashMap<>();
List<Long> missingIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 先从缓存获取
for (Long userId : userIds) {
User user = userCache.get(userId);
if (user != null) {
result.put(userId, user);
} else {
missingIds.add(userId);
}
}
// 2. 批量查询缺失的数据
if (!missingIds.isEmpty()) {
List<User> dbUsers = userMapper.selectBatchIds(missingIds);
for (User user : dbUsers) {
result.put(user.getId(), user);
userCache.put(user.getId(), user); // 放入缓存
}
}
return result;
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- JDK原生支持:无需引入第三方依赖
- 线程安全:分段锁/CAS保证并发安全
- 性能优秀:读操作完全无锁,写操作锁粒度小
- 简单轻量:代码简单,资源消耗小
缺点:
- 功能有限:缺乏过期、淘汰等高级功能
- 内存无法限制:可能造成内存溢出
- 需要手动管理:缓存策略需要自己实现
适用场景:
- 缓存数据量小且固定
- 不需要自动过期功能
- 作为更复杂缓存的底层实现
- 临时性、简单的缓存需求
有些小伙伴在项目初期喜欢用ConcurrentHashMap做缓存,因为它简单直接。
但随着业务复杂化,往往会遇到内存溢出、缓存清理等问题,这时候就需要更专业的缓存方案了。
04 方案二:LRU缓存
原理与特点
LRU(Least Recently Used,最近最少使用)是一种经典的缓存淘汰算法。
当缓存空间不足时,优先淘汰最久未被访问的数据。
LinkedHashMap是JDK提供的实现了LRU特性的Map实现。
它通过维护一个双向链表来记录访问顺序。
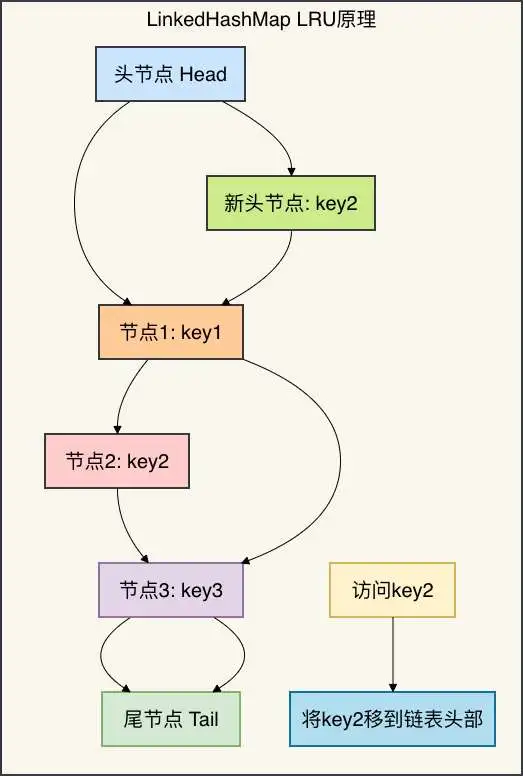
核心机制:
- 访问顺序:
accessOrder=true时,每次访问会将节点移到链表头部 - 淘汰策略:链表尾部的节点是最久未访问的
- 重写removeEldestEntry:控制何时删除最老节点
实战代码示例
import java.util.*;
/**
* 基于LinkedHashMap的LRU缓存
* 特点:自动淘汰最久未使用的数据
*/
public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private final int maxCapacity;
/**
* 创建LRU缓存
* @param maxCapacity 最大容量
*/
public LRUCache(int maxCapacity) {
// 第三个参数accessOrder为true表示按访问顺序排序
super(16, 0.75f, true);
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
/**
* 重写此方法决定何时删除最老的条目
* @param eldest 最老的条目(最近最少使用)
* @return true表示应该删除最老的条目
*/
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
// 当大小超过最大容量时,删除最老的条目
return size() > maxCapacity;
}
/**
* 获取缓存值(会更新访问顺序)
*/
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
synchronized (this) {
return super.get(key);
}
}
/**
* 放入缓存值
*/
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
synchronized (this) {
return super.put(key, value);
}
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public CacheStats getStats() {
return new CacheStats(size(), maxCapacity);
}
/**
* 获取最近访问的N个键
*/
public List<K> getRecentlyAccessed(int n) {
List<K> result = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator<K> iterator = keySet().iterator();
for (int i = 0; i < n && iterator.hasNext(); i++) {
result.add(iterator.next());
}
return result;
}
/**
* 缓存统计信息
*/
public static class CacheStats {
private final int currentSize;
private final int maxCapacity;
private final double usageRatio;
public CacheStats(int currentSize, int maxCapacity) {
this.currentSize = currentSize;
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
this.usageRatio = maxCapacity > 0 ? (double) currentSize / maxCapacity : 0;
}
// getters...
}
}
/**
* 线程安全的LRU缓存实现
*/
public class ConcurrentLRUCache<K, V> {
private final LRUCache<K, V> cache;
public ConcurrentLRUCache(int maxCapacity) {
this.cache = new LRUCache<>(maxCapacity);
}
/**
* 获取缓存值
*/
public V get(K key) {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.get(key);
}
}
/**
* 放入缓存值
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.put(key, value);
}
}
/**
* 批量放入缓存
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
synchronized (cache) {
cache.putAll(map);
}
}
/**
* 移除缓存
*/
public V remove(K key) {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
}
/**
* 清空缓存
*/
public void clear() {
synchronized (cache) {
cache.clear();
}
}
/**
* 获取缓存大小
*/
public int size() {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.size();
}
}
/**
* 检查缓存是否包含key
*/
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.containsKey(key);
}
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public LRUCache.CacheStats getStats() {
synchronized (cache) {
return cache.getStats();
}
}
}
/**
* 使用示例:商品信息缓存
*/
@Service
public class ProductServiceWithLRUCache {
@Autowired
private ProductMapper productMapper;
// LRU缓存,最多缓存1000个商品
private final ConcurrentLRUCache<Long, Product> productCache;
// 热门商品缓存(更小的LRU缓存)
private final ConcurrentLRUCache<Long, Product> hotProductCache;
public ProductServiceWithLRUCache() {
// 主缓存:1000个商品
productCache = new ConcurrentLRUCache<>(1000);
// 热门商品缓存:100个商品
hotProductCache = new ConcurrentLRUCache<>(100);
}
/**
* 获取商品信息
*/
public Product getProductById(Long productId) {
// 1. 先查热门商品缓存
Product product = hotProductCache.get(productId);
if (product != null) {
recordCacheHit("hot"); // 记录命中
return product;
}
// 2. 查主缓存
product = productCache.get(productId);
if (product != null) {
// 如果商品被频繁访问,移到热门缓存
if (isFrequentlyAccessed(productId)) {
hotProductCache.put(productId, product);
}
recordCacheHit("main");
return product;
}
// 3. 缓存未命中,查询数据库
product = productMapper.selectById(productId);
if (product != null) {
// 放入主缓存
productCache.put(productId, product);
recordCacheMiss();
}
return product;
}
/**
* 获取热门商品列表
*/
public List<Product> getHotProducts(int limit) {
// 直接从热门缓存获取最近访问的商品
// 注意:这只是简化示例,实际需要更复杂的热门度计算
List<Product> hotProducts = new ArrayList<>();
synchronized (hotProductCache) {
// 这里需要扩展ConcurrentLRUCache以支持获取所有值
// 实际实现中需要维护额外的数据结构
}
return hotProducts;
}
/**
* 更新商品信息(同时更新两个缓存)
*/
public void updateProduct(Product product) {
Long productId = product.getId();
// 1. 更新数据库
productMapper.updateById(product);
// 2. 更新缓存
productCache.put(productId, product);
hotProductCache.put(productId, product);
// 3. 记录更新日志
logProductUpdate(productId);
}
/**
* 批量失效缓存(当商品分类更新时)
*/
public void invalidateProductsByCategory(Long categoryId) {
// 在实际应用中,这里需要遍历缓存并删除对应分类的商品
// 为了性能,可以:
// 1. 使用分代缓存
// 2. 使用异步清理
// 3. 使用更细粒度的缓存键
System.out.println("商品分类更新,需要清理相关缓存: " + categoryId);
// 这里简化处理:清空所有缓存(生产环境不推荐)
// productCache.clear();
// hotProductCache.clear();
}
private boolean isFrequentlyAccessed(Long productId) {
// 简化实现:总是返回true
// 实际需要基于访问频率的热度算法
return true;
}
private void recordCacheHit(String cacheType) {
// 记录缓存命中,用于监控和调优
System.out.println("缓存命中 [" + cacheType + "]: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
private void recordCacheMiss() {
// 记录缓存未命中
System.out.println("缓存未命中: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
private void logProductUpdate(Long productId) {
// 记录商品更新
System.out.println("商品更新: " + productId + " at " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 自动淘汰:无需手动清理,防止内存溢出
- 访问模式优化:自动将热门数据保持在缓存中
- JDK原生:基于LinkedHashMap,无需额外依赖
- 简单有效:对于访问模式有明显热点的场景效果显著
缺点:
- 淘汰策略单一:只基于访问时间,不考虑访问频率
- 可能淘汰热点数据:如果缓存太小,可能误淘汰
- 并发性能:需要额外同步来保证线程安全
- 功能有限:缺乏过期时间等高级功能
适用场景:
- 数据访问有明显热点
- 缓存容量有限,需要自动淘汰
- 数据重要性相对均匀
- 作为缓存系统的一部分
有些小伙伴会发现,LRU缓存能解决内存溢出的问题,但对于“突然被大量访问的冷数据”场景,可能会淘汰掉真正的热点数据。
这时候就需要更智能的淘汰策略了。
05 方案三:Ehcache - 企业级本地缓存
原理与特点
Ehcache是一个成熟的、功能丰富的Java缓存框架,最初作为Hibernate的缓存提供者而闻名。
它支持内存+磁盘的多级缓存,适合缓存大量数据。
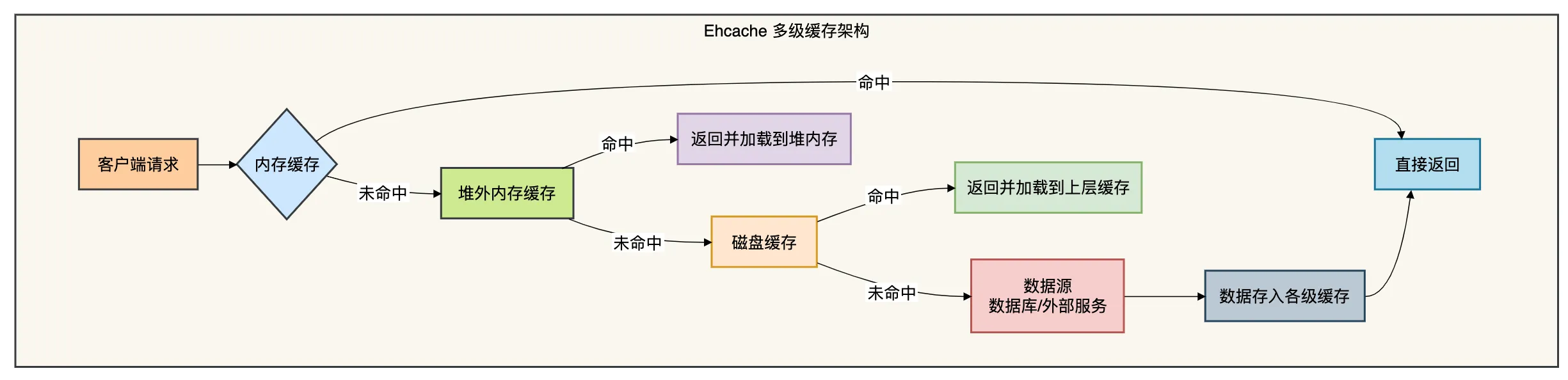
核心特性:
- 多级存储:堆内存 → 堆外内存 → 磁盘
- 丰富的淘汰策略:LRU、LFU、FIFO
- 集群支持:通过Terracotta实现分布式缓存
- 监控管理:JMX支持,完善的监控指标
实战代码示例
由于Ehcache功能丰富,配置相对复杂,这里展示其核心用法:
import net.sf.ehcache.Cache;
import net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager;
import net.sf.ehcache.Element;
import net.sf.ehcache.config.CacheConfiguration;
import net.sf.ehcache.config.PersistenceConfiguration;
import net.sf.ehcache.store.MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Ehcache缓存工具类
*/
public class EhcacheUtil {
private static CacheManager cacheManager;
static {
// 1. 创建CacheManager(通常从配置文件加载)
cacheManager = CacheManager.create();
// 2. 或者以编程方式配置
createUserCache();
createProductCache();
}
/**
* 创建用户缓存
*/
private static void createUserCache() {
// 缓存配置
CacheConfiguration cacheConfig = new CacheConfiguration()
.name("userCache") // 缓存名称
.maxEntriesLocalHeap(1000) // 堆内存最大条目数
.memoryStoreEvictionPolicy(MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy.LRU) // 淘汰策略
.timeToLiveSeconds(3600) // 存活时间(秒)
.timeToIdleSeconds(600) // 空闲时间(秒)
.diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds(120) // 磁盘过期检查间隔
.persistence(new PersistenceConfiguration()
.strategy(PersistenceConfiguration.Strategy.LOCALTEMPSWAP)); // 持久化策略
// 创建缓存
Cache cache = new Cache(cacheConfig);
// 添加到CacheManager
cacheManager.addCache(cache);
}
/**
* 创建商品缓存(使用堆外内存)
*/
private static void createProductCache() {
CacheConfiguration cacheConfig = new CacheConfiguration()
.name("productCache")
.maxEntriesLocalHeap(5000) // 堆内存条目数
.maxBytesLocalOffHeap(256, MemoryUnit.MEGABYTES) // 堆外内存256MB
.maxBytesLocalDisk(2, MemoryUnit.GIGABYTES) // 磁盘缓存2GB
.memoryStoreEvictionPolicy(MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy.LFU) // LFU淘汰策略
.timeToLiveSeconds(1800)
.timeToIdleSeconds(300)
.persistence(new PersistenceConfiguration()
.strategy(PersistenceConfiguration.Strategy.LOCALTEMPSWAP));
Cache cache = new Cache(cacheConfig);
cacheManager.addCache(cache);
}
/**
* 获取缓存实例
*/
public static Cache getCache(String cacheName) {
return cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
}
/**
* 放入缓存
*/
public static void put(String cacheName, Serializable key, Serializable value) {
Cache cache = getCache(cacheName);
if (cache != null) {
Element element = new Element(key, value);
cache.put(element);
}
}
/**
* 获取缓存值
*/
public static Object get(String cacheName, Serializable key) {
Cache cache = getCache(cacheName);
if (cache != null) {
Element element = cache.get(key);
return element != null ? element.getObjectValue() : null;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 移除缓存
*/
public static boolean remove(String cacheName, Serializable key) {
Cache cache = getCache(cacheName);
if (cache != null) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public static String getStats(String cacheName) {
Cache cache = getCache(cacheName);
if (cache != null) {
return String.format(
"缓存: %s, 大小: %d, 命中数: %d, 未命中数: %d, 命中率: %.2f%%",
cacheName,
cache.getSize(),
cache.getStatistics().cacheHitCount(),
cache.getStatistics().cacheMissCount(),
cache.getStatistics().cacheHitRatio() * 100
);
}
return "缓存不存在: " + cacheName;
}
}
/**
* 使用示例:订单服务
*/
@Service
public class OrderServiceWithEhcache {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
/**
* 获取订单详情(使用Ehcache)
*/
public OrderDetail getOrderDetail(Long orderId) {
String cacheName = "orderCache";
// 1. 先从缓存获取
OrderDetail detail = (OrderDetail) EhcacheUtil.get(cacheName, orderId);
if (detail != null) {
System.out.println("Ehcache缓存命中: " + orderId);
return detail;
}
// 2. 缓存未命中,查询数据库
System.out.println("Ehcache缓存未命中,查询数据库: " + orderId);
detail = orderMapper.selectOrderDetail(orderId);
if (detail != null) {
// 3. 放入缓存
EhcacheUtil.put(cacheName, orderId, detail);
// 4. 异步加载相关数据到缓存
loadRelatedDataToCache(detail);
}
return detail;
}
/**
* 批量获取订单(缓存优化)
*/
public List<OrderDetail> getOrderDetails(List<Long> orderIds) {
List<OrderDetail> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Long> missingIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 批量从缓存获取
for (Long orderId : orderIds) {
OrderDetail detail = (OrderDetail) EhcacheUtil.get("orderCache", orderId);
if (detail != null) {
result.add(detail);
} else {
missingIds.add(orderId);
}
}
// 2. 批量查询缺失的数据
if (!missingIds.isEmpty()) {
List<OrderDetail> dbDetails = orderMapper.selectOrderDetails(missingIds);
result.addAll(dbDetails);
// 3. 批量放入缓存
for (OrderDetail detail : dbDetails) {
EhcacheUtil.put("orderCache", detail.getOrderId(), detail);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 更新订单状态(同时更新缓存)
*/
@Transactional
public void updateOrderStatus(Long orderId, String status) {
// 1. 更新数据库
orderMapper.updateOrderStatus(orderId, status);
// 2. 使缓存失效(或更新缓存)
EhcacheUtil.remove("orderCache", orderId);
// 3. 可以选择重新加载到缓存
OrderDetail detail = orderMapper.selectOrderDetail(orderId);
if (detail != null) {
EhcacheUtil.put("orderCache", orderId, detail);
}
}
/**
* 异步加载相关数据到缓存
*/
private void loadRelatedDataToCache(OrderDetail orderDetail) {
// 这里可以异步加载用户信息、商品信息等
// 减少后续查询的缓存未命中
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
// 缓存用户信息
EhcacheUtil.put("userCache", orderDetail.getUserId(), orderDetail.getUserInfo());
// 缓存商品信息
for (OrderItem item : orderDetail.getItems()) {
EhcacheUtil.put("productCache", item.getProductId(), item.getProductInfo());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 异步操作,记录日志但不影响主流程
System.err.println("异步加载缓存失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public void printCacheStats() {
System.out.println("=== 缓存统计 ===");
System.out.println(EhcacheUtil.getStats("orderCache"));
System.out.println(EhcacheUtil.getStats("userCache"));
System.out.println(EhcacheUtil.getStats("productCache"));
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 功能全面:支持多级缓存、多种淘汰策略
- 企业级特性:集群支持、持久化、事务支持
- 成熟稳定:经过多年生产验证
- 监控完善:JMX支持,便于监控管理
缺点:
- 配置复杂:功能多导致配置复杂
- 较重:依赖较多,启动较慢
- API较老:部分API设计不够现代
- 社区活跃度下降:相比Caffeine等新框架
适用场景:
- 需要缓存大量数据(内存+磁盘)
- 需要集群缓存支持
- 企业级应用,需要完整解决方案
- 已有Ehcache使用经验的项目
有些小伙伴在企业级项目中接触过Ehcache,它的功能确实强大,但对于简单的缓存需求来说可能过于重量级了。
06 方案四:Caffeine - 高性能现代缓存
原理与特点
Caffeine是一个基于Java 8的高性能缓存库,由Guava Cache的原作者开发。它提供了近乎最优的命中率和卓越的并发性能。
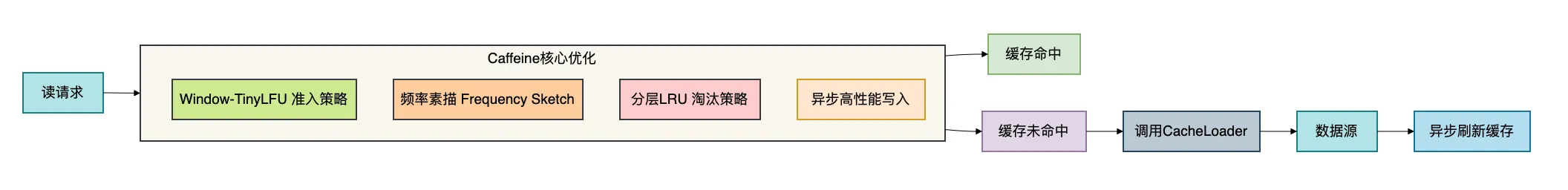
核心优化:
- Window-TinyLFU:结合LFU和LRU优点,提供更好的命中率
- 频率素描:用极小空间统计访问频率
- 异步操作:读不阻塞写,写不阻塞读
- Java 8优化:大量使用
CompletableFuture和StampedLock
实战代码示例
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Caffeine缓存示例
*/
@Service
public class CaffeineCacheService {
// 1. 基础缓存示例
private final Cache<Long, User> userCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000) // 最大容量
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(10)) // 写入后10分钟过期
.expireAfterAccess(Duration.ofMinutes(5)) // 访问后5分钟过期
.recordStats() // 开启统计
.build();
// 2. 异步加载缓存
private final AsyncLoadingCache<Long, Product> productCache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(5000)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofHours(1))
.refreshAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 写入30分钟后刷新
.recordStats()
.buildAsync(new AsyncCacheLoader<Long, Product>() {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Product> asyncLoad(Long productId,
Executor executor) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
loadProductFromDB(productId), executor);
}
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Product> asyncReload(Long productId,
Product oldValue, Executor executor) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
reloadProductFromDB(productId), executor);
}
});
// 3. 带权重缓存的例子(按对象大小缓存)
private final Cache<String, byte[]> largeDataCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(100 * 1024 * 1024) // 最大100MB
.weigher((String key, byte[] value) -> value.length) // 权重计算器
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofHours(2))
.recordStats()
.build();
/**
* 使用缓存获取用户信息
*/
public User getUserWithCache(Long userId) {
// 方式1:手动处理
User user = userCache.getIfPresent(userId);
if (user == null) {
user = loadUserFromDB(userId);
if (user != null) {
userCache.put(userId, user);
}
}
return user;
}
/**
* 使用LoadingCache自动加载
*/
public User getUserAutoLoad(Long userId) {
LoadingCache<Long, User> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
.build(this::loadUserFromDB); // 缓存未命中时调用
return loadingCache.get(userId);
}
/**
* 使用异步缓存获取商品信息
*/
public CompletableFuture<Product> getProductAsync(Long productId) {
return productCache.get(productId);
}
/**
* 批量获取商品
*/
public CompletableFuture<Iterable<Product>> getProductsAsync(
Iterable<Long> productIds) {
return productCache.getAll(productIds);
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public String getCacheStats() {
CacheStats stats = userCache.stats();
return String.format(
"命中率: %.2f%%, 命中数: %d, 未命中数: %d, 加载成功: %d, 加载失败: %d, 总加载时间: %dms",
stats.hitRate() * 100,
stats.hitCount(),
stats.missCount(),
stats.loadSuccessCount(),
stats.loadFailureCount(),
stats.totalLoadTime()
);
}
/**
* 高级用法:事件监听
*/
public void setupCacheWithListener() {
Cache<Long, Order> orderCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
.removalListener((Long key, Order order, RemovalCause cause) -> {
// 缓存条目被移除时的回调
System.out.printf("缓存移除: key=%s, cause=%s%n", key, cause);
// 可以根据不同的原因处理
switch (cause) {
case EXPLICIT: // 显式移除
System.out.println("显式移除缓存: " + key);
break;
case REPLACED: // 被替换
System.out.println("缓存被替换: " + key);
break;
case COLLECTED: // 垃圾回收
System.out.println("缓存被GC回收: " + key);
break;
case EXPIRED: // 过期
System.out.println("缓存过期: " + key);
break;
case SIZE: // 大小限制
System.out.println("因大小限制移除: " + key);
break;
}
})
.recordStats()
.build();
// 使用缓存
orderCache.put(1L, new Order(1L, "待支付"));
// 移除缓存(会触发EXPLICIT事件)
orderCache.invalidate(1L);
}
/**
* 复杂场景:分层缓存策略
*/
public void layeredCacheStrategy() {
// 第一层:小容量,超快访问(使用ConcurrentHashMap)
Cache<Long, User> L1Cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.build();
// 第二层:大容量,较慢访问(使用Caffeine)
Cache<Long, User> L2Cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10000)
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
.build();
// 第三层:异步加载,防止缓存穿透
AsyncLoadingCache<Long, User> L3Cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(50000)
.expireAfterWrite(Diration.ofHours(1))
.buildAsync(key -> loadUserFromDB(key));
// 使用分层缓存的示例
public User getUserMultiLevel(Long userId) {
// 1. 查L1缓存
User user = L1Cache.getIfPresent(userId);
if (user != null) {
recordHit("L1");
return user;
}
// 2. 查L2缓存
user = L2Cache.getIfPresent(userId);
if (user != null) {
// 回填L1缓存
L1Cache.put(userId, user);
recordHit("L2");
return user;
}
// 3. 查L3缓存(异步加载)
try {
user = L3Cache.get(userId).get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 回填L1和L2
L1Cache.put(userId, user);
L2Cache.put(userId, user);
recordHit("L3");
return user;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 缓存加载失败
recordMiss();
return loadUserFromDB(userId); // 降级到直接查DB
}
}
}
private User loadUserFromDB(Long userId) {
System.out.println("从数据库加载用户: " + userId);
// 模拟数据库查询
return new User(userId, "用户" + userId);
}
private Product loadProductFromDB(Long productId) {
System.out.println("从数据库加载商品: " + productId);
return new Product(productId, "商品" + productId);
}
private Product reloadProductFromDB(Long productId) {
System.out.println("刷新商品缓存: " + productId);
return new Product(productId, "刷新后的商品" + productId);
}
private void recordHit(String cacheLevel) {
// 记录命中统计
System.out.println("缓存命中 [" + cacheLevel + "]");
}
private void recordMiss() {
// 记录未命中
System.out.println("缓存未命中");
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 性能卓越:读性能接近
ConcurrentHashMap - 高命中率:Window-TinyLFU算法显著提升命中率
- 现代API:基于Java 8,支持异步、函数式编程
- 内存友好:智能的权重控制和淘汰策略
缺点:
- 较新:生态不如Guava Cache成熟
- 学习曲线:高级功能需要理解其算法原理
- 功能专注:主要关注内存缓存,不像Ehcache支持磁盘
适用场景:
- 对性能要求极高的场景
- 需要高命中率的缓存策略
- 现代Java项目(Java 8+)
- 作为Guava Cache的升级替代
有些小伙伴从Guava Cache迁移到Caffeine后,会发现命中率有明显提升,特别是在数据访问模式复杂多变的场景下。
07 方案五:Guava Cache - 经典的选择
原理与特点
Guava Cache是Google Guava库的一部分,是一个设计优雅、功能完善的本地缓存实现。
它提供了丰富的构建选项和灵活的过期策略。
实战代码示例
import com.google.common.cache.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Guava Cache使用示例
*/
@Service
public class GuavaCacheService {
// 1. 基础缓存示例
private final Cache<Long, User> userCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000) // 最大容量
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写入后10分钟过期
.expireAfterAccess(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 访问后5分钟过期
.concurrencyLevel(8) // 并发级别
.recordStats() // 开启统计
.build();
// 2. 带权重缓存的例子
private final Cache<String, byte[]> weightedCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(100 * 1024 * 1024) // 最大100MB
.weigher(new Weigher<String, byte[]>() {
@Override
public int weigh(String key, byte[] value) {
return value.length; // 按字节数组长度计算权重
}
})
.expireAfterWrite(2, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.build();
// 3. 使用CacheLoader自动加载
private final LoadingCache<Long, Product> productCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(5000)
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.refreshAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写入30分钟后刷新
.build(new CacheLoader<Long, Product>() {
@Override
public Product load(Long productId) {
// 缓存未命中时调用
return loadProductFromDB(productId);
}
@Override
public Product reload(Long productId, Product oldValue) {
// 刷新时调用(默认实现调用load)
return reloadProductFromDB(productId);
}
});
/**
* 基本用法:手动put/get
*/
public User getUserManual(Long userId) {
// 尝试获取缓存
User user = userCache.getIfPresent(userId);
if (user == null) {
// 缓存未命中,加载数据
user = loadUserFromDB(userId);
if (user != null) {
userCache.put(userId, user);
}
}
return user;
}
/**
* 使用CacheLoader自动加载
*/
public Product getProductAutoLoad(Long productId) {
try {
// 如果缓存不存在,会自动调用CacheLoader.load()
return productCache.get(productId);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// 处理加载异常
System.err.println("加载产品失败: " + productId);
return null;
}
}
/**
* 批量获取
*/
public Iterable<Product> getProductsAutoLoad(Iterable<Long> productIds) {
try {
// 批量获取,自动加载缺失的数据
return productCache.getAll(productIds).values();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("批量加载产品失败");
return null;
}
}
/**
* 缓存刷新示例
*/
public void refreshProduct(Long productId) {
// 单个刷新
productCache.refresh(productId);
// 或者批量刷新
// for (Long id : productIds) {
// productCache.refresh(id);
// }
}
/**
* 事件监听器
*/
public void setupCacheWithListener() {
RemovalListener<Long, User> removalListener = new RemovalListener<Long, User>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Long, User> notification) {
RemovalCause cause = notification.getCause();
Long userId = notification.getKey();
User user = notification.getValue();
System.out.printf("缓存移除: userId=%s, cause=%s%n", userId, cause);
// 根据不同的移除原因处理
switch (cause) {
case EXPLICIT: // 显式移除
System.out.println("主动移除用户缓存: " + userId);
break;
case REPLACED: // 被替换
System.out.println("用户缓存被替换: " + userId);
break;
case COLLECTED: // 垃圾回收
System.out.println("用户缓存被GC: " + userId);
break;
case EXPIRED: // 过期
System.out.println("用户缓存过期: " + userId);
// 可以在这里执行一些清理操作
cleanupUserResources(user);
break;
case SIZE: // 大小限制
System.out.println("因容量限制移除用户: " + userId);
break;
}
}
private void cleanupUserResources(User user) {
// 清理用户相关资源
if (user != null) {
System.out.println("清理用户资源: " + user.getId());
}
}
};
// 创建带监听器的缓存
Cache<Long, User> cacheWithListener = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.removalListener(removalListener)
.build();
// 使用缓存
cacheWithListener.put(1L, new User(1L, "测试用户"));
cacheWithListener.invalidate(1L); // 触发EXPLICIT移除
}
/**
* 统计信息
*/
public void printCacheStats() {
CacheStats stats = userCache.stats();
System.out.println("=== Guava Cache 统计 ===");
System.out.println("命中率: " + stats.hitRate());
System.out.println("命中数: " + stats.hitCount());
System.out.println("未命中数: " + stats.missCount());
System.out.println("加载成功数: " + stats.loadSuccessCount());
System.out.println("加载异常数: " + stats.loadExceptionCount());
System.out.println("总加载时间: " + stats.totalLoadTime() + "ns");
System.out.println("驱逐数: " + stats.evictionCount());
}
/**
* 复杂场景:多级缓存策略
*/
public void multiLevelCacheExample() {
// 第一级:高频小缓存
LoadingCache<Long, String> L1Cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.expireAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build(new CacheLoader<Long, String>() {
@Override
public String load(Long key) {
// L1未命中,查L2
return L2Cache.get(key);
}
});
// 第二级:低频大缓存
LoadingCache<Long, String> L2Cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(new CacheLoader<Long, String>() {
@Override
public String load(Long key) {
// L2未命中,查数据源
return loadFromDataSource(key);
}
});
// 使用多级缓存
public String getValueMultiLevel(Long key) {
try {
return L1Cache.get(key);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("多级缓存获取失败: " + key);
return loadFromDataSource(key);
}
}
}
// 辅助方法
private User loadUserFromDB(Long userId) {
System.out.println("从数据库加载用户: " + userId);
return new User(userId, "用户" + userId);
}
private Product loadProductFromDB(Long productId) {
System.out.println("从数据库加载商品: " + productId);
return new Product(productId, "商品" + productId);
}
private Product reloadProductFromDB(Long productId) {
System.out.println("刷新商品数据: " + productId);
return new Product(productId, "刷新后的商品" + productId);
}
private String loadFromDataSource(Long key) {
System.out.println("从数据源加载: " + key);
return "数据" + key;
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 设计优雅:API设计一致且易于使用
- 功能完善:支持权重、刷新、监听器等高级功能
- Google维护:质量有保障,文档完善
- 生态丰富:Guava库的其他功能可以协同工作
缺点:
- 性能不如Caffeine:在并发极高场景下性能稍差
- 停止演进:新功能开发基本停止
- 内存占用:统计信息等开销较大
- Java 8特性利用不足:基于较老的Java版本设计
适用场景:
- 已经使用Guava库的项目
- 对API设计优雅性要求高的场景
- 不需要极致性能的一般缓存需求
- 作为Caffeine的过渡方案
有些小伙伴的项目因为历史原因一直在用Guava Cache,它的稳定性和功能性确实能满足大多数需求。但如果是新项目,Caffeine可能是更好的选择。
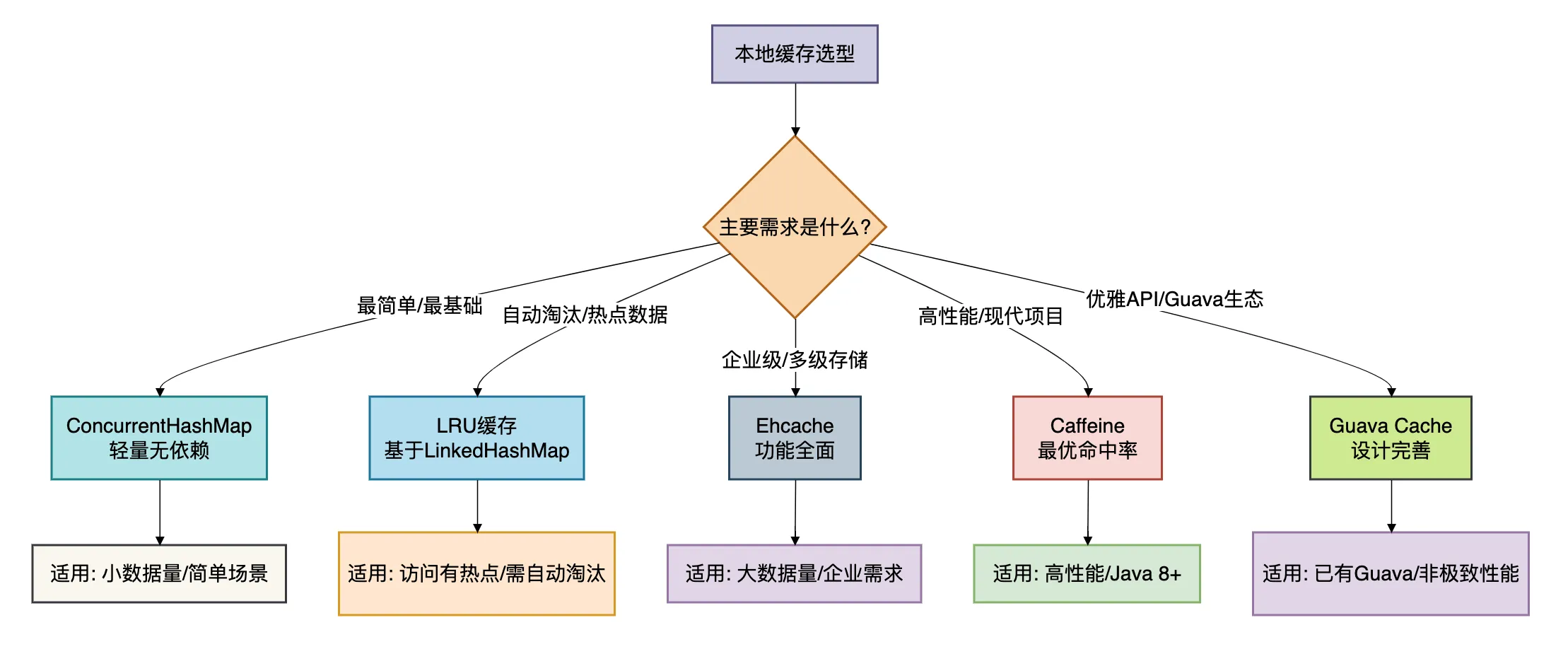
08 综合对比与选型指南
现在我们已经深入了解了5种本地缓存方案,如何在实际项目中选择呢?下面的对比图和选型指南可以帮助你做出决策。
方案对比总览
详细对比表
| 维度 | ConcurrentHashMap | LRU缓存 | Ehcache | Caffeine | Guava Cache |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易用性 | 极简 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 简单 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 复杂 ⭐⭐☆☆☆ | 中等 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 良好 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ |
| 功能完整性 | 基础 ⭐☆☆☆☆ | 基本 ⭐⭐☆☆☆ | 全面 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 丰富 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 完善 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ |
| 性能 | 极优 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 良好 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 中等 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 卓越 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 优秀 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ |
| 内存管理 | 无自动管理 ⭐☆☆☆☆ | LRU淘汰 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 多级管理 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 智能淘汰 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 完善管理 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ |
| 社区生态 | JDK自带 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | JDK自带 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 成熟但老 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 活跃增长 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 稳定但停滞 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ |
| 适用规模 | 小型 ⭐⭐☆☆☆ | 中小型 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | 中大型 ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 全规模 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 中小型 ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ |
选型决策指南
根据不同的业务场景和技术要求,我给出以下选型建议:
-
初创项目/原型验证 → ConcurrentHashMap 或 LRU缓存
- 理由:快速实现,无需引入外部依赖
- 注意:随着业务增长,需要重构为更专业的方案
-
高性能要求/现代Java项目 → Caffeine
- 理由:最优的性能和命中率
- 注意:需要Java 8+环境
-
企业级复杂需求 → Ehcache
- 理由:功能全面,支持集群和持久化
- 注意:配置较复杂,学习成本高
-
已有Guava生态/API设计优先 → Guava Cache
- 理由:优雅的API,良好的开发者体验
- 注意:性能不是最优,且不再积极开发
-
特定场景需求:
- 访问有明显热点 → LRU缓存
- 需要自定义淘汰策略 → 基于ConcurrentHashMap自实现
- 内存敏感场景 → Caffeine(智能权重控制)
- 需要监控统计 → Ehcache或Caffeine
总结
本地缓存是Java应用中提升性能的利器,选择正确的方案可以让系统性能得到质的提升。
让我们回顾一下核心要点:
-
ConcurrentHashMap是最基础的方案,适合简单场景或作为自定义缓存的基础。
-
LRU缓存基于LinkedHashMap,解决了自动淘汰的问题,适合访问有热点的场景。
-
Ehcache是企业级选择,功能全面但较重,适合复杂的企业应用。
-
Caffeine是现代高性能缓存库,提供了最优的命中率和并发性能,是新项目的首选。
-
Guava Cache设计优雅,API友好,适合已经使用Guava库或对API设计有要求的项目。
**记住,没有最好的缓存方案,只有最适合的缓存方案。
我个人的倾向是:对于新项目,优先考虑Caffeine;对于已有Guava的项目,可以继续使用Guava Cache;对于特别简单的需求,用ConcurrentHashMap或LRU缓存;对于需要企业级特性的场景,选择Ehcache。
缓存虽好,但也要合理使用。过度缓存会增加系统复杂性,缓存不一致会导致业务问题。
最后说一句(求关注,别白嫖我)
如果这篇文章对您有所帮助,或者有所启发的话,帮忙关注一下我的同名公众号:苏三说技术,您的支持是我坚持写作最大的动力。
求一键三连:点赞、转发、在看。
关注公众号:【苏三说技术】,在公众号中回复:进大厂,可以免费获取我最近整理的10万字的面试宝典,好多小伙伴靠这个宝典拿到了多家大厂的offer。
更多项目实战在我的技术网站:http://www.susan.net.cn/project



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号