第三届黄河流域公安院校网络安全技能挑战赛 reverse wp
qgd
该题目有两段flag
第一段是十六进制(猜测是加密流程)以及密文
将十六进制数据生成为十六进制文件,再用ida打开
按c强制转换为code
u,p构建函数

将红框处nop掉(不知道原理,乱按出来的)
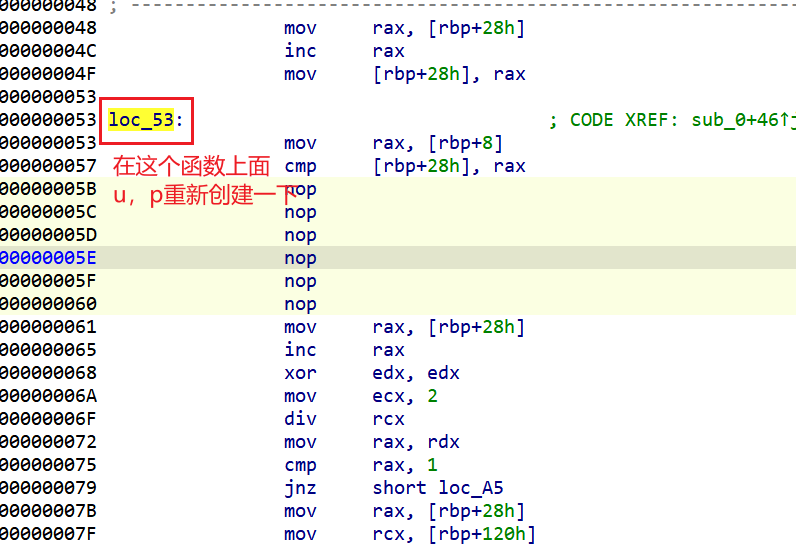
因为这个下面就是分支,因为有jnz跳转

这下看懂了
这个地方可能索引有点问题,和想的奇偶相反(多试试!)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int main(){
int a[]={88 ,47, 80 ,54 ,95 ,57, 90 ,54 ,94, 47};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i%2==0) printf("%c",a[i] ^ 0x31);
else printf("%c",a[i] ^ 0x58);
}
}
第一段iwannaknow
ai也能直接出逻辑哈
#include <stddef.h>
void transform_buffer(unsigned char* buffer, size_t length) {
if (buffer == NULL) return;
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 1) {
buffer[i] ^= 0x31; // XOR with '1'
} else {
buffer[i] ^= 0x58; // XOR with 'X'
}
}
}
来看第二段
python逆向比较简单
解包,反编译WO0o.pyc
from secret import decrypt
key = bytes.fromhex('EC3700DFCD4F364EC54B19C5E7E26DEF6A25087C4FCDF4F8507A40A9019E3B48BD70129D0141A5B8F089F280F4BE6CCD')
ciphertext = b'\xd4z\'0L\x10\xca\x0b\x0b\xaa\x15\xbeK0"\xbf\xb2\xc6\x05'
cipher = decrypt(ciphertext, key)
a = bytes(input('flag呢'), encoding='utf-8')
if a == cipher:
print('没错没错')
else:
print('不对不对')
去找secret.pyc反编译
def key_schedule(key: bytes) -> list:
S = list(range(128))
v6 = 0
for j in range(128):
v6 = (S[j] + key[j % len(key)] + v6) % 128
v6 = (v6 ^ 55) % 128
S[j], S[v6] = (S[v6], S[j])
return S
def next_byte(state: dict) -> int:
S = state['S']
state['i'] = (state['i'] + 1) % 128
state['j'] = (state['j'] + S[state['i']]) % 128
S[state['i']], S[state['j']] = (S[state['j']], S[state['i']])
v2 = S[(S[state['i']] + S[state['j']]) % 128]
return (16 * v2 | v2 >> 4) & 255
def decrypt(ciphertext: bytes, key: bytes) -> bytes:
state = {'S': key_schedule(key), 'i': 0, 'j': 0}
plaintext = bytearray()
for byte in ciphertext:
plaintext.append(byte ^ next_byte(state))
return bytes(plaintext)
RC4加密,我直接用这个加密代码解密的
key = bytes.fromhex('EC3700DFCD4F364EC54B19C5E7E26DEF6A25087C4FCDF4F8507A40A9019E3B48BD70129D0141A5B8F089F280F4BE6CCD')
ciphertext = b'\xd4z\'0L\x10\xca\x0b\x0b\xaa\x15\xbeK0"\xbf\xb2\xc6\x05'
def key_schedule(key: bytes) -> list:
S = list(range(128))
v6 = 0
for j in range(128):
v6 = (S[j] + key[j % len(key)] + v6) % 128
v6 = (v6 ^ 55) % 128
S[j], S[v6] = (S[v6], S[j])
return S
def next_byte(state: dict) -> int:
S = state['S']
state['i'] = (state['i'] + 1) % 128
state['j'] = (state['j'] + S[state['i']]) % 128
S[state['i']], S[state['j']] = (S[state['j']], S[state['i']])
v2 = S[(S[state['i']] + S[state['j']]) % 128]
return (16 * v2 | v2 >> 4) & 255
def decrypt(ciphertext: bytes, key: bytes) -> bytes:
state = {'S': key_schedule(key), 'i': 0, 'j': 0}
plaintext = bytearray()
for byte in ciphertext:
plaintext.append(byte ^ next_byte(state))
return bytes(plaintext)
cipher = decrypt(ciphertext, key)
print(cipher)
第二段what_DO_you_mean#@!
Victory Melody
VM逆向,注意opcode格式
三个一组
操作名 操作下标 操作值

容易找到这里

这里是在进行输入
看到是输入7位的字符串
从main函数动调能够找到j_memcpy函数
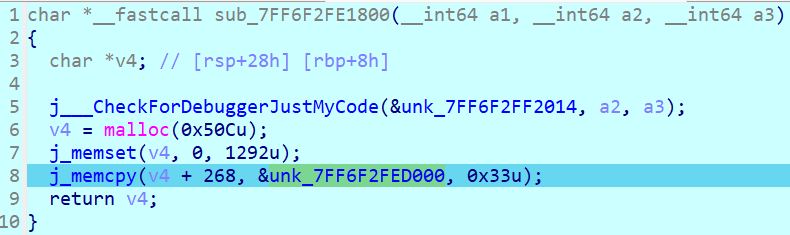
unk_7FF6F2FED000这里就是opcode
我们输入7个a进去,看加密结果
VM指令运行完之后,可以看到a变为了@
发现是在异或33,如果发现不了可以将输入的值变为不一样
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int a[]={0x5B, 0x58, 0x56, 0x6E, 0x11, 0x4E,0x0};
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);i++) {
printf("%c",a[i]^33);
}
}
//zywO0o!
算md5
R(复现)
参考wp:
http://xherlock.top/index.php/archives/1903/#goforit
https://astralprisma.github.io/2025/05/26/huanghe_25/
都快是对着源码做了,动调能解决很多反编译不清晰的问题
已知这是rc4
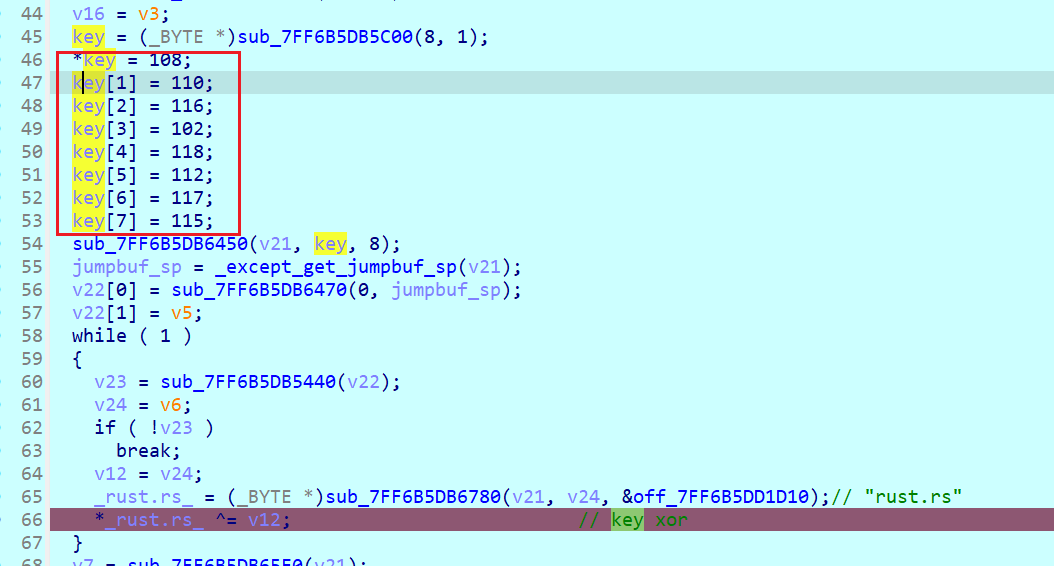
动调看v12的数据是(0 ~ 7)
所以对key:
for(int i =0 ;i<8;i++){
key[i] ^= i
}
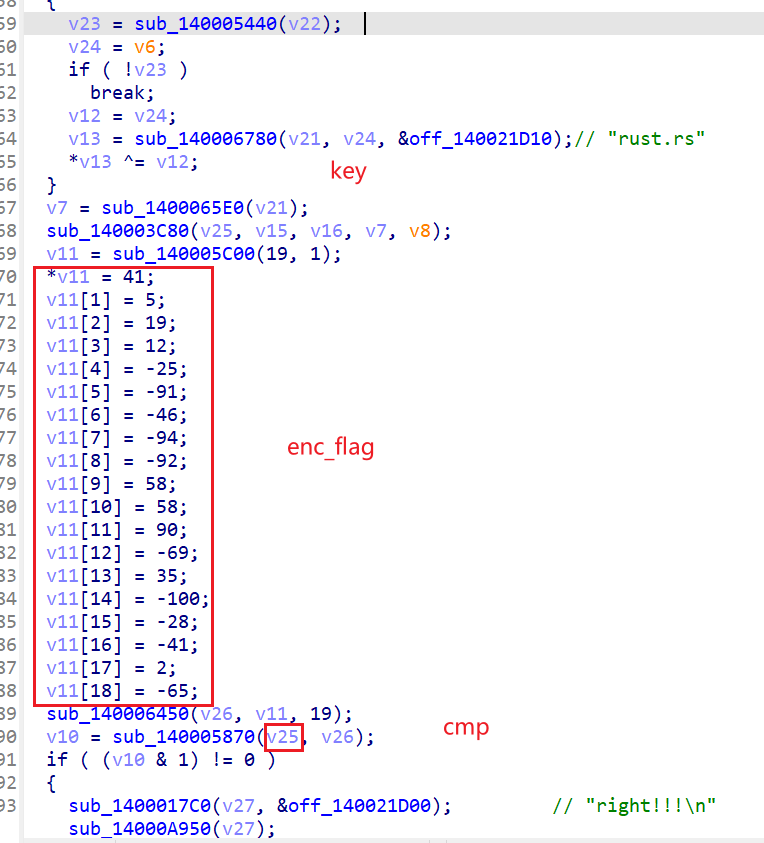
所以v25就是加密后的数据
sub_140003C80就是一个关键的加密函数
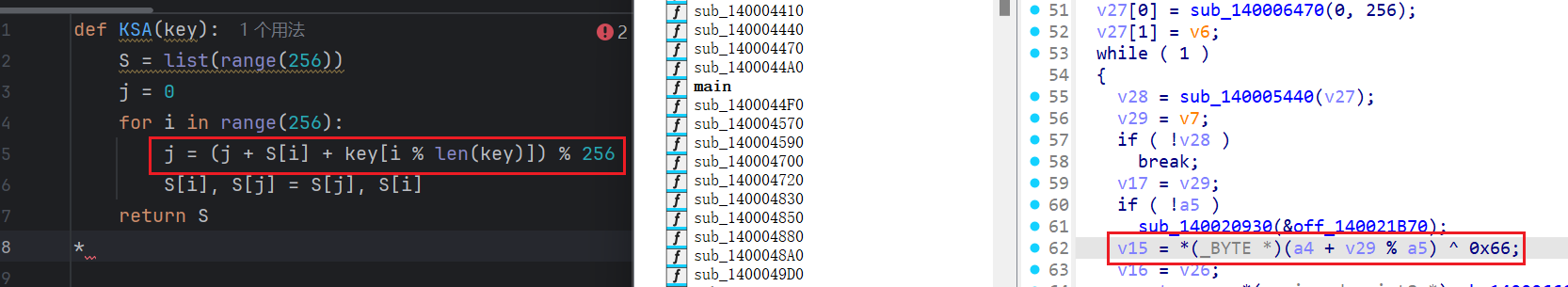
与标准的rc4加密对比一下,发现这里就是KSA算法,魔改的是异或0x66(其实感觉有点牵强)
一步一步走到这

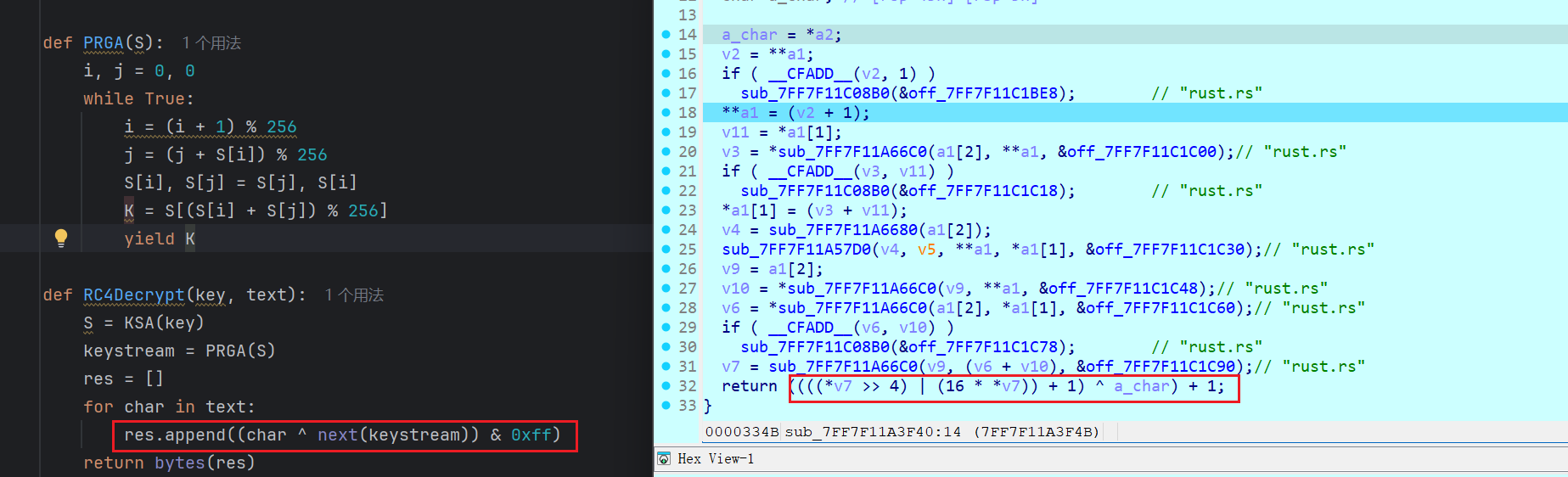
加密:
def KSA(key):
S = list(range(256))
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + S[i] + (key[i % len(key)] ^ 0x66 )) & 0xff
S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
return S
def PRGA(S):
i, j = 0, 0
while True:
i = (i + 1) % 256
j = (j + S[i]) % 256
S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
K = S[(S[i] + S[j]) % 256]
K_S = K >> 4 | K << 4
yield (K_S + 1) & 0xFF
def RC4Decrypt(key, text):
S = KSA(key)
keystream = PRGA(S)
res = []
for char in text:
res.append(((char ^ next(keystream)) + 1) & 0xff)
return bytes(res)
key = [108,110,116,102,118,112,117,115]
for i in range(len(key)):
key[i] ^= i
plaintext = [97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97]
Rc4encrypt = RC4Decrypt(key, plaintext)
print(Rc4encrypt)
可以与v25对比(单字节)
解密:
def KSA(key):
S = list(range(256))
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + S[i] + (key[i % len(key)] ^ 0x66 )) & 0xff
S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
return S
def PRGA(S):
i, j = 0, 0
while True:
i = (i + 1) % 256
j = (j + S[i]) % 256
S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
K = S[(S[i] + S[j]) % 256]
K_S = K >> 4 | K << 4
yield (K_S + 1) & 0xFF
def RC4Decrypt(key, text):
S = KSA(key)
keystream = PRGA(S)
res = []
for char in text:
char -= 1
res.append(((char ^ next(keystream))) & 0xff)
return bytes(res)
key = [108,110,116,102,118,112,117,115]
for i in range(len(key)):
key[i] ^= i
plaintext = [0x29,0x5,0x13,0xC,0xe7,0xa5,0xd2,0xa2,0xa4,0x3a,0x3a,0x5a,0xbb,0x23,0x9c,0xe4,0xd7,0x2,0xbf]
Rc4encrypt = RC4Decrypt(key, plaintext)
print(Rc4encrypt)
flag:flag{Y0uKn0wRu5tV@ryW@1l}
go for it(复现)
和rust不一样,这个难的是算法

异或部分:
加密:
e_a = a ^ c
e_b = e_a ^ c ^ b
e_c = c ^ e_b
解密:
c = e_c ^ e_b
a = c ^ e_a
b = e_b ^ a


加密:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <inttypes.h> // 用于PRIx64格式输出
int main() {
// 输入数据
char input[] = "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa";
uint64_t cipher[4] = {0};
// 处理每个8字节块
for (int block = 0; block < 4; block++) {
uint8_t parts[8] = {0};
uint8_t result[8] = {0};
// ===== 第一阶段:XOR变换 =====
memcpy(parts, input + block*8, 8);
int i = 0;
while (i < 4) { // 处理前4组(3字节一组)
uint8_t tmp1 = parts[i] ^ parts[i + 2];
uint8_t tmp2 = tmp1 ^ parts[i + 2] ^ parts[i + 1];
parts[i] = tmp1;
parts[i + 1] = tmp2;
parts[i + 2] ^= tmp2;
i += 3;
}
// 转换为uint64_t
uint64_t stage1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
stage1 |= (uint64_t)parts[i] << ((7 - i) * 8);
}
// ===== 第二阶段:64轮大整数运算 =====
int64_t stage2 = stage1;
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
if (stage2 < 0) {
stage2 = (2 * stage2) ^ 0x2EF20D07161E85F7;
} else {
stage2 *= 2;
}
}
// ===== 第三阶段:位重组 =====
// 分解为字节数组
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
parts[i] = (stage2 >> (i * 8)) & 0xFF;
}
// 循环左移5位函数
auto rol = [](uint8_t v, int n) {
return ((v << n) | (v >> (8 - n))) & 0xFF;
};
// 位重组
memset(result, 0, 8);
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
for (int m = 0; m < 8; m++) {
if (((0x80 >> k) & rol(parts[m], 5)) != 0) {
result[k] |= 0x80 >> m;
}
}
}
// 转换回uint64_t
cipher[block] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
cipher[block] |= (uint64_t)result[i] << (i * 8);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
printf("0x%016" PRIx64 ",", cipher[i]);
}
return 0;
}
解密:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 循环右移函数
uint8_t ror(uint8_t v, int n) {
return ((v >> n) | (v << (8 - n))) & 0xFF;
}
// 第一阶段解密:位重组逆操作
uint64_t dec3(uint64_t cipher) {
uint8_t parts[8] = {0};
uint8_t result[8] = {0};
uint64_t ret = 0;
// 将64位密文分解为字节数组
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
parts[i] = (cipher >> (i * 8)) & 0xFF;
}
// 位重组逆操作
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
for (int m = 0; m < 8; m++) {
if (parts[k] & (0x80 >> m)) {
result[m] |= ror(0x80 >> k, 5);
}
}
}
// 重组为64位整数
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
ret |= (uint64_t)result[i] << (i * 8);
}
return ret;
}
// 第二阶段解密:64轮大整数逆运算
uint64_t dec2(uint64_t cipher) {
int64_t tmp = cipher;
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
if (tmp & 1) {
tmp = (tmp ^ 0x2EF20D07161E85F7) / 2;
tmp |= 0x8000000000000000;
} else {
tmp = (uint64_t)tmp / 2;
}
}
return tmp;
}
// 第三阶段解密:XOR逆变换
void dec1(uint64_t cipher, char* plain) {
uint8_t tmp1, tmp2;
uint8_t parts[8] = {0};
// 将64位数据分解为字节数组(注意字节序)
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
parts[i] = (cipher >> ((7 - i) * 8)) & 0xFF;
}
// 3字节一组的XOR逆运算
int i = 0;
while (i < 4) {
tmp1 = parts[i];
tmp2 = parts[i + 1];
parts[i + 2] ^= tmp2;
parts[i + 1] = tmp1 ^ tmp2 ^ parts[i + 2];
parts[i] = tmp1 ^ parts[i + 2];
i += 3;
}
memcpy(plain, parts, 8);
}
int main() {
char flag[33] = {0}; // 32字符flag + 1个null终止符
uint64_t cipher[4] = {
0x08ADD5C04E5934C8,
0x199AC0E6DA4C2BC9,
0xFF83F5E87D5510B5,
0x58447D6AD4E38B74
};
// 对每个密文块进行解密
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
uint64_t step1 = dec3(cipher[i]); // 位重组逆操作
uint64_t step2 = dec2(step1); // 大整数逆运算
dec1(step2, flag + i * 8); // XOR逆变换
}
printf("%s", flag);
return 0;
}
好难。。。
最后这个算法嵌套变来变去的我没有完全搞清楚


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号